Brief Report
Vol. 32, N o. 1, 2020 81
Received July 9, 2018, Revised February 13, 2019, Accepted for publication June 11, 2019
Corresponding author: Hyun-Joo Lee, Department of Dermatology, Pusan National University Hospital, 179 Gudeok-ro, Seo-gu, Busan 49241, Korea. Tel:
82-51-240-7338, Fax: 82-51-245-9467, E-mail: sapphire81@hanmail.net ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1088-0975
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/li- censes/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Copyright © The Korean Dermatological Association and The Korean Society for Investigative Dermatology
https://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2020.32.1.81
Fistula of the Submandibular Gland Presenting as a Painful Mass in the Neck: A Rare Case
Dae-Lyong Ha
1,2, Hyang-Suk Ryu
1, Gun-Wook Kim
1,2, Hoon-Soo Kim
1,2, Byung-Soo Kim
1,2, Hyun-Chang Ko
1,3, Moon-Bum Kim
1,2, Hyun-Joo Lee
1,21Department of Dermatology, Pusan National University School of Medicine, 2Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, 3Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
Dear Editor:
Salivary gland fistula is an abnormal pathway involving the salivary gland or duct. Accurate diagnosis is achieved by observing clinical manifestations, radiographic findings, and surgical exploration. Dermatologists may be unfamiliar with salivary gland fistulas presenting as parotid fistulas or fistu- las of the submandibular gland because there are no such case reports in dermatologic literatures. We report a rare case of fistula of the submandibular gland and provide a brief review of the literature.
We received the patient’s consent form about publishing all photographic materials. A 53-year-old female presented with erythematous plaques and a painful, tender subcuta- neous mass on the left side of the neck (Fig. 1A). She had been diagnosed with sialadenitis a week before and had a sore throat after undergoing endoscopy. We initially diag- nosed her with pyoderma and performed a skin biopsy and computed tomography (CT) scan of the neck. Histopa- thologic results showed septal fibrosis with perivascular inflammatory infiltration in the mid-dermis and subcuta- neous fat layer and no evidence of bacterial infection, in- cluding tuberculosis, on tissue culture and special stain- ings of Ziehl–Neelsen, periodic acid Shiff and gram stain (Fig. 1B, C). The CT scan revealed fuzzy enhancing tubu- lar structures from the submandibular gland to the anterior part of the platysma muscle, consistent with symptoms of inflammation and fistula (Fig. 1D∼F). Routine blood ex-
amination showed no significant findings. Based on these findings, we diagnosed her with fistula of the sub- mandibular gland. It improved with conservative treatment using systemic antibiotics under close observation.
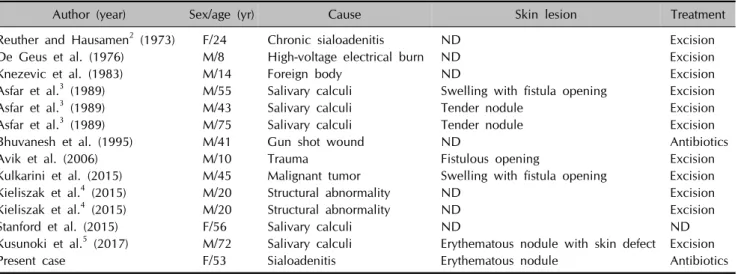
Salivary gland fistula usually originates from the parotid gland although it also rarely arises from the submandibu- lar gland1. Most previous reports were limited to parotid gland fistula; only 13 cases describing fistula of the sub- mandibular gland were found by using keyword, ‘subman- dibular gland fistula’, ‘submandibular fistula’, ‘submandibu- lar’ and ‘fistula’ and compatible with submandibular gland fistula on PubMed searching (Table 1)2-5. These cases list- ed causes of trauma1, sialadenitis2, calculi3, or structural anomaly4. Salivary gland fistula is caused by mechanical obstruction to the drainage of the salivary duct via natural pathways such as calculi or tumors pressing on the duct.
Because our case showed no such anomaly, we thought it developed as a complication of sialadenitis. The precise pathogenesis of sialadenitis and fistula formation is cur- rently unknown. The fistula tract in most cases communi- cated with other space such as paranasal sinus through in- ternal openings or had external openings on the skin or or- al cavity. Here, it connected the infected submandibular gland to the anterior part of the platysma muscle, thus penetrating the muscle. Only two of the previously re- ported 13 cases described a fistula with skin lesions show- ing cutaneous openings1. The opening in this case did not
Brief Report
82 Ann D ermatol
Table 1. Summary of case reports of submandibular gland fistula
Author (year) Sex/age (yr) Cause Skin lesion Treatment
Reuther and Hausamen2 (1973) F/24 Chronic sialoadenitis ND Excision
De Geus et al. (1976) M/8 High-voltage electrical burn ND Excision
Knezevic et al. (1983) M/14 Foreign body ND Excision
Asfar et al.3 (1989) M/55 Salivary calculi Swelling with fistula opening Excision
Asfar et al.3 (1989) M/43 Salivary calculi Tender nodule Excision
Asfar et al.3 (1989) M/75 Salivary calculi Tender nodule Excision
Bhuvanesh et al. (1995) M/41 Gun shot wound ND Antibiotics
Avik et al. (2006) M/10 Trauma Fistulous opening Excision
Kulkarini et al. (2015) M/45 Malignant tumor Swelling with fistula opening Excision
Kieliszak et al.4 (2015) M/20 Structural abnormality ND Excision
Kieliszak et al.4 (2015) M/20 Structural abnormality ND Excision
Stanford et al. (2015) F/56 Salivary calculi ND ND
Kusunoki et al.5 (2017) M/72 Salivary calculi Erythematous nodule with skin defect Excision
Present case F/53 Sialoadenitis Erythematous nodule Antibiotics
F: female, M: male, ND: not described.
Fig. 1. Erythematous nodule on the left side of the neck (A). Histopa- thologic findings showed upper dermal edema with lymphocytes and neutrophils infiltration in the mid to deep dermis, hematoxylin- eosin (H&E) ×20 (B), H&E, ×400 (C). Computed tomography scan rea- vled fuzzy enhancing tubular struc- tures (4 cm) from the left subman- dibular gland to the anterior aspect of the plastysma muscle (*), con- sistent with fistula and inflamation (D∼F).
Brief Report
Vol. 32, N o. 1, 2020 83
Received March 4, 2019, Revised May 15, 2019, Accepted for publication June 18, 2019
Corresponding author: Jin Park, Department of Dermatology, Chonbuk National University Medical School, 20 Geonji-ro, Deokjin-gu, Jeonju 54907, Korea. Tel:
82-63-250-2745, Fax: 82-63-250-1970, E-mail: airmd@jbnu.ac.kr ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8830-5479
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons. org/li- censes/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Copyright © The Korean Dermatological Association and The Korean Society for Investigative Dermatology
adhere to the skin, but was connected to the platysma muscle, presenting an erythematous nodule. It might be easily misdiagnosed, as it is extremely rare and the skin le- sion may present without any cutaneous opening. Derma- tologists should keep in mind the possibility of fistula of the submandibular gland when examining painful masses in the neck.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors have nothing to disclose.
ORCID
Dae-Lyong Ha, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2268-4795 Hyang-Suk Ryu, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1697-397X Gun-Wook Kim, https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1599-7045 Hoon-Soo Kim, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7649-1446 Byung-Soo Kim, https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0054-8570 Hyun-Chang Ko, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3459-5474
Moon-Bum Kim, https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4837-0214 Hyun-Joo Lee, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1088-0975
REFERENCES
1. Jana AK, Jaswal A, Sikder B, Jana U, Nandi TK. Fistula of sub- mandibular gland-a rare presentation. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2006;58:393-394.
2. Reuther J, Hausamen JE. [Extraoral salivary fistula of the sub- mandibular gland]. Zahnarztl Prax 1973;24:134-135. German.
3. Asfar SK, Steitiyeh MR, Abdul-Amir R. Giant salivary calculi:
an orocervical fistula caused by a submandibular gland cal- culus. Can J Surg 1989;32:295-296.
4. Kieliszak CR, Gill A, Faiz M, Joshi AS. Submandibular ductal fistula: an obstacle to sialendoscopy. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2015;141:373-376.
5. Kusunoki T, Homma H, Kidokoro Y, Yanai A, Hara S, Kobayashi Y, et al. Cervical fistula caused by submandi- bular sialolithiasis. Clin Pract 2017;7:985.
https://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2020.32.1.83
Pityriasis Amiantacea: An Epidemiologic Study of 44 Cases in Korean Patients
Hyun-Bin Kwak
1, Seok-Kweon Yun
1,2, Han-Uk Kim
1,2, Jin Park
1,21Department of Dermatology, Chonbuk National University Medical School, 2Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Chonbuk National University-Biomedical Research Institute of Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea
Dear Editor:
Pityriasis amiantacea (PA) is a unique clinical skin con- dition characterized by thick, asbestos-like, adherent scales that engulf the scalp hairs1. It has been reported as a clin- ical manifestation, or sequela, of various inflammatory or
infectious diseases of the scalp2-4. Although it is occasion- ally seen in clinical practice, the data on PA are scarce in the literature.
We investigated the epidemiologic and clinical character- istics of PA. We retrospectively analyzed a series of 44 PA