Cleidocranial dysplasia on cone-beam computed tomography
전체 글
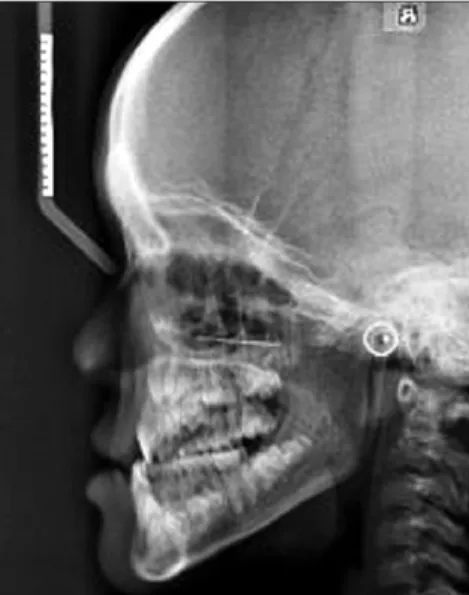
(2) Gun-Sun Lee and Jae-Duk Kim. 두개골의 단두증(Marie & Sainton, 1898; Nebgen et al., 1991;. 한 운동이 관찰되었으며 양안 격리증을 나타내었다(Fig. 1).. Kargul et al., 1997; Golan et al., 2000; Golan et al., 2002; Golan. 충분히 의사소통이 가능했으며 정신지체나 신체적 장애는 없. et al., 2003) 등이 있고, 치열에서는 유치의 만기잔존과 영구. 는 것으로 나타났다.. 치의 맹출지연, 그리고 미맹출 과잉치의 존재 등(Richardson. 후전방 흉부 방사선영상에서는 양쪽 쇄골의 결손과 함께 형. & Deussen, 1994; Jensen & Kreiborg, 1995; Atasu et al., 1996;. 성 저하된 견갑골을 관찰할 수 있었으며 흉곽 형태는 전체적. McNamara et al., 1999; Jeong & Hong, 2000)을 들 수 있다. 이. 으로 작았고 종 모양을 보였다(Fig. 2).. 밖에도 장골, 척추, 골반, 수족골 등의 변화 등이 보고되었다 (Martin 1765; Marie & Sainton, 1898). 방사선학적 소견은 대부분 임상소견과 일치한다. 한편 치의 학계에서는 파노라마 방사선영상의 역할이 강조되며(Jensen. 측방두부촬영방사선영상에서는 비골의 저형성, 얕은 터키 안(sella turcica), 치밀한 측두골의 추체부(petrous portion)를 보였으며, 긴 하악골의 상행지를 관찰할 수 있었다(Fig. 3). 파노라마 방사선영상에서는 유치열의 만기잔존과 그에 따. & Kreiborg, 1993; McNamara et al., 1999; Jeong & Hong, 2000; Kim et al., 2004), 하악골의 상지와 근돌기의 이상과 함께 상하 악의 부가적인 형태이상에 대하여 보고되었다. 최근 파노라마 방사선영상에 의한 통상검사에서 우연히 발견된 유치의 만기잔존과 영구치의 맹출지연, 그리고 다발 성 미맹출 과잉치가 함께 나타났으며 상, 하악골의 다양한 형태적 이상이 수반된 쇄골두개이골증의 일례를 경험하였 다. 이에 최신 영상기기인 cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT)를 통해 보다 정확한 정보를 관찰하여 보고하는 바이 다.. 증례보고 11세의 여자환자가 교정치료를 위하여 내원하였다. 과거의 다른 질환이나 수술 병력은 없었다. 신장은 128.6 cm 정도로 동일 연령의 평균 신장에 미치지 못. Fig. 2. The chest P-A image shows absence of clavicles, hypoplastic scapula, and bell-shaped thoracic rib cage.. 하였다. 상악의 양측 중절치는 정상 맹출되어 있었다. 어깨가 정중앙에서 만날 때까지 전방으로 움직여지는 견갑대의 과도. Fig. 1. Concave nasal bridge and ocular hypertelorism can be seen.. Fig. 3. Cephalometric radiograph shows the wide sutures, dense petrous portion, and shallow sellae turcica. The underdeveloped maxilla and nasal bone are recognizable.. 45.
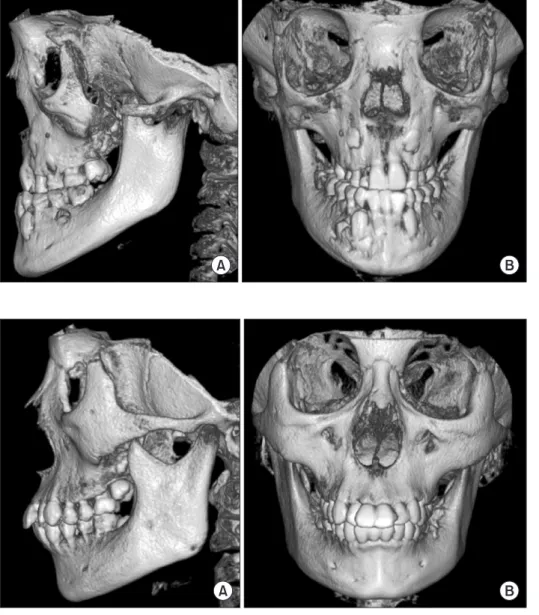
(3) Cleidocranial dysplasia on cone-beam computed tomography. 른 영구치의 맹출지연 및 다수의 매복 과잉치가 관찰되었다. 좌우 양측 관골궁은 하악골 근돌기의 하방으로 경사를 보였 다. 하악골의 양측 상행지는 전후 경계가 평행한 모양을 보였 고 길이가 정상보다 길게 관찰되었다. 그와 함께 하악골의 근 돌기가 후상방을 향한 모습을 나타내었다. 좌우 양측 하악각 부위의 피질골은 다소 넓은 두께를 나타내었다(Fig. 4). CBCT로 촬영하여 획득한 3차원 영상의 측면상에서 좌우 양측 관골궁이 명확히 관골과 단절되어 있음이 확인되었다. 그 양상은 관골측두봉합 위치로부터 전후방으로 상당부분이 결여되어 있었다(Fig. 5A). 형성부전되어 있는 관골궁은 3차 원 영상의 측면상에서 정상인(Fig. 6A)에 비해 다소 아래쪽으 로 만곡을 이루고 있었으며 하악골의 근돌기는 상후방으로 향하고 관골궁을 지나 그 상방까지 연장되어 있었다(Fig. 5A). 3차원 영상의 정면상에서는 양 안와 사이의 비골과 비교(nasal. Fig. 4. Panoramic image shows the downward curvature of both zygomatic arches with hypoplasia. In mandible, the ascending ramus having near parallel-sided borders, coronoid process facing upwards and posteriorly, and thickened cortical bone at the both angles can be seen. The prolonged retention of deciduous teeth with delayed eruption of permanent teeth and multiple embedded supernumerary teeth are recognizable.. Fig. 5. The zygomatic arches show the wide discontinuity forwardly and backwardly at the site of the zygomatico-temporal suture and downward curvatures. The ascending ramus of mandible shows near parallel-sided anterior and posterior borders. The long coronoid process facing upwards and posteriorly pass over the zygomatic arch showing downward curvature. The underdeveloped maxilla and the obtuse mandibular angle is recognizable (A). The frontal view of 3-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography image shows the wide and rectangular nose bridge (B).. Fig. 6. The lateral (A) and frontal view (B) of 3-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography image of normal patient.. 46.
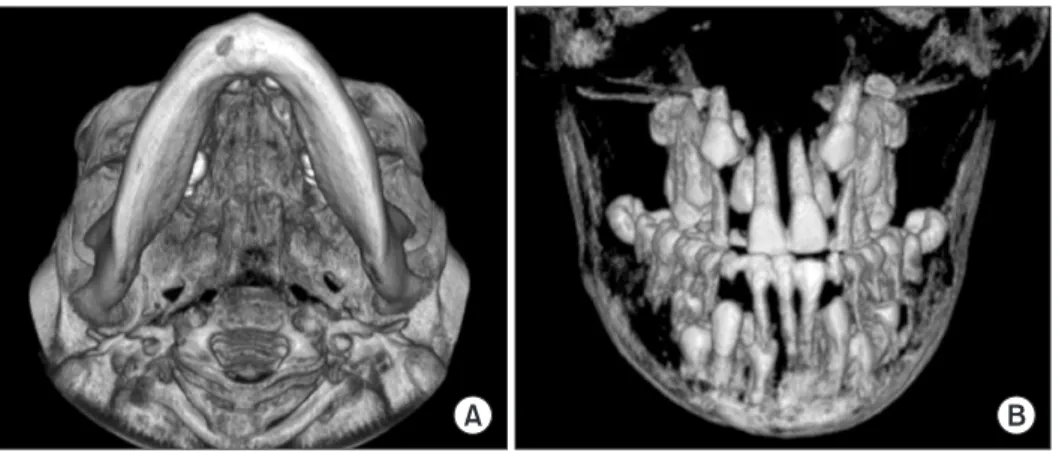
(4) Gun-Sun Lee and Jae-Duk Kim. Fig. 7. The basal view of 3-dimensional (3D) cone-beam computed tomography image shows the short distance from condylar head to the tip of coronoid process and the wide discontinuity of both zygomatic arches (A). 3D image of mixed dentition with supernumerary (B).. bridge)가 정상인(Fig. 6B)과 달리 직사각형을 이루며 넓었다. 되며(Bruce & Howard, 1969; Koch et al., 1978; Nebgen et al.,. (Fig. 5B).. 1991; Atasu et al., 1996; McNamara et al., 1999; Jeong & Hong,. 또한 하악골의 하악각이 컸으며 상행지의 양측 경계가 평. 2000), 특히 관상봉합과 삼각봉합(lambdoid suture) 부분에서. 행하게 올라갔고 길이도 비교적 길게 관찰되었다(Fig. 5A). 두. 봉간골이 흔히 나타나고(Yamamoto et al.,1989; Nebgen et al.,. 개골의 기저상에서도 하악과두와 근돌기 간의 거리가 비교적. 1991; Jensen & Kreiborg, 1993), 두개저의 얕은 터키안과 후. 짧게 나타났다(Fig. 7A). 치아들의 양상도 입체적으로 관찰하. 상상돌기(posterior clinoid process)의 저형성도 보고되었다. 여 파노라마 방사선영상에서 중첩되었던 과잉치를 확인하고. (Kreiborg et al., 1981).. 정확한 위치를 평가할 수 있었다(Fig. 7B).. 이번 증례에서는 봉합 폐쇄 지연이나 천문개방 그리고 봉간 골은 뚜렷하지 않았으나 측두골의 치밀한 추체부가 관찰되었. 고. 찰. 고 얕은 터키안의 모습을 나타내었다. 또한 하악전돌 경향을 나타내었는데, 이는 하악에서의 발. Golan 등(2003)에 의하면 이 질환이 발견되는 평균연령은 18.3세이다. 두개골의 단두증은 전두골과 두정골의 뚜렷한 돌출양상을 보이며(Koch et al., 1978; Atasu et al., 1996), 천문과 두개봉합. 육이상으로 하악전돌이 포함될 수 있으나 상악의 발육저하로 인한 가성 하악전돌 양상을 보이는 것으로 생각된다는 보고 (Harris et al., 1977; Järvinen, 1981; Yamamoto et al., 1989)와 일 치하는 것으로 보였다.. 의 폐쇄 지연은 때로 평생을 거쳐 개방된 채로 존재할 수 있다.. 악골 방사선사진에서 유치의 만기잔존과 그에 따른 영구치. 쇄골은 결손으로 인해 견갑대의 과도한 운동은 어깨가 중앙. 의 맹출지연, 그리고 다발성 매복과잉치도 쇄골두개형성이. 에서 만날 때까지 전방으로 움직일 수 있다(McNamara et al.,. 상을 인지할 수 있는 특징적인 소견이라 할 수 있다(Rushton,. 1999; Jeong & Hong, 2000).. 1937; Smith, 1968; Hitchin & Fairley, 1974; Koch et al., 1978;. 안면에서의 증상으로는 약간의 안구돌출과 양안 격리증. Jensen & Kreiborg, 1993; Richardson & Deussen, 1994; Jensen. 이 존재하며 외이관의 중심이 협소해지고 유양돌기의 과증. & Kreiborg, 1995; Atasu et al., 1996; McNamara et al., 1999;. 식으로 난청을 보이기도 한다(Koch et al., 1978). 많은 경우 비. Jeong & Hong, 2000).. 교(nasal bridge)가 함몰되어 있고 그 기저부는 넓어져 있으며. 이번 증례도 파노라마 방사선영상의 통상검사에서 유치의. (Atasu et al., 1996; Jeong & Hong, 2000), 부비동들은 발육저하. 만기잔존과 그에 따른 영구치의 맹출지연 및 다발성 매복과. 나 결손을 나타낸다(Koch et al., 1978; Atasu et al., 1996; Jeong. 잉치가 함께 나타난 치아이상이 발견되어 쇄골두개형성이상. & Hong, 2000). 이번 증례에서도 이러한 제반 소견들이 인정. 을 의심하였다.. 되었다.. Jensen과 Kreiborg (1993)의 보고에 의하면 하악골의 상행지. 흉부 방사선사진 영상에서 볼 수 있는 쇄골의 미발육과 더. 는 전후 경계가 평행에 가까운 모양을 보이고 길이가 정상보. 불어 작은 종모양의 흉곽(Bruce & Howard, 1969; Nebgen et. 다 길게 관찰된다고 하였다. 또한 근돌기가 정상에 비해 후상. al., 1991; Jeong & Hong, 2000)이 이번 증례에서도 확인되었다.. 방을 향하는 원심만곡을 보이며 그 끝은 가늘고 뾰족하다고. 두부 방사선사진 영상에서는 미폐쇄된 봉합과 천문이 관찰. 하였다. Farman 등(1993)도 후전방 두부 방사선사진에서 하악. 47.
(5) Cleidocranial dysplasia on cone-beam computed tomography. 골의 근돌기가 젖혀질 수 있음을 보고하였다. 이에 근거하여. 급하지 않았다. Kim 등(2004)도 이러한 형태이상을 보고하고. McNamara 등(1999)은 쇄골두개형성이상 9예의 파노라마 방. 있어 향후 계속 관찰이 필요하다고 생각되었다.. 사선영상에서 이러한 소견을 포함하여 다수의 악골의 형태이 상을 정리하여 보고하였다.. 이상 파노라마 방사선영상에서 쇄골두개형성이상의 진단 을 위해 가치가 있는 특징 중 그 판독이 명확치 않았던 소견. 이번 증례의 파노라마 방사선영상도 그들이 발표한 소견. 들이 3D CBCT 영상과 함께 비교되며 명확히 밝혀져, 향후. 과 일치하여 하악골의 상지가 평행한 양측 경계를 갖는 모양. CBCT를 이용하여 보다 계측적으로 방사선영상의 특징을 정. 을 보였고 길이가 정상보다 길게 관찰되었으며 또한 하악골. 리할 필요가 있다고 생각된다.. 의 근돌기가 후상방으로 향하고 있었다. 또한 관골궁이 하악. 감사의 글. 골 근돌기의 하방 경사 양상과 관골궁의 형성부전된 듯한 모 습이 관찰되었는데 이러한 소견들은 파노라마 방사선영상을 이용한 쇄골두개형성이상의 진단에 상당한 가치가 있다고 생 각되었다.. 이 논문은 2011년도 조선대학교 치과병원 학술연구비의 지 원을 받아 연구되었음.. 이에 대하여 Jensen과 Kreiborg (1993)도 관골과 비골의 발 육 저하가 나타날 수 있음을 언급하였으며, McNamara 등 (1999)도 쇄골두개형성이상 환자의 파노라마 방사선영상에 서 관골궁이 심한 하향경사를 보이며 때로 관골측두봉합부에 서 그 연결이 끊어져 있다고 보고하였다. 그러나 그가 보고한 증례 중 2예의 파노라마 방사선영상에서 좌측, 즉 편측의 관골 궁 형성부전을 판독하고 있다. 그러나 본 저자들이 그의 증례 들을 재판독한 소견으로는 좌우 양측 모두 관골궁의 형성부 전이 인정되었다. 진단적 가치가 있다고 생각되는 이러한 소견은 명확히 밝힐 필요가 있어 이번 증례에서 CBCT를 이용하여 3차원영상을 재구성하고 파노라마 방사선영상에서 나타난 관골궁의 형태 를 재평가하였다. 이번 증례의 파노라마 방사선영상에서 나타난 관골궁의 형 성부전 양상은 3차원 영상의 측면상에서 좌우 양측 관골궁이 명확히 관골과 단절되어 있음이 확인되었다. 또한 그 결여양 상은 관골측두봉합 위치로부터 전후방 양측으로 상당부분이 결여되어 있음이 확인되었다. 또한 파노라마 방사선영상에서 관골궁이 하방만곡된 모습 으로 나타난 모습은 3차원 영상의 측면상에서 다소 만곡을 인 정할 수 있으나, 하악골의 근돌기가 특징적 후상방으로 원심 만곡을 이루며 관골궁을 지나 그 상방까지 길게 연장되어 있 어 마치 근돌기 중간까지 관골궁이 내려와 있는 듯한 착시와 함께 과잉 판독될 수 있다고 생각되었다. 따라서 McNamara 등(1999)의 파노라마 방사선영상에서 관찰된 관골궁 만곡에 대한 판독은 더 많은 증례의 CBCT 영상과 함께 보완되어야 하겠다. 한편 이번 증례에서 하악골의 하악체 후방부위부터 좌우 양 측 우각부에 이르기까지 피질골이 두터운 양상을 나타내었 다. 이러한 소견은 McNamara 등(1999)이 발표한 증례의 파노 라마 방사선영상에서도 관찰되는 형태이상임에도 그들은 언. 48. 참고문헌 Atasu M, Dumlu A, Ozbayrak S: Multiple supernumerary teeth in association with cleidocranial dysplasia. J Clin Pediatr Dent 21:85-91, 1996. Bruce LD, Howard JG: Cleidocranial dysplasia: report of case. J Oral Surgery 27:41-43, 1969. Farman AG, Nortje CJ, Wood RE: Oral and Maxillofacial Diagnostic Imaging, St. Louis, Mosby, pp.115-117, 1993. Golan I, Preising M, Wagener H, Baumert U, Niederdellmann H, Lorenz B, Müssig D: A novel missense mutation of the CBFA1 gene in a family with cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD) and variable expressivity. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol 20:113-120, 2000. Golan I, Baumert U, Wagener H, Dauwerse J, Preising M, Lorenz B, Niederdellmann H, Müssig D: Atypical expression of cleidocranial dysplasia: clinical and molecular-genetic analysis. Orthod Craniofac Res 5:243-249, 2002. Golan I, Baumert U, Hrala BP, Schaumburger J, Wiech O, Grifka J, Müssig D: Symptoms and signs in cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD). Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 141:336-340, 2003. Harris RJ, Gaston GW, Avery JE, McCuen JM: Mandibular prognathism and apertognathia associated with cleidocranial dysostosis in a father and son. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 44:830-836, 1977. Hitchin AD, Fairley JM: Dental management in cleido-cranial dysostosis. Br J Oral Surg 12:46-55, 1974. Järvinen S: Cephalometric findings in three cases of cleidocranial dysostosis. Am J Orthod 79:184-191, 1981. Jensen BL, Kreiborg S: Development of the dentition in cleidocranial dysplasia. J Oral Pathol Med 19:89-93, 1990. Jensen BL, Kreiborg S: Craniofacial abnormalities in 52 school-age and adult patients with cleidocranial dysplasia. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol 13:98-108, 1993. Jensen BL, Kreiborg S: Craniofacial growth in cleidocranial dysplasia--a roentgencephalometric study. J Craniofac Genet.
(6) Gun-Sun Lee and Jae-Duk Kim. Dev Biol 15:35-43, 1995. Jeong SJ, Hong SK: Cleidocranial dysplasia: report of a case. Korean J Oral Maxillofac Radiol 30:229-234, 2000. (Korean) Kargul B, Salih IM, Yilmaz L, Dumlu A: Cleidocranial dysostosis: report of a case. J Clin Pediatr Dent 22:83-86, 1997. Kim JD, Lee CY, You CH: Cleidocranial dysplasia: a case report. Korean J Oral Maxillofac Radiol 34:55-59, 2004. (Korean) Koch PE, Hammer WB: Cleidocranial dysostosis: review of the literature and report of case. J Oral Surg 36:39-42, 1978. Kreiborg S, Jensen BL, Björk A, Skieller V: Abnormalities of the cranial base in cleidocranial dysostosis. Am J Orthod 79:549557, 1981. Marie P, Sainton P: Sur la dysostose cleido-cranienne hereditaire. Rev Neurol 6:835-838, 1898. Martin S: Sur un déplacement natural de la clavicule. J Méd Chir Pharmacol 23:456-460, 1765. McNamara CM, O'Riordan BC, Blake M, Sandy JR: Cleidocranial dysplasia: radiological appearances on dental panoramic radiography. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 28:89-97, 1999.. Nebgen D, Wood RS, Shapiro RD: Management of a mandibular fracture in a patient with cleidocranial dysplasia: report of a case and review of the literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 49:405-409, 1991. Otto F, Kanegane H, Mundlos S: Mutations in the RUNX2 gene in patients with cleidocranial dysplasia. Hum Mutat 19:209-216, 2002. Richardson A, Deussen FF: Facial and dental anomalies in cleidocranial dysplasia: a study of 17 cases. Int J Paediatr Dent 4:225-231, 1994. Rushton MA: The failure of eruption in cleido-cranial dysostosis. Br Dent J 63:641-645, 1937. Smith NH: A histologic study of cementum in a case of cleidocranial dysostosis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 25:470478, 1968. Yamamoto H, Sakae T, Davies JE: Cleidocranial dysplasia: a light microscope, electron microscope, and crystallographic study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 68:195-200, 1989.. 49.
(7)
수치
관련 문서
Use the average shear flow method to calculate the shear throughout each of the panels in the idealized tapered box beam pictured in Figure 4 9 13 Table 4 9 4 lists the
Operational qualification testing generally includes matters on depth dose distribution and electron beam energy calculation, average beam current, conveyor
KEY WORDS : Computed tomography, Dual energy, Renal stone, Uric acid stone, Non-uric acid stone,
저작권법에 따른 이용자의 권리는 위의 내용에 의하여 영향을 받지 않습니다.. 이것은 이용허락규약 (Legal Code) 을 이해하기
Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the morphologic characteristics of the interalveolar foramen and to analyze according to sex and age using cone
인형극은 흥미 호기심 자극 강력한 도구 어린이 , 학부모 , 시민 위한 과학문화 확산. 예술은
A cone is called strongly convex if it does not contain a nontrivial linear subspace. In this paper, every cone is assumed to be strongly convex. A polyhedral cone is
In the present study, as a preliminary study, a LACC-based Compton CT was developed to estimate the activity of the spot inside the radioactive waste drum. To