Abstract : Atrial fibrillation (AF), the most common sustained arrhythmia, confers an independ- ent risk factor for stoke. If the disease is not treated, stroke risk will increase more than five times, and about one in three people will experience a stroke during their life time. Therefore, AF needs active management, and anticoagulation therapy is effective in the prevention of stroke.
Warfarin and aspirin, the medicines for the prevention and treatment of thromboembolism, are effective in the prevention of stroke in AF. Medication is determined by stroke risk, generally classified by CHADS
2score. Warfarin is recommended primarily for high-risk patients, and aspirin is recommended for low-risk patients and those unable to take warfarin. Despite the combined warfarin-aspirin therapy is not recommended in general, complementary effects are expected due to different mechanisms of the drug. However, some cases have been reported that the combination of these medications just administered to increase bleeding risks and did not represent a remarkable therapeutic effect.
Therefore, this study is in 2011, Jan. 1 to Oct. 31 in outpatients with AF who underwent the anticoagulation therapy, and patients were classified according to medication uses. This study was analyzed cardiovascular diseases, medical treatments, and hematologic data. In addition, this
심방세동 환자에서 Warfarin 단일요법과 Warfarin-Aspirin 병용요법 간의 출혈경향 발생과 뇌졸중 예방효과 고찰
�
연세대학교 세브란스병원 약무국
Risk of Bleeding and Effect of Stroke Prevention Between Warfarin Single Therapy and Warfarin-Aspirin Combination
Therapy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
Ji Eun Park, Jung Eun Lee, In Ah Seo, Jong Hee Ko, Ji Hyune Ahn
�, Eun Sun Son, Sung Eun Kim, Hyun Joo Suk
Department of Pharmacy, Yonsei University Healthcare System 50 Yonsei-ro, Seodeamun-gu, Seoul, 120-752, Korea
회원학술보고
연구배경 및 목적
부정맥의 가장 일반적인 형태인 심방세동(atrial fibrillation, AF)은 심방의 여러 부위가 무질서하게 뛰면서 불규칙한 맥박을 형성하는 질환으로 높은 이 환율과 사망률을 야기한다.
1-3)또한 불규칙한 맥박으 로 인해 혈전 생성의 가능성이 증가하므로 뇌졸중의 위험인자로 분류되며 지속되는 경우 그 위험도가 5 배 이상 증가하므로 적극적인 관리가 필요하다.
2-4)뇌졸중의 예방에는 주로 warfarin과 aspirin이 사용 되며 두 약제의 사용은 일반적으로 CHADS
2score에 의해 결정된다(Table 1).
1-3, 5-7)CHADS
2score는 심부 전(congestive heart failure), 고혈압 (hyperten- sion), 당뇨(diabetes mellitus), 75세 이상인 경우 각 1점, 이전에 뇌졸중이나 TIA(transient ischemic attack) 경험이 있는 경우 2점으로 최대 6점까지 점수 가 부여되고, 그 점수가 높아질수록 뇌졸중의 위험도 가 높아진다(Table 2, Table 3). 뇌졸중 예방을 위한 약물요법 또한 CHADS
2score에 따라 권고된다.
Score에 따라 저위험군, 중등도위험군, 고위험군으로
study retrospectively analyze the status of anticoagulation therapy in patients with AF.
The warfarin group and warfarin+aspirin group were 54 and 51 patients and average duration of drug administration were 4.7 and 3.6 months, respectively. Bleeding events occurred in 5 and 6 patients in warfarin group and warfarin+aspirn group, respectively. Retrospective analysis of the two drugs showed no significant differences between the bleeding risk and stroke prevention, additional research is needed for the clinical evaluation of the combination therapy of warfarin and aspirin.
[Key words] Atrial fibrillation, Warfarin, Aspirin, Combination therapy, Bleeding risk, Stroke
투고일자 2012. 7. 4; 심사완료일자 2012. 11. 13; 게재확정일자 2012. 12. 20�교신저자 안지현 Tel:02-2228-6929 E-mail:jhahn923@yuhs.ac
None or aspirin Aspirin or warfarin Warfarin
Anticoagulation Therapy
01
2 or greater
Score
Low Moderate Moderate or high
Risk
Table 1. Medication based on CHADS
2score
Congestive heart failure Hypertension
Age≥75 Diabetes mellitus
Stroke/TIA*/thromboembolism Maximum score
Risk factor
C H A D S2
1 1 1 1 2 6
Score Table 2. CHADS
2score
*Transient ischemic attack
나뉘며, 저위험군(score=0)일 경우 약물요법이 시행되 지 않거나 aspirin 단독 요법이 권고된다. 중등도위험 군(score=1)일 경우 warfarin 또는 aspirin 단독요법 이 권고되며 고위험군(score≥2)일 경우 warfarin 단 독요법이 권고되지만 warfarin과 aspirin 병용요법에 대한 명확한 치료지침은 제시되어 있지 않다.
5, 6)Warfarin과 aspirin은 서로 다른 기전을 가지고 있다. Warfarin은 vitamin K epoxide의 재생을 차단하여 vitamin K dependent clotting factor (factor Ⅱ∙Ⅶ∙Ⅸ∙ Ⅹ, anticoagulant proteins C∙S)의 합성을 저해함으로써 항응고 효과를 나타낸 다. Aspirin은 acetylation을 통해 cyclooxyge- nase를 비가역적으로 저해하여 prostaglandin의 합성과 혈소판의 응집을 저해한다.
따라서 warfarin과 aspirin의 병용요법은 두 약제 의 서로 다른 기전으로 인한 상호보완적인 효과가 기 대되는 약물요법이며, 실제로 본 병원에서도 많은 환 자들에게 사용되고 있다.
9)하지만 유의한 효과가 없 고 출혈 경향을 높일 뿐이라는 연구 결과가 보고된 바 있으며, 두 약제 병용요법에 대한 명확한 치료 지 침이 제시되어 있지 않다.
9-11)본 연구는 warfarin과 aspirin 병용요법에 대한 임상적 평가를 위해 진행되었다.
연구방법
1. 연구 기간 및 연구 대상
2011년 1월 1일부터 2011년 10월 31일까지 세브란 스병원에서 warfarin 처방으로 복약 상담 의뢰된 외래환자들 중 심방세동 환자를 대상으로 Warfarin 단독복용 환자군, Warfarin+Aspirin 병용복용 환 자군의 두 군으로 분류하여 각각 54명, 51명으로 총 105명을 분석하였다.
(1) 연구 기간
Warfarin 시작 또는 warfarin+aspirin 시작일로 부터 최대 6개월까지
- 복용중단: 약제 중단 3주 이상일 경우
- Clopidogrel, triflusal 등 다른 항혈전제 복용을 추가로 시작한 경우는 그 전날을 종료일로 한다.
(2) 연구 대상
① Warfarin을 처음 복용하는 환자를 대상으로 한다.
- Aspirin 복용 이력이 있는 환자는 환자군에 포 함한다.
- Clopidogrel, triflusal 등 다른 항혈전제 복용 이력이 있는 환자는 환자군에 포함한다.
② 약물 복용 기간 1개월 이상인 환자를 대상으로 한다.
- 출혈증상으로 1개월 이전에 복용을 중단한 경우 는 포함한다.
③ 연구기간 중 측정된 평균 INR(international normalized ratio)이 1.5 이상, 2.5 미만인 환자를 대상으로 한다.
2. 환자분석
대상 환자들의 전자의무기록 (EMR: eletronic medical record), 복약상담기록지, 통합검사결과 등을 통해 자료를 수집하여 후향적 연구방법으로 분 석하였다.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
CHADS
2score
1.9 2.8 4.0 5.9 8.5 12.5 18.2
Stroke risk(%)
Table 3. CHADS
2score and stroke risk
① 환자 기본 정보
성별, 연령, CHADS
2score, 기저질환
② 약제 복용기간, 복용 중단기간 - 출혈 발생 여부와 그 처치
Major bleeding: 두개내 출혈, 경막하 출혈, 복막후 출혈, 출혈로 인한 약제 중단, 장기내 출혈 등 입원을 유발한 출혈
Minor bleeding: 코피, 잇몸출혈 등 major bleeding을 제외한 모든 출혈
- 뇌졸중 발생 여부와 그 처치 - 혈액학적 수치 (INR) 3. 통계방법
SPSS version 18.0을 사용하여 chi-square test 또는 Fisher’ s exact test를 시행하였다. 각 항목은 p-value가 0.05 미만일 경우 유의성이 있는 것으로 평가하였다.
연구결과
1. 환자 기본 정보
(1) 성별(Fig. 1)
대상환자 총 105명 중 남성이 56.2% (59명), 여성 이 43.8%(46명)로 남성의 비율이 높았다.
Warfarin+Aspirin 병용군에서 남성 60.8%(31 명), 여성 39.2%(20명)으로 남성의 비율이 높았으 며, Warfarin 단독군에서도 남성 51.9%(28명), 여 성 48.1%(26명)으로 남성의 비율이 높았다.
(2) 연령(Fig. 2)
대상의 평균 연령은 Warfarin+Aspirin 병용군이 66.1세, Warfarin 단독군이 65.9세로 큰 차이를 보 이지 않았다. 연령대의 경우 65세 이상 75세 미만인 군이 40%(42명)로 가장 높은 비율을 차지하였으며, 55세 이상 65세 미만인 군이 그 다음을 차지하였다 (30.5%, 32명).
Fig. 1 Gender
(3) CHADS
2score
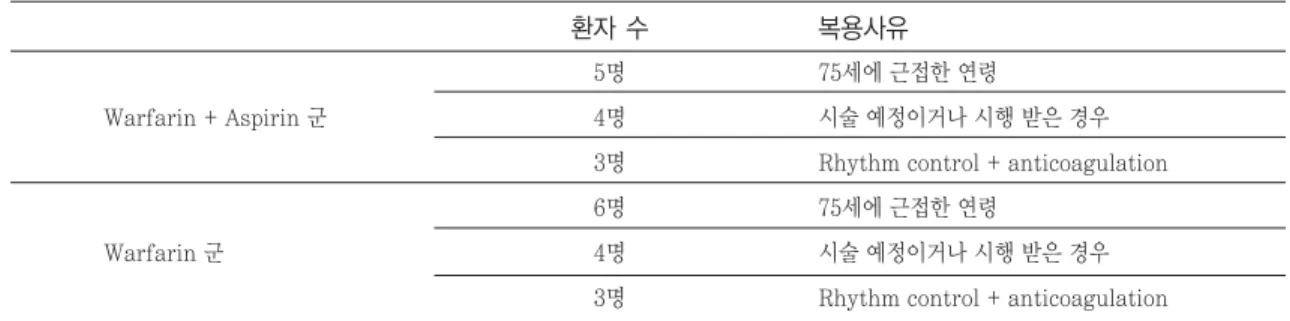
평균 점수는 Warfarin+Aspirin 병용군 1.53, Warfarin 단독군 1.31로 큰 차이가 없었다(Table 4). 점수가 0(저위험군으로 약물요법 시행되지 않거 나 aspirin 단독요법 권고)인 경우임에도 warfarin 을 복용한 환자는 Warfarin+Aspirin 병용군에 12 명, Warfarin 단독군에 13명 분석되었으며 대부분 이 시술 예정이거나 시행 받은 경우(8명), 처음 심방 세동 진단받아 항부정맥제로 조절하며 항응고요법을 같이 하는 경우(6명), 75세에 근접한 경우(11명) 등이 었다(Table 5).
(4) 기저질환(Table 6)
CHADS
2score와 관련이 있는 hypertension, congestive heart failure, diabetes mellitus, cerebral infarction 등의 질환이 높은 비율로 나타 났으며, 그 외 dyslipidemia, coronary artery obstructive disease, tricuspid regurgitation 등 의 질환이 높은 비율을 차지하였다.
2. 약제 복용 기간
(1) 약제 복용 기간(Table 7)
평균 약제 기간은 Warfarin+Aspirin 병용군 3.6 개월, Warfarin 단독군 4.7개월로 단독군이 1개월 정도 더 길었다.
(2) 약제 중단 기간(Table 8)
3주 미만의 약제 중단 경험이 있는 환자의 경우 Warfarin+Aspirin 병용군에 10명, Warfarin 단독 군에 5명이 분석되었으며, 대부분이 각종 시술과 수 술을 위해 단기간 복용 중단한 경우였다.
3. 출혈 또는 뇌졸중 증상 유무와 그 처치
(1) 출혈 증상(Table 9)
① Major bleeding
Warfarin 단독군에서만 1명(두개내 출혈) 발생하 였으며, 타 병원을 내원하여 치료받은 경우였다.
② Minor bleeding
Warfarin+Aspirin 병용군 6명, Warfarin 단독 군에서 4명이 발생하였으며 대부분 눈 충혈이나 멍 이 심하게 드는 증상을 호소한 경우였다.
(2) 뇌졸중 증상
두 군 모두에서 발생하지 않았다.
4. 혈액학적 수치
(1) 평균 INR(Table 10)
Warfarin+Aspirin 병용군은 2.05, Warfarin 단독군은 2.01으로 나타났다.
Warfarin + Aspirin 군 Warfarin 군
1.53 1.31
CHADS
2score (평균) Table 4. Average CHADS
2score
Fig. 2 Age
Hypertension Diabetes mellitus Dyslipidemia
Coronary artery disease Heart failure
Tricuspid regurgitation Cerebral infarction Mitral regurgitation Mitral stenosis Cancer Aortic stenosis Angina pectoris Hypothyroidism
Premature ventricular contraction Arrythmia
Hyperthyroidism Cardiomyopathy Aneurysm
18 12 12 13 7 10
7 7 4 3 3 3 2 1 1 1 0 0
Warfarin+Aspirin군
27 11 3 2 5 0 3 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1
Warfarin군
45 23 15 15 12 10 10 8 4 4 3 3 3 1 1 1 1 1
합계
Warfarin + Aspirin 군Warfarin 군
5명 4명 3명 6명 4명 3명
환자 수
75세에 근접한 연령
시술 예정이거나 시행 받은 경우 Rhythm control + anticoagulation 75세에 근접한 연령
시술 예정이거나 시행 받은 경우 Rhythm control + anticoagulation
복용사유
Table 5. The number of low-risk(score=0) patients who take warfarin
Table 6. Comorbidities
3.6 개월 4.7 개월
평균 복용 기간 (2011.1.1~10.31)
Warfarin + Aspirin군Warfarin군
Table 7. Average period of drug taking
Warfarin + Aspirin군
Warfarin군
심하게 멍듦 침에 피가 섞임
눈 충혈 잇몸출혈 두개내 출혈
심하게 멍듦
Sputum에 출혈양상 눈 충혈
3명 1명 1명 1명 1명
2명
1명 1명
환자 수
Minor
Major
Minor
출혈양상
- - -
응급실 내원하여 압박지혈 발생 시 타병원 내원 Warfarin 감량 (1명) 동네 병원 내원 (1명)
- -
처치
Warfarin+Aspirin군
Warfarin군
10명
5명
환자수
5명 2명 1명 1명 1명 2명 1명 1명
7일 4일, 7일
10일 8일 3일 7일 측정불가
3일
중단 기간
RFCA*시술 치과치료 비뇨기과 조직검사
PTCA�시술 대장내시경 RFCA*시술 코골이 수술 INR 수치가 높게 측정됨(6 이상)
사유 Table 8. Reasons for treatment interruption
* Radiofrequency catheter ablation
�Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty
Table 9. Bleeding events
Warfarin + Aspirin군 Warfarin군
2.05 2.01
평균 INR
209회 396회
총 측정 횟수
4.1회 7.3회
평균 측정 횟수
3.6 개월 4.7 개월
평균 복용 기간 (2011.1.1~10.31) Table 10. INR
중단하지 않음
약제중단
(2) 평균 측정 빈도
Warfarin+Aspirin 병용군과 Warfarin 단독군의 평균 측정 횟수는 각각 4.1회, 7.3회이고, 해당 기간 중의 평균 복용 기간은 각각 3.6개월, 4.8개월로 병 용군은 월평균 약 1회, 단독군은 약 2회의 빈도로 측 정하였다(Table 10).
(3) 목표 I NR 수치를 벗어난 경우가 발생한 환자 수
- 목표 INR은 치료지침 상에서는 2.0에서 3.0사 이가 권고되지만, 동양인은 서양인에 비해 출혈 경향 이 높다고 보고되어 있으며,
12)실제로 본원에서도 주 로 1.5~2.5를 목표로 조절하고 있었다. 따라서 INR 수치가 3.0 이상인 경우와 2.5 이상인 경우로 나누 어 조사하였다.
- INR 수치가 3.0 이상인 경우가 발생한 환자는 Warfarin+Aspirin 병용군 19명, Warfarin 단독군 20명이었고, 2.5 이상인 경우는 병용군 27명, 단독 군 29명으로 분석되었다(Table 11).
결론 및 고찰
부정맥의 가장 일반적인 형태인 심방세동은 불규칙 한 맥박으로 인해 뇌졸중의 위험인자로 분류되는 질 환이다.
1-4)따라서 뇌졸중의 예방을 위해 적극적인 관리가 필요한 질환이며 약물요법으로 warfarin과 aspirin이 주로 사용된다.
1-3, 5-7)뇌졸중 위험도에 따 른 약제의 사용은 주로 CHADS
2score에 따라 결정 되지만 warfarin과 aspirin 병용요법에 대한 명확 한 치료지침은 제시되어 있지 않다.
5, 6)Warfarin과
aspirin 병용요법은 서로 다른 기전으로 인한 상호 보완적인 효과가 기대되는 약물요법이지만 유의한 효과가 없이 출혈 경향을 높일 뿐이라는 연구결과도 보고되고 있다.
9-11)본 연구결과 출혈 증상의 경우 Warfarin+Aspirin 병용군에서는 minor bleeding 6명, Warfarin 단독군에서는 major bleeding 1명, minor bleeding 4명으로 두 군간의 유의한 차이를 보이지 않았다(p>0.05). 또한 두 군 모두 뇌졸중 증 상이 발생하지 않아 뇌졸중 예방 효과에 대한 비교가 불가능하였다. 하지만 후향적 연구로 자료 수집이 용 의하지 않았던 점, 환자군이 비교적 소규모이고 외래 환자를 대상으로 하여 미세한 출혈 경향의 관찰은 환 자의 기억에만 의존해야 한다는 한계점들을 고려할 때, 출혈 관련 증상 발생 및 뇌졸중 예방 효과에 대한 유의한 차이는 없었으나 (p>0.05), warfarin과 aspirin 병용요법의 임상적 평가를 위하여 추가적인 연구가 필요할 것으로 사료된다.
참고문헌
1) A. G. Turpie : New oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation, European Heart Journal, 29, 155-165 (2007)
2) G. Y. H. Lip : The role of aspirin for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation, Nature Reviews Cardiology, 8, 602-606 (2011)
3) R. G. Hart, L. A. Pearce : Current status of stroke risk stratification in patients with atrial fibrillation, Stroke, 40, 2607- 2610 (2009)
4) J. L. Halperin, R. G. Hart : Atrial fibril- lation and stroke: new ideas, persisting dilemmas, Stroke, 19, 937-941 (1988) 5) V. Fuster, L. E. Ryden, D. S. Cannom, H. J.
Crijns, A. B. Curtis, K. A. Ellenbogen, J. L.
Halperin, J. Y. Heuzey, G. N. Kay, J. E.
Lowe, S. B. Olsson, E. N. Prystowsky, J. L.
Tamargo, S. Wann, S. C. Smith, A. K.
Warfarin + Aspirin군 Warfarin군
19
20
3.0 이상
Event 발생한 환자수 (명)
27
29
2.5 이상 Table 11. The number of patients with inappropriate INR
´