서 론
헬리코박터 파일로리(Helicobacter pylori)는 위 점액층과 위 상피세 포 사이에 존재하는 그람 음성 간균으로, 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염 이 위 점막 손상을 유발하여 만성위염, 소화성궤양, 위암, 변연부 B세 포 림프종을 유발한다는 것은 잘 알려진 사실이다. 최근에 만성적인 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염과 비만, 인슐린저항성, 당뇨병, 지질이상,
관상동맥심장질환과의 관련성이 제기되어 왔고 현재까지도 이와 관 련된 많은 연구들이 진행되고 있다.
그중 헬리코박터 파일로리와 관상동맥심장질환과의 연관성에 대 한 연구는 1994년 처음 제기되었고1) 현재까지도 결론이 나오지 않은 상태이다. 만성적인 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염으로 위에서 interleu- kin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), inter- feron-γ (INF-γ) 등의 사이토카인들이 분비되어 이들이 지방조직과
Original Article
헬리코박터 파일로리 감염과 Framingham Risk Score와의 연관성
김회경, 김유리*, 하길용, 이 완
부산광역시의료원 가정의학과
Association between Helicobacter pylori Infection and the Framingham Risk Score
Hoi-Kyoung Kim, Yu-Lee Kim*, Kil-Yong Ha, Wan Lee
Department of Family Medicine, Busan Medical Center, Busan, Korea
Ba ckground: Several studies have reported that Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is associated with cardiovascular disease, whereas other studies have shown contrary results; thus, this association remains unclear. The Framingham risk score (FRS) is a conventional clinical risk score is used to determine 10-year cardiovascular risk. The aim of our study was to confirm the association between H. pylori infection and the FRS.
Me thods: This study included 1,310 healthy subjects who had visited the Busan Medical Center from January 2013 to December 2014. The subjects underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy with the rapid urease test (CLO test) to confirm H. pylori infection and completed questionnaires about age, smoking, and medical history. Blood pressure, serum total cholesterol, and high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels were determined. The subjects were divided into the H. pylori-positive group and the H. pylori-negative group.
Re sults: The FRS was the highest in the H. pylori-positive group, but the difference in the scores between groups was not statistically significant (P> 0.05).
The subjects were divided into three risk groups on the basis of the FRS; the proportion of H. pylori infection was higher in the high-risk group than in the low-risk and intermediate-risk groups. However, the differences in proportions were not statistically significant (P> 0.05). In multiple logistic regression models, a high total cholesterol level was associated with the presence of H. pylori infection (odds ratio, 1.003; 95% confidence interval, 1.001 to 1.006; P= 0.043).
Co nclusion: Although not statistically significant, H. pylori infection correlated with a high FRS. Moreover, this infection correlated with the cardiovascular risk factor such as a high total cholesterol level.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; Cardiovascular Disease; Risk Assessment http://www.kafm.or.kr/kjfp.2015.5.2.95 pISSN 2233-9019 · eISSN 2233-9116 Korean J Fam Pract. 2015;5(2):95-99
KJFP
Korean Journal of Family PracticeReceived February 13, 2015 Accepted June 23, 2015 Corresponding author Yu-Lee Kim
Tel: 010-2644-4904, Fax: +82-51-507-3001 E-mail: 07721052@hanmail.net
Copyright © 2015 The Korean Academy of Family Medicine
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons At- tribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Hoi-Kyoung Kim, et al. Association between Helicobacter pylori Infection and the Framingham Risk Score
Korean Journal of Family Practice
KJFP
간에서 지질대사를 변화시켜 죽상동맥경화를 유발하는 것으로 추 정하고 있다.2,3) 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염과 관상동맥심장질환과의 연관성에 대한 동물실험을 살펴보면 Chen 등4)의 연구에서는 헬리코 박터 파일로리에 감염된 쥐에서 죽상동맥경화증의 빈도가 높은 것 이 확인되었으나 Mach 등5)의 쥐를 대상으로 한 연구에서는 헬리코 박터 파일로리 감염이 죽상동맥경화에 영향을 미치지 못한다는 결 과가 나왔다. 관상동맥심장질환 환자들을 대상으로 한 연구들을 살 펴보면 Jafarzadeh 등6)의 연구에서는 대조군에 비해 급성 심근경색 과 불안정형 협심증 환자에서 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염률이 높았 고, Khodaii 등7)의 연구에서는 급성 심근경색 환자에서 대조군에 비 해 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염률과 cytotoxin-associated gene A (CagA) 양성인 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염률이 높았다. Ikeda 등8)의 연구에 서는 심근경색과 뇌경색 환자에서 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염률이 높지 않았으나 CagA 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염률은 대조군에 비해 높았다. 그리고 Liu 등9)의 메타분석결과 심근경색의 위험인자로 헬 리코박터 파일로리 감염이 연관성이 있다는 결과가 나왔다. 그러나 다른 연구10,11)에서는 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염이 관상동맥심장질 환의 위험인자임을 밝히지 못하였다.
한편 관상동맥심장질환의 위험도를 평가하고 위험인자 관리를 위 한 전통적인 지침으로는 미국의 Framingham risk score12)와 유럽의 systemic coronary risk evaluation system13)이 있다. 그중 외래에서 쉽게 시행할 수 있는 Framingham risk score는 20-79세의 성인에서 성별에 따라 연령, 흡연, 수축기혈압, 총 콜레스테롤 및 고밀도지단백 콜레스 테롤을 점수화하여 향후 10년간 관상동맥심장질환에 의한 위험도 를 평가하게 된다.
이에 본 연구에서는 건강검진센터를 방문한 성인 남녀를 대상으로 하여 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염과 Framingham risk score와의 관련성 과 관상동맥심장질환의 위험인자와의 관련성을 알아보고자 한다.
방 법
1. 연구대상
2013년 1월부터 2014년 12월까지 부산광역시의료원 건강검진센터 를 방문하여 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염검사를 시행한 20대 이상 성 인 남녀 1,454명을 대상으로 하였다. 문진을 통해 협심증과 심근경색 증을 포함하는 관상동맥 질환의 과거력 또는 현병력이 있는 경우, 당 뇨병의 현병력이 있는 경우, 공복혈당 측정 결과 126 mg/dL 이상으로 당뇨병이 의심되는 경우를 제외하고 최종 1,310명을 대상으로 본 연 구를 시행하였다.
2. 연구방법
건강검진 방문자의 자기기입식 설문지와 의무기록을 통하여 병력 및 흡연력을 확인하였고 고밀도지단백 콜레스테롤, 총 콜레스테롤 검사를 시행하였다. 혈액분석은 최소 12시간 이상의 공복상태에서 정맥혈을 채취하여 원심분리 후 혈청 지질을 측정하였다(TBA- 2000FR; Toshiba, Tokyo, Japan). 혈압은 수축기 및 이완기혈압이 140 mm Hg 및 90 mm Hg이 넘는 경우에는 5분 이상 안정을 취한 후 다시 측정한 값으로 하였다. 흡연력은 National Cholesterol Education Pro- gram’s Adult Treatment Panel III (NCEP ATP III)에서 제시한 Framing- ham risk score12)에 따라서 지난 달에 흡연을 했는지 여부로 판단하였 다. 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염 여부는 급속요소분해효소검사로 정 하였으며 위 전정부 대만(1조각)에서 급속요소분해효소 검사(CLO test; Kimberly-Clark, Draper, UT, USA)를 시행하여 결과가 양성 소견 이면, 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염을 확진하였다.
NCEP ATP III에서 제시한 Framingham risk score12)는 성별에 따른 연령, 흡연 여부, 고혈압 치료 여부, 수축기혈압, 총 콜레스테롤, 고밀 도지단백 콜레스테롤을 점수화하여 향후 10년간 관상동맥심장질환 에 의한 위험도를 평가하는 것이다. 연구대상자에 각 변수별로 점수 를 매겼고, 합산한 총 위험점수와 이에 대응하는 관상동맥심장질환 의 10년 위험도를 추정하였다. 10년 위험도가 10% 미만일 경우 저위 험군, 10-20%일 경우 중간위험군, 20%를 초과할 경우 고위험군으로 분류하였다.
3. 통계방법
자료의 통계분석은 PASW SPSS ver. 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA)을 이용하였으며 연속형 변수 자료는 평균 ± 표준편차로 제시 하였다. 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염 여부에 따른 대상자의 특성은 독 립표본 t-검정법과 카이제곱검정을 이용하여 분석하였으며 헬리코 박터 파일로리 감염과 Framingham risk score와의 관계는 카이제곱 검정을 이용하여 분석하였다. 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염과 관상동 맥심장질환 위험요인들과의 연관성은 다중 로지스틱회귀분석을 이 용하였다. 신뢰구간은 95%, 통계 유의수준은 P값 0.05 미만으로 정의 하였다.
결 과
1. 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염 여부에 따른 대상자의 특성
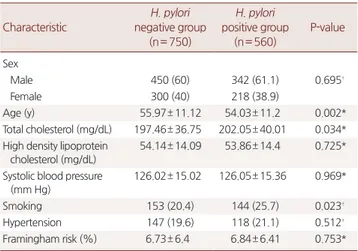
대상자 총 1,310명 중 헬리코박터 파일로리 양성군은 560명이었고 헬리코박터 파일로리 음성군은 750명이었다. 연령은 양성군에서 54.03±11.2세, 음성군에서 55.97±11.12세로 음성군에서 더 높은 값
김회경 외. 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염과 Framingham Risk Score와의 연관성 Korean Journal of Family Practice
KJFP
을 보였다(P= 0.002). 총 콜레스테롤 수치는 양성군에서 202.05 ± 40.01 mg/dL, 음성군에서 197.46±36.75 mg/dL로 양성군에서 높았고 통계적으로 의미 있는 결과가 나왔다(P= 0.034). 고밀도지단백 콜레 스테롤 수치는 양성군에서 낮고, 수축기혈압은 양성군에서 높았으 나 통계적으로 의미는 없었다(Table 1).
2. 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염과 Framingham Risk Score와의 관계 Framingham risk score의 평균값은 헬리코박터 파일로리 양성군에 서 6.84%±6.41%, 음성군에서 6.73%±6.4%로 양성군에서 높았지만 통 계적으로 의미는 없었다(P>0.05) (Table 1). Framingham risk score에 따른 관상동맥심장질환 발생의 저위험군, 중간위험군보다 고위험군 에서 헬리코박터 파일로리 양성의 비율이 더 높았지만 통계적인 의 미는 없었다(P>0.05) (Table 2).
3. 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염과 관상동맥심장질환 위험요인들과의 연관성
헬리코박터 파일로리 감염과 관상동맥심장질환 위험요인들이 독
립적으로 연관이 있는지 알아보기 위해 위험요인들에 대한 다중 로 지스틱회귀분석을 한 결과 연령이 낮을수록 헬리코박터 파일로리에 감염된 비율이 높았고(odds ratio [OR], 0.980; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.969 to 0.993; P= 0.002), 총 콜레스테롤 수치는 헬리코박터 파일 로리 감염과 양의 상관관계가 있었다(OR, 1.003; 95% CI, 1.001 to 1.006; P= 0.043). 그 외에 고밀도지단백 콜레스테롤은 음의 상관관계 를 보이고 수축기혈압, 흡연, 고혈압, Framingham risk는 양의 상관관 계를 보였으나 통계적으로 의미는 없었다(P>0.05) (Table 3).
고 찰
관상동맥심장질환은 수위를 차지하는 사망원인14)으로 중요한 임 상적 의미를 가진다. 이러한 관상동맥심장질환의 위험인자로는 당뇨 병, 고혈압, 이상지질혈증, 흡연, 비만, 가족력 등이 알려져 있다.15) 최 근 관상동맥심장질환의 위험인자로 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염이 제 기되고 있어6-9) 본 연구에서도 이러한 가설을 뒷받침하고자 하였으 나 관상동맥심장질환 발생 10년 위험도인 Framingham risk와 헬리코 박터 파일로리 감염의 상관관계에 대한 본 연구결과는 통계적으로 유의한 의미를 갖지 못하였다. 관상동맥심장질환의 위험인자 중 하 나인 총 콜레스테롤 수치만이 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염과 통계적 으로 유의한 양의 상관관계를 보여 의미 있는 결과라고 볼 수 있다.
만성적인 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염으로 인하여 위에서 IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, INF-γ 등의 사이토카인들이 분비되어 이들이 지방조직과 간 에서 지질대사를 변화시켜 죽상동맥경화를 유발하는 것으로 추정 하고 있다.2,3) 여러 연구16,17)에서 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염이 총 콜레 스테롤, 저밀도지단백 콜레스테롤, lipoprotein(a), apolipoprotein B, 중 성지방의 혈중 농도를 올리고, 고밀도지단백 콜레스테롤과 apolipo- protein A-1의 농도를 낮추는 결과는 보여주었다. 본 연구에서도 대조 Table 1. Characteristics of participants
Characteristic
H. pylori negative group
(n= 750)
H. pylori positive group
(n= 560)
P-value
Sex
Male 450 (60) 342 (61.1) 0.695†
Female 300 (40) 218 (38.9)
Age (y) 55.97± 11.12 54.03± 11.2 0.002*
Total cholesterol (mg/dL) 197.46± 36.75 202.05± 40.01 0.034*
High density lipoprotein cholesterol (mg/dL)
54.14± 14.09 53.86± 14.4 0.725*
Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg)
126.02± 15.02 126.05± 15.36 0.969*
Smoking 153 (20.4) 144 (25.7) 0.023†
Hypertension 147 (19.6) 118 (21.1) 0.512†
Framingham risk (%) 6.73± 6.4 6.84± 6.41 0.753*
Values are presented as number (%) or mean± SD.
H. pylori, Helicobacter pylori.
*Calculated by independent t-test. †Calculated by chi-square test.
Table 2. The correlation of H. pylori infection with Framingham 10- year coronary heart disease risk
Framingham risk
H. pylori negative group
(n= 750)
H. pylori positive group
(n= 560)
P-value*
Low risk 535 (57.72) 392 (42.29) 0.484
Intermediate risk 191 (57.19) 143 (42.82)
High risk 24 (48.98) 25 (51.03)
Values are presented as number (%).
H. pylori, Helicobacter pylori.
*Calculated by chi-square test.
Table 3. Multiple logistic regression analysis of Helicobacter pylori in- fection and potential confounding variables
Variable Odds ratio 95% confidence
intervals P-value*
Sex 1.105 0.806 to 1.516 0.537
Age (y) 0.980 0.969 to 0.993 0.002
Total cholesterol (mg/dL) 1.003 1.001 to 1.006 0.043 High density lipoprotein
cholesterol (mg/dL)
0.999 0.991 to 1.008 0.775
Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) 1.001 0.995 to 1.007 0.843
Hypertension 1.277 0.935 to 1.746 0.124
Smoking 1.251 0.904 to 1.731 0.177
Framingham risk (%) 1.007 0.974 to 1.042 0.676
*Calculated by multiple logistic regression analysis.
Hoi-Kyoung Kim, et al. Association between Helicobacter pylori Infection and the Framingham Risk Score
Korean Journal of Family Practice
KJFP
군에 비해 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염환자에서 총 콜레스테롤 수치 가 상승한 결과를 보여주었고 이는 이러한 연구들을 뒷받침할 수 있 어 의미 있는 결과라고 생각된다. 물론 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염이 이러한 지질 조성 변화에 영향을 주지 않는다는 보고18,19)도 있기 때 문에 이에 대한 대규모 연구들이 필요할 것으로 생각된다.
본 연구에서 헬리코박터 파일로리의 만성적인 감염으로 인하여 여러 가지 염증물질이 분비되어 죽상동맥경화를 유발하는 것으로 추정되고 있다.2,3) 특히 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염과 관상동맥심장질 환이 모두 중년 이후에 발병률이 높은 것으로 되어 있어 만성적인 경 과가 중요한 것으로 생각된다.1,20) 그러나 본 연구결과에서는 헬리코 박터 파일로리 음성군의 연령이 더 높았다. 2013년 Lim 등21)의 우리 나라 전 연령층을 대상으로 한 대규모의 역학 연구에 따르면 이전에 제균치료를 받지 않은 무증상 대상자의 경우 20세에서 59세까지는 연령이 증가함에 따라 헬리코박터 파일로리에 대한 항체 양성률이 증가하다가 60세부터는 헬리코박터 파일로리에 대한 항체 양성률이 꾸준히 유지되었다. 본 연구에서는 제균치료 여부에 대해 고려하지 않았기 때문에 이러한 결과가 나온 것으로 여겨진다.
본 연구에서는 몇 가지 제한점이 있다. 첫째는 대상자가 충분히 무 작위화되지 않았다. 종합건간검진을 위해 내원한 사람을 대상으로 하였기 때문에 그 대상자가 경제적 여건이 되어 주기적으로 건강을 체크하고 관리하는 사람이 대부분이었다. 둘째는 병력과 흡연력은 대상자가 직접 작성한 설문지를 통하여 확인하여 그 신뢰도가 떨어 질 수 있다. 셋째는 본 연구에서는 헬리코박터 파일로리 제균치료 여 부에 대해 고려하지 않았다는 점이다. 헬리코박터 파일로리 제균치 료 후 관상동맥심장질환의 위험도가 낮아졌다는 직접적인 연구는 없으나 제균치료 후 관상동맥심장질환의 위험인자인 지질조성의 변 화에 대한 여러 보고가 있다. 제균치료 후 총 콜레스테롤과 저밀도지 단백 콜레스테롤의 수치가 감소하였다는 긍정적인 연구22)와 제균치 료 후 총 콜레스테롤과 중성지방이 현저히 증가하였다는 부정적인 연구 결과23-25) 모두 존재한다. 그래서 헬리코박터 파일로리 제균치료 여부에 대해 고려하지 않았다는 점이 또 하나의 한계가 될 수 있다.
결론적으로 본 연구에서 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염은 Framing- ham risk score에 의한 관상동맥심장질환 10년 위험도와 통계적으로 의미 있는 상관관계는 확인되지 않았고 향후 관상동맥심장질환 위험 인자로서의 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염에 대한 더 많은 연구가 필요 할 것으로 생각된다. 그러나 관상동맥심장질환의 위험인자 중 하나 인 총 콜레스테롤 수치가 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염과 통계적으로 유의한 양의 상관관계를 보인 것은 의미 있는 결과라고 볼 수 있다.
요 약
연구배경: 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염으로 관상동맥심장질환이 유 발된다는 가설이 제시되었고 이에 대한 많은 연구들이 진행되었으 나 아직 결론은 나오지 않았다. Framingham risk score는 관상동맥심 장질환의 위험도를 평가하기 위한 것으로 본 연구는 Framingham risk score를 이용하여 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염과 관상동맥심장질 환 위험도와의 연관성을 알아보고자 하였다.
방법: 2013년 1월부터 2014년 12월까지 부산광역시의료원 건강검진 센터를 방문하여 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염검사를 시행한 총 1,310명 을 대상으로 하였다. 급속요소분해효소 검사를 통하여 헬리코박터 파일로리 양성군과 음성군을 구분하였다. 나이, 병력, 흡연력을 확인 하고 혈압, 총 콜레스테롤, 고밀도지단백 콜레스테롤 농도를 측정하 였다.
결과: 관상동맥심장질환 발생 10년 위험도인 Framingham risk는 헬 리코박터 파일로리 양성군에서 높았지만 통계적으로 의미는 없었다 (P> 0.05). Framingham risk score에 따른 저위험군, 중간위험군, 고위 험군 사이에서의 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염과의 연관성 조사에서도 저위험군과 중간위험군보다 고위험군에서 헬리코박터 파일로리 양 성군의 비율이 더 높았지만 통계적으로 의미는 없었다(P>0.05). 헬리 코박터 파일로리 감염과 관상동맥심장질환 위험요인들에 대한 다 중 로지스틱회귀분석을 한 결과 총 콜레스테롤은 헬리코박터 파일 로리 감염과 양의 상관관계가 있었다(odds ratio, 1.003; 95% confi- dence interval, 1.001 to 1.006; P= 0.043).
결론: 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염과 Framingham risk score에 의한 관 상동맥심장질환 발생 10년 위험도 사이에 의미 있는 연관관계가 확 인되지 않았지만, 관상동맥심장질환의 위험인자인 총 콜레스테롤 수치는 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염과 의미 있는 양의 상관관계를 보 였다.
중심단어: 헬리코박터 파일로리; 관상동맥심장질환; 위험도 평가
REFERENCES
1. Mendal l MA, Goggin PM, Molineaux N, Levy J, Toosy T, Strachan D, et al.
Relation of Helicobacter pylori infection and coronary heart disease. Br Heart J 1994;71:437-9.
2. Mendall MA, Patel P, Asante M, Ballam L, Morris J, Strachan DP, et al. Rela- tion of serum cytokine concentrations to cardiovascular risk factors and cor- onary heart disease. Heart 1997;78:273-7.
3. Crabtree JE, Shallcross TM, Heatley RV, Wyatt JI. Mucosal tumour necrosis
김회경 외. 헬리코박터 파일로리 감염과 Framingham Risk Score와의 연관성 Korean Journal of Family Practice
KJFP
factor alpha and interleukin-6 in patients with Helicobacter pylori associated gastritis. Gut 1991;32:1473-7.
4. Chen XH, Wang JB, Wang YS, Liu ZM, Li Y. Helicobacter pylori infection enhances atherosclerosis in high-cholesterol diet fed C57BL/6 mice. Zhong- hua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 2010;38:259-63.
5. Mach F, Sukhova GK, Michetti M, Libby P, Michetti P. Influence of Helico- bacter pylori infection during atherogenesis in vivo in mice. Circ Res 2002;90:E1-4.
6. Jafarzadeh A, Nemati M, Tahmasbi M, Ahmadi P, Rezayati MT, Sayadi AR.
The association between infection burden in Iranian patients with acute myocardial infarction and unstable angina. Acta Med Indones 2011;43:105- 11.
7. Khodaii Z, Vakili H, Ghaderian SM, Najar RA, Panah AS. Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with acute myocardial infarction. Coron Ar- tery Dis 2011;22:6-11.
8. Ikeda A, Iso H, Sasazuki S, Inoue M, Tsugane S; JPHC Study Group. The combination of Helicobacter pylori- and cytotoxin-associated gene-A sero- positivity in relation to the risk of myocardial infarction in middle-aged Japa- nese: The Japan Public Health Center-based study. Atherosclerosis 2013;230:67-72.
9. Liu J, Wang F, Shi S. Helicobacter pylori infection increase the risk of myo- cardial infarction: a meta-analysis of 26 studies involving more than 20,000 participants. Helicobacter 2015;20:176-83.
10. Danesh J, Collins R, Peto R. Chronic infections and coronary heart disease:
is there a link? Lancet 1997;350:430-6.
11. Lee SY, Kim DK, Son HJ, Lee JH, Kim YH, Kim JJ, et al. The impact of Heli- cobacter pylori infection on coronary heart disease in a Korean population.
Korean J Gastroenterol 2004;44:193-8.
12. Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cho- lesterol in Adults. Executive summary of the third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evalua- tion, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001;285:2486-97.
13. De Backer G, Ambrosioni E, Borch-Johnsen K, Brotons C, Cifkova R, Dal- longeville J, et al. European guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice. Third Joint Task Force of European and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice. Eur Heart J 2003;24:1601-10.
14. Korea National Statistical Office. Annual report on the cause of death statis- tics [Internet]. Daejeon: Statistics Korea; c1996 [cited 2014 Sep 23]. Available from: http://kostat.go.kr.
15. National Institutes of Health. What are coronary heart disease risk factors?
[Internet]. Bethesda: National Institutes of Health; c1930 [cited 2015 Jun 9].
Available from: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov.
16. Laurila A, Bloigu A, Nayha S, Hassi J, Leinonen M, Saikku P. Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with elevated serum lipids. Atherosclerosis 1999;142:207-10.
17. Chimienti G, Russo F, Lamanuzzi BL, Nardulli M, Messa C, Di Leo A, et al.
Helicobacter pylori is associated with modified lipid profile: impact on lipoprotein(a). Clin Biochem 2003;36:359-65.
18. Elizalde JI, Pique JM, Moreno V, Morillas JD, Elizalde I, Bujanda L, et al. In- fluence of Helicobacter pylori infection and eradication on blood lipids and fibrinogen. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002;16:577-86.
19. Adiloglu AK, Can R, Kinay O, Aridogan BC. Infection with Chlamydia pneumoniae but not Helicobacter pylori is related to elevated apolipoprotein B levels. Acta Cardiol 2005;60:599-604.
20. Blaser MJ. Helicobacters are indigenous to the human stomach: duodenal ulceration is due to changes in gastric microecology in the modern era. Gut 1998;43:721-7.
21. Lim SH, Kwon JW, Kim N, Kim GH, Kang JM, Park MJ, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of Helicobacter pylori infection in Korea: nationwide multicenter study over 13 years. BMC Gastroenterol 2013;13:104.
22. Majka J, Rog T, Konturek PC, Konturek SJ, Bielanski W, Kowalsky M, et al.
Influence of chronic Helicobacter pylori infection on ischemic cerebral stroke risk factors. Med Sci Monit 2002;8:CR675-84.
23. Furuta T, Shirai N, Xiao F, Takashima M, Hanai H. Effect of Helicobacter py- lori infection and its eradication on nutrition. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002;16:799-806.
24. Fujiwara Y, Higuchi K, Arafa UA, Uchida T, Tominaga K, Watanabe T, et al.
Long-term effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on quality of life, body mass index, and newly developed diseases in Japanese patients with peptic ulcer disease. Hepatogastroenterology 2002;49:1298-302.
25. Kamada T, Hata J, Kusunoki H, Ito M, Tanaka S, Kawamura Y, et al. Eradica- tion of Helicobacter pylori increases the incidence of hyperlipidaemia and obesity in peptic ulcer patients. Dig Liver Dis 2005;37:39-43.