서론
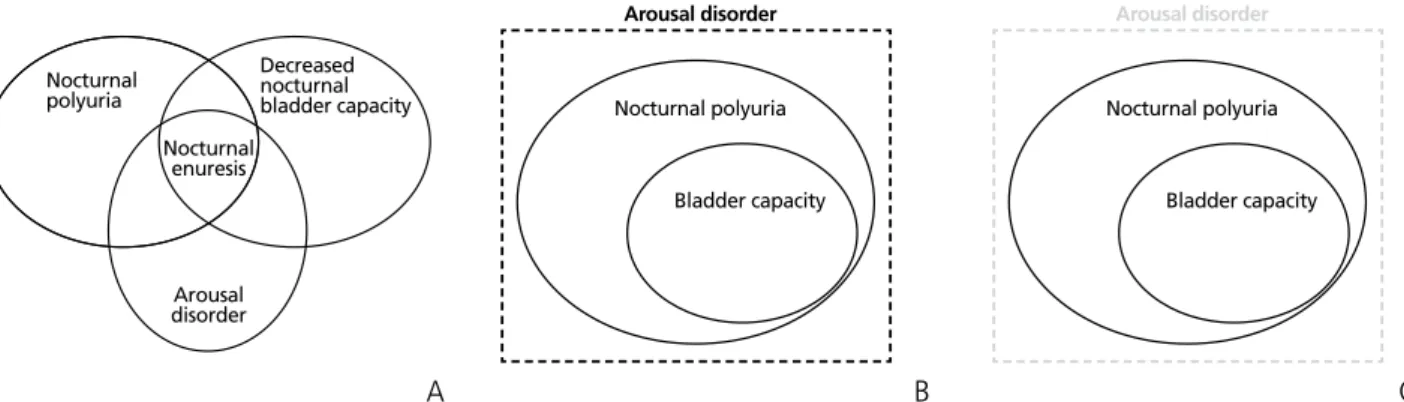
5세 이상의 아이에서 자는 도중 간헐적으로 요실금이 발 생되는 질환을 야뇨증이라고 한다[1]. 이러한 야뇨증은 흔 히 야간다뇨, 야간 방광용적 감소 및 각성장애가 원인이 되 어 발생한다(Figure 1A) [2]. 이를 다르게 설명하면, 수면 도 중 방광용적보다 많은 소변량이 만들어진 상태를 각성하지 못하고 배뇨를 하는 것이 야뇨증의 원인이 된다(Figure 1B).
만약 수면 도중 방광용적보다 많은 소변량이 만들어진 상태 를 각성하게 되어 잠을 깨서 소변을 보게 되면 야간뇨가 된다 (Figure 1C). 야뇨증 치료는 이러한 원인들을 조절하는 것으로,
수면도중 발생하는 소변량을 줄이기 위하여 행동치료 및 항 이뇨호르몬 치료를 시행하며, 야간 방광용적을 늘리기 위하 여 항콜린제 혹은 베타3 길항제를 사용하고, 각성장애를 호 전시키기 위하여 알람치료이나 삼환계 항우울제를 사용하고 있다. 이러한 치료 중 항이뇨호르몬과 항콜린제, 삼환계 항 우울제 등의 약물치료는 약물을 중단하게 되면 다시 재발하 기 때문에 완치를 목적으로 하는 치료는 아니다[3-5]. 하지 만 알람치료의 경우는 치료를 중단하더라도 절반 가량에서 야뇨증이 치료된 상태가 유지되기 때문에 완치를 목적으로 하는 치료라고 할 수 있다[6].
야뇨증은 방광용적의 증가와 야뇨에 대한 각성장애가 호 전되면서 치료 없이 1년에 15% 가량 스스로 호전되는 경 향을 보인다(Figure 2) [7,8]. Figure 2에서 볼 수 있듯이 생후 9세까지는 야뇨증이 치료 없이도 스스로 호전되는 경 향을 보이기 때문에, 야뇨증에 대한 치료 방법을 고려할 때 9세를 기준으로 전후가 달라져야 한다. 9세 이전 야뇨증 환 자의 경우 치료 없이 호전될 가능성은 있으나, 야뇨증 치료
치료에 반응하지 않는 야뇨증 환자의 관리
김 성 철 | 인제대학교 의과대학 해운대백병원 비뇨기과
Management of patients with refractory nocturnal enuresis
Seong Cheol Kim, MD
Department of Urology, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea
Received: September 2, 2017 Accepted: September 16, 2017 Corresponding author: Seong Cheol Kim
E-mail: H00181@paik.ac.kr
© Korean Medical Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.
org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
There are two types of refractory nocturnal enuresis. The first type corresponds to patients who are refractory from initial success, and the second type refers to refractory nocturnal enuresis after long-term success, in patients who cannot discontinue medications for enuresis. In the former type, it is necessary to determine whether the timing of medications is appropriate, whether the usage of antidiuretics is appropriate, whether any lifestyle changes have taken place, and whether there are secondary causes of enuresis. In the latter type, enuretic alarm treatment should be considered initially, and it is then important to investigate whether a respiratory obstruction is present in patients with nocturnal polyuria, whether the patient is constipated, and whether patients with non-monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis have lower urinary tract symptoms or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
Key Words: Nocturnal enuresis; Drug therapy; Drug resistance
를 통하여 친구들과 외박을 하거나 캠프 활동 등의 사회 생 활에서 제약이 없게 해주고[9], 자존심을 키워줄 필요가 있다 [10]. 그래서 이 시기의 치료목표는 야뇨증이 자연 치유되 는 시기까지 야뇨증이 없도록 유지하는 것이다. 9세 이후부 터는 야뇨증의 자연치유를 기대하기 어렵기 때문에 보다 적 극적인 치료가 필요하며, 이 시기의 치료는 약물치료 없이도 야뇨증이 없도록 유지하는 것, 즉 완치에 그 목표를 둔다. 그 렇기 때문에 치료에 반응하지 않는 야뇨증에 대하여 논의할 때 상기 2가지 시기를 나누어서 고려해야 한다. 자연치유를 기대할 수 있는 시기에서 치료에 반응하지 않는 야뇨증은 약 물치료나 행동치료 등으로 야뇨증상이 없어지지 않는 경우 이며, 일차치료에 반응하지 않는 야뇨증을 의미한다. 자연치
유를 기대할 수 없는 시기에서 치료에 반 응하지 않는 야뇨증은 약물치료를 중단 할 수 없는 경우이며, 장기적으로 치료에 반응하지 않는 야뇨증, 즉 완치가 되지 않았음을 의미한다.
이번 특집에서는 치료에 반응하지 않 는 야뇨증에 대하여 고려해야 할 사항들 에 대하여 알아보고 이를 위한 해결책에 대하여 기술해 보고자 한다.
일차치료에 실패한 경우
1. 치료시기가 적절하지 않은 경우 야뇨증은 5세 이후까지 자는 중 요실금이 유지되는 경우로 정의된다[1]. 5세 이후 방문하는 야뇨증 환자들에게 방문 이 후부터 약물치료를 시작하는 것에 대해서는 많은 논의가 필 요하다. 앞서 이야기 하였듯이 야뇨증의 치료에 사용되는 약 물들의 경우 완치를 목적으로 하기보다는 야뇨증이 자연 치 유되는 시기까지 증상을 없애는 것이 목적이기 때문에, 빠른 시기에 약물치료를 시작하는 것은 약물치료를 더 오랫동안 해야 할 필요가 있다는 것을 의미한다. 또한 치료 시작시기가 치료 실패와 중요한 관련이 있는 이유는 야뇨증 환자의 치료 에 대한 동기부여와 관련이 있기 때문이다. 환자 본인이 치료 를 필요로 하는 시기에 약물치료를 시작하게 되면, 동기 부여 로 인하여 행동치료를 더욱 적극적으로 하게 되고, 치료 이행
Figure 1. Pathophysiology of nocturnal enuresis. (A) The Venn diagram using three causative factors of nocturnal enuresis. (B) New concept of Venn diagram to explain the pathophysiology of nocturnal enuresis which use the difference between bladder capacity and nocturnal urine volume. (C) The pathophysiology of nocturia.
Nocturnal enuresis Nocturnal polyuria
Decreased nocturnal bladder capacity
Arousal disorder
Bladder capacity Nocturnal polyuria
Arousal disorder
Bladder capacity Nocturnal polyuria
Arousal disorder
A B C
Figure 2. The prevalence of nocturnal enuresis according to age. (A) The prevalence of nocturnal enuresis tends to decrease by about 15% per year without treatment until the age of 9 years. (B) There is no difference in prevalence after 9 years old. Natural healing can be expected until 9 years old, but it is hard to expect it after that time. Modified from Yeung CK, et al. BJU Int 2006;97:1069-1073 [7].
Prevalence of nocturnal enuresis (%)
5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Age (year)
25
20
15
10
5
0
A B
율이 높아지기 때문에 치료 실패 가능성이 줄어들게 된다. 그 래서 International Childrenʼs Continence Society에서는 야 뇨증 환자의 약물치료 시기를 6세 이후로 권장하고 있다[11].
야뇨증의 적절한 치료시기는 나이의 절대값을 정하여 기준 을 정하기 보다는 야뇨증을 앓고 있는 아이가 불편감과 치료의 필요성을 느끼는 시기로 정하는 것이 더 좋을 것이다. 특히 최 근에는 친구집에서 자고 오거나, 캠프 등의 활동이 많아지고 있기 때문에 이전의 기준으로 치료 시작시기를 결정하는 것은 좋은 방법이 될 수 없다. 그래서 5세 이상의 아이에서 야뇨증 이 진단될 경우, 환자가 치료에 대한 필요성을 느끼지 못할 경 우에는 부모와 상담하여 행동치료 위주로 치료를 하고, 환자가 치료에 대한 필요성을 느끼거나 사회생활에서의 불편감을 나 타내는 시기가 되었을 경우 약물치료를 권장하는 것이 좋다.
2. 항이뇨호르몬(데스모프레신) 치료방법이 적절하지 않은 경우
1) 약역동학적 문제
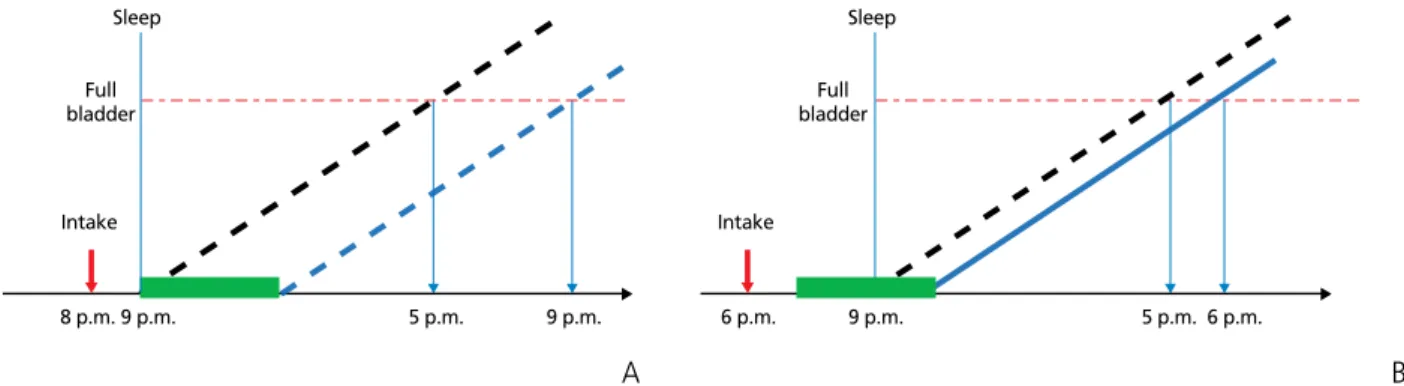
데스모프레신(미니린)은 약물복용 후 1시간 이후부터 4- 5시간 동안 소변 생성량을 줄이는 효과를 가지고 있다[12].
그렇기 때문에 약물복용방법이 잘못된 경우에는 약물치료에 반응이 없을 수 있다. 수면시간 중 4-5시간 동안 소변 생성량 을 줄이는 데스모프레신의 효과를 최대한 얻기 위해서는 수 면 전 1시간 이내에 약물을 복용해야 한다(Figure 3). 또한 수 면 시간이 긴 아이의 경우는 데스모프레신의 약효 유지기간 인 4-5시간이 부족할 수 있다. 이럴 경우 약용량의 증량이
필요하나 효과가 없을 경우, 일차치료의 목적으로는 수면시 간 중간에 깨워서 소변을 보게 하는 것도 방법이 될 수 있다.
2) 비단일증상성 야뇨증
비단일증상성 야뇨증의 경우는 데스모프레신 단독치료로 효과가 없을 가능성이 매우 높다. 이러한 경우는 방광용적을 이용하면 쉽게 판단할 수 있는데, 나이에 비하여 방광용적이 약 50% 정도인 경우는 데스모프레신 단독치료에 전혀 반응 을 하지 않을 가능성이 높다[13]. 방광용적이 줄어들어 있는 비단일증상성 야뇨증으로 진단된 경우에는 데스모프렌신 치 료에 항콜린제를 추가하면 15%가량 치료 반응률을 올릴 수 있으며, 효과가 없을 경우 항콜린제 용량을 증량하면 추가적 인 효과를 얻을 수 있다[14].
3) 정제와 구강붕해정
데스모프레신은 2가지 제형(정제와 구강붕해정)이 널리 사용되고 있다. 정제에 비하여 구강붕해정의 경우는 약물복 용 시 수분섭취가 필요 없고, 약물에 대한 치료 이행률이 더 높으며, 식이와 관련이 없어 약물복용 후 일정한 혈중농도를 유지할 수 있는 장점들이 있다[15,16]. 이러한 이유로 정제 를 이용한 약물치료에 반응이 없을 경우는 구강붕해정으로 변경해보는 것이 좋다.
4) 행동치료를 같이 시행해야 한다
행동치료를 통하여 방광용적과 야간 소변 생성량 간의 차 이를 줄이는 것은 매우 중요하다. 차이가 줄어들게 되면 약 물치료의 효과가 증가될 뿐만 아니라 필요한 약물의 개수나 용량을 줄일 수 있게 되며, 치료 후 재발을 줄일 수 있다[17].
Figure 3. Relationship between time of desmopressin administration and drug effect. Desmopressin reduces urine for 4 to 5 hours from 1 hour after taking the drug.
(A) If patients take the desmopressin after 8 p.m. in them who sleeps at 9 p.m., they will be able to fully exercise the effect of the drug because the time of the effect of the desmopressin is included during the sleeping time. (B) On the other hand, if patients take the desmopressin at 6 p.m., which is earlier than that, they will not be able to take all of effect of it because it takes effect during only 2 to 3 hours. Dotted line: night urine production in patient with nocturnal enuresis. Solid line: night urine production after desmopressin administration. Green box: desmopressin effect zone.
Sleep
Intake
8 p.m. 9 p.m. 5 p.m. 9 p.m.
Full bladder
Sleep
Intake
6 p.m. 9 p.m. 5 p.m. 6 p.m.
Full bladder
A B
3. 생활방식의 변화가 있는 경우
약물치료에 반응을 보이던 환자에서 어느 순간부터 다시 반응이 없을 경우 생활방식에서의 변화가 있는지 확인을 해 야 한다. 우선적으로 고려해야 할 상황은 야간 수분섭취의 증가가 있는지 확인해야 한다. 이를 위해서 주간 수분섭취량 이 줄어들었는지, 야간에 운동량이 증가하지 않았는지, 저녁 식사시간이 늦어지지 않았는지를 확인해야 한다. 특히 이들 중, 최근에는 부모의 직장생활로 인한 늦은 저녁식사시간으 로 인하여 수면과 저녁식사시간의 간격이 짧아져 효과적인 행동치료가 이루어지지 않는 경우가 많다.
4. 이차적인 요인을 가지고 있는 경우
야뇨증에 대한 기존의 치료법에도 불구하고 전혀 다른 임 상양상을 나타내는 경우 이차적인 요인이 있는지 고려해야 한다. 특히 약물치료로 야간 소변량이 줄어들었는데도 불구 하고 일정한 시간에 야뇨증이 발생하거나, 동일한 치료에 불 규칙적인 치료반응을 보이거나, 어떠한 약물치료에도 전혀 반응을 보이지 않으면 이차적인 요인을 고려해야 한다. 이 차적인 요인의 가장 대표적인 경우가 스트레스가 심한 상황 이다[18]. 이럴 경우에는 필요 시 정신과 전문의와 같이 진료 를 보는 것이 중요하다. 그 이외에 당뇨나 요붕증, 약물복용 및 신경인성 방광 등의 원인이 있을 수 있다.
장기적으로 치료에 실패한 경우
1. 각성장애가 지속되는 경우
앞에서 기술하였듯이 9세 이후에는 야뇨증의 유병률이 차 이가 없기 때문에 더 이상 약물치료를 통하여 야뇨증의 자연 치유를 기다리기는 것은 옳은 방법이 아니다. 알람치료는 수 면 중 요실금에 대한 각성을 호전시키는 방법으로 야뇨증에 대한 각성장애가 있는 환아들에 사용할 수 있으며, 치료중단 후 거의 절반 정도에서 효과가 유지되기 때문에 완치를 목적 으로 하는 치료가 될 수 있다[6]. 알람치료에 효과가 있는 환 아들에게 추가로 자기 전에 물을 먹은 뒤 알람치료를 지속하 게 하는 overlearning 방법은 재발률을 절반으로 줄이는 효
과가 있다[6]. 하지만 알람치료를 통하여 야뇨증에 대한 각 성을 회복하지 못한 경우 차선책으로 선택할 방법에 대해서 는 아직 뚜렷하게 거론되고 있는 것은 없다.
2. 방광용적과 야간소변량의 차이가 지속적인 경우 야뇨증에 대한 각성이 없더라도 수면 중 방광용적만큼 야 간소변량이 만들어지지 않으면 야뇨증이 발생하지 않는다.
그래서 각성이 회복되지 않더라도 방광용적과 야간소변량의 차이를 우선적으로 없애는 것도 좋은 방법이 된다.
1) 야간다뇨
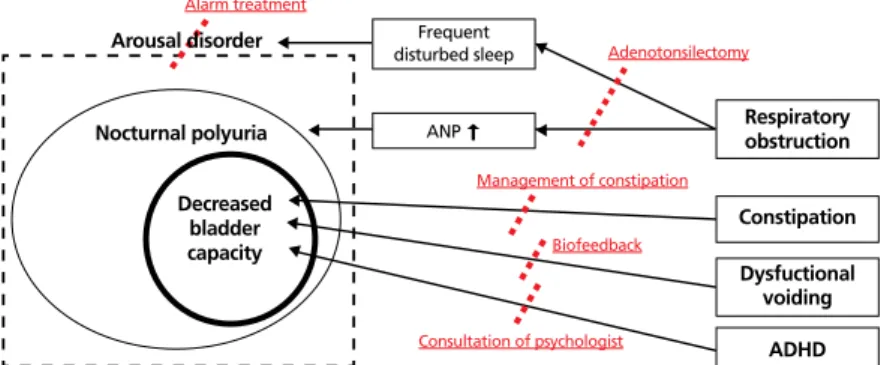
치료에 반응하지 않는 야간다뇨의 가장 대표적인 경우는 수면 중 호흡기 폐색이다[19]. 수면 중 호흡기 폐색은 혈중 atrial natriuretic peptide의 상승으로 야간다뇨의 원인이 되며[20], 그 외 반복적인 수면박탈로 인한 수면 중 각성장애 의 원인이 되기도 한다[21]. 약물치료에 반응이 없는 야뇨증 환아들의 경우 코골이나 편도비대증이 있는지 확인을 해야 하며, 진단된 경우에는 야뇨증 호전을 위하여 아데노이드편 도절제술이나 구개확장술 등이 필요하다[22-24].
2) 비단일증상성 야뇨증
아무리 야간 소변량을 줄이더라도 방광용적이 적은 경우 에는 효과를 보지 못하는 경우가 있다. 앞서 기술하였듯이 항콜린제의 사용이 증상호전에 매우 도움이 되지만, 거의 대부분 약물중단 후 재발되기 때문에 비단일증상성 야뇨증 을 일으키는 근본적인 원인을 해결하려 노력해야 한다[25].
우선적으로 변비를 해결해야 한다. 변비를 치료하는 것만으 로도 주간 요실금 등이 스스로 해결되기 때문에 이러한 환 아들에서 변비의 치료는 매우 중요하다[26]. 두 번째는 하부 요로증상이 나타날 수 있는 요인을 해결해야 한다. 대표적 인 경우가 비기능성배뇨이며, 야뇨증 환아가 이 질환이 의 심되는 경우에는 요역동학검사나 근전도·요속도검사를 통 하여 진단 후 바이오피드백을 이용하여 치료를 받아야 한 다. 마지막으로 교정가능한 행동장애가 있는지 학인해야 한 다. 주의력 결핍 및 과잉행동장애는 야뇨증의 한 원인이 되 기 때문에 의심이 될 경우 정신과 전문의의 진료가 필요하 다. 장기적으로 치료에 실패한 경우에 대하여 요약하였다 (Figure 4).
결론
야뇨증을 치료하기에 앞서 환자 및 보호자에게 야뇨증에 대한 정확한 정보를 설명하는 것이 중요하다. 이를 바탕으 로 환자 및 보호자는 질환에 대한 자연경과를 이해하고 야 뇨증 치료에 반응이 없더라도 의사의 치료방법에 수긍하여 따라오게 된다. 야뇨증의 치료는 시기에 따라서 치료의 목 표를 다르게 잡아야 한다. 자연치유가 가능한 시기에 약물 치료를 시도할 때는 치료에 대한 동기를 가지고 있는 환자 를 대상으로 적절한 약물선택이 이루어져야 약물치료의 반
응율을 높일 수 있다. 만약 약물치료 후 이전과 다른 경과를 보이거나 갑작스러 운 변화가 있을 경우 다른 원인이나 생 활환경의 변화가 있는지 확인이 필요하 다. 더 이상 자연치유를 기다리기 어렵 다고 판단되는 시기까지 약물치료를 중 단할 수 없을 때는 좀 더 적극적인 치 료가 필요하다. 야뇨증에 대한 각성장 애를 치료하기 위하여 알람치료를 시작 하고, 수면 중 호흡기폐색이나 비단일증 상성 야뇨증의 해결 가능한 원인이 있 는지 확인하고 치료하는 것이 중요하다 (Table 1).
찾아보기말: 야뇨증; 약물치료; 약물저항
ORCID
Seong Cheol Kim, http://orcid.org/0000-0003- 0228-0037
REFERENCES
1. Austin PF, Bauer SB, Bower W, Chase J, Franco I, Hoebeke P, Rittig S, Walle JV, von Gontard A, Wright A, Yang SS, Neveus T. The standardization of termi- nology of lower urinary tract function in children and adolescents: update report from the standardization committee of the International Childrenʼs Continence Society. Neurourol Urodyn. 2016;35:471- 481.
2. Austin PF, Vricella GJ. Functional dis-orders of the lower urinary tract in child-ren. In: Campdell MF, Walsh PC, Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, editors. Campbell-Walsh urology. 11th ed.
Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2016. p. 3297-3316.
3. Glazener CM, Evans JH. Desmopressin for nocturnal enuresis in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2002;(3):CD002112.
4. Glazener CM, Evans JH, Peto RE. Drugs for nocturnal enu- resis in children (other than desmopressin and tricyclics).
Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003;(4):CD002238.
5. Caldwell PH, Sureshkumar P, Wong WC. Tricyclic and related drugs for nocturnal enuresis in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016;(1):CD002117.
Figure 4. Refractory from long-term success. ANP, atrial natriuretic peptide; ADHD, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
Alarm treatment
Adenotonsilectomy
Management of constipation
Consultation of psychologist Biofeedback
Respiratory obstruction Frequent
disturbed sleep
Constipation Dysfuctional
voiding ADHD ANP
Arousal disorder
Nocturnal polyuria
Decreased bladder capacity
Table1. Summary of the management of patients with refractory nocturnal enuresis Period Before 9 years old
(when natural healing can be expected) After 9 years old (when natural healing can not be expected) Goal of treatment Maintain no nocturnal enuresis until
natural healing Maintain no nocturnal enuresis without medications Considerations and
managements 1. Is the timing of medication appropriate?
Postpone the medication until patient is motivated
2. Is the usage of antidiuretics appropriate?
Take a pill within 1 hour before going to bed
Add the anticholinergics in patient with NMSNE
Melt is better than tablet
Combination with behavioral treatment 3. Were there any changes in life styles?
When the clinical course changed suddenly
4. Are there secondary causes for enuresis?
When the clinical course is different from others
1. Persistent arousal disorder Alarm treatment
2. Persistently more amount of night urine production than bladder
capacity
Nocturnal polyuria: investigate a respiratory obstruction NMSNE: management of
constipation, LUTS, ADHD
NMSNE, non-monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis; LUTS, lower urinary tract symptom; ADHD, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
6. Glazener CM, Evans JH, Peto RE. Alarm interventions for nocturnal enuresis in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005;(2):CD002911.
7. Yeung CK, Sreedhar B, Sihoe JD, Sit FK, Lau J. Differences in characteristics of nocturnal enuresis between children and adolescents: a critical appraisal from a large epidemiological study. BJU Int 2006;97:1069-1073.
8. Forsythe WI, Redmond A. Enuresis and spontaneous cure rate: study of 1129 enuretis. Arch Dis Child 1974;49:259-263.
9. Jalkut MW, Lerman SE, Churchill BM. Enuresis. Pediatr Clin North Am 2001;48:1461-1488.
10. Hagglof B, Andren O, Bergstrom E, Marklund L, Wendelius M. Self-esteem in children with nocturnal enuresis and urin- ary incontinence: improvement of self-esteem after treatment.
Eur Urol 1998;33 Suppl 3:16-9.
11. Neveus T, Eggert P, Evans J, Macedo A, Rittig S, Tekgul S, Vande Walle J, Yeung CK, Robson L; International Childrenʼs Continence Society. Evaluation of and treatment for mono- symptomatic enuresis: a standardization document from the International Childrenʼs Continence Society. J Urol 2010;183:
441-447.
12. De Guchtenaere A, Van Herzeele C, Raes A, Dehoorne J, Hoebeke P, Van Laecke E, Vande Walle J. Oral lyophylizate formulation of desmopressin: superior pharmacodynamics compared to tablet due to low food interaction. J Urol 2011;
185:2308-2313.
13. Montaldo P, Tafuro L, Rea M, Narciso V, Iossa AC, Del Gado R. Desmopressin and oxybutynin in monosymptomatic noc- turnal enuresis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-con- trolled trial and an assessment of predictive factors. BJU Int 2012;110:E381-E386.
14. Berkenwald A, Pires J, Ellsworth P. Evaluating use of higher dose oxybutynin in combination with desmopressin for refra- ctory nocturnal enuresis. J Pediatr Urol 2016;12:220.e1-220.e6.
15. Lottmann H, Froeling F, Alloussi S, El-Radhi AS, Rittig S, Riis A, Persson BE. A randomised comparison of oral des- mopressin lyophilisate (MELT) and tablet formulations in children and adolescents with primary nocturnal enuresis. Int J Clin Pract 2007;61:1454-1460.
16. De Bruyne P, De Guchtenaere A, Van Herzeele C, Raes A, Dehoorne J, Hoebeke P, Van Laecke E, Vande Walle J. Phar- macokinetics of desmopressin administered as tablet and oral lyophilisate formulation in children with monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis. Eur J Pediatr 2014;173:223-228.
17. Ferrara P, Del Volgo V, Romano V, Scarpelli V, De Gara L, Miggiano GA. Combined dietary recommendations, desmo- pressin, and behavioral interventions may be effective first- line treatment in resolution of enuresis. Urol J 2015;12:2228- 2232.
18. Akan S, Urkmez A, Yildirim C, Sahin A, Yuksel OH, Verit A.
Late-onset secondary nocturnal enuresis in adolescents asso- ciated with post-traumatic stress disorder developed after a traffic accident. Arch Ital Urol Androl 2015;87:250-251.
19. Neveus T, Leissner L, Rudblad S, Bazargani F. Respiration during sleep in children with therapy-resistant enuresis. Acta Paediatr 2014;103:300-304.
20. Everaert K, Pevernagie D, Oosterlinck W. Nocturnal enuresis provoked by an obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J Urol 1995;153:1236.
21. Neveus T. Pathogenesis of enuresis: towards a new under- standing. Int J Urol 2017;24:174-182.
22. Park S, Lee JM, Sim CS, Kim JG, Nam JG, Lee TH, Han MW, Kwon JK, Lee JC. Impact of adenotonsillectomy on nocturnal enuresis in children with sleep-disordered breathing: a prospective study. Laryngoscope 2016;126:1241-1245.
23. Kovacevic L, Lu H, Wolfe-Christensen C, Abdulhamid I, Thottam PJ, Lulgjuraj M, Madgy DN, Lakshmanan Y. Adeno- tonsillectomy normalizes hormones and urinary electrolytes in children with nocturnal enuresis and sleep-disordered breathing. Urology 2015;86:158-161.
24. Poorsattar-Bejeh Mir K, Poorsattar-Bejeh Mir A, Poorsattar- Bejeh Mir M, Moradi-Lakeh M, Balmeh P, Nosrati K. Rapid palatal expansion to treat nocturnal enuretic children: a sys- tematic review and meta-analysis. J Dent (Shiraz) 2015;16:
138-148.
25. Franco I, von Gontard A, De Gennaro M; International Childrensʼs Continence Society. Evaluation and treatment of nonmonosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis: a standardization document from the International Childrenʼs Continence Society. J Pediatr Urol 2013;9:234-243.
26. Loening-Baucke V. Prevalence rates for constipation and fae- cal and urinary incontinence. Arch Dis Child 2007;92:486- 489.
Peer Reviewers’ Commentary
본 논문은 야뇨증의 자연경과와, 약물치료의 시기와 치료에 반응 을 하지 않는 야뇨증 환자의 관리에 대해 소개를 하고 있다. 야뇨 증은 5세 이상의 아이에서 잠자는 중에 간헐적으로 요실금이 발 생되는 질환으로 생후 9세까지는 방광용적의 증가와 야뇨에 대 한 각성장애가 호전되면서 스스로 좋아지는 경향을 보이기 때문 에 야뇨증을 치료하기에 앞서 환자 및 보호자에게 야뇨증에 대해 설명하는 것이 중요하다. 저자는 자연 치유가 가능한 시기에 치 료에 대한 동기를 가지고 있는 환자를 대상으로 적절한 약물 선 택을 하고, 약물 치료 후 이전과 다른 경과를 보이거나 갑작스러 운 변화가 있을 경우 다른 원인이나 생활환경의 변화가 있는지 확인이 필요하다고 한다. 자연 치유를 기다리기 어렵다고 판단되 는 시기까지 약물 치료를 중단할 수 없을 때는 좀 더 적극적인 치 료가 필요하다고 한다. 본 논문은 치료에 반응하지 않는 야뇨증 에 대해서 고려할 사항과 해결책을 제시하고 있어 야뇨증 치료에 좋은 지침이 될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
[정리: 편집위원회]