대한두경부종양학회지, 제33권 제2호, 2017. pp.49-53 Korean Journal of Head & Neck Oncology, Vol.33, No.2
http://doi.org/10.21593/kjhno/2017.33.2.49 ISSN 1229-5183(Print) / ISSN 2586-2553(Online)
낭성 림프관종으로 오인한 전장 낭종 환자 1예
주재우⋅오경호⋅권순영+
고려대학교 의과대학 안산병원 이비인후-두경부외과학교실
A case of congenital foregut cyst; misdiagnosed as cystic hygroma
Jae Woo Joo, MD, Kyung Ho Oh, MD, Soon Young Kwon, MD, PhD+
Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Gyeonggi-do, Korea
= Abstract =
Foregut cystic developmental malformations are rare developmental anomalies. It is important to diagnose the diseases and manage them properly because these cysts may generate feeding or respiratory difficulties depending on the size and location of the lesions.
A newborn was referred for a congenital cervical swelling to our clinic on the second day of his life. Neck SONO and MRI showed an about 6cm sized cystic mass at left submandibular area. Aspirations and sclerotherapies were done repeatedly due to recurred cystic mass. Under the suspicious of cystic hygroma, the mass and sub- mandibular gland were excised. Histologically, it was a benign cyst including gastrointestinal and bronchogenic mucosa and pancreatic tissue. Foregut cyst was suggested for the final diagnosis and the patient was discharged at 9 days after the operation without a complication. He has visited our out-patient department.
Although several image studies have been introduced to find out foregut cyst, it is difficult to go through differ- ential diagnosis because of similarity of other benign tumor. Further studies for early diagnosis of cervical foregut cyst are needed for preventing possible related problems.
Key W ords:Foregut cyst, congenital, cervical
R eceived R e v i s e d
A ccepted
: July 20, 2017
: September 13, 2017(1차수정) October 10, 2017(2차수정) : October 16, 2017
+Corresponding author: 권순영
경기도 안산시 단원구 적금로 123 고려대학교 안산병원 이 비인후-두경부외과
Tel: 031-412-5170 Fax: 031-412-5174 E-mail: entkwon@korea.ac.kr
서 론
전장은 인두, 하부호흡기계 및 식도, 위, 십이지장, 간 담계를 포함하는 상부위장관계로 분화될 수 있다.1)전장 낭종은 태아의 발달과정에서 발생하는 드문 질환으로 낭종의 크기와 위치에 따라 식이나 호흡문제를 유발할 수 있기 때문에 적절한 진단과 조기 치료가 중요하다.2,3) 그러나 전장 낭종의 임상적 특징들은 두경부에서 발생할
수 있는 다른 종양들과 유사하므로 임상 의사들은 이 질환에 대한 이해도를 높여 적절한 진단과 수술적 치료 가 늦춰지지 않도록 해야 한다.1,4)
저자들은 낭성 림프관 종으로 오인한 선천성 경부 전 장 낭종 1 예를 경험하였기에 문헌고찰과 함께 이를 보고 하는 바이다.
증 례
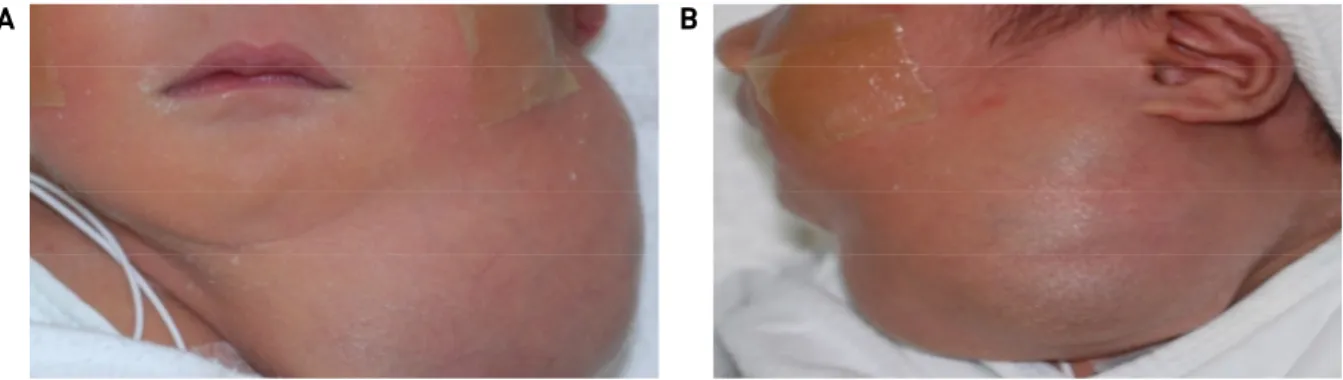
생 후 이틀 된 남아가 좌측 경부 종물 주소로 본과로 진료 의뢰 되었다. 신체검진 상 좌측 하악부에서 부드러 운 낭성 종괴가 촉지 되었다. (Fig. 1A., Fig. 1B.) 이어 시행한 경부 초음파 검사상 엽상 모양의 큰 낭종이 확인 되어 자기공명영상 촬영 후 흡인 치료를 계획하였다.
(Fig. 2) T2 조영 증강 이미지에서 병변은 최장 직경 약 6cm 크기의 고 신호로 관찰되었고 T1 조영 증강 이미지
A
B
Fig. 1A., 1B. Profiles of the patient. A soft mass was on his left submandibular area.
Fig. 2. SONO shows a huge lobular shape cystic mass. 100cc yellow and clear fluid was aspirated from the cyst.
A
Fig. 3A. About 6cm sized mass was seen as high signal at T2-weighted image.
B
Fig. 3B. The mass was low signal at T1-weighted image.
Fig. 4. Previous cystic mass was decreased after sclerotherapy. Fig. 5. Preoperative neck CT showed a multilobulated 5.9cm x 3.0cm x 5.4cm sized cystic mass extending from left submandibular to sublingular area.
Fig. 6. Ovoid shaped specimen.
A
B
C
D
E
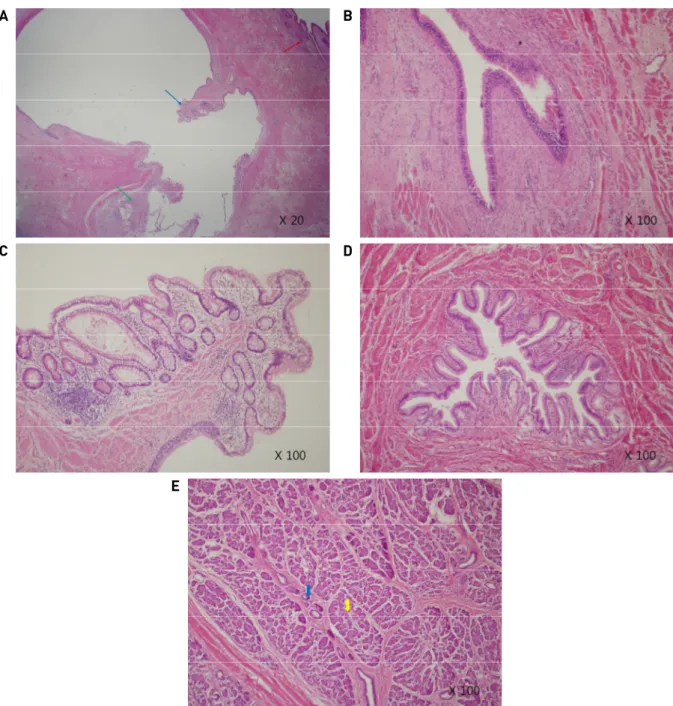
Fig. 7A. Red arrow – bronchial mucosa, Blue arrow – colonic mucosa, Green arrow – gastric mucosa. Fig. 7B. Bronchial mucosa.
Fig. 7C. Colon mucosa. Fig. 7D. Gastric mucosa. Fig. 7E. Blue arrow – pancreas duct, yellow arrow - acinar cells.
에서는 저 신호로 보이는 양상이었다. (Fig. 3A., Fig. 3B.) 낭성 수종 진단 하 약 100cc 가량의 노란색의 장액성 액 체를 종괴에서 흡인하였으나 이틀 후 다시 크기 증가되어 에탄올을 이용한 경화요법을 시행하였다. (Fig. 4) 이 후 외래 경과관찰 도중 증상 호전 악화 반복되어 3년 동안 총 7차례에 걸쳐 흡인을 반복하였고 환아 부모님 동의 하에 수술적 절제를 결정하였다. 술 전 시행한 경부 전산 화단층촬영을 통해 좌측 설하부 및 하악부에 걸쳐 5.9cm x 3.0cm x 5.4cm 크기의 경계가 분명하고 내부가 다엽성 인 종괴를 확인하였다. (Fig. 5) 수술장에서 좌측 경부 설골 상연 높이부터 설 기저부 하방까지 주변조직과 심하 게 유착 되어있는 낭종을 일괴 절제하였다. (Fig. 6) 조직 검사 결과 낭종 내부에서 위장관조직, 기관지점막, 췌장 조직이 확인되었고 전장 낭종으로 최종 진단되었다. (Fig.
7A. – Fig. 7E.) 환아는 술 후 9일째 합병증 없이 퇴원하였 고 2년째 외래 통해 경과관찰 중이다.
고 찰
두경부 영역에서 전장 낭종은 신생아의 발달과정에서 이루어지는 드문 양성 종양이다.5)현재까지 몇몇 전장 낭종과 관련된 증례들이 보고되고 있으며 호흡기계나 소화기계와 관련된 심각한 문제들을 발생 시킬 수 있는 것으로 알려져 있다.6,7) 뿐만 아니라, 장기간 치료되지 않은 전장 낭종의 경우 악성으로 변화되는 증례들 또한 보고 된바 있다.8)따라서 다른 선천적 경부 종물과의 빠 른 감별진단 및 적절한 수술적 절제와 조직검사가 필요 하다.
소아에서 대부분의 경부 양성 종양은 염증성 종양이다.
이러한 종양들은 항생제와 같은 약물치료로 자연스럽게 사라지는 경우가 많지만 본 증례보고의 경우와 같이 낭성 종괴가 지속되거나 재발하는 경우 선천성 종양에 대한 고려가 필요하다.9) 전장 낭종 환자들은 증상을 보이지 않을 수도 있으나 식이곤란, 호흡곤란, 반복적인 출혈 및 갈색 액체의 배출이 설부에서 이루어질 수 있다.10,11)
자기공명영상이나 전산화단층촬영은 전장 낭종의 술 전 검사로 유용할 수 있다. 해당 영상의학적 기법을 통한 병변의 모양만으로는 갑상설관 낭종이나 유피 낭종과 같은 양성 경부 종양과 감별진단이 힘들다. 하지만 병변 의 발생 위치까지 고려했을 때는 그 진단적 가치가 높아 질 수 있기 때문이다. 두경부 영역에서 전장 낭종은 구강 저부와 설부에서 가장 많이 발견되며, 구인두부, 전경부 등에서도 관찰되고 있기 때문에 이와 같은 부위에서 낭 종이 관찰된다면 전장 낭종을 의심해볼 필요가 있겠다.1)
최종 진단을 위해서는 조직검사가 필요하며 종양이 평활 근육층으로 둘러 쌓여있고 전장에서 기원한 상피를 가지 는 동시에 전장과 붙어있을 때 전장 낭종으로 확진할 수 있다.12)
수술적 절제술 외에 경화요법이 전장낭종의 치료에 사 용될 수 있을 것으로 생각된다. 2010년 기관지성 낭종 환자 3명을 대상으로한 논문에서 낭종의 세침흡인 후 bleomycin을 이용한 경화요법의 효용성이 확인되었다.13) 하지만 아직 경화요법에 대한 효과에 대한 대규모 스터 디가 이루어지지는 않은 만큼 관련된 추가 연구가 필요 하다.
완전한 수술적 절제 후 재발은 전장 낭종에서 흔하지 않은 것으로 알려져 있다. 1987년부터 2007년까지 22명 의 조직학적으로 확인된 전장 낭종 환자들을 대상으로 한 후향적 연구에서 완전한 수술적 절제 후 평균 관찰기 간 2.4년(11개월~6년)동안 재발된 환자는 없었다.1)
본 증례의 경우 처음에는 경부 낭성 수종으로 의심되 었던 환아가 조직학적으로 경부 전장 낭종으로 확진이 되었다. 경부 초음파 및 자기공명영상 등 다양한 영상의 학적 검사를 시행하여 병변의 형태, 위치를 고려하였지 만 조기 진단이 실제로 쉽지 않았다. 복부와 흉부에 위치 한 전장 낭종을 진단하는데 있어 내시경하 초음파기법이 유용성을 확인한 연구가 보고된 바 있다. 1995년 7명의 전장 낭종 환자들을 대상으로 한 스터디에서 모든 환자 들을 내시경하 초음파를 이용하여 정확한 진단을 이루어 냈다.14)하지만 초음파 또한 본 증례에서처럼 다른 양성 낭종과의 감별이 쉽지 않기 때문에 전장 낭종의 진단을 위한 대규모의 환자들을 대상으로 한 다 기관 연구가 추가적으로 이루어져야 할 것이며 새로운 진단기법을 찾기 위한 노력이 필요하겠다.
중심 단어:전장 낭종, 선천성, 경부
References
1) Kieran SM, Robson CD, Nose V, Rahbar R. Foregut duplication cysts in the head and neck: presentation, diagnosis, and management.
Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010;136:778-782.
2) Sharma S, Nezakatgoo N, Sreenivasan P, Vanatta J, Jabbour N.
Foregut cystic developmental malformation: new taxonomy and classification--unifying embryopathological concepts. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2009;52:461-472.
3) Luo Y, Shillingford N, Koempel JA. Histopathologic Finding of Both Gastric and Respiratory Epithelia in a Lingual Foregut Cyst. Case Rep Med. 2015;2015:278376.
4) Cohen SR, Geller KA, Birns JW, Thompson JW, Meyer BW, Lindesmith GG. Foregut cysts in infants and children. Diagnosis
and management. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1982;91:622-627.
5) Edwards J, Pearson S, Zalzal G. Foregut duplication cyst of the hypopharynx. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005;131:
1112-1115.
6) Gantwerker EA, Hughes AL, Silvera VM, Vargas SO, Rahbar R.
Management of a large antenatally recognized foregut duplica- tion cyst of the tongue causing respiratory distress at birth. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014;140:1065-1069.
7) Knod JL, Garrison AP, Frischer JS, Dickie B. Foregut duplica- tion cyst associated with esophageal atresia and trache- oesophageal fistula: a case report and literature review. J Pediatr Surg. 2013;48:E5-7.
8) Volchok J, Jaffer A, Cooper T, Al-Sabbagh A, Cavalli G.
Adenocarcinoma arising in a lingual foregut duplication cyst.
Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007;133:717-719.
9) Mehta RP, Faquin WC, Cunningham MJ. Cervical bronchogenic cysts: a consideration in the differential diagnosis of pediatric
cervical cystic masses. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2004;
68:563-568.
10) Parikh DH, Ibrahim SK, Cook RC. Peptic ulceration in a lingual sinus. J Pediatr Surg. 1991;26:99-100.
11) Lipsett J, Sparnon AL, Byard RW. Embryogenesis of enter- ocystomas-enteric duplication cysts of the tongue. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1993;75:626-630.
12) Qi BQ, Beasley SW, Williams AK. Evidence of a common patho- genesis for foregut duplications and esophageal atresia with tra- cheo-esophageal fistula. Anat Rec. 2001;264:93-100.
13) Li L, Zeng XQ, Li YH. CT-guided percutaneous large-needle as- piration and bleomycin sclerotherapy for bronchogenic cyst: re- port of four cases. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010;21:1045-1049.
14) Geller A, Wang KK, DiMagno EP. Diagnosis of foregut duplica- tion cysts by endoscopic ultrasonography. Gastroenterology.
1995;109:838-842.