LPS 로 유발한 대식세포의 염증반응과 마우스 귀 부종에 대한 구멍갈파래 에탄올 추출물의 항염증 효과
김민지1, 김민주1, 김꽃봉우리1, 박선희1, 최현덕2, 박소영1, 장미란3, 임무혁4, 안동현1*
1부경대학교식품공학과/식품연구소
2부경대학교수산과학연구소
3식품의약품안전처건강기능식품정책과
4대구대학교식품공학과
Received: September 19, 2016 / Revised: November 16, 2016 / Accepted: November 24, 2016
서 론
일상생활에서일어나는면역반응은인체내부에서발생하 는생리적보호활동이며염증은우리의눈으로흔히확인 할수있는면역반응중하나이다. 외부로부터의세균에감 염되거나물리적, 화학적자극을받게되면우리몸에서는 그자극을인지하고방어기작을나타내어외부의자극을완 화시키거나균을제거하고손상된조직을회복할수있도록
한다. 하지만그반응이과다하게되면염증의형태로발생
하게되며염증은특히대식세포(macrophage)가가장큰관
여를한다[15]. 대식세포에는다양한 receptor가존재하며여 러가지숙주반응과관련하여항상성을유지시킨다. 균이 침입함과동시에혈관의투과성이증대되면서혈관내로염 증과관련된물질이분비되어통증을유발하고, 붉어지며붓 고 열을 발생시키기도 한다[14]. 대식세포는 여러 가지
cytokine들을분비하여직접적으로외부의물질을파괴하거
나다른면역세포들을모아염증반응을매개한다. 염증에관
여하는 cytokine은다양하게존재하나그중에서도 tumor
necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin- 6 (IL-6)가 대표적이며 대식세포의 tall like receptor 4 Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Ethanol Extracts from Ulva pertusa Kjellman on LPS-induced RAW 264.7 Cells and Mouse Model
Min-Ji Kim1, Min-Ju Kim1, Koth-Bong-Woo-Ri Kim1, Sun-Hee Park1, Hyeun-Deok Choi2, So-Yeong Park1, Mi-RanJang3, Moo-Hyeog Im4, and Dong-HyunAhn1*
1Department of Food Science & Technology/Institute of Food Science, Pukyong National University, Busan 48513, Republic of Korea
2Institute of Fisheries Sciences, Pukyong National University, Busan 46041, Republic of Korea
3Health Functional Food Policy Division, Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, Chungcheongbuk-do 28519, Republic of Korea
4Department of Food Science and Biotechnology, Daegu University, Gyeongsan 38453, Republic of Korea
Recently, various marine algae have been considered as a natural resource for anti-inflammation. In this research, we investigated the anti-inflammatory activity of Ulva pertusa Kjellman ethanol extract (UPKEE). This study showed that UPKEE inhibited the secretion of cytokines including IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β, and reduced the expression of NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) as well as iNOS and COX-2. In the formation of mouse ear edema test, three doses (10, 50, 250 mg/kg body weight) of UPKEE showed inhibitory activity after inducing inflammation using croton oil. In conclusion, we found that UPKEE showed an inhibitory effect on NF-κB and MAPKs, and reduced the secretion of inflammatory cytokines. This result suggests that UPKEE can be used as a natural anti-inflammatory resource in food industry.
Keywords: Ulva pertusa Kjellman, anti-inflammation, NF-κB, MAPKs
*Corresponding author
Tel: +82-51-629-5831, Fax: +82-51-629-5824 E-mail: dhahn@pknu.ac.kr
© 2016, The Korean Society for Microbiology and Biotechnology
(TLR4)로부터인식되어신호전달의반응으로인하여전사 인자들의활성화가일어나게된다. 대표적인연쇄반응에는 nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)와 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPKs)가있다. 외부의자극이나침입한균을제
거하기위해분비된염증매개 cytokine이과다하게분비되
면여러가지염증질환에기여하게되는것이다[5]. 핵으로
전사된 NF-κB는 cytokine 이외에도 inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)의 유전자를 발현시킨다. 염증반응이시작되면 cytokine은과량분비가 일어나염증관련질환을일으키며, 염증성 cytokine 등에의 하여발현된 iNOS는 nitric oxide (NO)의생성을촉진시킨
다[23]. NO는우리몸에서병리학적으로중요한역할을수
행하며박테리아를죽여면역반응에관여하지만이분비량 이과도하게증가할경우에는숙주에심화된염증반응을일 으켜부정적인결과를초래한다고알려져있다[18]. COX는 일반적으로 COX-1과 COX-2 두가지의이성질체로존재하 는단백질이다. 특히염증에서는 COX-2가 PGE2를생성시 켜염증반응을일으키는데 COX-2의발현은세포가손상되 거나고통, 부종및발열, 신생혈관형성및전이같은종양
생성과관련이깊은것으로알려져있다[4]. MAPKs의활성
은대식세포에서일어나며 extra cellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK), p-38과 같은주요 3개의인자가존재한다. 이러한 signaling pathway 의활성을억제함으로써염증성 cytokine의분비량을억제 하고자하며유효물질을천연물로부터확인하고자현재많
은관련연구들이진행되고있다[10]. 본연구에서사용된구
멍갈파래(Ulva pertusa Kjellman)는녹조류의하나로단독 혹은 2−3가닥으로뭉쳐서자라며 10−30 cm 또는그이상에 달한다. 담수가유입되는지역에많이자라며다량의미네랄 을농축하고있고, 식이섬유에의한정장작용[1, 22] 등과같 은그효능이입증된바있다. 구멍갈파래는특히황산기를
함유한다당을다량함유하고있어이로인한항종양성[23],
항바이러스성[2], 면역증진의효과[20], 혈액의항응고작
용[17] 등의효과가보고되고있다. 따라서본연구에서는구
멍갈파래에탄올추출물을이용하여항염증활성을확인하 고식품, 의약품분야에서의천연소재로써활용가능성을밝 히고자한다.
재료 및 방법
실험 재료
본실험에서사용한구멍갈파래는 2015년도연화리에서 채집해온것으로자연건조이후동결건조를 2일이상실시 하였다. 동결건조가완료된구멍갈파래시료는분말화한후 진공포장하여−20℃에서보관하였다. 분말을이용하여에
탄올추출 24시간씩 3회실시하고농축하여이를본실험의 재료로사용하였다.
실험동물
수컷의생후 8주령 ICR 마우스를귀부종및귀조직실
험에 사용하였다. 마우스는 오리엔트바이오(Orient Co.,
Korea)로부터구입을하였다. 실험에사용한마우스는온
도 20±2℃, 습도 50±10%, 12시간의 명암주기가유지되 는동물실에서 1주일간안정기를가진이후에실험을진행 할수있도록하였다. 본동물실험은 부경대학교동물실 험윤리위원회로부터 동물실험 승인을 받아 수행하였다 (2015-04).
세포배양
한국세포주은행(KCLB 40071)에서 분양받은 대식세포 RAW 264.7을사용하여세포배양을실시하였다. RAW 264.7 cell은 DMEM 배지 10%에 inactivated fetal bovine serum 과 1% penicillin-streptomycin 10%를첨가한배지를배양 액으로하여배양을실시하였으며배양조건은 37℃, 5% CO2
를유지할수있도록하였다. 실험을진행하는과정중에사 용된모든세포들은전체 plate의 80−90% 정도의밀도로자
랐을때계대배양을하였고 20 passages를넘기지않은세
포만사용하였다. 세포 독성 측정
본실험에서사용한구멍갈파래에탄올추출물의세포독 성을 평가하기 위하여 MTT assay를실시하였다. 1 × 106 cells/ml의 RAW 264.7 cell을 plate에분주하고 20시간 전 배양을실시하였다. 이후에 1 μg/ml의 LPS와농도별(0.1, 1, 10, 50, 100 μg/ml)로구멍갈파래에탄올추출물을첨가하여 37℃, 5% CO2 조건의 incubator (MCO-15AC, Sanyo, Japan)에서 24시간배양하였다. 24시간배양을완료한후 5 mg/ml 농도의 MTT 시약을분주하여 2시간재배양하였 다. 이를 4℃, 2,000 rpm에서 10분간원심분리(UNION 32R, Hanil Co., Korea)하여상층액을걷어낸이후, 각각의 well 에 DMSO를첨가하여 microplate reader (Model 550, Bio- rad, USA)의 540 nm에서흡광도(obtical density (O.D))를측정 을하였다. 세포독성은다음과같은식에의거하여계산하 였다.
Cell Cytotoxicity (%) = sample 흡광도/ control 흡광도× 100
Nitric Oxides(NO) 생성량 측정
NO 생성량을측정하기위하여본실험은 Kim 등[14]의방 법에따라서 Raw cell 264.7 cell을 DMEM 배지를이용하여
2.5 × 105 cells/ml로 조절한 후 24 well plate에 접종하고 5% CO2 incubator (MCO-15AC, Sanyo, Japan)에서 20시 간전배양을실시하였다. 이후, 세포에 1 μg/ml의 LPS와 0.1, 1, 10, 50, 100 μg/ml의구멍갈파래에탄올추출물를처 리하였으며다시 24시간배양을실시하였다. 배양이완료된
후 배양액의 상층액을 얻었고 동량의 griess 시약(1%
sulfanilamide + 0.1% naphthylendiamine dihydrochloride, 1:1)을첨가하여실온에서 10분간 반응시키고, microplate reader (Model 550, Bio-rad, USA)를 이용하여 540 nm에 서흡광도를측정하였다. NO의농도는배양액내의 nitrite 농도를 griess 반응[16]을이용하여측정하였고세포배양액 내 NO의농도는 sodium nitrite (NaNO2)의농도별표준곡 선과비교하여산출하였다.
염증관련 cytokines 분비량 측정
염증과 관련된 세포배양액 내의 TNF-α, IL-6 및 IL-1β cytokine의 분비량을 ELISA kit (Mouse ELISA set, BD Bioscience, USA)를이용하여측정을실시하였다. ELISA법
은 Kim 등[11]의방법에따라분비량을측정하기전하룻밤
정도 ELISA microplate에 capture antibody로 anti-mouse TNF-α, IL-6 및 IL-1β를분주하여 4℃에서 coating하였다. 이를 0.05% Tween 20이 포함된 PBST로 세척하고 10%
FBS 용액으로 blocking 실시하고 PBST로세척한 뒤, 각
microplate에 NO를측정하였던것과동일한배양상층액을
분주하고실온에서 2시간반응시켰다. 다시 PBST로세척한 뒤희석한 biotinylated anti-mouse TNF-α, IL-6 detection antibody와 streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase conjugate를 첨가하여실온에서 1시간반응시켰다. 여기서 IL-1β의경우, biotinylated anti-mouse IL-1β detection antibody를첨가 하여 1시간 반응 후, streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase conjugate를첨가하여 30분반응시켰다. 그후, 이를다시 PBST로세척한다음, OPD 용액을첨가하여실온에서 30분 동안 암반응시켰다. 2 N H2SO4로 반응을 종료시킨 후, microplate reader (Model 550, Bio-rad, USA)를이용하여
490 nm에서흡광도를측정하였다.
iNOS, COX-2, NF-κB 측정
RAW 264.7세포를배양하여구멍갈파래에탄올추출물이
세포질내에생성되는 iNOS, COX-2 및 NF-κB의발현량에 미치는영향을알아보았다. RAW 264.7 세포의배양이끝난 세포를 획득하여 PBS (phosphate buffered saline)로 3회 세척을반복한후, cytosol extraction lysis buffer [50 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, 1%
deoxycholate, 5 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF), 1 μg/ml aprotinin, 1% Triton X-100, and 0.1% NP-40] 및
nulclear extraction lysis buffer (10 mM HEPES, 100 mM NaCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 0.1 mM EDTA, 0.1 mM DTT)를 각각 사용하여 30분간 4℃에서 lysis를실시하였다. 이후 12,000 rpm에서 20분간원심분리하여세포막성분등을제 거하였다. 단백질 농도는 BCA protein assay kit (Pierce, USA)를 사용하여 정량하였으며, 30 μl의 lysate를 10%
SDS-PAGE로단백질을분리하였다. 분리된단백질을 PVDF
(polyvinylidene difluoride) membrane (Bio-rad, USA)에 70 mA에서 1시간 30분동안전사시킨후, 5% skim milk가 포함된 TBSS (tris buffered saline; pH7.5) 용액으로상온 에서 2시간동안 blocking하였다. anti-mouse iNOS, COX- 2 및 NF-κB를사용하여 1:500으로희석하고상온에서 2시 간반응시킨후 TBSS로 3회세정한것을이용하여 iNOS, COX-2 및 NF-κB의발현양을검토하기위한항체로이용 하였다. 2차항체로 HRP (horse radish peroxidase)가결합 된 anti-mouse IgG 및 anti-rabbit IgG를 1:2,000으로희석 하여 상온에서 1시간반응시킨후, TBSS로 3회세정하여 ECL 기질과 1−3분간반응한후각각의단백질밴드는 Gene tool (Syngene software)를이용하여가시화하였다.
MAP kinase (JNK, ERK, p38) 발현량 측정
MAPKs의발현량을측정하기위하여 RAW 264.7 세포를
1 × 106 cells/ml로 18시간배양을실시하고구멍갈파래에 탄올추출물을처리하여 30분동안본배양을실시하였다.
배양이후 iNOS, COX-2와동일한방법으로실험이진행되
었다. 인산화된 c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), extracellular signalregulated kinase (ERK), p38 protein kinase (p38)
의 발현량을 측정하기 위하여 anti-mouse JNK, ERK 및
p38 (Cell Signalling Technology Inc., USA) 항체를 1:500으로 희석하여사용하였다.
귀 부종 측정 및 조직 관찰
귀부종및조직에 관한실험을 하기위해사용된 생후 8주령의수컷 ICR 마우스에 Kim [10] 등의방법에따라 10, 50, 250 mg/kg· body weight의농도별구멍갈파래에탄올추 출물을 200 μl씩경구투여하였다. 1시간후, 2.5% croton oil 을 20 μl/ear 농도로도포하여귀부종을유발시켰다. 마우 스의오른쪽귀에 croton oil을처리한이후 5시간지난뒤에 귀두께를측정하였으며 croton oil을처리한이후에두께의 증가를부종의형성으로보기로하였다. 귀조직에침윤된 mast cell과귀조직두께변화를측정하기위하여 ICR 마 우스의오른쪽귀에구멍갈파래에탄올추출물을 100 mg/
ml 농도로 20 μl씩도포하고 15분뒤, 5% croton oil을 20 μl 씩도포하였다. 그로부터 6시간이후에 diethylether로마취 사시켜귀조직을절제하였으며이는 10% formaldehyde로
72시간고정할수있도록하였다. 고정하고난후, 파라핀블 록을만들어박편을제조하고 hematoxylin-eosin과 toluidine-
blue 염색을하여조직을관찰하였다.
Edema formation (%) =
Sample의귀두께 / Control의귀두께 × 100
통계처리
위의 실험에대한 결과의 유의차 검정은 SAS software
(SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, USA)에서평균값을분산분석 하고 Duncan's multiple range test 법에따라 p < 0.05 수 준에서검정하도록하였다.
결과 및 고찰
세포 독성 측정
구멍갈파래에탄올추출물이대식세포에미치는독성을평 가하기 위하여세포 내 미토콘드리아의활성을 측정하는 MTT assay를실시하였다. RAW 264.7 cell에추출물을 0.1, 1, 10, 50 및 100 μg/ml의농도로처리하고 24시간배양한후 세포의생존율을확인해본결과, 모든처리농도에서유의적 인차이를보이지않았으며이를통하여세포독성이나타나 지않음을확인하였다(Fig. 1).
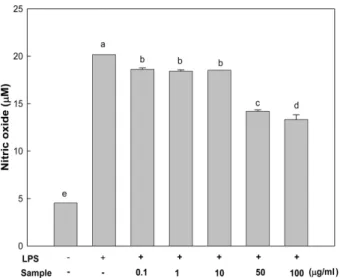
Nitric oxide (NO) 생성 억제 효과
NO는인체내에서방어기능을수행하며이외에도신호전 달기능, 신경독성, 혈관확장등의여러가지생리적기능 을가지고있다. 외부의자극이나균의침입이발생되면이 를제거하고인체를보호하기위한 NO의분비량은증가하 게되나, 분비량의정도가정상범위이상으로나타나게되 면조직의손상이나염증질환을유발하게되는것으로알려
져있다[19]. 이에따라구멍갈파래에탄올추출물이 NO 생
성정도에미치는영향을측정하기위하여 RAW 264.7 cell
을 LPS로활성화시킨후에구멍갈파래에탄올추출물을농 도별(0.1, 1, 10, 50, 100 μg/ml)로처리하여 NO 생성량측정 을실시하였다. 그결과, 구멍갈파래에탄올추출물을처리 한경우 NO의생성량은 LPS를처리했을때와비교하여농 도 의존적으로 감소함을 확인할 수 있었다(Fig. 2). 특히, 50μg/ml의농도이후부터는 LPS 단독처리구와비교시 34%
이상의 NO의생성량감소를확인할수있었다. 이러한결과
는 Kang 등[9]의연구에서사용된갈조류인다시마뿌리에
탄올추출물을같은실험조건에서실시했을때 100 μg/ml의 농도에서 28%의 NO 생성억제효과를보인결과보다더높 은저해활성을보였다.
염증 관련 cytokines 생성 억제 효과
RAW 264.7 세포는그람음성균의세포외막에존재하는
내독소 LPS의자극에의하여여러가지염증매개인자의분 Fig. 1. Effect of Ulva pertusa Kjellman ethanol extract
(UPKEE) on the cell cytotoxicity of RAW 264.7 cells. Cells were incubated in the presence of UPKEE (0.1, 1, 10, 50, and 100μg/
ml) for 24 h. Cell cytotoxicity was determined by MTT assay. Cell cytotoxicity (% of control) = (sample O.D. / control O.D.) × 100.
Means with letter (a) above the bars are not significantly different (p > 0.05).
Fig. 2. Inhibitory effect of Ulva pertusa Kjellman ethanol extract (UPKEE) on the production of nitric oxide in LPS- induced RAW 264.7 cells. Cells were incubated in the presence of LPS (1 μg/ml) alone or in combination with UPKEE (0.1, 1, 10, 50, and 100 μg/ml) for 24 h. The culture media of the treated cells were used to measure NO level. Means with different letters (a- d) above the bars are significantly different (p < 0.05).
비를촉진한다[12]. 대표적염증성 cytokine인 TNF-α는바 이러스감염에대한저항의기능을가진중요한염증관련 cytokine이며이는 IL-1β와 IL-6의발현을조절하는것으로 밝혀져있다[8]. IL-1β는국소염증반응을매개하며 T 세포 의활성화와 B 세포의성숙을돕는다. 염증반응시시상하 부에작용하여발열증상을일으키는것으로알려져있다[9].
또한, IL-6는 T 세포를활성화하고염증매개물질을발현시
켜후천성면역을개시하는물질로알려져있다[11]. 염증성
cytokine의생성량에대한구멍갈파래에탄올추출물의효
과를알아보기위하여 RAW 264.7 cell에 LPS 처리한이후, 구
멍갈파래에탄올추출물을농도별로처리하여 ELISA 방법
으로측정하였다. 그결과, IL-6, TNF-α및 IL-1β의농도가 모두농도의존적으로감소하는것을확인하였다(Fig. 3). IL- 6와 TNF-α는 LPS만처리한경우와비교하였을때, 0.1 μg/
ml의처리구부터농도의존적으로감소하는경향을보였다. IL-
1β는모든농도에서 LPS 단독처리구에비하여감소함을보
였으며특히 100 μg/ml의농도에서는 LPS 단독처리구의발
현량에비하여약 51% 정도의확연한감소량을 확인할수
있었다. 이결과는꽃지누아리에탄올추출물을같은농도별
로처리했을때나타나는결과와유사하며[11], 이를통하여
구멍갈파래에탄올추출물이 RAW 264.7 Cell에서염증과
관련된 cytokine을효과적으로억제한다고사료된다.
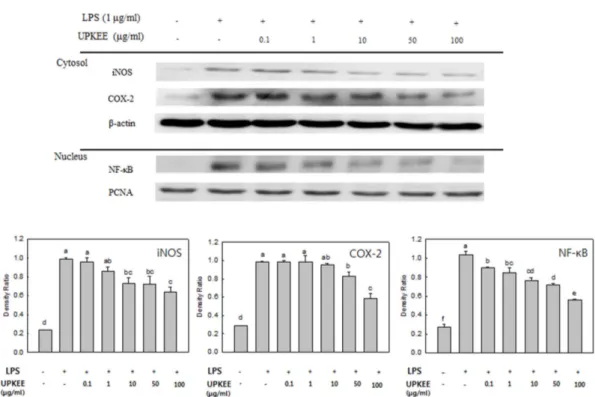
iNOS, COX-2 및 NF-kB 발현 억제 효과
외부의물질이침입하여대식세포가작용하게되면 NF- κB는인산화됨으로써활성화되어핵내로이동된다. 핵내 에서유전자발현이일어나면 iNOS, COX-2를합성한다[15].
NO의합성효소인 iNOS는외부자극으로부터유도되며장시 간동안다량의 NO를분비하며 NO는조직의손상, 부종과 같은염증질환을촉진하며다른염증매개물질의생합성을 촉진하여염증을심화시킨다[9, 11]. NF-κB는다양한 cytokine 의 합성을조절하는 전사인자로, 염증의 반응에서 iNOS,
COX-2, NF-κB의생성및활성억제를확인함으로써항염
증의효과를기대할수있다. 따라서, RAW 264.7 cell에구 멍갈파래에탄올추출물을 0.1 μg/ml의농도부터 100 μg/ml
농도로처리하고각단백질의발현량을 western blot을이
용하여측정하였다. 그결과(Fig. 4), LPS 단독처리구에서 모든단백질의발현량이현저하게증가하였으나 iNOS 및
COX-2의발현량은농도의존적으로감소하였으며최종농도
인 100 μg/ml 농도처리구에서 LPS 단독처리와비교시각 각 36% 및 40%의발현량이감소됨을확인하였다. 또한, 염 증관련전사인자인 NF-κB의발현량은추출물 0.1 μg/ml의 처리농도부터농도의존적으로감소하는경향을보였다. 이 러한결과는잘피에탄올추출물을처리했을경우와유사한 Fig. 3. Inhibitory effect of Ulva pertusa Kjellman ethanol
extract(UPKEE) on the production of IL-6 (A), TNF-α (B), and IL-1β (C) in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Cells were incubated in the presence of LPS (1 μg/ml) alone or with various concen- trations of UPKEE (0.1, 1, 10, 50, and 100 μg/ml). The levels of pro- inflammatory cytokines in the cell culture media were measured by ELISA. Means with different letters (a-e) above the bars are sig- nificantly different (p < 0.05).
Fig. 4. Effect of Ulva pertusa Kjellman ethanol extract (UPKEE) on LPS-induced iNOS, COX-2, and NF-κB p65 expression in LPS- induced RAW 246.7 cells. The levels of iNOS, COX-2 in the cytosolic protein and the p65 subunit of NF-κB in nuclear protein were deter- mined by western blot analysis. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of UPKEE (0.1, 1, 10, 50, and 100 μg/
ml) and LPS (1 μg/ml) for 18 h or 30 min and the proteins were detected using specific antibodies. For quantification, the expression data were normalized to the PCNA signal. Means with different letters (a-f) above the bars are significantly different (p < 0.05).
Fig. 5. Effect of Ulva pertusa Kjellman ethanol extract (UPKEE) on MAPKs expression in LPS-induced RAW 246.7 cells. The levels of p-p38, p-ERK, and p-JNK in the cytosolic protein were determined by western blot analysis. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of UPKEE (0.1, 1, 10, 50, and 100 μg/ml) and LPS (1 μg/ml) for 30 min, and the proteins were detected using specific antibodies. Means with different letters (a-g) above the bars are significantly different (p < 0.05).
결과를 보였으며[10], 이외에도 참도박 에탄올 추출물이 iNOS와 COX-2를저해하는항염증효과[3]에서유사한결 과를나타내었다. 이상의결과를바탕으로구멍갈파래에탄 올추출물처리농도에따른효과적인 NF-κB의발현량억
제에의해염증성 cytokine 생성량이감소한것으로사료된
다. 또한 NO의생성량과관련있는 iNOS의농도의존적발 현량의감소는 NO 분비량감소결과와도관계가있음을나 타내었다.
MAPKs 발현 억제 효과
MAPKs는 NF-κB의활성화에영향을주는가장대표적인
신호분자로알려져있으며세포내에서인산화됨으로써활
성화되고다양한염증매개인자의생성에영향을주며[3] 염
증관련반응이시작되면대식세포내의 ERK, p38과같은
MAPKs의활성화가일어나며핵내로이동하여다른면역
활성인자들을인산화시켜염증반응을더욱활성화시킨다 [6]. 따라서 MAPKs의발현량을 Western blot으로분석한결 과, LPS 단독처리구에서 p38, ERK, JNK의발현량은모두 증가하게나타났으며이와비교하여농도별구멍갈파래에
탄올추출물을처리에의하여 LPS 단독처리구와비교하여
각각의신호분자들의발현량이농도의존적으로감소함을 확인하였다(Fig. 5). 특히인산화된 p38의발현량은 LPS 처
리구의발현량에비하여추출물 100 μg/ml의농도에서약
43%의비교적높은억제효과를확인하였다. 이는꽃지누아
리에탄올추출물[11]을이용하여살펴본 MAPKs 발현량억
제효능과유사하며, 이상의결과를종합하였을때구멍갈파
래에탄올추출물이인산화된 MAPKs 인자들의신호전달경
로를효과적으로억제함으로써항염증의효과를가지는것 으로사료된다.
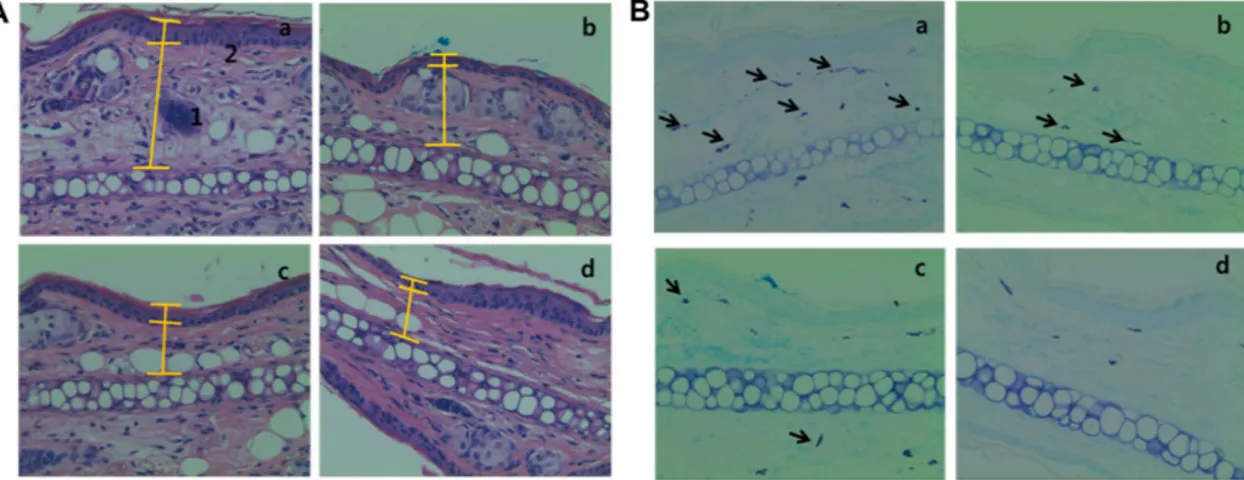
귀 부종 억제효과의 조직학적 관찰
염증에는발열증상, 혈관확장, 부종등여러가지가시적 인생리현상을나타내며, 염증반응매개물질들에의해염증 이촉진되면혈관의이완및혈관투과도를증가시키고, 식 균작용을하는과립세포, 수지상세포및 B 세포등을모이 게하여활성화시킨다. 비만세포(mast cell)는신체의거의 모든조직에존재하며외부자극으로부터활성화된 mast cell
은다양한 protease나히스타민과같은혈관확장물질을분
비함으로써병원균에대한숙주의방어기작과관련이깊은
것으로알려져있다[21, 24]. 따라서, 합성스테로이드제인
prednisolone 및구멍갈파래에탄올추출물이귀부종및조
Fig. 6. Inhibition of Ulva pertusa Kjellman ethanol extracts (UPKEE) on croton oil-induced mouse ear edema. Means with different letters (a-f ) above the bars are significantly different (p < 0.05).
Fig. 7. Photomicrograph of transverse section p < 0.05ns of mice ears sensitized with topical application of 5% croton oil (v/v) in acetone (a-c) or vehicle acetone (d, non-inflamed), stained with hematoxylin-eosin (A) and toluidine-blue (B) examined under light microscopy (magnification: ×200). Treatments: vehicle 2% Tween 80 (a), prednisolone 0.08 mg/ear (b), and UPKEE 20μl/
ear (c). The numbers 1 and 2 indicate dermis and epidermis, respectively and the arrows indicate mast cells.
직에미치는영향을알아보기위하여 croton oil로염증을유 발하고귀두께측정을실시하였다. 그결과, croton oil을단 독으로처리한대조군과비교하였을때두처리구모두농도 의존적인귀부종완화효과를나타내었다(Fig. 6). 특히, 250
mg/kg· body weight의구멍갈파래 에탄올추출물처리 시
prednisolone을 50 mg/kg· body weight 농도로경구투여했 을때와유사한정도의귀부종완화효과를확인하였다. 마 우스귀조직관찰의결과, croton oil만처리한경우와비교 하였을때구멍갈파래에탄올추출물을처리한경우경피와 진피의두께가얇아진것을확인하였다(Fig. 7). 이는추출물 을경구투여후귀두께가감소한결과와유사하며, 대조구 인 prednisolone 처리구보다더높은효과를나타내었다. 이 와더불어 toluidine-blue 염색을통하여조직내 mast cell 침윤정도를확인한결과, 추출물의처리이후 mast cell의 침윤정도가현저히감소함을보였으며, 이는귀부종억제 효과를보인것에영향을미치는것으로사료된다. 이결과 는잘피에탄올추출물을 250 mg/kg· body weight 처리구에 서대조구인 prednisolone 50 mg/kg· body weight로처리했 을때와비슷한귀두께감소및조직학적변화를보인연구 결과와유사하였다[10]. 이외에도비틀대에탄올추출물[13]
과외톨개메탄올추출물[7]이미치는귀부종의항염증효 과에서추출물을 250 mg/kg· body weight 처리했을때나타 나는귀의부종완화효과연구결과와유사한것을확인하였 다. 그러나합성스테로이드제인 prednisolone은항염제로서 많이사용되지만위장장애를비롯한다양한부작용이보고
되고있다[19]. 따라서 UPKEE가보이는항염증효과는해
조류에탄올추출물에 polyphenol 계열의화합물들이다량
함유되어있기때문이라고생각되며, 이는 prednisolone과 같은합성제제들을대체할수있는천연항염증제로서의적 용가능성이크다고사료된다.
요 약
대식세포에대하여구멍갈파래에탄올추출물의독성결과
를확인해본결과독성은나타나지않았으며, LPS에의하여
유도되는 NO와염증성 cytokine의분비량은구멍갈파래에
탄올추출물의농도의존적으로감소함을확인하였다. 또한 구멍갈파래에탄올추출물로인해 NF-κB 및 MAPKs의신 호전달을억제함으로써염증매개성물질의발현억제에효 과가있는지알아본결과, 구멍갈파래에탄올추출물은각각 iNOS, COX-2, NF-κB 및 MAPKs의활성을효과적으로억 제하였고그에따른염증매개인자들의생성도효과적으로 억제되는것을확인하였다. 마지막으로추출물이마우스귀 부종에미치는영향을살펴본결과, 대조군의경피와진피의 두께에비해추출물처리군의조직두께가상대적으로현저
히줄어들었으며귀조직에침윤된 mast cell의감소에도추 출물이그효과를현저하게나타냄을확인하였다. 본연구 결과들을종합해보았을때, 구멍갈파래의에탄올추출물은 항염증활성을가지는새로운천연물질로이용가능하여고 부가가치제품개발이가능한천연소재로판단된다.
Acknowledgments
This research was a part of the project titled Yeongnam Seagrant funded by Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, Korea.
References
1. Ayako Y, Koichi Y, Keiichi O. 1999. Iodine distribution in blades of several laminarias grown in the same sea area. Bull. Jpn. Soc.
Sci. Fish. 58: 1373-1379.
2. Azuine MA, Goswami UC, Katal JJ. 1992. Antimutagenic and anticarcinogenic effect of carotenoids and dietary palm oil.
Nutr. Cancer. 17: 287-295.
3. Bae NY, Kim MJ, Kim KBWR, Ahn NK, Choi YU, Park JH, et al.
2015. Anti-inflammatory effect of ethanol extract from Grate- loupia elliptica Holmes on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflam- matory responses in RAW 264.7 cells and mice ears. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 44: 1128-1136.
4. Cho BO, Yin HH, Fang CZ, Ha HO, Kim SJ, Jeong Sl, et al. 2015.
Synergistic anti-inflammatory effect of rosmarinic acid and luteolin in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 macro- phage cells. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 47: 119-125.
5. Qin D, Zhou YI, Zhang SZ, Cao JM, Xu LY, Fang GD, et al. 2015.
Anti-inflammation of Tripterygium wilfordii polycoride on mac- rophages and its regulation to inflammation via TLR4/NF-κB.
CHM 7: 155-161.
6. Eum WS, Lee KJ, Kim DW, Lim SS, Kang IJ, Park J, et al. 2013.
Anti-inflammatory effects of extracts from Caesalpinia sappan L. on skin inflammation. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 42: 1513- 1517.
7. Jeong DH, Kim KBWR, Kim MJ, Kang BK, Ahn DH. 2014. Anti- inflammatory activity of methanol extract and nhexane frac- tion mojabanchromanol b from Myagropsis myagroides. Life Sci. 114: 12-19.
8. Ji JD. 2005. Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Hanyang Med.
Rev. 25: 43-52.
9. Kang BK, Kim KBWR, Kim MJ, Bark SW, Pak WM, Kim BR, et al.
2014. Anti-inflammatory activity of an ethanol extract of Lami- naria japonica root on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflamma- tory responses in RAW 264.7 cells. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol.
46: 729-733.
10. Kim MJ, Bae NY, Kim KBWR, Park JH, Park SH, Cho YJ, et al. 2015.
Anti-inflammatory effect of Zostera marina ethanolic extract on LPS induced RAW264.7 cells and mouse model. KSBB J. 30:
182-190.
11. Kim MJ, Bae NY, Kim KBWR, Park JH, Park SH, Choi JS, et al. 2016.
Anti-inflammatory effect of Grateloupia imbricata holmes etha- nol extract on LPS-Induced RAW 264.7 cells. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 5: 181-187.
12. Kim MJ, Bea NY, Kim KBWR, Park JH, Park SH, Cho YJ, et al. 2015.
Anti-inflammatory effect of water extract from tuna heart on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 cells. Korean Soc. Biotechnol. Bioeng. J. 30: 326-331.
13. Kim MJ, Kim KBWR, Jeong DH, Ahn DH. 2013. Anti-inflamma- tory activity of ethanolic extract of Sargassum sagamianum in RAW 264.7 cells. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 22: 1113-1120.
14. Kim MJ, Bae NY, Kim KBWR, Park JH, Park SH, Jang MR, et al.
2016. Anti-inflammatory effect of Chondrus nipponicus Yendo ethanol extract on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 cells. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 45:
194-201.
15. Lee HN, Lim DY, Lim SS, Kim JD, Park JHY. 2011. Anti-inflamma- tory effect of ethanol extract from Eupatorium japonicum.
Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 43: 65-71.
16. Lee ST, Jeong YR, Ha MH, Kim SH, Byun MW, Jo SK. 2000. Induc- tion of nitric oxide and TNF-α by herbal plant extracts in mouse macrophages. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci Nutr. 29: 342-348.
17. Margret RJ, Kumaresan S, Ravikumar S. 2009. A preliminary study on the anti-inflammatory activity of methanol extract of
Ulva lactuca in rat. J. Environ. Biol. 30: 899-902.
18. Marks-Konczalk J, Chu SC, Moss J. 1998. Cytokine-mediated transcriptional induction of the human inducible nitiric oxide synthase gene requires both activator protein and nuclear fac- tor kapaB-binding sites. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 22201-22208.
19. Miwa K, Kambara H, Kawai C. 1983. Effect of aspirinin large doses on attacks of variant angina. Am. Heart J. 105: 351-355.
20. Nathan C. 1992. Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mamma- lian cells. FASEB J. 6: 3051-3064.
21. Park JH, Kwon DY, Lee SK. 2014. Effects of Hoesaeng-san etha- nol extract on the human mast cell-mediated inflammatory responses. Korean J. Oriental Physiol. Pathol. 28: 45-52.
22. Ray B, Lahye M. 1995. Cell-wall polysaccharides from the marine green alga Ulva rigida (Ulvaes, chlorphyta), extraction and chemical composition. Carbohydr. Res. 274: 251-261.
23. Shon DH, Choi DW, Kim MH. 2012. Improvement of anti- inflammation activity of Gardeniae fructus extract by the treat- ment of β-glucosidase. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 44: 331-336.
24. Tete S, Tripodi D, Rosati M, Conti F, Maccauro G, Saggini A, et al.
2008. The role of mast cells in innate and adaptive immunity.
Life Sci. J. 18: 891-896.
25. Yoo JS, Cheun BS, Kim NG. 2001. Determination of Na+ channel blocker in seaweeds. Korean J. Environ. Biol. 19: 107-112.