ARTICLE Vol. 2, No. 2, November 2009
논문접수일: 2009년 10월 16일 / 심사완료일: 2009년 11월 3일
교신저자: 윤종호, 서울시 송파구 풍납2동 388-1, 138-736, 울산대학교 의과대학 서울아산병원 외과 Tel: 02-3010-3931, Fax: 02-3010-6962, E-mail: gsyoon@amc.seoul.kr 본 연구는 아산생명과학 연구소의 연구비(2009-475) 지원에 의해 이루어졌음.
Sunitinib이 갑상선 유두암 세포주의 성장 및 침습에 미치는 영향
아산생명과학 연구소1, 울산대학교 의과대학 서울아산병원 내분비내과2, 외과3
한두희1, 최현정1, 김원구2, 김의영2, 김태용2, 김원배2, 송영기2, 윤종호3
Effects of Sunitinib on the Growth and Invasion of Thyroid Papillary Cancer Cell Line
Doo Hee Han
1, Hyun-Jeung Choi
1, Won Gu Kim
2, Eui Young Kim
2, Tae Yong Kim
2, Won Bae Kim
2, Young Kee Shong
2and Jong Ho Yoon
3Asan Institute of Life Sciences
1; and Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism
2; Surgery
3, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
Background and Objectives: Thyroid papillary cancer was known to have a good prognosis but it could have poor prognosis if there is local invasion or metastasis. Sunitinib, a multitargeted tyrosine-kinase inhibitor, has been reported to have an anticancer effect in experimental and clinical studies. In this study, we evaluated the effect of sunitinib on cell growth, migration, adherence in papillary thyroid cancer cell. Materials and Methods:
We have evaluated the effect of sunitinib on TPC-1 (papillary thyroid cancer cell) and NPA (melanoma cell).
Expression of target gene was evaluated by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and immunoblot. Cell viability was measured by colorimetric assay and invasiveness of cancer cell was measured by migration assay and by anchorage independent growth assay. The change of protein level associated with cell proliferation and cell cycle were evaluated by immunoblot assay. Results: The expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) and platelet derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) were more prominent in NPA cell than TPC-1 cell. The proliferation of cancer cells were decreased by sunitinib in dose-dependent manner and NPA cell was more susceptible to sunitinib. The migration and anchoring dependent growth of cancer cells were more decreased in NPA cell by sunitinib. Cyclin inhibitor, p21
Waf1/Cip1and p27
Kip1were suppressed by sunitinib only in TPC-1 cell, but not in NPA cell. Conclusion: Sunitinib suppressed cancer cell proliferation and migration in NPA and TPC-1 cell. Sunitinib was less sensitive in papillary thyroid cancer cell than malignant melanoma cell. This difference could be related with suppression of p21
Waf1/Cip1and p27
Kip1by sunitinib in TPC-1 cell.
Key Words: Thyroid cancer, Papillary carcinoma, Sunitinib, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor, p21
Waf1/Cip1, p27
Kip1서 론
내분비 기관의 암 중 가장 흔한 것이 갑상선암이며 ,
1)우리나라를 비롯해서 전세계적으로 최근 10년 이내에 가장 급속도로 증가하고 있는 암 중 하나이다.
2,3)2008
년 10월 15일 중앙암등록본부에서 발표한 자료에 의하
면 , 2003∼2005년에 가장 많이 발생하는 암 중에 갑상
선암은 5위로 나타났다. 또한 여성의 경우 갑상선암은
유방암에 이어 2번째로 많은 암이었으며, 1999년 대비
2005년 44.9% 증가한 유방암에 비해 242.9% 증가하여
여성의 주요 암 중 발생이 가장 많이 증가한 암이다
(http://www.ncc. re.kr/index.jsp).
전체 갑상선암 중 가장 흔히 발견되는 암은 유두암 으로 90% 이상을 차지한다. 유두암은 전체적으로 매우 천천히 자라며, 예후도 갑상선암 중 가장 좋아서 10년 생존율이 약 95%이다. 이처럼, 갑상선암이 치료가 잘 되고 완치율이 높은 암이기는 하지만 재발하거나 다른 장기로 전이 될 가능성은 항상 있으며, 재발된 갑상선 유두암의 경우 50∼60%의 높은 사망률을 보이고, 기도 와 식도 등의 주변장기로 침습한 경우 불량한 예후를 보인다고 보고된바 있다.
4,5)하지만, 침습성과 원격전이 등을 동반한 공격적인 성향의 갑상선암의 분자생물학 적인 병인과 기전, 치료법이나, 표적치료제에 대해서는 아직 연구가 충분하지 않은 실정이다.
Tyrosine kinase는 신호 전달 과정의 중요한 매개물 질이며, 세포의 성장과 분화, 대사작용과 세포 예정사 등의 다양한 생물학적 과정의 중요한 역할을 한다. 최 근 연구에서는 암에서 tyrosine kinase의 병리생리학적 인 역할이 밝혀지고 있다. 보통 정상 세포에서의 tyrosine kinase의 활성은 엄격하게 조절되지만, 돌연변 이 등으로 인하여 과발현 되었을 경우 암을 유발할 수 있는 인자로 작용할 수 있다. 변질된 tyrosine kinase 같 은 암세포 종양형성 활성 요소는 선택적인 tyrosine kinase 길항제에 의해서 막을 수 있다.
6)이러한 tyrosine kinase 길항제 중에서 vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF) 수용체 억제를 통한 VEGF경로에 영향을 미 치는 물질 중 하나가 SU11248로, 현재는 sunitinib (Sunitinib malate; Sutent; SU11248; LC Lab, Woburn, MA)으로 명명된 물질이다. Sunitinib은 Class III와 class IV 수용체인 VEGF 수용체(VEGFR)에 길항하는 tyro- sine kinase 억제제로, platelet-drived growth factors 수용 체 (PDGFR), fetal liver tyrosine kinase receptor 3 (Flt-3), c-KIT 등에도 작용을 한다.
7,8)또한, 위장관 기질 종양, 전이된 신세포 종양 등 혈관 형성 억제 및 항암작용에 그 효과가 인정되어 사용되고 있고 ,
9,10)현재 여러 암에 서 임상시험이 진행되고 있다.
11,12)하지만, 아직 sunitinib이 갑상선암에 미치는 영향에 대한 분자생물 학적인 기전과 임상적인 부분에 대한 연구는 미비한 실정이다.
본 연구에서는 VEGFR 길항제인 sunitinib이 갑상선 암 세포의 침습이나 성장에 영향을 직접 줄 가능성에 착안하여 기획되었다 . 즉, sunitinib은 원래 종양의 혈관 내피 세포에 작용하여 그 항암 작용을 나타내는 것이 지만, 최근의 임상연구를 통하여 sunitinib이 정상 갑상 선 세포에도 독성을 나타낼 가능성이 발견되었다.
13,14)이러한 사실들은 sunitinib이 혈관내피세포에만 작용하 는 것이 아니라 갑상선암 세포에도 직접 작용할 가능 성을 시사하나 아직 이에 관한 연구는 전무한 실정이 다. 따라서, 본 연구는 VEGFR 길항제인 sunitinib이 혈 관내피 세포가 아닌 암세포의 침습성과 성장에 직접 영향을 끼칠 가능성과 갑상선암 치료제로서의 가능성 을 알아보고자 하였다.
대상 및 방법
재료
Sunitinib는 LC Lab (Woburn, MA)에서 구입하였으 며 , 세포 배양에 필요한 우태아 혈청과 RPMI 배양액 및 penicillin-streptomycin계 항생제, 트립신-EDTA, 인 산염 완충 용액 (PBS)은 Gibco BRL (New York, NY)에 서 구입하였다 . Colorimetric Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) 은 Dojindo Laboratories (Kumamoto, Japan)에서 구입 하였다. RevertAid Fist Strand cDNA 합성키트는 Fer- mentas (Glen Burnie, MD), BioMix DNA 중합효소와 아가로오스는 Bioline (Taunton, MA)에서 구입하였으 며 , 단백질 정량에 사용된 Quant-iT
TMProtein Assay Kit는 Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA)에서 구입하였다.
VEGFR-2, Flt-3와 PDGFR-β에 대한 항체는 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc. (Santa Cruz, CA), p21
Waf1/Cip1에 대한 항체는 BD bioscience (San Jose, CA), AKT, phospho-AKT, ERK, phosphor-ERK, p27
Kip1에 대한 항 체와 cell Lysis Buffer (10X)는 Cell signaling Tech- nology (San diego, CA), 이차 항체인 HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit, anti-mouse IgG는 Vector Laboratories (Bur- lingame, CA)에서 Western Blotting Luminol Reagent는 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc. (Santa Cruz, CA)에서 구 입하였으며, 그 외에 사용된 화학 약품들은 Sigma- Aldrich (St. Louis, MO)에서 구입하였다.
세포주 및 배양
갑상선암 세포주인 TPC-1과 흑색종 세포주인 NPA 를 10%의 우태아혈청과 항생제가 함유된 RPMI-1640 배양액으로 5% CO
2, 37
oC 항온 배양기에서 배양하였 다. 배양액은 2∼3일마다 교환하였으며 세포가 70∼
80% 정도 자라면 계대 배양을 하였다. 세포사멸을 보
기 위한 실험에서는 96 우물 배양판에 2×10
3개씩의 세
포를 분주하여 24시간 후에 혈청이 포함되지 않은
RPMI 배양액으로 바꾸어 주고, 24시간 후 정해진 농도
의 sunitinib을 처리하였다. 역전사 중합효소 연쇄반응
Table 1. RT PCR oligonucleotide primer sequences and product sizes
Gene Gene bank Primer sequences Product size (bp)
GAPDH NM 002046 Forward 5’-CGAGATCCCTCCAAAATCAA-3’ 321
Reverse 5’-GTCTTCTGGGTGGCAGTGAT-3’
Flt-3 NM 004119 Forward 5’-CAAGTGCTGTGCATACAATTCCC-3’ 207
Reverse 5’-ACCTGTACCATCTGTAGCTGG-3’
VEGFR-2 AF 063658 Forward 5’-GTGACCAACATGGAGTCGTG-3’ 660
Reverse 5’-CCAGAGATTCCATGCCACTT-3’
PDGFR-β NM 002609 Forward 5’-AATGTCTCCAGCACCTTCGT-3’ 434
Reverse 5’-AGCGGATGTGGTAAGGCATA-3’
GAPDH: glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, FLT-3: fetal liver tyrosine kinase receptor-3, VEGFR-2: vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2, PDGFR-β: platelet derived growth factor receptor-β
(RT-PCR)과 웨스턴블롯을 위한 실험에서는 60 mm 배 양 접시에 1×10
5개의 세포를 분주하여 70% 정도 자랐 을 때 혈청이 포함되지 않은 RPMI 배양액으로 바꾸어 주고, 24시간 후 정해진 농도의sunitinib을 처리하였다.
세포 생존 분석(Cell Viability Assay)
Sunitinib이 세포 생존에 미치는 영향을 확인하기 위 해서 CCK-8을 이용한 발색 분석법을 사용하였다. 96 우물 배양판에 각 우물 당 2×10
3개씩의 세포를 분주하 여 24시간 후에 혈청이 포함되지 않은 RPMI 배양액으 로 바꾸어 주고, 24시간 후 정해진 농도의 sunitinib이 포함된 RPMI 배양액으로 갈아주고 72시간 동안 세포 배양기에서 배양하였다. 배양액을 제거하고 PBS 용액 으로 2번 세척한 후 CCK-8의 농도가 10%가 되도록 혈 청을 포함하지 않은 배양액과 희석하여 각 우물당 100 μ l씩 첨가하였다. 세포 배양기에서 1∼2시간 동안 배 양한 후 , 세포의 탈수소효소의 활성도에 의한 formazan 염료 발색을 측정하기 위해 Spectramax Microplate 분 광 광도계(Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA)에서 450 nm의 파장으로 흡광도를 측정하였다.
이동측정(Migration Assay)
세포의 이동측정을 위해 , 세포를 6 우물 배양판에 깔 아 100% 밀집도를 보일 때까지 배양기에서 배양하였 다 . 플라스틱 끝을 이용하여 약 1 mm 정도의 넓이로 세포층을 균일하게 긁어내어 세포가 없는 부분(Clear zone)을 만들어 주었으며, 부유물을 제거하기 위해 혈 청이 첨가되지 않은 배양액으로 2회 세척하였다. 세척 후 혈청이 첨가되지 않은 배양액에 sunitinib을 처리하 여 배양하고 , 세포를 Axiovert S100 현미경(Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany)과 AxioCam 디지털 카메라(Carl Zeiss)를 사용하여 촬영하였다.
비부착증식측정(Anchorage Independent Growth Assay)
비부착증식을 측정하기 위하여 반고형 한천평판(soft agar)에 세포를 배양하여 집락을 형성하는 정도를 평가 하였다. 60 mm 배양접시에 멸균된 1%의 정제한천 (agarose) 용액과 10%의 혈청이 포함된 2배 농도의 RPMI 배양액 2.5 ml 정도 부어 상온에서 굳힌 후 바닥 층을 형성시켰다. 세포배양 층을 만들기 위해 멸균된 0.6%의 정제한천용액과 20%의 혈청이 포함된 2배 농 도의 RPMI 배양액 동량을 섞고, 1.5×10
5개의 세포와 sunitinib을 섞어 바닥층 위에 붓고 고르게 섞어주었다.
배양층이 굳을 때까지 상온에 방치해 둔 후, 한천이 마 르는 것을 방지해 주기 위해 sunitinib와 10%의 혈청이 포함된 RPMI 배양액 1 ml를 배양층위에 첨가해 주고, 2주 동안 배양하며 매일 집락이 형성되는 것을 관찰하 였다.
역전사 중합효소 연쇄반응(RT-PCR) 분석
암세포주로부터 추출한 2 ug의 RNA에서 RevertAid First Stand cDNA 합성 키트(Fermentas)를 이용하여 첫 가닥의 cDNA를 합성하였다. VEGFR-2의 역전사 중합 효소 연쇄반응(RT-PCR)은 94
oC에서 45초간 분리, 59.8
oC에서 60초간 결합, 72
oC에서 45초간 합성되는 과 정을 40주기에 걸쳐서 DNA를 증폭하였다. GAPDH는 94
oC에서 분리, 55
oC에서 결합, 72
oC에서 합성되는 과 정을 각각 30초씩 25회 반복하여 DNA를 증폭하였다.
RT-PCR에 사용된 시동체(primer)의 염기 서열과 증폭
된 생성물의 크기는 Table 1과 같다. 역전사 중합효소
연쇄반응의 생성물은 1% 한천젤에서 전기 영동하였으
며 , Gel-doc 시스템 에서 사진을 찍어 확인하였다.
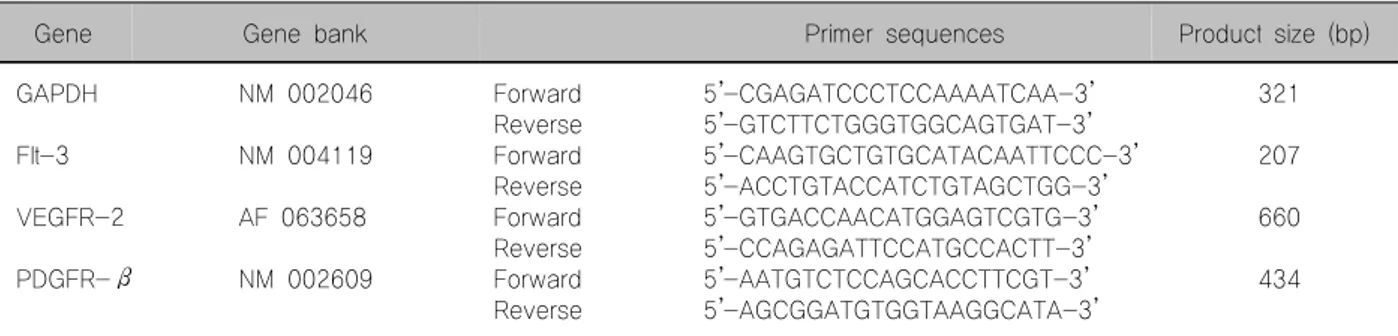
Fig. 1. Comparison of expression of target genes by Sunitinib in human cancer cell line, NPA and TPC-1. Cells were exposed to the indicated concentration of Sunitinib and expression of target genes were analyzed by RT-PCR and Western blot. (A) NPA, (B) TPC-1.
Fig. 2. Effect of Sunitinib on cell viability in human cancer cell lines, NPA, and TPC-1. Cells were exposed to the indicated concentration (0∼50μM) of Sunitinib for 72 hours, and cell viability was determined by CCK assay as described in
“Materials and Methods”. Data presented are mean±SD for five independent experiments. CCK: cell counting kit-8, N:
NPA, T: TPC-1.
웨스턴블롯분석
차가운 PBS 용액으로 세포를 2회 세척한 후, 단백질 분해효소 억제제를 첨가한 세포용해완충액을 이용하 여 세포를 모아 4
oC, 13,000 rpm에서 30분 동안 원심 분리하고 단백질을 포함하는 상층액을 분리하였다. 단 백질 정량은 Quant-iT
TMProtein Assay Kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA)를 이용하였다. 25 ug의 단백질을 4∼12%
SDS-PAGE 젤에서 전기영동하여 전개시킨 후, 니트로 셀룰로즈막(Amersham Bioscience, Pisctaway, NJ)으로 이동시켰다. 막을 해당 일차항체와 12시간 동안 냉장 반응 시킨 후 , HRP가 연결되어 있는 이차항체로 1시간 동안 반응시키고 Western Blotting Luminol Reagent로 필름에 감광시켰다 .
결 과
갑상선암 세포주에서 Flt-3, VEGFR-2 및 PDGFR- β의 발현
Sunitinib의 주된 표적 수용체인 VEGFR-2, PDGFR- β 및 Flt-3의 발현을 갑상선암 세포주인 TPC-1과 흑 색종 세포주인 NPA 세포에서 RT-PCR과 웨스턴블롯 분석을 통해 확인하였다. VEGFR-2와 PDGFR-β는 NPA, TPC-1 모두에서 발현되었으나, 갑상선암 세포주 인 TPC-1이 NPA보다 VEGFR-2와 PDGFR-β 발현량 이 모두 상대적으로 낮았다 . Flt-3는 TPC-1과 NPA 모 두에서 발현되지 않았다 (Fig. 1).
Sunitinib 농도에 따른 갑상선암 세포 성장 억제
Sunitinib이 갑상선암 세포의 생존에 미치는 영향을
확인하기 위하여 TPC-1과 NPA에서 다양한 농도의
sunitinib으로 72시간 동안 처리하고 생존 세포의 수를
CCK-8을 통해서 확인하였다. Sunitinib 처리 후 세포의
생존율은 NPA, TPC-1 세포주 모두에서 농도의존적으
로 감소하였다 (Fig. 2). 흑색종 세포주인 NPA 경우에는
약 2μM의 농도에서 세포의 성장이 억제되기 시작하
였으며, 5μM의 농도에서 세포의 성장이 50% 가량 억
제되었으나 , 갑상선암 세포주인 TPC-1은 같은 농도의
sunitinib에서 성장 억제 효과가 상대적으로 적었다.
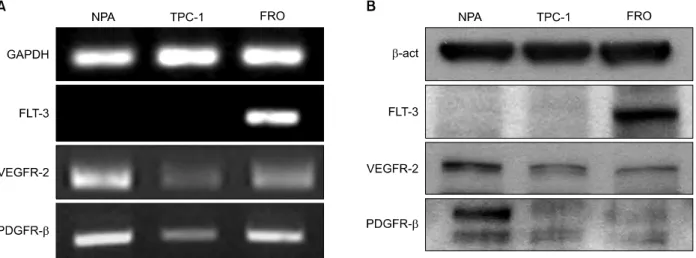
Fig. 3. Effect of Sunitinib on migration of human cancer cell line, NPA and TPC-1. Migration assay: The scratch wounds were created in cells monolayer and incubated with the indicated concentration of Sunitinib. After 2 days, cells were photographed through inverted microscope under 100X magnification. (A) NPA, (B) TPC-1.
Sunitinib이 갑상선암에서 세포의 이동 및 비부착 증 식에 미치는 영향
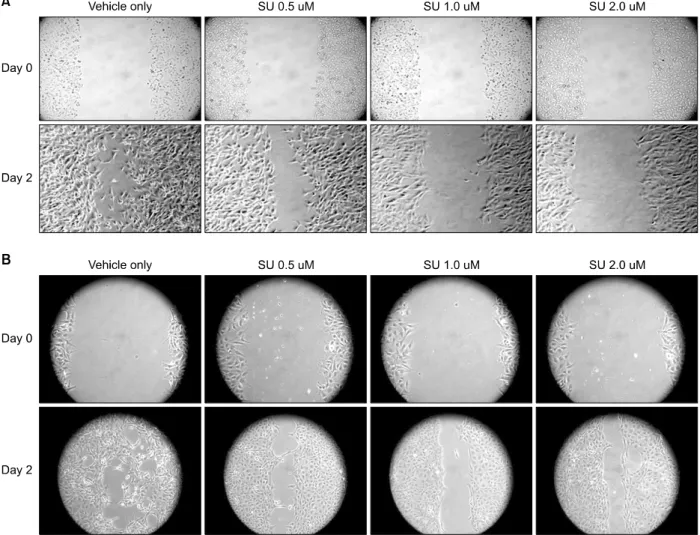
Sunitinib이 암세포의 이동 및 비부착 증식에 미치는 영향을 확인하였다. Sunitinib을 처리한 암세포에서는 2일 후에 세포가 없는 부분을 메우는 정도가 농도의존 적으로 감소하는 것을 확인할 수 있었으며 , 갑상선암 세포주인 TPC-1에서 흑색종 세포인 NPA보다 sunitinib 의한 세포 이동 억제효과가 적게 나타났다(Fig. 3). 비 부착 증식을 확인하기 위하여 반고형한천평판에서 집 락형성을 측정한 실험에서도 sunitinib은 농도의존적으 로 집락 형성을 감소시켰으며, 갑상선암 세포주인 TPC-1에서 NPA보다 sunitinib에 대한 세포의 비부착 억제 효과가 더 적게 나타났다(Fig. 4).
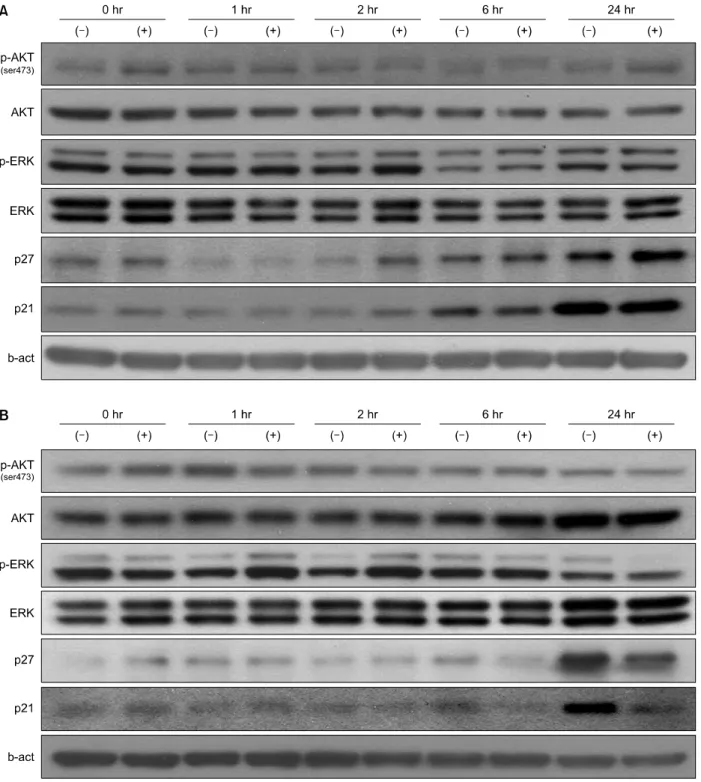
갑상선암 세포주에 대한 sunitinib의 신호전달
선행된 실험들에서는 갑상선암 세포주인 TPC-1에 서 NPA와 비교하여 sunitinib에 의한 세포 성장 및 침 습의 억제효과가 적게 나타남을 확인하였다. Sunitinib 이 암세포의 신호 전달에 미치는 영향을 확인하기 위 해서 암세포의 생존이 최소한으로 억제되는 농도인 2 μ M의 sunitinib을 이용하였다. NPA와 TPC-1 세포에 2μM의 sunitinib을 처리 후 시간 별로 세포를 용해하 여 단백질을 추출한 후 웨스턴블롯 측정을 통해 단백 질 변화를 확인하였다 . Sunitinib 처리 후 NPA와 TPC-1 세포 모두에서 인산화된 ERK 및 AKT에는 유의한 변 화를 확인할 수 없었다. Sunitinib은 NPA 세포에서
p21
Waf1/Cip1과 p27
Kip1의 단백질 발현량에 큰 영향을 주지
못했다(Fig. 5A). 하지만, TPC-1 세포에는 p21
Waf1/Cip1과
p27
Kip1이 증가되는 것이 sunitinib에 의해서 억제되는
Fig. 4. Effect of Sunitinib on anchorage independent colony formation of human cancer cell line, NPA and TPC-1. Anchorage independent growth assay: Cells were cultured in soft agar plate with the indicated concentration of Sunitinib as “Materials and Methods”. After 2 weeks, cells were stained overnight in a solution of 10μg/ml iodonitrophenyl tetrazolium violet and scanned by FluorS Multi-Imager. (A) NPA, (B) TPC-1.
것을 확인할 수 있었다(Fig. 5B).
고 찰
갑상선암 세포주인 TPC-1과 비갑상선 세포주인 NPA 모두 sunitinib의 작용 수용체인 VEGFR-2, FLT3, PDGFR-β를
15,16)발현 하였지만, NPA와 비교하여 갑 상선암 세포 TPC-1에서는 VEGFR-2, FLT-3의 발현량 이 적었다. Tyrosine kinase 길항제인 sunitinib에 의해 서 세포 성장, 침습, 비부착 증식 억제 효과는 두 세포 에서 모두 관찰 되었다. TPC-1은 다른 암세포에서 기 존에 알려진 세포증식억제 농도 보다는 높은 10μM 이상의 농도에서 세포성장이 억제되고, 0.5∼2μM의 농도에서 세포의 이주와 침습, 세포 군집형성을 억제 함을 확인하였다.
15,16)하지만, NPA는 5μM 정도의 더 낮은 농도에서 세포성장 및 이주 , 침습이 억제 되었다.
즉 , sunitinib은 암세포의 생존을 억제하고 세포 이주, 비부착성 세포성장, 침습 저해를 통해 암의 진행과 전 이를 억제할 수 있는 가능성을 보였지만, 갑상선암 세 포는 흑색종 세포에 비해서 sunitinib에 저항성을 보이
는 것을 확인할 수 있었다.
본 연구에서는 갑상선암 세포 TPC-1에서 흑색종 세 포인 NPA 보다 같은 농도의 sunitinib에서 더 높은 생 존율을 보이는 것을 확인하였으며 , 웨스턴블럿 분석을 통하여 sunitinib에 의한 효과가 암세포의 VEGFR-2 수 용체의 하위 신호 전달 체계의 활성화 관련을 밝혀냄 으로써 sunitinib에 대한 저항성의 기전을 일부 확인할 수 있었다. VEGFR-2의 하위 신호 전달 체계 중 AKT 와 ERK는 세포의 생존, 성장, 증식 등에 관여하며,
17,18)GSK-3β의 인산화를 막거나 cyclin D1의 분해를 억제 하고, cyclin dependent kinase (CDK) 억제자인
p21
Waf1/Cip1, p27
Kip1를 억제하는 효과를 통해서 세포주기
조절에도 관여하는 것으로 알려져 있다.
19,20)하지만, NPA와 TPC-1 모두에서 sunitinib은 AKT와 ERK의 인 산화를 억제하지 않았으며, TPC-1 세포에서 p21
Waf1/Cip1과 p27
Kip1의 단백발현이 억제되는 반면, NPA 세포에서 는 억제되지 않음을 확인할 수 있었다.
p21
Waf1/Cip1, p27
Kip1은 세포주기조절 인자로써 cyclin,
CDK, CDK inhibitor (CDKI)의 상호작용에 의해 작용
한다. CDKI는 INK family, CIP/KIP family로 나누며,
Fig. 5. Effect of Sunitinib on activation of p21Waf1/Cip1, p27Kip1 and AKT, ERK in NPA and TPC-1 cells. Cells were exposed to 10uM Sunitinib for 0~24 hours and activation patterns of p21Waf1/Cip1, p27Kip1 and AKT, ERK were determined by immunoblot analysis as described in methods. (A) NPA, (B) TPC-1.
본 연구에서 관찰한 p21
Waf1/Cip1, p27
Kip1는 CIP/KIP family로 G1기에서 S기로 작용하는 여러 cyclin/CDK complex를 억제하는 역할을 한다.
21)p27
Kip1은 G1에서 S기로 세포주기가 넘어가는 과정에 작용하여 세포분 열을 억제하고, 세포간의 유착에도 관여한다.
22)p21
Waf1/Cip1은 CDK2/cyclinE와 CDK2/cyclinA를 억제하
여 CDK2에 의해 억제되는 DNA 복제 관련 효소의 작 용이 억제되며 , 주로 DNA 손상에 대해서 p53활성에 의해 작용된다.
23,24)하지만 독립적으로 활성화 되기도
한다.
25,26)또한 p21
Waf1/Cip1은 DNA 손상 시 세포주기 G1
기에서 S기로 작용하는 것을 억제하여 종양의 발달을
억제하는 인자로 알려져 있다. 갑상선암에 대한 연구
에서는 p21
Waf1/Cip1이 병리학적으로 갑상선암 발달에 중 요역할을 하지 않는다는 연구도 있으나 ,
27,28)면역조직 화학염색에서 양성인 경우 임상경과가 좋지 않다는 연 구도 있다 .
29,30)본 연구를 통해서는 갑상선 유두암 세포 인 TPC-1세포에서 cell cycle inhibitor인 p21
Waf1/Cip1, p27
Kip1가 sunitinib에 의해 감소하여 결과적으로 세포증 식 억제 효과가 감소하였다고 추정된다. 또한 sunitinib 의 target 수용체의 발현량이 TPC-1에서는 더 적기 때 문에 갑상선암 세포주인 TPC-1의 성장, 침습, 비부착 증식 억제효과가 비갑상선 세포주인 NPA에 비해 적게 나타났다고도 추정해 볼 수 있다. 하지만, 이 두 가지 세포에서 나타나는 sunitinib에 의한 성장 억제의 효과 는 현재로서는 확인할 수 없었으며, ERK나 AKT 활성 이 sunitinib에 의해 억제되지 않은 것 또한 확인할 수 없어서 자세한 기전에 관하여는 추가적인 연구가 필요 할 것으로 판단된다.
결 론
본 연구에서는 새로운 tyrosine kinase 길항제인 sunitinib은 갑상선 유두암 세포의 증식과 침습성을 직 접 억제 하기는 하지만, p21
Waf1/Cip1, p27
Kip1의 활성화 차 이 등으로 인해 흑색종 세포주에서 보다 그 억제 정도 가 미약하므로 갑상선 암의 치료제로 사용하기는 부적 합할 것으로 사료된다. 또한 성장 억제 효과는 VEGF- 수용체 및 PDGF-수용체를 통하여 이루어질 것으로 사료되나, 향후 치료에 대한 응용 가능성을 확실히 하 기 위해 수용체 후 신호전달 체계에 대해서는 추가적 인 연구를 통해 더 많은 연구가 필요하다 .
중심 단어: 갑상선암, 유두암, Sunitinib, 타이로 신 키나아제 억제제, p21Waf1/Cip1, p27Kip1.
References
1) Sherman SI. Thyroid carcinoma. Lancet 2003;361(9356):501-
11.
2) Davies L, Welch HG. Increasing incidence of thyroid cancer
in the United States, 1973-2002. JAMA 2006;295(18):2164-7.
3) Lubina A, Cohen O, Barchana M, Liphshiz I, Vered I, Sadetzki S, et al. Time trends of incidence rates of thyroid
cancer in Israel: what might explain the sharp increase. Thyroid 2006;16(10):1033-40.
4) Kang JM, Kim TS, Noh DY, Youn YK, Choe KJ, Oh SK.
Prognostic factors for locally invasive papillary thyroid carcino- mas. J Korea Surg Soc 2000;59(4):478-87.
5) Schlumberger M, Tubiana M, De Vathaire F, Hill C, Gardet
P, Travagli JP, et al. Long-term results of treatment of 283
patients with lung and bone metastases from differentiated thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1986;63(4):960-7.
6) Paul MK, Mukhopadhyay AK. Tyrosine kinase - Role and
significance in cancer. Int J Med Sci 2005;1(2):101-15.
7) Arora A, Scholar EM. Role of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in
cancer therapy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2005;315(3):971-9.
8) Chow LQ, Eckhardt SG. Sunitinib: From rational design to
clinical efficacy. J Clin Oncol 2007;25(7):884-96.
9) Adams VR, Leggas M. Sunitinib malate for the treatment of
metastatic renal cell carcinoma and gastrointestinal stromal tu- mors. Clin Ther 2007;29(7):1338-53.
10) Faivre S, Delbaldo C, Vera K, Robert C, Lozahic S, Lassau N, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetic, and antitumor activity of
SU11248, a novel oral multitarget tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with cancer. J Clin Oncol 2006;24(1):25-35.
11) Burstein HJ, Elias AD, Rugo HS, Cobleigh MA, Wolff AC, Eisenberg PD, et al. Phase II study of sunitinib malate, an oral
multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with meta- static breast cancer previously treated with an anthracycline and a taxane. J Clin Oncol 2008;26(11):1810-6.
12) Socinski MA, Novello S, Brahmer JR, Rosell R, Sanchez JM, Belani CP, et al. Multicenter, phase II trial of sunitinib in
previously treated, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 2008;26(4):650-6.
13) Desai J, Yassa L, Marqusee E, George S, Frates MC, Chen MH, et al. Hypothyroidism after sunitinib treatment for patients
with gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Ann Intern Med 2006;
145(9):660-4.
14) Mannavola D, Coco P, Vannucchi G, Bertuelli R, Carletto M, Casali PG, et al. A novel tyrosine-kinase selective inhibitor,
sunitinib, induces transient hypothyroidism by blocking iodine uptake. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007;92(9):3531-4.
15) Abrams TJ, Lee LB, Murray LJ, Pryer NK, Cherrington JM.
SU11248 inhibits KIT and platelet-derived growth factor recep- tor beta in preclinical models of human small cell lung cancer.
Mol Cancer Ther 2003;2(5):471-8.
16) Mendel DB, Laird AD, Xin X, Louie SG, Christensen JG, Li G, et al. In vivo antitumor activity of SU11248, a novel
tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors: Determination of a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship. Clin Can- cer Res 2003;9(1):327-37.
17) Burgering BM, Coffer PJ. Protein kinase B (c-Akt) in
phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase signal transduction. Nature 1995;376 (6541):599-602.
18) Trinh XB, Tjalma WA, Vermeulen PB, Van den Eynden G, Van der Auwera I, Van Laere SJ, et al. The VEGF pathway
and the AKT/mTOR/p70S6K1 signalling pathway in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer 2009;100(6):971-8.
19) Diehl JA, Cheng M, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ. Glycogen synthase
kinase-3beta regulates cyclin D1 proteolysis and subcellular localization. Genes Dev 1998;12(22):3499-511.
20) Gesbert F, Sellers WR, Signoretti S, Loda M, Griffin JD.
BCR/ABL regulates expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase
inhibitor p27Kip1 through the phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/AKT
pathway. J Biol Chem 2000;275(50):39223-30.
21) Chilosi M, Doglioni C, Magalini A, Inghirami G, Krampera M, Nadali G, et al. p21/WAF1 cyclin-kinase inhibitor expression
in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas: A potential marker of p53 tumor- suppressor gene function. Blood 1996;88(10):4012-20.
22) Go JH. Expression pattern of p27 protein in primary gastirc
lymphomas. Cancer Res Treat 2001;33(4):318-23.
23) el-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, et al. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor
suppression. Cell 1993;75(4):817-25.
24) Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K, Elledge SJ. The
p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell 1993;75(4):805-16.
25) Michieli P, Chedid M, Lin D, Pierce JH, Mercer WE, Givol D. Induction of WAF1/CIP1 by a p53-independent pathway.
Cancer Res 1994;54(13):3391-5.
26) Parker SB, Eichele G, Zhang P, Rawls A, Sands AT, Bradley A, et al. p53-independent expression of p21Cip1 in muscle and
other terminally differentiating cells. Science 1995;267(5200):
1024-7.
27) Mizukami Y, Nonomura A, Michigishi T, Noguchi M, Nakamura S, Hashimoto T. Differential (Ha-, K- and N-) ras
p21 expression in benign and malignant human thyroid tumors:
An immunohistochemical study. Anticancer Res 1995;15(3):
755-9.
28) Okayasu I, Osakabe T, Onozawa M, Mikami T, Fujiwara M.
p53 and p21(WAF1) expression in lymphocytic thyroiditis and thyroid tumors. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 1998;88(2):183- 91.
29) Akslen LA, Varhaug JE. Oncoproteins and tumor progression
in papillary thyroid carcinoma: Presence of epidermal growth factor receptor, c-erbB-2 protein, estrogen receptor related protein, p21-ras protein, and proliferation indicators in relation to tumor recurrences and patient survival. Cancer 1995;76(9):
1643-54.
30) Basolo F, Pinchera A, Fugazzola L, Fontanini G, Elisei R, Romei C, et al. Expression of p21 ras protein as a prognostic