저작자표시-비영리 2.0 대한민국 이용자는 아래의 조건을 따르는 경우에 한하여 자유롭게 l 이 저작물을 복제, 배포, 전송, 전시, 공연 및 방송할 수 있습니다. l 이차적 저작물을 작성할 수 있습니다. 다음과 같은 조건을 따라야 합니다: l 귀하는, 이 저작물의 재이용이나 배포의 경우, 이 저작물에 적용된 이용허락조건 을 명확하게 나타내어야 합니다. l 저작권자로부터 별도의 허가를 받으면 이러한 조건들은 적용되지 않습니다. 저작권법에 따른 이용자의 권리는 위의 내용에 의하여 영향을 받지 않습니다. 이것은 이용허락규약(Legal Code)을 이해하기 쉽게 요약한 것입니다. Disclaimer 저작자표시. 귀하는 원저작자를 표시하여야 합니다. 비영리. 귀하는 이 저작물을 영리 목적으로 이용할 수 없습니다.
Identification of nursing activities at general
medical and surgical nursing units
in Vietnam
by
Nguyen Thi Hong Minh
Master’s Thesis
Department of Nursing Sciences
The Graduate School, Ajou University
Identification of nursing activities at general
Medical and Surgical nursing units
in Vietnam
by
Nguyen Thi Hong Minh
A Thesis Submitted to the Graduate School of Ajou University
in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for The Degree
of Master of Science in Nursing
Supervised by
Mi Sook Song, RN, Ph.D
Department of Nursing Sciences
The Graduate School, Ajou University
This certifies that the Thesis
of Nguyen Thi Hong Minh is approved.
The Graduate School, Ajou University
December 23, 2010
Hyera Yoo, RN, PhD
Myung Sun Hyun, RN, PhD
Mi Sook Song, RN, PhD, Chair
SUPERVISORY COMMITTEE
i
I would like to express my heartiest gratitude to Professor Mi Sook Song for her sincere guidance and encouragement during this research. It is my great pleasure to pay my gratitude to Professor Myung Sun Hyun and Hyera Yoo, members of dissertation committee, for their efforts and valuable advice in order to improve my thesis paper. Thank you once again Professors. My deepest gratitude goes to all of the Professors who have taught me, encouraged me, and guided me in Ajou University. Thanks to these Professors for their tireless efforts, kindness, and endless help in building my theoretical and practical base and their sincere guidelines from time after time.
My special thanks to the Chairman of Ajou University who gave me the full tuition fee scholarship for my course at Ajou. I would like to take this opportunity to thank Ms. Kim and Ms. Beak and other staff who work in administration office, for their useful information to follow this Master’s Degree.
I would like to say ‘Thank you’ to Board of Managers of The Ho Chi Minh University Medical Center (UMC) in Vietnam, who gave me the opportunity to participate in this Master’s course. Moreover, I would like to thank the management of Ajou, Ho Chi Minh UMC and Thong nhat hospital especially Ms. Nguyen Thi Ngoc Suong, the director of nursing department, Ho Chi Minh UMC. She provided the study sites and helped in the cooperation of the nurse managers and staff nurses who participated in the survey. This research would not have been possible without their assistance.
Gratitude must be expressed to Fatima Muhammad Anwar. She never stopped encouraging me and provided me with sincere and generous friendship. Finally, I would like to thank my family for their endless support to pursue this degree.
ii
Table of Contents Acknowledgements ... i List of Contents ... ii List of Tables ... iv Abstract ... 1 Chapter1. Introduction... 3Statement of the problem ... 3
Purpose of the study ... 4
Significant of the study ... 5
Definition of terms ...
6
Chapter 2. Review of the Literature ... 8
Nursing activity ... 8
Pattern of nursing activities at medical and surgical nursing units ... 9
Average time of each nursing activity ... 9
Average frequency of each nursing activity ... 11
Proportion of direct and indirect nursing activities ... 11
Chapter 3. Research Method ... 14
Research design and procedure ... 14
Instruments ... 14
Data collection and procedure ... 15
Data analysis ... 16
Chapter 4. Results ... 17
iii
Findings ... 19
Question 1: Which nursing activities were performed by Vietnamese nurses at medical and surgical units? ... 19
Question 2: How much time and frequency for each nursing activity during a shift per nurse at medical and surgical nursing units? ... 24
Question 3: What was the proportion of direct and indirect nursing time during a shift per nurse at medical and surgical nursing units? ... 32
Question 4: What was the job independence level of each nursing activity? ... 38
Chapter 5. Discussion and Conclusion ... 44
Summary of findings and discussion ... 44
Limitations of the study ... 48
Conclusion ... 49
Appendix A - The nursing activities were not performed by Vietnamese nurses at general medical and surgical nursing units ... 50
Appendix B - The 135 nursing activities that were identified by Korean nurses in Park and Song (2000) study ... 51
Appendix C - Inform consent form ... 56
Appendix D - Questionnaire, the 145 nursing activities of instrument ... 57
iv
List of Tables
Table 1 General characteristics of the subjects ... 18
Table 2 The nursing activities were performed by Vietnamese nurses at general medical and surgical nursing units ... 22
Table 3 The average nursing time and frequency of each direct nursing activity during a shift per nurse at general medical and surgical nursing units ... 27
Table 4 The average nursing time and frequency of each direct nursing activity during a shift per nurse at general medical and surgical nursing units ... 32
Table 5 The average nursing time of each direct nursing domain during a shift per nurse .. 34
Table 6 The average nursing time of each indirect nursing domain during a shift per nurse ... 35
Table 7 The nursing time spend for direct and indirect nursing activities by unit during a shift per nurse ... 36
Table 8 Comparison of nursing time by nursing domain between medical and surgical nursing units... 37
1
Abstract
The purpose of this research is: to explore nursing activities performed by Vietnamese nurses; to identify time of each nursing activity that is performed by medical and surgical nurses and proportion of direct and indirect nursing time; to identify the job independence level of each nursing activity.
The sample consisted of 201 nurses working in two hospitals in Vietnam. The instrument used to collect data from two hospitals was a questionnaire including 145 nursing activities, which was developed by the Korean nurses and modified by the leader group of Vietnamese nurses.
Each nursing activity was described for time, frequency and job independence level. The 120 nursing activities were performed by the medical nurses and 123 nursing activities were performed by the surgical nurses.
Average time of each nursing activity, in which the nurses spend the most time, is 31.1 minutes for transfusion and the lowest time is 0.5 minute for respiratory pattern measurement or body weight measurement.
Average frequency of each nursing activity, which the nurses performed most commonly at both units are blood pressure check, pulse check, monitoring, and medication management. The lowest frequency for the activity performed by the Vietnamese nurses is the complete isolation for infection prevention and tube feeding via gastrostomy.
The highest percentage for direct nursing time is of safety with 25.1% and 31.5% respectively for day and night shift at medical nursing unit. The 27.1% and 28.1% respectively is of safety for day shift and night shift at surgical nursing unit. The lowest percentage is of hygiene with 0.9% for day shift at medical nursing unit. Also, 0% is of communication and assistance during night shift at surgical nursing unit.
The highest percentage for indirect nursing time is of recording with 58.9% at surgical nursing unit and 49.7% at medical nursing unit for day shift.
The total of nursing time is 68.6% (3.62 hours) and 31.4% (1.65 hours) for direct and indirect nursing activities respectively for the day shift in the medical nursing unit. The 69.6% (3.04 hours) and 40.5% (2.07 hours) are the direct and indirect nursing time respectively for day shift by a nurse at the surgical nursing unit.
2
The total of nursing time is 70.8% (4.19 hours) and 29.2% (1.72 hours) for direct and indirect nursing activities respectively for the night shift in medical nursing unit. The 57.9% (3.67 hours) and 42.1% (2.67 hours) are the direct and indirect nursing time respectively for night shift by a nurse at the surgical nursing unit.
The 71 nursing activities were identified to be completely independent and none of the nursing activity was completely dependent.
This study adds to describe the current situation in Vietnamese Hospitals. Overall, the direct nursing time is higher than the indirect nursing time in both units. The percentage of direct nursing activities at medical unit is higher than at the surgical nursing unit, which is used to build up the nursing cost.
Much time is spent for indirect nursing activities at surgical nursing unit calculated 40.5% for day shift and 42.1% for night shift, in which the nurse spend for recording is very high and needs to be controlled.
The percentage of spiritual support and communication, which involves admission interview, consulting, personal education, religious support and communication, is very low and it needs to be improved through proper nursing education.
3
Chapter 1 Introduction
Statement of the Problem
In Vietnam, January 2011, the nursing license will be issued to introduce that nursing has become a profession from just vocation. The draft content of the new issue contains reformed nursing functionalities, responsibilities; authority and job independence in the nursing profession. One of the main functions in nursing is counseling and education but these days the nurses are mostly managing paper records and performing the medical doctor orders in Vietnam. Currently, the analysis based on nursing activities will explore some trends to improve the activities performed by nurses which are appropriate to the nursing license.
Nowadays, the Vietnamese nurses at the medical and surgical nursing units have become more demanding regarding their nursing cost; they think that they have not received an appropriate nursing cost from nursing service, based on nursing activities. The nurses working at surgical unit always attain more nursing cost than the nurses at the medical nursing unit. For this reason, the nursing activities that nurses perform for patients are buried in the total cost of care for the patients. For example, the cost being paid by the patients is the same for both medical and surgical nursing units for all illness levels and the number of patients in both units is the same. But, as the medical unit nurses have to perform more direct nursing activities, they can take care of less number of patients as compared to the surgical unit nurses. As a result, surgical unit nurses get paid more than the medical unit nurses based on taking care of the number of patients.
In Vietnam, during 1989, a new medical insurance plan was introduced that was based on the medical fee-for-service system. This plan, according to Vietnamese Ministry of Health insurance, will be implemented nationally in 2014. Thus, the need for appropriate research on the nursing activities that can be used to build the nursing costs was of prime interest. Although attempts to identify nursing activities have been underway for few years in Vietnam, no valid data exists so far.
Buchan (2000) explored all previous studies to determine foundation of making nursing cost through direct nursing care and its impact on essential factors. These factors are
4
time consumed for the care and degree of job independence level. The nursing cost includes the total hours of nursing staff required to take care of the patients under the direct nursing activities.
One of the problems is the lack of willingness on the part of Vietnamese nurses to study nursing activities as an independent field. Rather, nursing activities are viewed as a dependent field as a part of medicine, and not considered worthy for separate investigation. Another related problem is that the nursing in Vietnam is not an established profession. The struggles in Vietnam today mirror the same efforts in the Korea a few decades ago.
To analyze the current nursing activities like how the nurses spend their time during a shift, proper research needs to be done on this topic to explore the various dimensions of nursing functions in Vietnam. Korea and the developed countries efforts define nursing as a professional discipline for over years but still this discipline of nursing has not yet built into a unique body of knowledge in many other under developed countries.
Nursing’s worldviews have been presented in many conceptual models or frameworks (Johnson, 1980; King, 1971; Newman, 1980; Orem, 1971; Rogers, 1970). These worldviews (called grand theories), despite their contribution to identify nursing as a profession, have been criticized for their lack of applicability to nursing practice. As the senior nurse has started to pay attention to useful clinical knowledge, a practice-oriented nursing process model has been highlighted.
Recent emphasis on determining the cost of nursing services in Vietnam highlights the need for investigating nursing activities. There is a paucity of descriptive research on activities performed by nurses and a lack of agreement about the definition and measurement of nursing activities. This study identifies nursing activities performed by Vietnamese nurses by using 145 nursing activities that were developed by Korean nurses and modified by a leading nursing group in Vietnam. Each nursing activity was examined for three essential factors: the time spent by nurses on each activity, frequency of care, and the job independence level.
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of this study is fourth fold: first, to explore nursing activities performed by Vietnamese nurses at medical and surgical nursing units; second, to identify nursing time
5
and frequency for each nursing activity; third, to identify the proportion of direct and indirect nursing time and fourth, to identify the job independence level of each nursing activity.
The following research questions are addressed:
1. Which nursing activities were performed by Vietnamese nurses at medical and surgical nursing units?
2. How much time and frequency for each nursing activity during a shift per nurse at medical and surgical nursing units?
3. What was the proportion of direct and indirect nursing time during a shift per nurse at medical and surgical nursing units?
4. What was the job independence level of each nursing activity? Significance of the Study
This research is a beginning effort to identify current nursing activities performed by Vietnamese nurses with a major emphasis on the nursing activities that are performed and not performed at medical and surgical nursing units. Through this study, the Vietnamese nurses will have general rules for using their time efficiently. And also they can recognize various dimensions in order to improve nursing role based on nursing activities i.e., which appropriate time and frequency should be adopted for each nursing activity.
In addition, the nursing activities will add to the knowledge of nursing practice in Vietnam as well as contribute to the growing body of work for the classification of nursing activities. As a profession, nursing has not yet being identified as a specialized body of knowledge. The identification of nursing activities assists the profession towards the development of a specialized body of knowledge.
The cost built from nursing activities is mainly through direct nursing activities. The cost information is foundation in evaluating the effectiveness and quality of nursing care. Furthermore, the Vietnamese nursing society cannot control and negotiate a nursing budget if they do not have the information about the activities that nurses perform.
6
Definition of Terms Nursing activity
Theoretical definition
A nursing activity is any treatment based upon clinical judgment and knowledge, which a nurse performs to enhance patient/client outcomes. Nursing activities include both direct and indirect nursing activities (McCloskey and Bulechek, 1996).
Operational definition
There is a list of nursing activities developed by Korean nurses and modified by the leader group of Vietnamese nurses. This list consists of 145 different nursing activities.
The 145 nursing activities are coded into the 14 nursing domains, in which 11 nursing domains are described for direct nursing activities and 3 domains are described for indirect nursing activities.
Each nursing activity is defined for a nurse in order to perform one of the interventions. Each nursing activity performed by Vietnamese nurses is evaluated through time, frequency and job independence level of the activity.
Direct and indirect nursing activity
Theoretical definition
A direct nursing activity or direct nursing intervention is a treatment performed through direct interaction with a patient. Direct nursing activities are interventions which include both the physiological and psychosocial nursing actions; both are ‘laying on of hand’ actions and more supportive in nature (McCloskey et al., 1996).
An indirect nursing activity is the activity related to a specific individual patient but not considered as ‘hands-on care’ (e.g., team meetings, patient documentation and telephone liaison) (Heather Williams, 2009).
Operational definition
Direct nursing activities are care activities performed in the presence of patients. There is 131 direct nursing activities were classified into 11 nursing domains. Those direct nursing domains are respiration, nutrition, elimination, exercise and posture, comport, hygiene, safety, spiritual, medication, assisting others and communication care.
7
There is 14 nursing activities were classified into 3 indirect nursing domains. Indirect nursing activities are those activities that include controlled substance checking, recording data in clinical records and the environmental management.
Job independence
Theoretical definition
The freedom to organize their own work, make their own decisions, etc. without needing help from other people (Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary-7th edition, 2007).
Operational definition
The operational definition of job independence is the level of self confidence of the nurse when she/he performs each nursing activity.
Each nursing activity was measured for job independence level, built from 5 levels Likert scale e.g., those 5 levels are completely independent, somewhat independent, neutral independent, somewhat dependent and completely dependent.
If the nurse can perform a nursing activity with complete independence, it means the nurse can do the activity by herself. They don’t need to take any help from medical doctor and/or other staff. The high independence level is associated with high education and much clinical experiences such as a senior nurse.
8
Chapter 2
Review of the Literature
This chapter contains a discussion of selected background and research literature relevant to the studies of previous nursing activities, the pattern of nursing activities at general medical and surgical nursing units.
Nursing Activity
McCloskey et al. (1996) explored nursing role and function through analysis of the activities of the nurses. Thus, in the conceptualization of nursing function, nurses are primarily coordinators of care instead of merely being care givers. These coordinating functions relate both to direct and indirect nursing activities. The central concept of the ‘glue function’ is that it is nurses who maintain the holistic overview of care given by all members of the health care team.
In 1989, the national implementation of medical insurance system in Korea has accelerated the need for research about nursing activities and their cost. The studies based on nursing activities to determine the nursing costs were conducted by Park, 1988; Park, Whang and Lee, 1992; and Young (1995).
Park and Lee (1992) identified 128 nursing activities, drawn from Henderson’s daily living activities and other literatures, to calculate nursing costs. The 16 nursing domains included in the study were: respiration, nutrition, elimination, exercise, rest, arrangement of bed, temperature maintenance, personal hygiene, security, communication, spiritual support, self-achievement, leisure, health counseling and education and. The nursing activities were examined by using a five- point Likert scale for these factors: level of professional skill, degree of independence and performance of the care. Interestingly, activities performed less than 50% of the time by a nurse and given less than 9 marks in all above three items were excluded as a means to determine nursing cost. Finally, 83 activities in 16 nursing care domains were selected to build the nursing costs. Some nursing activities that nurses perform for patients were removed due to non relevance to costs.
In a review of the dissertations conducted by Young (1995) showed that the research on nursing activities was mentioned above which lacks both conceptual and methodological bases e.g., the instruments used to define nursing activities were not assessed for validity or
9
reliability. Thus, Young did another study, which identify the nursing intervention in Korea. The nursing interventions use questionnaire developed by Iowa Intervention Project team for data collection. This study sample consisted of 443 nurses working in two hospitals in Korea. The research result showed that the 336 intervention for direct nursing activities in the Nursing Intervention Classification (NIC) were used by Korean nurses. Twenty-one interventions were used at least daily. Nurses working in various specialties performed similar interventions as well as those interventions that were unique to their area of specialty. Educated and experienced nurses performed more interventions more often than less educated and less experienced nurses.
Research by Park, Sung and Song (2000) is the classification of standard nursing activities in Korea. Nursing activities provided for the inpatients currently in Korea were identified and classified using a taxonomy which was developed by the researcher in this study through the Delphi process. The result of this research classified 135 nursing activities into 12 nursing domains in which 10 nursing domains for direct nursing activities and 2 nursing domains for indirect nursing activities. The direct nursing domains are respiration, nutrition, elimination, exercise, comport, hygiene, safety, spiritual, support, medication, communication and others assisting. The indirect nursing domains are communication and nurse station management. The pilot of this study was conducted in two hospitals to verify validity and appropriateness of nursing activities. The content validity index was 0.95 which was calculated by 6 clinical practice experts.
Overall, the above study adds to the growing body of work that uses nursing activities to build the nursing cost of nursing services, enhance quality of nursing care, and build a unique body of knowledge in nursing.
Pattern of Nursing Activities at the Medical and Surgical Nursing Units Average time and frequency of each nursing activity
Average time of each nursing activity
Nursing time of each nursing activity in special units was measured by nursing intensity. In this study, the patients whom the nurses took care at medical and surgical nursing unit were mildly ill (acuity I) and moderately ill (acuity II).
The research of Park and Song (1999) on estimation of nursing costs for hospitalized patients using the resource-based relative value scale identified the nursing time based on
10
each nursing activity. The results of Park described 11 nursing activities which were performed from 1 to 3 minutes e.g., respiration rate check, respiration pattern observation, breath sound measurement, body weight measurement, body height measurement, abdominal circumference measurement, at el. There are 53 nursing activities that need from 4 to 6 minutes to be performed e.g., postural drainage, physiotherapy, naso-oral suction, tracheal
suction, nasal prong, O2 mask apply, humidifies apply, CVP measurement, nursing
procedure related to TPN infusion, nursing related to IVH infusion, hot and cold pack apply, completely isolation for infection prevention, at el. There are 8 nursing activities that need from 7 to 9 minutes to be performed e.g., nursing procedure related to T-cannula exchange, observation and maintenance of respiration, nursing procedure related to nasogastric tube inserting, nursing procedure related to skeletal traction, encourage sleep, clothes change & at el. There are 30 nursing activities that need from 10 to 12 minutes to be performed e.g., mouth to mouth respiration, ambu bagging, partial feeding assistance, retention enema, gas enema, and at el. There are 10 nursing activities that need from 13 to 15 minutes to be performed e.g., intake and output measurement, bililary drainage maintenance, encourage rest, creations instruction. There are 6 nursing activities that need from 16 to 18 minutes to be performed e.g., cleansing enema, diaper change and skin care, admission interview, counseling. There are 5 nursing activities that need from 19 to 21 minutes to be performed e.g., total feeding assistance, tub bathing, nursing procedure on deathbed. There are 3 nursing activities that need from 22 to 24 minutes to be performed e.g., nursing procedure related to peritoneal dialysis prepare, start, finish; glycerin enema; walking accompany. There is 1 nursing activities that need from 25 to 27 minutes to be performed e.g., partial isolation for infection prevention. There are 9 nursing activities that need from 28 to 30 minutes to be performed e.g., completely isolation for infection prevention, nursing procedure related to hemodialysis prepare or start or finish, hemo-vac and sump tube drainage maintenance, bathing in bed, group education and handing over to nurses on next shift.
11
Average frequency of each nursing activity
Young (1995) used most frequently by Korean nurses is vital sign monitoring, fall prevention, oxygen therapy, heat and cold application, medication management and specimen management. The nursing activities used most frequency in general surgical nursing unit are identified medication management, tissue perfusion management, thermoregulation, respiratory management, electrolyte and acid base management, skin/wound management, exercise and safety. In medical nursing unit, the nursing activities used most frequently are electrolyte and acid base management, tissue perfusion management, medication management, respiration management, thermoregulation, nutrition support, physical comport promotion, elimination management and safety.
In short, the study of Young showed that there is a significant difference in frequency of nursing activities among medical and surgical nursing units. The most frequently occurring activity is electrolyte and acid base management at medical nursing unit and medication management at surgical nursing unit as shown above.
Proportion of direct and indirect nursing activities
In medical unit, William (2009) analyzed nursing activities as a Neuro-rehabilitation setting by work sampling. They have identified 108 nursing activities and observed the time that nurses spend in taking care of the patients such as 46% for direct patient care, 25% for indirect patient care, 10% for unit-related and 19% for personal time. The majority of Registered Nurses (RNs) workload was patient-related (75% of activities), with 14% allocated to medication administration and 19% to patient-related communication with members of the multi-disciplinary team.
In surgical unit, Desjardins et al. (2008) was conducted in response to perceptions that the surgical nursing staff was spending an excessive amount of time on non-nursing care. A sample of 30 nurse shifts was observed by trained observers who timed nurses' activities for their entire working shift using a hand-held Personal Digital Assistant (PDA). Activities were grouped into four main domains: direct patient care, indirect patient care, non-nursing and personal activities. The mean proportions of each nurse shift spent on the main activity domains were: direct care 32.8%, indirect care 55.7%, non-nursing tasks 9.0% and personal 2.5%. Three activities (communication among health professionals, medication verification/preparation and documentation) comprised 78.9% of indirect care time. Greater
12
time on indirect care was associated with work on night shifts and on the short-stay at the surgical unit. Subsequent work reorganization focused on reducing time spent on communication and medications.
In Korea, Park and Song (1990) study, the nursing hours during a day for the acuity I of patient intensity is 3.9 hours at medical nursing unit and 3.2 hours at surgical nursing unit. The Korean nurses spend 5.4 hours for acuity II of patient intensity at medical nursing unit and 4.5 hours at surgical nursing unit.
In summary, the proportion of direct nursing time at medical nursing unit is always higher than surgical nursing unit. For this reason, Lim (2008) showed that the nursing activities which built the nursing cost at medical unit were more than the activities at the surgical nursing.
In Vietnam, the research on nursing has limitations, where nursing is known as vocation. The job education level in nursing is not high e.g., there is just one Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) and around 50 Masters of Nursing in Science (MSN) for now. Thus, any research work produced by the educated nurses is not much and further narrows down the scope of research on nursing activities.
Thuan (2001) explored nurse’s time spent for direct nursing care which is 2 hours/shift at general surgical ward. The nurse’s spend their 19.3% of the time for vital sign, 4.2% of the time for nursing procedure, 35.1% of the time for medication care, 23.1 % of the time for measurement and monitoring, 1.6% of the time for nutrition care, 0.7% of the time for assisting doctors technically, 0.5% of the time for assisting doctors on a ward round and 15.5% of the time for communication and teaching patient.
Knowledge development in nursing science has progressed rapidly since 1961, when the nursing process was introduced to nursing practice. Nursing science has been moving from grand theories reflecting nursing’s worldviews to middle-range theories focused on practically useful knowledge. The classifications of nursing interventions contribute to building the middle-range theories. In particular, a classification of nursing activities helps to establish nursing as a discipline.
In Vietnam, there have been few studies on nursing activities for identifying the direct nursing time and no valid data has yet been reported. The research on nursing activities is limited because of the lack of instruments based on both conceptual and
13
methodological knowledge. Therefore, I would like to do a thorough study and perform research on nursing activities in order to identify the pattern of nursing activities at medical and surgical nursing units in Vietnam.
14
Chapter 3 Methodology
Research Design and Procedure
This study used a cross-sectional, descriptive design, with the object to identify the nursing activities were performed by Vietnamese at medical and surgical nursing units.
The study took place in two teaching hospitals located in Ho Chi Minh (HCM) city: The Ho Chi Minh university hospital and Thong Nhat nation’s hospital with 600 beds and 815 beds respectively.
Approval for implementation of this study was obtained from the two hospitals. All participants were given clear, simple explanations about the study and a consent form was signed by each participant before the study took place. The privacy of the participants was protected by using numbers only. The period of data collection for this study was from July 2010 to September 2010.
The samples were the registered nurses in the two teaching hospitals. Those registered nurses worked as staff, administrators and head nurses. A total of 250 nurses working in medical and surgical nursing unit at the two hospitals were asked to participate in this study and 201 (80%) nurses filled out a survey questionnaire. Thus, the sample for the analysis comprised 201 nurses. The HCM UMC consists of 101 nurses where 51 nurses work at the surgical unit and 50 nurses work the medical unit; the Thong Nhat hospital consists of 100 nurses with 50 nurses working for each of the general surgical and medical units.
Instrument
The tool consisted of 145 nursing activities, in which 135 nursing activities were developed by Korean nurses and 10 nursing activities were developed by a leader group in Vietnam from literature review.
The 135 nursing activities were identified and classified using a taxonomy which was developed by Park, Sung and Song (2000) through the Delphi process. The pilot of Park and Song was conducted in two hospitals to verify validity and appropriateness of nursing activities. The content validity index was 0.95 which was calculated by 6 clinical practice experts.
15
The questionnaire consists of two parts. In the first part, all 131 direct nursing activities are classified into 11 nursing domains. In the second part, all 14 indirect nursing activities are categorized in 3 nursing domains. There are a total of 145 nursing activities with 14 nursing domains and definitions are listed in the Appendix D. The 11 direct nursing domains consisted of respiration care, nutrition care, elimination care, exercise and posture maintenance, comport nursing, hygiene care, safety care, spiritual support, medication, communication, and others assisting. The 3 nursing domains involved recording, checking, and the equipment and environment management.
The instrument was first translated into Vietnamese language by the researcher so that it could be understandable by the Vietnamese nurses. Also this translated questionnaire was reviewed, modified and added by several Vietnamese nurses, including senior nurses and a leader group who is working at the two hospitals and doing this research.
The method of this research is self-reported. The participants have to memorize what kind of the nursing activities they perform and how much time they spend for each nursing activity which participant performed during a shift. For the first part of the questionnaire, respondents were asked to record which nursing activities were performed during a shift, and each nursing activity was reported by time. The second part of questionnaire was reported by frequency of each nursing activity. The questionnaire was used to evaluate the job independence levels based on five point Likert scale for each nursing activity.
Data Collection and Procedure
To obtain research permission for the study sites, preliminary discussions were held with the directors of nursing and permission letter was obtained from the directors in order to conduct research at site. The director was cooperation about the project. A cover letter explaining the purpose of the study, a consent form, and the questionnaire were then administrated to the subjects. All nurses working at medical and surgical nursing units in both of the two hospitals were asked to complete the survey.
Three procedures are used for this study: firstly, there is a questionnaire consisting of 135 the nursing activities that were developed by a leading nursing group; this nursing group was compiled based on the nursing activities classified by the Korean nurses in 2000. The 9 nursing activities were collected from literature reviews. Secondly, questionnaires
16
were sent to Vietnamese nurses and they self-reported. Finally, the results of the Vietnamese survey were analyzed to identify time, frequency and job independence level of each nursing activity.
Data Analysis
The data was entered and processed using SPSS 17.0 statistics software. Then, the pattern of nursing activities was compared between the medical and surgical nursing units. The statistics that are used to analyze such as mean, frequency, percent, standard deviation, and Mann-Whitney test.
17
Chapter 4 The Results
Description of the Subjects
Demographic characteristics of the 201 nurses (subjects) are represented in Table 1.The average age of the subjects is 29.4 (±6.9) years. The majority of the subjects have age from 23 to 39 years (58.2%), then from 30 to 39 years (26.4%); after that more than 40 years (9.0%), then less than 22 years (6.5%). In short, almost 64.7% of the respondents have an age of less than 30 years.
The average clinical experience of the subjects is 6.7 (±6.3) years. The majority of the subjects have a clinical experience from 1 to 5 years (47.3%), then 6 to 10 years (28.9%), after that more than 10 years (16.9%), then less than 1 year (7.0%). In short, almost 83.1% of the subjects in this study have a less than 10 years of clinical experience.
About three fourths (78.6%) of the nurses were diploma holders and one fourth (21.4%) of the nurses have bachelor’s degree.
About 90.5% of the nurses were reported by the day shift working 9.5 hours; and 9.5% of the nurses were reported by the night shift working 14.5 hours.
18
Table 1
General Characteristics of the Subjects
Demographic variables N % Age Less than 22 13 6.5 23-29 117 58.2 30-39 53 26.4 40-60 18 9.0 Mean(±SD) 29.4(±6.9)
Clinical experience (year)
Less than 1 14 7.0 1-5 95 47.3 6-10 58 28.9 More than 10 34 16.9 Mean(±SD) 6.7(±6.3) Education Diploma (2 years) 158 78.6 Bachelor(4 years) 43 21.4 Work shift Day (7:00-17:30) 9:30 hours 182 90.5 Night (16:30-7:00) 14:30hours 19 9.5 Unit Medical 101 50.2 Surgical 100 49.8 Hospital A 101 50.2 B 100 49.8 Total 201 100.0
19
Findings
Question 1: Which nursing activities were performed by Vietnamese nurses at general medical and surgical units?
To answer the first research question, the questionnaire data is described by determining the number of respondents in each nursing activity for recorded time and frequency. The nursing activities were performed by Vietnamese nurses at general medical and surgical nursing unit in which were listed in Table 2.
The Table indicates 145 nursing activities involving 14 nursing domains; each of the nursing domains involves various specialized nursing activities. The direct nursing activities are identified by 11 nursing domains such as respiration care, nutrition care, elimination care, exercise and posture maintenance, comport care, hygiene care, safety care, spiritual support, counseling and education, medication, communication, others assisting; and indirect nursing activities are identified by 3 nursing domains such as recording, checking, and management of equipment and environment.
The 114 nursing activities, performed at the two units are e.g., respiratory rate measurement, respiratory pattern measurement, respiratory sound measurement, postural drainage, physiotherapy, naso-oral suction, tracheal suction, nursing procedure r/t intubation, nasal prong, O2 mask apply, humidifies apply, observation & maintenance of respiratory,
body weight measurement, blood sugar level measurement, body height measurement, I/O measurement, CVP measurement, total feeding assistance, partial feeding assistance, nursing r/t nasogastric tube inserting, tube feeding, nursing procedure r/t TPN infusion, retention enema, gas enema, encourage skin care, stool sampling, simple catheterization, nursing r/t indwelling catheterization, bladder training, bladder irrigation, assistance of bed span use, diaper change & skin care, urine sampling, urine e specific gravity measurement, gastric drainage maintenance, sputum sampling and 24 hour time sampling et al.
The 114 nursing activities were performed by two units which are mentioned above. There are 6 more special nursing activities that were performed only by the medical nurses e.g., nursing r/t T-cannula exchange, tube feeding via gastrostomy, shaving, completed isolation for infection prevention, nursing r/t partial restraint, nursing r/t partial restraint, religious support. In surgical nursing unit, 9 more nursing activities were performed by the
20
nurses, that are cleansing enema, glycerin enema, thoracic drainage maintenance, bililary drainage maintenance, hemo-vac & drainage maintenance, assistance on prosthesis use, assistance on crutch use, bed bathing and sitting bathing.
Table 2
The Nursing Activities were Performed by Vietnamese Nurses at General Medical and Surgical Nursing Units
Nursing domain
Medical nursing unit Surgical nursing unit
Respiration Respiratory rate measurement Respiratory rate measurement
Respiratory pattern measurement Respiratory pattern measurement
Respiratory sound measurement Respiratory sound measurement
Postural drainage Postural drainage
Physiotherapy Physiotherapy
Naso-oral suction Naso-oral suction
Tracheal suction Tracheal suction
Nursing procedure r/t intubation Nursing procedure r/t intubation
Nasal prong, O2 mask apply Nasal prong, O2 mask apply
humidifies apply humidifies apply
Observation & maintenance of resp Observation & maintenance of resp
T-cannula exchange
Nutrition Body weight measurement Body weight measurement
Body height measurement Body height measurement
Blood sugar level measurement Blood sugar level measurement
I/O measurement I/O measurement
CVP measurement CVP measurement
Total feeding assistance Total feeding assistance
Partial feeding assistance Partial feeding assistance
nasogastric tube inserting nasogastric tube inserting
Tube feeding Tube feeding
Nursing procedure r/t TPN infusion Nursing procedure r/t TPN infusion
Blood sampling Blood sampling
Tube feeding via gastrostomy
21
Gas enema Gas enema
encourage skin care encourage skin care
Stool sampling Stool sampling
Simple catheterization Simple catheterization
Nursing r/t indwelling cathe. Nursing r/t indwelling cathe.
Bladder training Bladder training
Bladder irrigation Bladder irrigation
Assistance of bed span use Assistance of bed span use
Diaper change & skin care Diaper change & skin care
Urine sampling Urine sampling
Urine e specific gravity measurement
Urine e specific gravity measurement
Gastric drainage maintenance Gastric drainage maintenance
Drainage fluid sampling Drainage fluid sampling
Sputum sampling Sputum sampling
24 hour time sampling 24 hour time sampling
Cleansing enema Glycerin enema
Thoracic drainage maintenance Bililary drainage maintenance Hemo-vac & drainage maintenance
Exercise Simple position change Simple position change
& posture Position change using Stryker Position change using Stryker
maintenance Position change circle bed Position change circle bed
Exercise & position change Exercise & position change
Nursing for prevention contracture Nursing for prevention contracture
Nursing procedure r/t skin traction Nursing procedure r/t skin traction
Nursing pro. r/t skeletal traction Nursing pro. r/t skeletal traction
Simple assistance on exercise Simple assistance on exercise
Passive ROM exercise Passive ROM exercise
Assistance of mobility patient Assistance of mobility patient
Transfer of patient using wheelchair Transfer of patient using wheelchair
Transfer of patient using stretcher Transfer of patient using stretcher
22
Assistance on crutch use
Comfort Encourage sleep Encourage sleep
Encourage rest Encourage rest
Body temperature measurement Body temperature measurement
Hot & cold pack apply Hot & cold pack apply
Application of hot & cold regulator Application of hot & cold regulator
Humidity regulation Humidity regulation
Nursing r/t diversion & relaxation Nursing r/t diversion & relaxation
Accomplish encourage Accomplish encourage
Recreation instruction Recreation instruction
Walk accompany Walk accompany
Hygiene Nail cavity cleansing Nail cavity cleansing
Mouth nursing Mouth nursing
Total change of sheet Total change of sheet
Partial change of sheet Partial change of sheet
Clothes change Clothes change
Bed bathing Sits bath
Safety Partial isolation for infect. prevent. Partial isolation for infect. prevent.
Skin massage for bed sore prevents. Skin massage for bed sore prevents.
Simple dressing Simple dressing
Complex dressing Complex dressing
Opiod & poison check Opiod & poison check
Close obser. for suicide prevention Close observ. for suicide prevention
Nursing for fall down prevention Nursing for fall down prevention
Isolation & close observation Isolation & close observation Obser. & check for fire preven. Obser. & check for fire prevention
Consciousness check Consciousness check
CVP check CVP check
Blood pressure check Blood pressure check
Pulse check Pulse check
Monitoring Monitoring
Nursing r/t partial restraint Comp isolation for infection pre.
23
ShavingSpiritual Clergy counseling consult Clergy counseling consult
support Family support of terminal patient Family support of terminal patient
Nursing procedure on deathbed Nursing procedure on deathbed
Admission interview Admission interview
Counseling Counseling
Personal education Personal education
Group education Group education
Religious support
Medication Oral medication Oral medication
General intravenous infusion General intravenous infusion
Intra. infusion via heparin lock Intra. infusion via heparin lock
Intravenous infusion via central line Intravenous infusion via central line
Intramuscular injection Intramuscular injection
Subcutaneous injection Subcutaneous injection
Droplet apply Droplet apply
Suppository apply Suppository apply
Transfusion Transfusion
Communication Coordination & consulting b/t personal
Coordination & consulting b/t personal
Coordination & consulting b/t units Coordination & consulting b/t units
Assisting Assisting doctors on a ward round Assisting doctors on a ward round
Others Assisting doctors with tech
procedures
Assisting doctors with tech procedures
Assisting (radiographer, endoscopy) Assisting (radiographer, endoscopy)
Recording Documentation of patient care Documentation of patient care
Documentation of ward management
Documentation of ward management
Management of patient chart Management of patient chart
Recording infor through computer Recording infor through computer
Handing over to nurses on next shift Handing over to nurses on next shift
Checking Others (e.g., label printing) Others (e.g., label printing)
Order checking Order checking
Lab finding review Lab finding review
24
Management Equipment management Equipment management
of Sterilizing equipments management Sterilizing equipments management
equipment Supplies management Supplies management
and Medication management Medication management
environment Ward environment management Ward environment management
The performance analysis is done using average time and frequency of each nursing activity which the medical and surgical nursing unit recorded during a shift. The 129 nursing activities were identified for the direct and indirect nursing activity. Out of those, 114 nursing activities were performed both at medical and surgical nursing units, and some 9 special nursing activities were added in the list of surgical unit nursing activities and 6 special nursing activities were added in the list of medical unit nursing activities.
In summary, there are 123 nursing activities that were performed regularly and 22 nursing activities that were not performed at the surgical nursing unit. Similarly, there are 120 nursing activities that were performed and 25 nursing activities that were not performed by the medical nursing unit.
Question 2: How much time and frequency for each nursing activity during a shift per nurse at medical and surgical nursing units?
The average nursing time and frequency for each nursing activity that were performed at the medical and surgical nursing units are listed below in Table 4 and 5.
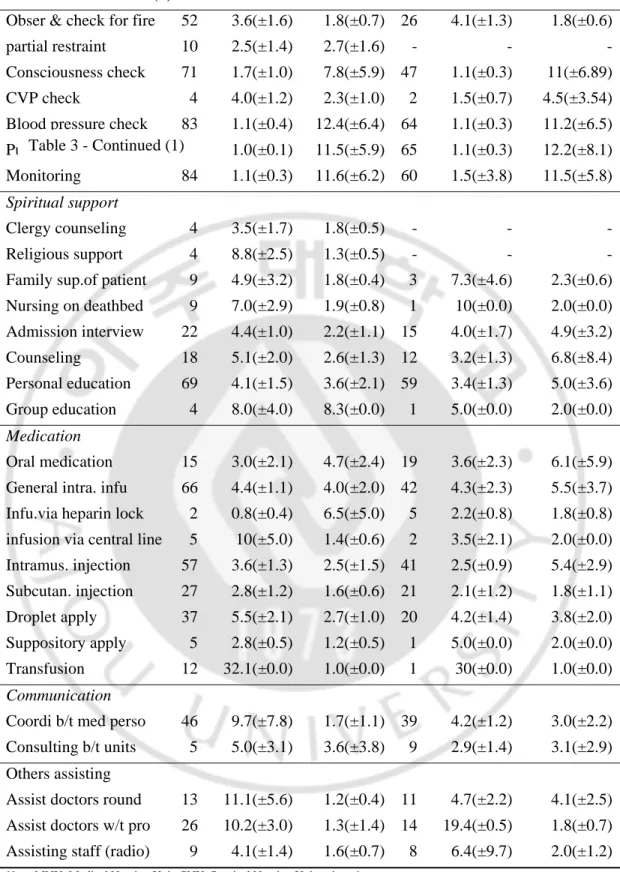
The nursing activities such as blood pressure check, respiratory rate measurement, respiratory pattern measurement, respiratory sound measurement, body temperature measurement, pulse check, monitoring, consciousness check, and management of patient chart are calculated more than 10 times during a shift per a nurse.
The nursing activities such as naso-oral suction, tracheal suction, nursing procedure r/t T-cannula exchange, nursing procedure r/t intubation, observation and maintenance of respirator, feeding assistance, application of hot & cold regular, nursing procedure r/t diversion and relax, accomplish encourage, walk accompany, shaving, nail cavity cleansing, sits bath, isolation & closely of observation, CVP check, clergy counseling consulting, religious support, group education, intravenous infusion via heparin lock, intravenous
25
infusion via central line, and coordination and consulting between units are performed with less frequency i.e., less than 3 times during a shift per nurse at the both units.
The nursing activities such as blood sugar measurement, intake and output measurement, tube feeding, nursing procedure r/t TPN infusion, encourage skin care, simple position change, position change using Stryker, position change circle bed, nursing procedure r/t skin traction, nursing procedure r/t skeletal traction, and transfusion are performed with higher frequency at the medical nursing unit than the surgical nursing unit.
On the other hand, the nursing activities such as cleansing enema, glycerin enema, retention enema, gas enema, thoracic drainage maintenance, bililary drainage maintenance, and hemo-vac & sump tube drainage maintenance are performed more regularly at surgical nursing unit than medical nursing unit.
The average nursing time of each nursing activity at medical and surgical nursing unit is listed in Table 3. The nursing activity in which the nurses spend the longest time is transfusion with 31.1(±10.5) minutes, assisting doctors with technique procedures takes 10.2(±3.0) minutes at medical unit and 19.4(±10.3) minutes at surgical unit, coordination and consulting for people take 9.7(±7.8) minutes and complex dressing takes 12.5(±5.7) minutes. There is a difference in nursing time for the nursing activities between the two units e.g., counseling personal takes 9.7 minutes at medical unit and 4.2 minutes at surgical unit; assisting doctor on a ward round takes 11.1 minutes at medical and 4.7 minutes at surgical unit; sterilizing equipments management takes 4.9 minutes at medical and 9.2 minutes at surgical unit.
For a detailed explanation, there are 38 nursing activities which take less than 3 minutes to be performed e.g., respiration sound measurement, respiration of pattern measurement, infusion via heparin lock, management of patient chart, nursing procedure r/t T-cannula, diaper change & skin care, pulse check , body temperature , close observation for suicide, monitoring, blood pressure check, body height, measurement, body weight measurement, postural drainage humidifies apply, stool sampling, consciousness check,
assistance of bed span use, nasal prong, O2 mask apply, observation and maintenance of
respirator, nursing procedure related to diversion and relax, order checking, naso-oral suction, urine sampling, blood sugar level measurement, CVP measurement, position change
26
using, stryker, intake and output measurement, encourage rest nursing procedure related to partial restraint, lab finding review et al.
There are 68 nursing activities that need from 4 to 6 minutes to be performed e.g., encourage skin care, nursing procedure for fall down prevention, oral medication, gastric drainage maintenance, encourage sleep, recreation instruction, partial change of sheet, simple position change, tracheal suction, humidity regulation, clergy counseling consult, record information computer, blood sampling, nursing procedure for prevention contraction, intramuscular injection, transfer using stretcher, exercise and position, assistance of mobility disturbance, observation & check for fire, position change circle bed, bladder training et al.
There are 14 nursing activities that need from 7 to 9 minutes to be performed e.g., sterilizing equip management, family support of patient, document of ward management, nursing procedure related to TPN infusion, supplies management, simple dressing, nursing related to intubation, nursing procedure on deathbed, drainage fluid sampling, group education, religious support, cleansing enema and assisting staff (radiography).
There are 5 nursing activities that need from 10 to 12 minutes to be performed e.g., retention enema infusion via central line, assist doctors on a ward round, complex dressing and coordinating & consulting between medical personal.
There are 2 nursing activities that take from 13 to 15 minutes to be performed e.g., assist doctors with technique procedure, complete isolate for infecting prevention.
There is 1 nursing activity that takes from 16 to 18 minutes to be performed such as bed bathing.
There is 1 nursing activity that takes more than 30 minutes to be performed such as transfusion.
The average time of each nursing activity which was performed by medical and surgical nursing unit is almost the same. However, there are nursing activities with different average time of performance at medical and surgical nursing unit such as 10 and 4.1 minutes for retention enema, 10 and 3.5 minutes forinfusion via central line,
10.2 and 19.4 minutes
for assisting doctors on technique procedure, 11.1 and 4.7 minutes for
assistingdoctors on a ward round,
4.0 and 1.5 minutes for
CVP checking,4.9 and 9.2 minutes for
sterilizing equipment management,
4.9 and 7.3 minutes for
family support of patient,5.0
27
9.7 and 5.2 minutes for
coordinating & consulting b/t medical personal for the medical and surgical unit respectively.Table 3
The Frequency and Average Time of Each Direct Nursing Activity during a Shift per Nurse at Medical and Surgical Units
Direct MNU (n=100) SNU (n=101)
Nursing activities n Mean(±SD) Fre(±SD) n Mean(±SD) Fre(±SD)
Respiration
Resp. rate measure 86 0.9(±0.2) 12.3(±6.5) 65 0.8(±0.2) 11.5(±7.8)
Resp. pattern measure 76 0.7(±0.3) 12.1(±5.8) 48 0.6(±0.2) 14.8(±16.2)
Resp. sound measure 72 0.6(±0.2) 11.5(±5.7) 47 0.6(±0.2) 12.5(±6.7)
Postural drainage 31 1.4(±0.6) 3.5(±4.1) 14 1.1(±0.3) 2.0(±1.0) Physiotherapy 15 4.3(±1.4) 2.3(±2.7) 15 3.2(±1.6) 3.3(±2.8) Naso-oral suction 3 2.0(±1.0) 2.7(±1.5) 3 2.7(±2.1) 1.7(±0.6) Tracheal suction 5 3.2(±1.8) 4.4(±3.4) 3 5.0(±0.0) 2.3(±2.3) NA r/t T-cannular 1 1.0(±0.0) 2.0(±0.0) - - -Nursing /t intubation 3 6.7(±2.9) 1.7(±0.6) 1 10(±0.0) 1.0(±0.0)
Nasal prong, O2 mask 33 1.9(±0.8) 1.8(±0.9) 14 2.6(±1.3) 1.9(±1.2)
humidifies apply 25 1.5(±0.9) 1.8(±1.1) 8 2.1(±1.5) 1.9(±1.4)
Observation of resp 4 2.0(±0.0) 2.3(±0.5) 3 1.0(±0.0) 7.7(±10.7)
Nutrition
Body weight measure 22 1.3(±0.5) 1.8(±1.0) 31 0.8(±0.3) 6.6(±8.8)
Body height measure. 20 1.3(±0.4) 1.5(±0.8) 31 0.8(±0.3) 6.6(±8.8)
Blood sugar 40 2.2(±0.9) 2.0(±1.1) 23 1.9(±0.9) 2.0(±1.2)
I/O measurement 27 2.4(±1.5) 2.7(±2.2) 9 2.8(±1.7) 3.9(±4.7)
CVP measurement 7 2.4(±1.1) 2.6(±1.5) 2 1.0(±0.0) 11.5(±6.4)
feeding assistance 2 5.0(±0.0) 2.0(±1.4) 2 1.5(±0.7) 6.5(±4.9)
Partial feeding assis 32 4.0(±1.3) 2.4(±1.9) 31 2.5(±1.7) 4.6(±3.7)
Naso tube inserting 9 4.2(±2.6) 2.7(±1.8) 5 5.0(±0.0) 1.4(±0.5)
Tube feeding 20 4.5(±2.3) 3.4(±1.7) 6 6.0(±3.5) 1.7(±0.8)
Feeding via gastro 1 5.0(±0.0) 5.0(±0.0) - -
-TPN infusion 58 6.0(±2.3) 3.3(±1.9) 38 7.1(±4.4) 4.1(±3.3)
28
Blood sampling 57 3.6(±1.3) 2.6(±1.7) 40 3.5(±1.4) 2.5(±1.7) Elimination Cleansing enema - - - 18 6.5(±4.0) 4.1(±4.8) Glycerin enema - - - 9 1.4(±0.5) 4.3(±2.4) Retention enema 1 10(±0.0) 2.0(±0.0) 9 4.1(±1.7) 3.2(±3.0) Gas enema 4 4.3(±1.5) 2.0(±0.8) 16 2.5(±1.6) 3.1(±1.9)encourage skin care 17 3.0(±0.9) 1.9(±0.7) 7 3.3(±1.3) 1.6(±0.5)
Stool sampling 7 1.7(±0.8) 1.0(±0.0) 1 1.0(±0.0) 1.0(±0.0)
Simple catheterization 13 4.8(±0.6) 1.8(±0.8) 15 5.2(±4.3) 1.7(±0.8)
indwelling cath. 6 5.2(±2.9) 2.5(±1.1) 14 5.0(±1.7) 2.4(±1.5)
Bladder training 11 3.9(±2.5) 1.8(±1.0) 11 4.1(±1.6) 1.6(±0.9)
Bladder irrigation 9 4.9(±6.0) 2.3(±1.3) 6 4.5(±1.2) 1.5(±0.8)
Assist of bed span use 5 1.8(±0.5) 1.8(±0.5) 5 3.2(±1.7) 1.6(±0.6)
Skin care 1 1.0(±0.0) 2.0(±0.0) 1 2.0(±0.0) 2.0(±0.0)
Urine sampling 16 2.0(±1.4) 1.9(±0.8) 12 2.0(±0.4) 2.5(±2.7)
Urine measure 21 2.3(±0.6) 2.1(±1.3) 7 4.9(±0.9) 3.3(±2.0)
Thoracic drainage - - - 5 3.6(±1.3) 4.4(±3.1)
Bililary drainage - - - 11 3.4(±2.5) 3.0(±2.6)
Hemo-vac & drainage - - - 3 3.7(±2.3) 4.0(±1.7)
Gastric maintenance 4 3.0(±2.3) 1.5(±0.6) 10 2.3(±1.1) 2.8(±2.6)
Drain. fluid sampling 5 7.8(±6.6) 1.2(±0.5) 4 1.5(±0.6) 1.0(±0.0)
Sputum sampling 16 2.4(±1.4) 1.3(±0.5) 3 3.3(±1.5) 1.0(±0.0)
24 hours time sampling 14 4.9(±5.0) 1.4(±0.8) 3 5.7(±1.2) 1.3(±0.6)
Exercise
Simple posi.change 30 3.2(±1.3) 2.4(±1.3) 9 3.7(±1.3) 3.2(±2.7)
Posi. change Stryker 7 2.4(±1.1) 3.1(±1.4) - -
-Position w/t circle bed 13 3.9(±1.4) 1.5(±0.7) 1 2.0(±0.0) 2.0(±0.0)
Exe patient 5 3.6(±1.5) 2.8(±1.1) 3 4.0(±1.7) 2.0(±1.0)
Prevention contract 15 3.6(±1.3) 2.7(±2.2) 2 2.5(±0.7) 1.0(±0.0)
Kin traction 13 4.8(±1.8) 1.7(±0.9) 1 2.0(±0.0) 1.0(±0.0)
skeletal traction 12 2.8(±1.1) 2.5(±1.1) 5 1.4(±0.6) 3.4(±2.5)
Simple assist on exe 10 4.1(±1.5) 1.5(±0.5) 10 3.6(±1.9) 2.8(±1.6)
Assist on pros. use - - - 3 5.7(±4.0) 2.3(±0.6)
29
Passive ROM exercise 20 4.4(±1.1) 3.8(±2.3) 15 3.7(±1.3) 2.7(±1.8)
mobility distur 14 3.6(±1.6) 2.0(±1.2) 16 3.8(±1.4) 2.8(±2.4)
Transfer using wheel 17 4.0(±2.0) 1.8(±1.2) 20 4.1(±1.4) 2.1(±0.8)
Transfer using stretcher 7 3.6(±1.4) 1.9(±1.1) 5 4.4(±1.3) 2.0(±1.2)
Comport
Encourage sleep 18 3.1(±1.1) 2.6(±1.3) 10 1.7(±0.7) 3.6(±3.5)
Encourage rest 44 2.5(±0.8) 3.5(±1.9) 27 1.6(±0.8) 6.5(±5.8)
Body temperature 73 1.0(±0.2) 11.1(±6.1) 53 1.4(±0.6) 10.2(±6.8)
Hot & cold pack apply 6 4.5(±1.2) 1.7(±0.5) 5 4.4(±0.9) 2.2(±1.1)
Apply hot & cold 2 5.0(±0.0) 3.5(±0.7) 1 15(±0.0) 1.0(±0.0)
Humidity regulation 44 3.5(±1.6) 5.0(±4.1) 32 2.7(±1.10) 4.7(±2.6)
N. diversion & relax 1 2.0(±0.0) 2.0(±0.0) 1 1.0(±0.0) 10(±0.0)
Accomplish encourage 2 4.0(±1.4) 2.5(±2.1) 6 5.2(±5.9) 4.0(±4.2) Recreation instruction 55 3.1(±1.3) 5.6(±4.2) 34 2.9(±1.6) 6.1(±5.0) Walk accompany 1 2.0(±0.0) 5.0(±0.0) 1 5.0(±0.0) 1.0(±0.0) Hygiene Bed bathing - - - 2 17.5(±3.5) 1.5(±0.7) Shaving 2 5.0(±0.0) 3.0(±0.0) - -
-Nail cavity cleansing 2 5.0(±0.0) 3.0(±0.0) 3 1.3(±0.6) 5.0(±4.6)
Perinea nursing 8 4.1(±2.8) 2.0(±1.1) 4 4.3(±1.5) 2.0(±1.4)
Sits bath - - - 1 5.0(±0.0) 1.0(±0.0)
Total change of sheet 15 2.9(±1.7) 1.3(±0.5) 13 2.4(±0.8) 3.6(±2.9)
Partial change of sheet 11 3.1(±1.7) 1.5(±0.8) 15 3.5(±1.4) 3.0(±3.0)
Clothes change 11 2.9(±1.4) 1.2(±0.4) 9 2.4(±1.0) 4.0(±3.4)
Safety
Compl. iso to inf. pre 1 15(±0.0) 1.0(±0.0) - -
-Part. iso for infection 9 5.0(±0.0) 1.3(±0.5) 8 3.8(±1.5) 3.8(±3.7)
bed sore preventing 19 4.4(±1.1) 2.3(±1.5) 6 3.7(±1.5) 1.5(±0.6)
Simple dressing 37 6.5(±2.1) 2.1(±1.0) 36 5.3(±1.1) 3.6(±2.3)
Complex dressing 24 12.5(±5.7) 1.3(±0.5) 26 11(±3.8) 2.8(±2.4)
Opiod & poison check 27 5.2(±3.0) 1.6(±0.7) 20 5.1(±2.5) 1.9(±2.1)
obser for suicide 1 1.0(±0.0) 5.0(±0.0) 3 4.3(±4.9) 2.3(±1.5)
Fall down prevention 36 3.0(±1.5) 2.5(±1.3) 28 3.1(±1.4) 2.7(±1.4)
30
Obser & check for fire 52 3.6(±1.6) 1.8(±0.7) 26 4.1(±1.3) 1.8(±0.6)
partial restraint 10 2.5(±1.4) 2.7(±1.6) - -
-Consciousness check 71 1.7(±1.0) 7.8(±5.9) 47 1.1(±0.3) 11(±6.89)
CVP check 4 4.0(±1.2) 2.3(±1.0) 2 1.5(±0.7) 4.5(±3.54)
Blood pressure check 83 1.1(±0.4) 12.4(±6.4) 64 1.1(±0.3) 11.2(±6.5)
Pulse check 83 1.0(±0.1) 11.5(±5.9) 65 1.1(±0.3) 12.2(±8.1)
Monitoring 84 1.1(±0.3) 11.6(±6.2) 60 1.5(±3.8) 11.5(±5.8)
Spiritual support
Clergy counseling 4 3.5(±1.7) 1.8(±0.5) - -
-Religious support 4 8.8(±2.5) 1.3(±0.5) - -
-Family sup.of patient 9 4.9(±3.2) 1.8(±0.4) 3 7.3(±4.6) 2.3(±0.6)
Nursing on deathbed 9 7.0(±2.9) 1.9(±0.8) 1 10(±0.0) 2.0(±0.0) Admission interview 22 4.4(±1.0) 2.2(±1.1) 15 4.0(±1.7) 4.9(±3.2) Counseling 18 5.1(±2.0) 2.6(±1.3) 12 3.2(±1.3) 6.8(±8.4) Personal education 69 4.1(±1.5) 3.6(±2.1) 59 3.4(±1.3) 5.0(±3.6) Group education 4 8.0(±4.0) 8.3(±0.0) 1 5.0(±0.0) 2.0(±0.0) Medication Oral medication 15 3.0(±2.1) 4.7(±2.4) 19 3.6(±2.3) 6.1(±5.9)
General intra. infu 66 4.4(±1.1) 4.0(±2.0) 42 4.3(±2.3) 5.5(±3.7)
Infu.via heparin lock 2 0.8(±0.4) 6.5(±5.0) 5 2.2(±0.8) 1.8(±0.8)
infusion via central line 5 10(±5.0) 1.4(±0.6) 2 3.5(±2.1) 2.0(±0.0)
Intramus. injection 57 3.6(±1.3) 2.5(±1.5) 41 2.5(±0.9) 5.4(±2.9) Subcutan. injection 27 2.8(±1.2) 1.6(±0.6) 21 2.1(±1.2) 1.8(±1.1) Droplet apply 37 5.5(±2.1) 2.7(±1.0) 20 4.2(±1.4) 3.8(±2.0) Suppository apply 5 2.8(±0.5) 1.2(±0.5) 1 5.0(±0.0) 2.0(±0.0) Transfusion 12 32.1(±0.0) 1.0(±0.0) 1 30(±0.0) 1.0(±0.0) Communication
Coordi b/t med perso 46 9.7(±7.8) 1.7(±1.1) 39 4.2(±1.2) 3.0(±2.2)
Consulting b/t units 5 5.0(±3.1) 3.6(±3.8) 9 2.9(±1.4) 3.1(±2.9)
Others assisting
Assist doctors round 13 11.1(±5.6) 1.2(±0.4) 11 4.7(±2.2) 4.1(±2.5)
Assist doctors w/t pro 26 10.2(±3.0) 1.3(±1.4) 14 19.4(±0.5) 1.8(±0.7)
Assisting staff (radio) 9 4.1(±1.4) 1.6(±0.7) 8 6.4(±9.7) 2.0(±1.2)
Note. MNU, Medical Nursing Unit; SNU, Surgical Nursing Unit; min, minute.
31
The indirect nursing activities such as recording of document patient care, patient charting, order checking, recording on computer, medication management are calculated more than 5 times during a shift per nurse at both units.
The indirect nursing activities such as equipment, sterilizing equipment and supplies management are calculated less than 2 times during a shift per nurse at both units.
The indirect nursing activities such as lab finding review, film checking and arrangement, supplies management and ward environment are calculated from 2 to 5 times during a shift per nurse at both units.
There are differences of frequency for the indirect nursing activities between the two units; e.g., recording of document patient care takes 5 times at medical nursing unit and takes 9.6 times at surgical nursing unit; films checking take 2.5 times at medical nursing unit and take 6.6 times at surgical nursing unit.
There are 3 indirect nursing activities that take from 5 to 10 minutes to be performed e.g., document of ward management, handing over shift to shift and supplies management.
There are 2 indirect nursing activities that take less time about 2 minutes to be performed such as patient charting and lab finding review.
The nursing activities such as equipment management, medication management and recording of document on computer need to take from 2 to 5 minutes to be performed.
There is a difference of the nursing time for the indirect nursing activities between the two units; e.g., sterilizing equipment management takes 4.9 minutes at medical nursing unit and takes 9.2 minutes at surgical nursing unit.
The nursing activity need to take much time and frequency to be performed is recording of patient document with 5 to 10 minutes and 4 to 6 times.
32
Table 4
The Frequency and Average Time of Each Indirect Nursing Activity during a Shift per Nurse at Medical and Surgical Units
Indirect MNU (n=100) SNU (n=101)
Nursing activities N Mean(±SD) Fre(±SD) N Mean(±SD) Fre(±SD)
Recording
Docu of patient care 84 4.2(±1.3) 5.0(±2.3) 71 5.3(±6.8) 9.6(±8.0)
Docu of ward manage 52 5.5(±4.3) 2.3(±1.3) 46 6.4(±4.8) 3.6(±3.5)
patient chart 78 0.9(±0.2) 11.4(±6.2) 61 1.5(±1.9) 12.6(±8.2)
Record on computer 46 3.5(±3.0) 5.6(±3.9) 47 4.0(±3.9) 8.8(±5.4)
Handing over shift 76 5.3(±2.2) 1.5(±1.0) 68 5.6(±4.3) 3.3(±5.6)
Others (label) 57 2.6(±1.5) 4.7(±3.8) 66 2.3(±2.3) 6.8(±5.7)
Checking
Order checking 92 2.0(±0.8) 7.4(±5.1) 79 3.3(±3.9) 8.3(±6.0)
Lab finding review 56 2.6(±1.3) 2.3(±2.2) 46 2.2(±1.2) 4.5(±4.1)
Film checking & arrange 39 4.0(±1.4) 2.5(±2.2) 35 4.1(±2.9) 6.6(±2.4)
Equipment checking
Equipment management 51 5.1(±3.8) 1.5(±1.1) 42 5.1(±1.7) 1.4(±0.8) Sterilizing equip ma 32 4.9(±1.0) 1.3(±0.5) 30 9.2(±7.5) 1.3(±0.5) Supplies management 38 6.3(±6.4) 1.3(±0.7) 33 7.7(±7.1) 1.5(±0.7) Medication management 83 4.5(±1.5) 5.7(±3.3) 55 5.2(±3.2) 4.4(±2.7) Ward environment 43 4.1(±1.6) 2.3(±1.0) 38 5.2(±2.4) 2.5(±1.3)
Note. MNU, Medical Nursing Unit; SNU, Surgical Nursing Unit; min, minute.
In short, the medical nurses used the higher frequency of nursing activities as compared to the surgical nurses for the nursing domains like nutrition nursing, exercise & posture maintenance and safety. On the other hand, the surgical nurses used higher nursing activities frequency as compared with medical nurses for the nursing domains like caring focused on elimination, recording and checking.
Question 3: What was the proportion of direct and indirect nursing time during a shift by nurse at medical and surgical nursing units?
The Table 5 shows the nursing time for each nursing domain during a day shift at medical nursing unit. Almost 24.9 minutes spend for respiration, 26.0 minutes for nutrition, (Unit, min)
33
8.0 minutes for elimination, 12.7 minutes for exercise, 27.6 minutes for comfort, 2.0 minutes for hygiene, 54.4 minutes for safety, 18.2 minutes for spiritual support, 30.4 minutes for medication, 7.5 minutes for communication, and 5.3 minutes for assistance.
The Table 5 also shows the nursing time for each nursing domain during a day shift at surgical nursing unit. Almost 16.1 minutes spend for respiration, 20.6 minutes for nutrition, 15.8 minutes is for elimination, 8.2 minutes for exercise, 18.9 minutes for comport, 4.0 minutes for hygiene, 49.5 minutes for safety, 14.6 minutes for spiritual support, 21.7 minutes for medication, 5.0 minutes for communication, and 8.3 minutes for assistance.
For the day shift, the highest percentage is of safety for direct nursing activities with 54.4 minutes (25.1%) at medical and 49.5 minutes (27.1%) at surgical nursing unit. The lowest percentage is of hygiene with 2.0 minutes (0.9%) at medical and 2.9 minutes (2.2%) at surgical nursing units.
For the night shift, the highest percentage is of safety for direct nursing activities with 79.2 minutes (31.5%) by medical nurse and 68.8 minutes (28.1%) by surgical nurse. The lowest percentage is of communication with 1.5 minutes (0.6%) by medical nurse and 0.0 minutes (0.0%) by surgical nurse.
The differences of the nursing time at the two units, based on the nursing domains by the day shift are elimination nursing, communication nursing and other’s assistance. Almost 8.0 minutes (3.7%) and 15.8 minutes (8.7%) of nursing time is taken for elimination, 7.5 minutes (3.4%) and 5.0 minutes (2.7%) of nursing time is taken for communication and 5.3 minutes (2.4%) and 8.3 minutes (4.5%) of nursing time is taken for other’s assistance at medical and surgical nursing units respectively.
The difference of nursing time based on the nursing domains by the night shift is 25.3 minutes (11.5%) and 12.7 minutes (5.1%) for elimination nursing domain at surgical nursing unit and medical nursing unit respectively. The elimination time is higher for the surgical nursing unit than the medical nursing unit.