Copyright ⓒ2009, The Microbiological Society of Korea
300
분열효모에서 spNab2 유전자의 결실돌연변이 및 과발현에 대한 분석
윤진호
성신여자대학교 자연과학대학 생명과학·화학부 및 기초과학연구소
mRNA 의 3' 말단형성 뿐만 아니라, 성숙한 mRNA의 핵에서 세포질로의 이동에 중요한 역할을 하는 출아효모 Saccharomyces cerevisiae의 폴리(A)-RNA 결합단백질인 Nab2와 유사한 분열효모 Schizosaccharomyces pombe의 단백질을 암호화하는 유전자(spNab2로 명명)의 결실돌연변이주(deletion mutant)를 제조하여 그 특성을 조사하 였다. 이배체인 S. pombe 균주에 하나의 spNab2 유전자만을 결실시킨 후 4분체분석(tetrad analysis)을 수행한 결 과, S. cerevisiae NAB2와는 다르게 이 유전자는 생장에 반드시 필요하지 않았다. 또한 spNab2 결실돌연변이는 mRNA 의 핵에서 세포질로의 이동도 정상적으로 보였다. spNab2의 역할을 알아보기 위해, 티아민에 의해 발현이 조절되는 강력한 프러모터를 이용하여 spNab2를 과발현시켰다. spNab2 유전자가 과발현되면, 세포의 생장이 심 하게 억제되었으며, 폴리(A)-RNA가 핵 안에 축적되고 세포질에서는 줄어들었다. 또한 GFP 융합단백질을 이용 하여 spNab2 단백질의 세포 내 위치를 관찰한 결과, spNab2-GFP는 주로 핵 안에 존재하였지만 세포질에서도 관 찰되었다. 이와 같은 결과들은 spNab2 유전자 역시 mRNA의 핵에서 세포질로의 이동에 관여하고 있음을 시사한 다.
Key words □ spNab2, mRNA export, deletion mutant, over-expression, S. pombe
진핵생물에서는 핵 안에서 전사된 mRNA 전구체가 여러 가공 과정(5' 캡핑, 스플라이싱, 3' 폴리아데닐화 등)을 거쳐 성숙한 mRNA 가 되며, 오직 성숙한 mRNA만이 선택적으로 핵에서 세 포질로 나와 단백질 합성에 이용된다(15). 그러므로 폴리(A)-RNA 의 핵에서 세포질로의 이동(mRNA export)은 mRNA의 가공과정 뿐만 아니라 전사 그 자체와도 연관된 매우 복잡한 과정이다(3, 4, 19). RNA 중합효소II에 의해 전사된 mRNA 전사체는 수많은 이형 핵 리보단백질(heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins, hnRNP) 과 결합하여 아주 커다란 mRNP 중합체를 이루며, 이러한 mRNP 중합체는 mRNA가 전사되는 순간부터 소멸할 때까지 시 간적, 공간적으로 결합단백질이 달라지는 역동적인 구조를 이루 고 있다(5, 12).
mRNP export 에는 하등 진핵생물인 효모에서부터 인간에 이르 기까지 진화적으로 잘 보전되어 있는 export 수용체(효모에서는 Mex67-Mtr2, 후생생물에서는 TAP-p15 또는 NXF1-NXT1)와 많 은 export 어댑터 단백질들이 관여한다(11, 12, 13). 어떻게 오직 성숙한 mRNA만 선택되는지는 불명확하지만, mRNA와 비특이 적이고 약한 결합을 하는 export 수용체 단백질을 mRNP로 불러 모으기 위해서는 여러 어댑터 단백질이 반드시 필요한 것으로 알려져 있다(12). 어댑터 단백질들은 export 수용체를 불러 모으 는 기능 이외에도 mRNA 전사 및 가공과정의 중요한 인자로써 작동하고 있으므로, 이러한 과정들과 mRNA export를 연결하는 역할도 담당하는 것으로 여겨진다. 이러한 어댑터에는 TREX
(transcription export) 복합체, TREX-2 복합체(Sac3-Thp1-Cdc31- Sus1 복합체), RNA 결합단백질인 Npl3, 그리고 폴리(A) 결합단 백질인 Nab2 등이 알려져 있다(12, 13).
출아효모인 Saccharomyces cerevisae의 hnRNP 단백질인 Nab2 (nuclear abundant poly(A) RNA binding protein 2) 는 폴리(A) RNA 에 결합하는 단백질로 처음 알려졌으며, 출아효모 생장과 mRNA export 에 필수적이다(2, 9, 10). Nab2 단백질은 주로 핵 안에서 관찰되지만 핵과 세포질을 왕복할 수 있다(9, 6). Nab2 단백질이 핵 안으로 들어가기 위해서는 karyopherin 패밀리에 속 하는 이동수용체인 Kap104가 필요하며, Nab2 단백질의 핵에서 세포질로 나오는 과정에는 아르기닌 메틸전이효소인 Hmt1이 관 여하고 mRNA의 전사가 진행되고 있어야 한다(9, 14). Nab2 단 백질은 export 어댑터 단백질로서의 기능 이외에도 핵 안에서 또 다른 폴리(A) RNA 결합단백질인 Pab1 단백질과 상호작용하여 폴리(A) 꼬리의 길이를 조절한다(10). 또한 Nab2 단백질은 핵공 복합체(nuclear pore complex) 결합단백질인 Mlp1 단백질과 상호 작용하여 아직 가공과정이 진행 중이거나 잘못 가공된 mRNP 복 합체가 세포질로 나가지 못하게 하고 결국 핵 안에서 분해되도록 하는 mRNP의 질적인 관리에도 관여하는 것으로 보고되었다(7).
출아효모인 S. cerevisae와 분열효모는 S. pombe는 모두 자낭 곰팡이(Ascomycota)에 속하는 하등 진핵생물로서 진핵생물의 기 본적인 생명현상을 연구하는 모델생명체로 많이 연구되고 있지 만, 여러 면에서 많은 차이점을 보인다. 그러므로 진핵생물의 전 체적인 mRNA export 기작을 이해하기 위해서는 상호보완적인 관계에 있는 두 효모들을 비교분석하는 것이 바람직하다. 본 실 험에서는 S. cerevisae의 Nab2 단백질과 유사한 S. pombe의 단
*To whom correspondence should be addressed.
Tel: 82-2-920-7675, Fax: 82-2-920-7675
E-mail: jhoyoon@sungshin.ac.kr
백질을 암호화하는 유전자(SPAC14C4.06c)를 결실시키거나 과발 현시켜 mRNA export에서의 기능을 알아보자 하였다.
재료 및 방법 균주, 배지 및 배양조건
기본적인 분열효모의 배양과 유전학적인 기술은 S. pombe 표 준 방법을 사용하였다(1, 20). 본 실험에 사용된 분열효모 S.
pombe 균주는 Table 1에 정리하였다. 재조합 플라스미드의 증폭 과 선택을 위한 형질전환용 균주로 대장균(E. coli) Top10
’을 사 용하였으며, 대장균의 배양을 위해서는 일반적으로 사용되는 Luria-Bertani (LB : 0.5% 효모 추출물, 1% bacto-trypton, 1%
염화나트륨) 액체 배지를 사용하였고, 필요시에는 엠피실린 (ampicillin) 을 100 µg/ml로 첨가하여 37
oC 에서 키웠다. 분열효모 균주의 배양을 위한 배지는 EMM (Edinburgh minimal medium) 과 YES (Yeast extract with supplements : 0.5% 효모 추출물, 3% 포도당, 보충제 : 225 mg/L 아데닌, 류신, 유라실) 배지를 사 용하였고, 28
oC 에서 배양하였다. nmt 프로모터의 억제를 위해서 는 EMM 배지에 15 µM 티아민(thiamin)을 첨가하여 사용하였으 며, 고형 배지는 2% agar를 첨가하였다.
결실돌연변이체와 플라스미드 제조
∆spNab2::ura4
+결실돌연변이는 double-joint PCR에 의한 one- step 유전자결실 방법을 사용하여 제조하였다(22).
∆spNab2::ura4
+DNA 단편을 제작하기 위한 PCR 프라이머는 다 음과 같다. 5For (5'-GATCATCATCGTGTGAAGAC-3'), 5Rev ( 5 ' - A C ATATA G C C A GT G G G AT T T GTA G C TA GT C AT G TTGTTGGTTTACAGTCA-3'), 3For (5'-GGTGTTGGAACAG AATAAATTAGATGAACAACTTCATGTTCCTTCTGTGT-3'), 3Rev (5'-CTGTATCATTAGCCTCGTCA-3'), 5Nest (5'-AACTCG TTGCCCTCAAACTG-3'), 3Nest (5'-CTACGAGGACTACGAG AAGA-3'). 3 번째 PCR 후에 증폭된 ∆spNab2::ura4
+DNA 단편 은 젤-분리 후에 이배체 SP286 균주에 형질전환하였다. Ura
+형 질전환체 중에서 PCR과 Southern blot으로 결실돌연변이체를 선 별하였다. 이렇게 얻은 SP286(∆spNab2) 균주로부터 사분체분석 을 통하여 반수체인 spNab2 결실돌연변이를 얻었다. 3X-Nab2 또는 41X-Nab2 플라스미드 제작을 위해서는 XhoI 인식부위를 첨가한 Nab2-7 (GCACTCGAGATGACTACATTACTGGAAAC), BamH 인식부위를 첨가한 Nab2-8 (GCTGGATCCTTACACA
GAAGGAACATGAA) 프라이머를 사용한 PCR으로 spNab2 ORF 를 증폭하였다. 증폭한 DNA 절편을 XhoI과 BamHI으로 절 단하여, pREP3X 또는 pREP41X 플라스미드의 XhoI과 BamHI 절단부위로 클로닝하였다.
In situ 혼성화(hybridization)
세포 내의 폴리(A)-RNA의 분포를 알아보기 위한 in situ 혼성화 는 이전 논문에 서술되어 있다(21). 혼성화 탐침으로는 α- digoxygenin 을 3' 말단에 붙인 Oligo-(dT)
50을 사용하였다. 형광현미 경으로 혼성화 탐침을 관찰하기 위해서는 FITC-anti-digoxygenin Fab 항체(Roche Applied Science, Germany)를 사용하였다. DNA 염색을 위해서는 4
’, 6
’-Diamidino-2
’-phenyindole (DAPI) 을 사용하 였다.
결과 및 고찰 spNab2 결실돌연변이주의 제작과 분석
성숙한 mRNA의 export와 생장에 필수적인 역할을 하는 출아 효모 S. cerevisiae의 폴리(A)-RNA 결합단백질인 Nab2 단백질과 유사한 단백질을 암호화하는 open reading frame (ORF)인 SPAC14C4.06c 를 분열효모인 S. pombe의 유전체 database (Sanger Center, UK) 에서 찾았다. 이 ORF는 2개의 인트론이 있 으며, 307개 아미노산으로 이루어진 예상 분자량 33.9 kDa의 단 백질을 암호화하고 있다. 525개의 아미노산으로 이루어진 S.
cerevisiae Nab2 단백질에 비해 다소 짧지만, 이 단백질의 아미노 산 서열은 Nab2와 65.5%의 유사성을 보이므로, 이 유전자를 spNab2 로 명명하였다. S. cerevisiae Nab2 단백질은 4개의 영역 (domain) 으로 구성되어 있다: 독특한 N-말단 영역, 글루타민이 풍부한 (QQQP) 영역, 아르기닌-글리신(RGG) 영역, zinc finger 영역(2). 기능이 알려지지 않고 생장에 필요하지 않은 QQQP 영 역, 그리고 Nab2 단백질이 핵으로 이동하는데 필요한 RGG 영 역은 spNab2에는 보존되어 있지 않았지만, mRNA export에 필 요한 N-말단 영역은 높은 유사성을 보였다(16). 또한 폴리(A)- RNA 와 Nab2의 결합에 중요한 C-말단 부위의 zinc finger 영역 은 분열효모에서도 보존되어 있었지만, S. cerevisiae에서는 CCCH 유형의 zinc finger 모티프가 7개 존재하는 반면 S.
pombe 에서는 3개만 존재하였다. 같은 유형의 zinc finger 모티프 와 mRNA export에 필수적인 영역에서 유사성이 높으므로, spNab2 도 mRNA의 핵 밖으로 수송에 관여하는지를 알아보고자 Table 1. S. pombe strains used in this study
Strains Genotype Source
AY217 h
-leu1-32 ura4-d18 21
SP286 h
+/h
+leu1-32/leu1-32 ura4-d18/ura4-d18 ade6-M210/ade6-M216 17 SP286 ( ∆spNab2) h
+/h
+leu1-32/leu1-32 ura4-d18/ura4-d18 ade6-M210/ade6-M216, ∆spNab2::ura4
+/spNab2
+This study AY217 (3X-Nab2 or 41X-Nab2 ) h
-leu1-32 ura4-d18 /3X-Nab2 or 41X-Nab2 This study
∆spNab2 (GFP-Nab2 or Nab2-GFP) h
-leu1-32 ura4-d18 ∆spNab2::ura4
+/GFP-Nab2 or Nab2-GFP This study
결실돌연변이 균주를 제작하여 특성을 연구하였다.
영양요구 선별유전자인 ura4
+로 치환된 spNab2 결실돌연변이 균주를 만들기 위해서, spNab2::ura4
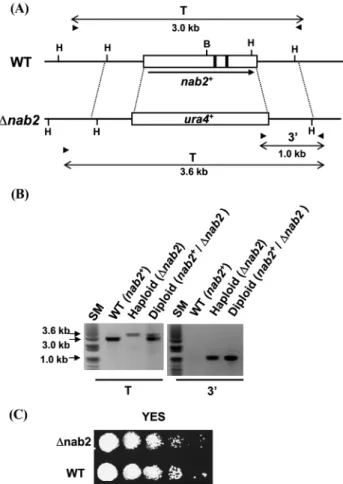
+DNA 단편을 double-joint PCR 방법에 의해 제작한 후, 이배체 균주인 SP286에 형질전환 시켜 유라실이 없는 배지에서 자라는 형질전환체를 얻었다(Fig.
1A). 이 형질전환체들로부터 2개의 spNab2 유전자 중 하나만 ura4
+유전자로 치환된 형질전환체(∆spNab2::ura4
+/spNab2
+) 를 선별하기 위해, 형질전환체의 DNA를 추출하여 PCR을 수행하였 다. 대조군으로 사용한 spNab2 유전자가 야생형인 균주는 3.0 kb
의 DNA가 증폭되는 것에 비해 3.6 kb도 증폭되는 결실돌연변이 를 선별하였으며(Fig. 1B), Southern blotting으로 확인하였다(자 료 미제시). 이렇게 얻은 SP286(∆spNab2) 균주는 교배형이 h
+/ h
+로 유성생식에 의한 포자형성을 하지 않는다. 하지만 h
+/h
+유 전자형은 낮은 빈도이지만(10
-3) 포자형성을 할 수 있는 h
+/h
90이배체로 자발적으로 전환되므로, h
+/h
90이배체를 선별한 다음 4 분체분석을 수행하였다. 하나의 이배체 세포는 감수분열에 의해 4 개의 반수체 포자(4분체)를 형성하므로, 10개의 4분체를 미세조 작기(micromanipulator)로 각각 분리하여 배양하였다. 분석한 10 개의 사분체 모두에서 4개의 자낭포자들이 모두 콜로니로 생장 하였다(자료 미제시). 콜로니를 형성한 4개의 포자 중 2개는 유 라실-영양요구 표현형을 보이는 야생형 spNab2
+유전자를 가진 반수체이고, 나머지 2개의 포자는 유라실이 없는 배지에서도 자 라는 것으로 보아 spNab2 유전자가 결실된 ∆spNab2::ura4
+유 전자형을 갖는 반수체 포자였다. 이렇게 만들어진 spNab2 결실 돌연변이 균주는 야생형 균주와 거의 유사한 생장 속도를 보여 주었다(Fig. 1C). 이 실험 결과는 생장에 필수적인 출아효모의 NAB2 유전자와는 다르게 분열효모의 spNab2 유전자는 생장에 필수적이지 않다는 것을 의미한다.
spNab2 결실돌연변이 균주(∆spNab2::ura4
+) 가 mRNA의 수송 에 결함을 보이는지를 알아보기 위해, 야생형(spNab2
+) 균주와 spNab2 결실돌연변이 균주에서 폴리(A)-RNA의 분포를 in situ 혼성화를 통해 조사하였다. spNab2 결실돌연변이도 야생형 균주 와 마찬가지로 폴리(A)-RNA가 세포 전체에 퍼져있는 분포를 보 이는 것으로 보아(Fig. 2), mRNA의 대량수송에는 큰 결함이 없 는 것으로 사료된다.
spNab2 과발현 균주의 제작과 분석
spNab2 유전자가 S. cerevisiae NAB2와는 다르게 생장에 필수 적이지 않고, 결실되더라도 mRNA export에 큰 결함을 보이지 않으므로, 이 유전자의 기능을 알아보기 위하여 spNab2 유전자 를 과발현(over-expression) 할 수 있는 균주를 제작하였다. 먼저 spNab2 유전자의 단백질을 암호화하는 ORF만을 nmt1 프로모터 에 붙여서, spNab2의 전사가 티아민에 의해 조절되는 3X-Nab2 와 41X-Nab2 플라스미드를 제작하였다. nmt1 프로모터는 배지 에 티아민이 없으면 전사가 유도되고, 티아민이 존재하면 전사가 Fig. 1. S. pombe ∆nab2 deletion mutants are viable. (A) A schematic
diagram representing the constucts of the nab2 null allele in S. pombe.
Most of the nab2 open reading frame region was replaced by the marker gene, ura4
+, by one-step gene disruption method. The spNab2 ORF is represented by open boxes and two introns are denoted by closed boxes. The direction of transcription is shown by arrow under the ORF. The positions of PCR primers for confirmation of wild type and null alleles are indicated by arrowheads, and the expected size of PCR products is also shown. B, BamHI; H, HindIII. (B) Confirmation of the disruption of the nab2 locus. Genomic DNAs isolated from wild type (WT), Diploid disrupted one of the nab2 locus (nab2
+/ ∆nab2), and ∆nab2 haploid strains. The positions of PCR primers for confirmation of wild type and null alleles are indicated by arrowheads.
(C) Growth of ∆nab2 knockout mutant and wild type (WT). Wild type and nab2 disrupted cells were spotted in 10-fold serial dilutions onto YES plate and incubated for 4 days at 28
oC.
Fig. 2. Poly(A)
+RNA localization in ∆nab2 mutants and wild type
cells. Cells were grown to the mid-log phase in appropriately
supplemented EMM medium at 28
oC. Coincident DAPI staining is
shown in the right panels.
억제되는 프로모터이다(18). pREP3X 플라스미드에 있는 야생형 nmt1 프로모터는 강력한 프로모터로 티아민이 없는 배지에서 발 현 정도가 매우 높으며, pREP41X 플라스미드에 존재하는 돌연 변이 nmt1 프로모터는 발현정도가 야생형에 비해 좀 약하다(8).
이렇게 제작된 플라스미드들을 야생형 반수체 균주(AY217)에 형 질전환시켰다. 이렇게 제작된 균주들은 염색체에서 발현되는 spNab2 유전자 이외에 플라스미드에서 spNab2가 더 발현된다.
이렇게 제작된 AY217(3X-Nab2 또는 41X-Nab2) 균주는 티아민 이 있는 배지(+B1)에서는 플라스미드의 spNab2 유전자의 발현이 억제되므로, 빈 플라스미드가 형질전환된 대조군과 마찬가지로 정상적인 생장을 보였다(Fig. 3A). 하지만 흥미롭게도 티아민이 없는 배지(-B1)에서 플라스미드의 spNab2 유전자가 과발현되면 생장에 심각한 장애를 보였다. 발현이 많은 3X-Nab2가 41X- nab2 에 비해 더 심한 생장 억제 효과를 보였다(Fig. 3A). 대조군 은 티아민에 상관없이 잘 자랐다.
spNab2 유전자의 과발현이 생장에 심각한 저해현상을 보이므 로, 이러한 성장억제가 mRNA의 export에 관련이 있는지 알아보 기 위해 폴리(A)-RNA의 세포내 분포를 in situ 혼성화 통해 조
사하였다. 대조군인 빈 플라스미드를 가지고 있는 균주와 3X- Nab2 또는 41X-Nab2를 가지고 있는 균주들을 티아민이 있는 배 지에서 키우다가 둘로 나누어 하나는 티아민이 없는, 그리고 나 머지 하나는 티아민을 첨가한 배지에서 18시간 더 키웠다. 빈 플라스미드를 가지고 있는 대조군은 티아민의 유무에 상관없이 poly(A)
+RNA 가 세포질 전체에 정상적으로 퍼져있었다(Fig. 3B).
하지만 3X-Nab2 또는 41X-Nab2를 가지고 있는 균주들은 모두 spNab2 유전자가 과발현되는 조건(티아민이 없는 배지)에서는 poly(A)
+RNA 가 핵 안에 매우 강하게 축적되었으며 세포질에는 줄어들었다(Fig. 3B). 이것은 spNab2 유전자가 과발현되는 경우 mRNA 의 세포질로의 이동에 심각한 이상이 생긴다는 것을 의미 한다. 이러한 실험 결과는 생장과 mRNA export에 필수적인 역 할을 하는 출아효모의 Nab2와는 다르게, 분열효모의 spNab2는 mRNA export 에 보조적인 역할을 담당하거나 비슷한 역할을 하 는 또 다른 단백질이 존재함을 시사한다.
spNab2 단백질의 세포 내 위치
spNab2 유전자가 암호화하는 단백질의 세포 내 위치를 알아보
Fig. 3. Nab2 over-expression cause the defects of cell growth and mRNA export. (A) Growth of wild type (AY217) transformed with empty vector,
41X-Nab2, and 3X-Nab2. Strains was monitored by spot assay for 5 days in repressed or over-expressed conditions. (B) Cells were grown to the
mid-log phase in appropriately supplemented EMM medium in the presence of thiamine (+B1) at 28
oC. The cells were then washed and shifted to
EMM medium without (-B1) or with thiamine (+B1), and were grown for 18 h. Coincident DAPI staining is shown in the right panels.
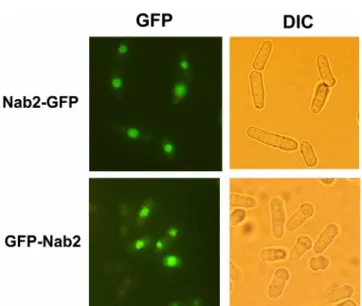
기 위하여 GFP (Green Fluorescence Protein)를 이용하였다. 이 를 위해 GFP 벡터인 pZA69와 pREP81-EGFPc에 spNab2 ORF 를 클로닝하였다. 이렇게 제작한 GFP-Nab2와 Nab2-GFP 플라스 미드는 각각 spNab2의 N-말단 또는 C-말단에 GFP가 위치한다.
이 플라스미드들을 염색체에서 발현된 spNab2와 경쟁하지 않도 록 ∆spNab2 균주에 형질전환하였다. 이러한 GFP-spNab2 융합단 백질도 과발현되면 spNab2 과발현과 마찬가지로 생장이 억제되 고 mRNA export에 결함을 보인다(자료 미제시). 형광현미경으로 융합단백질의 세포 내 위치를 관찰하면, N-말단 또는 C-말단에 GFP 가 융합된 spNab2 융합단백질 모두 핵 안에서 강하게 위치 하였지만 세포질에서도 약하게 관찰되었다(Fig. 4). 이와 같은 결 과는 핵과 세포질을 왕복할 수 있는 출아효모의 Nab2와 마찬가 지로 spNab2도 주로 핵 안에서 mRNA export에 관여할 가능성 을 시사한다.
한편, 출아효모의 Nab2와 같이 mRNA export이외에 폴리(A) 꼬리의 길이 조절이나 mRNA의 질적인 관리에도 분열효모의 spNab2 가 관여하는지를 알아보는 것도 흥미로울 것이다.
감사의 말
이 논문은 2009년도 성신여자대학교 학술연구조성비 지원에 의하여 연구되었음.
참고문헌
1. Alfa, C., P. Fantes, J. Hyams, M. Mcleod, and E. Warbrick. 1993.
Experiments with Fission Yeast. Cold Spring Harbor, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, N.Y., USA.
2. Anderson, J.T., S.M. Wilson, K.V. Datar, and M.S. Swanson. 1993.
NAB2: a yeast nuclear polyadenylated RNA-binding protein essential for cell viability. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13, 2730-2741.
3. Cole, C.N. and J.J. Scarcelli. 2006. Transport of messenger RNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 18, 299- 306.
4. Cullen, B.R. 2003. Nuclear RNA export. J. Cell Sci. 116, 587-597.
5. Darzacq, X., R.H. Singer, and Y. Shav-Tal. 2005. Dynamics of transcription and mRNA export. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 17, 332- 339.
6. Duncan, K., J.G. Umen, and C. Guthrie. 2000. A putative ubiquitin ligase required for efficient mRNA export differentially affects hnRNP transport. Curr. Biol. 10, 687-696.
7. Fasken, M.B., M. Stewart, and A.H. Corbett. 2008. Functional sig- nificance of the interaction between the mRNA-binding protein, Nab2, and the nuclear pore-associated protein, Mlp1, in mRNA export. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 27130-27143.
8. Forsburg, S.L. 1993 Comparison of Schizosaccharomyces pombe expression systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 21, 2955-2956.
9. Green, D.M., K.A. Marfatia, E.B. Crafton, X. Zhang, X. Cheng, and A.H. Corbett. 2002. Nab2p is required for poly(A) RNA export in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and is regulated by arginine methylation via Hmt1p. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 7752-7760.
10. Hector, R.E., K.R. Nykamp, S. Dheur, J.T. Anderson, P.J. Non, C.R. Urbinati, S.M. Wilson, L. Minvielle-Sebastia, and M.S.
Swanson. 2002. Dual requirement for yeast hnRNP Nab2p in mRNA poly(A) tail length control and nuclear export. EMBO J.
21, 1800-1810.
11. Izaurralde, E. 2002. A novel family of nuclear transport receptors mediates the export of messenger RNA to the cytoplasm. Eur. J.
Cell Biol. 81, 577-584.
12. Kelly, S.M. and A.H. Corbett. 2009. Messenger RNA export from the nucleus: a series of molecular wardrobe changes. Traffic 10, 1199-1208.
13. Khler, A. and E. Hurt. 2007. Exporting RNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 761-773.
14. Lee, D.C. and J.D. Aitchison. 1999. Kap104p-mediated nuclear import. Nuclear localization signals in mRNA-binding proteins and the role of Ran and Rna. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 29031-29037.
15. Lei, E.P. and P.A. Silver. 2002. Protein and RNA export from the nucleus. Dev. Cell 2, 261-272.
16. Marfatia, K.A., E.B. Crafton, D.M. Green, and A.H. Corbett.
2003. Domain analysis of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae heteroge- neous nuclear ribonucleoprotein, Nab2p. Dissecting the require- ments for Nab2p-facilitated poly(A) RNA export. J. Biol. Chem.
278, 6731-6740.
17. Matsumoto, T. and D. Beach. 1991. Premature initiation of mitosis in yeast lacking RCC1 or an interacting GTPase. Cell 66, 347-360.
18. Maundrell, K. 1993. Thiamine-repressible expression vectors pREP and pRIP for fission yeast. Gene 123, 127-130.
19. Moore, M.J. 2005. From birth to death: the complex lives of eukaryotic mRNAs. Science 309, 1514-1518.
20. Moreno, S., A. Klar, and P. Nurse. 1991. Molecular genetic analy- sis of fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Methods Enzy- mol. 194, 795-823.
21. Yoon, J.H., D. Love, A. Guhathakurta, J.A. Hanover, and R. Dhar.
2000. Mex67p of Schizosaccharomyces pombe interacts with Rae1p in mediating mRNA export. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 8767-8782.
Fig. 4. Localization of Nab2 proteins fused to GFP. Nab2 was tagged
with GFP at its amino-terminal (GFP-Nab2) or carboxy-terminal end
(Nab2-GFP). Cells were grown to the mid-log phase in appropriately
supplemented EMM medium in the presence of thiamine (GFP-Nab2)
or in the absence of thiamine (Nab2-GFP) at 28
oC. Coincident
differntial interference contrast (DIC) images are also shown in the
bottom panels.
22. Yu, J.H., Z. Hamari, K.H. Han, J.A. Seo, Y. Reyes-Domnguez, and C. Scazzocchio. 2004. Double-joint PCR: a PCR-based molecular tool for gene manipulations in filamentous fungi. Fungal Genet.
Biol. 41, 973-981.
(Received December 1, 2009/Accepted December 11, 2009)
ABSTRACT : Effects of spNab2 Deletion and Over-Expression on mRNA Export
Jin Ho Yoon (Basic Science Research Institute, School of Biological Science and Chemistry, College of Natural Sciences, Sungshin Women's University, Seoul 136-742, Republic of Korea) We constructed the deletion mutants of fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe spNab2 gene that is homol- ogous to poly(A)-binding protein NAB2 in budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which plays crucial roles in mRNA 3' end formation and mRNA export from nucleus into the cytoplasm. A null mutant in an h+/ h+ diploid strain was constructed by replacing the spNab2-coding region with an ura4+ gene using one-step gene dis- ruption method. Tetrad analysis showed that the spNab2 is not essential for vegetative growth and mRNA export. However, over-expression of spNab2 cause the severe growth defects and intensive accumulation of poly(A) RNA in the nucleus. Also, the spNab2-GFP fusions were localized mainly in the nucleus. These results suggest that spNab2 is also involved in mRNA export out of the nucleus.