고령환자에서 수장 잠김 금속판을 이용한 요골 원위부 골 절 치료 결과
The Results of Unstable Distal Radius Fracture Following Volar Locking Plate Fixation in Elderly Patients
김재광 • 이승준
이화여자대학교 의학전문대학원 정형외과학교실
목적: 본 논문은 고령의 요골 원위부 골절 환자에서 수장 잠김 금속판을 이용한 내고정시 수술 직후의 골절 정복이 수술 후 1년에도 유지되 는 지와 환자의 나이와 골밀도가 영상학적 결과에 영향을 미치는지에 대한 것이다.
대상 및 방법: 65세 이상, 38명의 요골 원위부 골절이 발생한 환자에 대해 수장 잠김 금속판을 이용한 내고정술을 시행하였다. 수술 직후 와 1년 경과된 후의 손목 단순 방사선 사진을 비교하였고 요측 경사(radial inclination), 수장측 경사(volar tilt), 척골 변위(ulnar variance), 관절내 층형성(step off)을 각각 측정해서 비교하였다. 그리고 환자 나이, 골밀도와 4가지 영상학적 지표들의 상관성에 대해 평가하였다. 기 능적 평가는 악력, 손목의 운동범위 등을 평가하였다.
결과: 모든 환자에서 수술 직후 정복은 수술 후 1년 후에 정복의 소실 없이 골유합을 얻을 수 있었다. 환자 나이, 골밀도와 4가지 방사선학 적 지표의 변화 간에는 유의한 상관 관계가 없었다.
결론: 고령 환자의 불안정한 요골 원위부 골절에서 관혈적 정복술 및 수장 잠김 금속판의 사용은 정복 소실 없이 골유합을 보여 만족할 만 한 임상적 결과를 보였다. 또한 골유합 시까지 환자의 나이, 골밀도는 영상학적 지표들의 변화와 상관성은 없었다.
색인단어: 고령환자, 요골 원위부 골절, 수장 잠김 금속판
접수일 2010년 6월 15일 게재확정일 2011년 5월 31일 교신저자 김재광
서울시 양천구 목6동 911-1, 이화여자대학교 의학전문대학원 정형외과학교실 TEL 02-2650-2591, FAX 02-2642-0349
E-mail kimjk@ewha.ac.kr
*본 연구는 2010년 이화여자대학교 목동병원 임상연구비 지원으로 이루어졌음.
*본 논문의 요지는 2009년도 대한정형외과학회 추계학술대회에서 발표되었음.
Copyright © 2011 by The Korean Orthopaedic Association
“This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.”
대한정형외과학회지:제 46권 제 5호 2011
서 론
요골 원위부 골절은 고령에서 발생하는 상지 골절 중 흔한 골절 로 최근 평균 수명이 증가됨에 따라 발생 빈도가 과거에 비해 증 가 하고 있다.1) 이전의 연구에서는 요골 원위부 골절의 발생은 골 다공증과 연관성이 있고, 특히 노인환자에서는 골다공증으로 인 한 불안정한 골절이 흔하고 골절 정복후의 유지 또한 어렵다고 보고하고 있다.2,3) 근래에는 노인환자의 수명연장과 더불어 스포
츠 및 여가활동 증가 등 사회, 문화적 여건의 변화로 골절 후 기능 적 결과에 대한 관심이 높아짐에 따라 적극적인 치료를 시행하고 있다.4) 따라서 수장 잠김 금속판은 요골 원위부 골절에서 효과적 인 치료 방법으로 제시되고 있다.4,5)
본 연구는 고령환자에서의 불안정한 요골 원위부 골절을 수장 잠김 금속판으로 고정시 수술 직후 골절 정복이 수술 후 1년째에 도 유지 되는지와 환자의 나이, 골밀도와 영상학적 지표간의 상 관성에 대해 알아 보고자 하였다. 또한 수술 후 기능적 결과에 대 해서도 평가하였다.
대상 및 방법
1. 환자
2006년 3월에서 2007년 3월까지 65세 이상의 불안정한 요골 원위 부 골절 환자 43명을 대상으로 하였으며 1년 이상 추시가 가능한
38명의 환자 중 여성은 33명, 남성은 5명이었다. 환자의 평균 나이 는 73세(65-88세), 평균 추적 기간은 19개월이었다(12-36개월). 모 든 환자들은 2.4 mm 수장 잠김 금속판(Synthes, Paoli, PA)을 사용 하여 고정하였다. 수술 직후부터 모든 수지의 능동적 관절 운동 을 시행시켰고 수술 후 2주간 단상지 부목을 유지하였으며 수술 후 2주째 손목의 능동적 관절 운동을 시행하였다. 본 연구에서는 동반된 상지의 손상이 있거나 다른 장기 손상이 동반된 경우, 양 측 원위 요골 골절 환자는 제외하였다.
2. 영상학적 평가
골절의 정도는 AO/OTA system를 이용하여 분류하였고 외상 상 태에서 전후 방향과 측면의 정확한 방사선 사진을 얻기 위해서 최선의 노력을 하였다. 불안정한 요골 골절은 2 mm 이상의 틈 (gap) 혹은 층 형성(step off)을 가지는 관절 내 골절이거나 5 mm 이상의 요골 단축(Radial shortening)이 있는 경우, 20o 이상의 후방 경사각 있는 골절로 정의하였다.
손목의 단순 방사선 사진은 수술 직후, 수술 후 1년이 경과된 사진을 비교하였으며 요측 경사, 수장측 경사, 척골 변위와 요골 원위 관절 내 층형성을 측정하여 비교하였다. 골절 정복 및 고정 후 요골 높이의 2 mm 이상 감소하거나, 요측 경사 5o 이상, 수장 측 기울기 10o 이상 감소 및 관절 내 층형성이 2 mm 이상인 경우 에는 정복 유지의 실패로 간주하였다.
요측 경사와 수장측 경사는 Goldfarb method, 척골 변위는 Me- doff method를 이용하여 평가하였다.6,7) 요추(L2-L4)의 골밀도는 술 후 2주에 Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (Prodigy Advance;
GE healthcare, Madison, WI)를 이용하여 평가하였다.
3. 임상적 평가
손목 기능은 수술 후 각각 3, 6, 12개월에 악력, 손목의 운동범위, Modified Mayo wrist score (MMWS),8) Disability of arm, shoulder, hand (DASH)9) 그리고 시각적 아날로그 통증점수(VAS)를 이용하 여 평가하였다.
악력은 팔꿈치를 90도로 굽히고 전완을 중립 회전한 상태에 서 Jamar dynamometer (Sammons Preston, Bolingbrook, Illinois) 을 이용해 측정하였고, 그 값은 건측의 값과의 비율로 평가하였 다. 우리는 악력계산에서 오른손잡이일 경우 10% 힘의 증가를 감 안하였으나, 왼손잡이일 경우는 이를 보정하지 않았다.10) 손목의 관절 운동범위는(굴곡, 신전, 회외전, 회내전) Goniometer를 이용 하여 측정 그에 상응하는 건측에 대한 백분율 값을 산출하였다.
MMWS는 100을 정상적인 손목기능을 나타내는 값으로 측정하 였고, 각 통증(25점), 관절 운동 범위(25점), 악력(25점), 기능상태 (25점)를 합산하였다. DASH 질문지는 30개 항목으로 이루어졌는 데 21가지는 특정한 활동을 수행하는 능력을, 9가지는 관련 증상 에 대한 것으로 0에서 100까지의 범위를 가지며 더 높은 점수가 더 큰 장애상태를 의미하고, VAS 점수는 0에서 10까지의 범위로, 0은 통증이 없는 상태를 그리고 10은 최대의 통증이 있는 상태로 평가하였다.
4. 통계학적 분석
수술 직후와 1년 후의 방사선 사진에서 요측경사, 수장측 경사, 척골변위의 변화, 관절 내 층형성의 비교에 Wilcoxon signed rank test를 사용하였다. 환자의 나이, 골밀도와 영상학적 지표들의 변 화 사이의 상관 관계는 Pearson's correlation test를 사용하였다. p 값이 0.05 미만인 경우를 통계학적 유의성이 있는 것으로 간주하 였다.
결 과
AO/OTA 분류에 의해, A군이 12명, C군이 26명이었다. 단순 방사 선 사진상 모든 예에서 수술 직후의 골절 정복은 실패 없이 수술 후 1년 후에도 유지되었고, 수술 후 1년 경과 시에 골유합이 관찰 되었다. 요측 경사는 수술 직후 22o, 수술 후 1년에는 22o, 수장측 경사각은 수술 직후 4.5o, 수술 후 1년에는 4.3o였으며, 척골변위는 수술 직후 0.4o, 수술 후 1년에는 0.7o이었다. 관절 내 층형성은 수
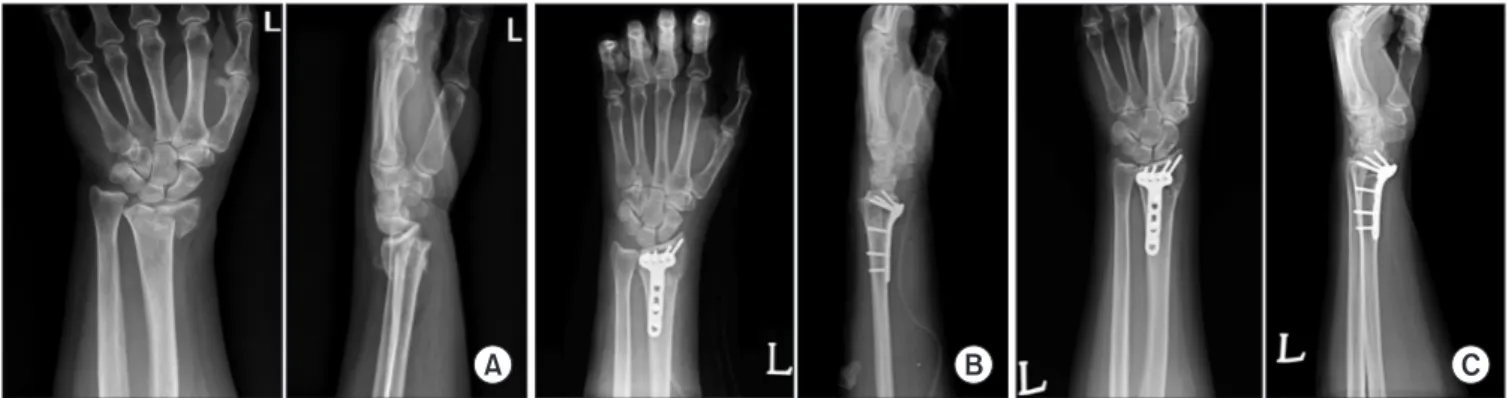
Figure 1. (A) Anteroposterior and lateral radiographs of wrist in a 70-year-old female (AO C2 type fracture). (B) Postoperative anteroposterior and lateral radiographs. (C) Postoperative 1 year anteroposterior and lateral radiographs.
술 직후 0.45 mm, 수술 후 1년에는 0.47 mm이었다(Fig. 1, Table 1).
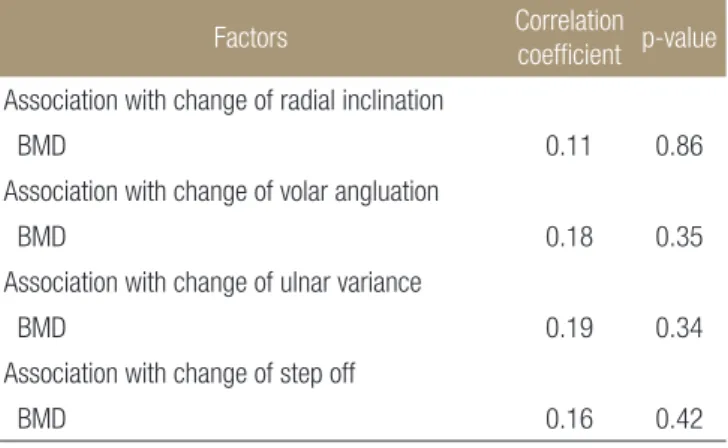
영상학적 지표의 수술 직후와 수술 후 1년 사이의 변화와 나이 와의 상관계수는 0.16, 0.11, 0.15, 0.18이며 통계학적인 유의한 차 이를 발견할 수 없었다(Table 2). 또한 골밀도와 영상학적 지표의 변화간에 상관 계수는 0.11, 0.18, 0.19, 0.16이며, 통계학적인 유의 한 차이를 발견 할 수 없었다(Table 3).
굴곡, 신전, 악력, DASH, MMWS, VAS 는 12개월 동안의 수술 후 관찰기간 동안 지속적으로 호전을 보였고 회내전, 회외전은 수술 후 첫 6개월 동안 호전을 보였으나, 수술 후 6개월째부터 1 년 사이에는 큰 변화가 없었다(Table 4).
고 찰
방사선학적으로 나타나는 요골 단축, 후방 경사각은 기능적 결과 를 결정하는 데에 있어서 중요한 역할을 하며, 최근의 연구는 노 인에 있어서 골절의 해부학적 정복과 영상학적 결과의 중요성을 강조하고 있다.4,12-15) 이러한 이유로 2005년 미국에서 고령의 요골 원위부 골절의 내고정술 비율은 1996년보다 5배 이상 증가 하였 다.5)
잠김 금속판의 고정술은 금속판과 골 사이의 마찰에 의해서 안정성을 얻는 것이 아닌, 하중을 버틸 수 있게 잠김 나사와 금 속판 구조의 기계적인 연결에 의한 것이며 고정을 골 나사(bone thread)에 의존하지 않는다. 또한 나사못은 금속판에서의 풀리지 않아 잠김 나사와 금속판의 구조가 골에서 전체적으로 빠져 나오
는 등의 실패가 있지 않는 한 초기의 고정 실패는 없다.16) 수장측 잠김 금속판은 요골 원위부의 해부학적 구조에 특화되어 있으며 고령 환자의 골절 안정화에 효과적인 치료 방법으로 보고 되고 있다.16)
Orbay와 Fernandez는 수장 잠김 금속판으로 23명의 고령 환자 에서 후향적 연구를 통해 DASH 점수 등에서 좋은 임상적 결과를 보고 하였다.3) 최근의 전향적인 연구에서는 수장 잠김 금속판으 로 고정하였을 때 젊은 환자군과 고령 환자군에서 비슷한 기능적 결과를 보고하고 있다.10) 이렇듯 이전의 여러 연구들은 주로 수장 잠김 금속판에 대한 임상적인 결과에만 초점을 맞춰 왔지만 본 연구는 고령 환자에서 수장 잠김 금속판으로 고정하여 수술 직후 의 골절 정복이 골유합 시까지 유지됨을 영상학적 지표와 기능적 인 결과를 모두에서 확인 할 수 있었다.
나이의 증가와 골다공증은 요골 원위부 골절의 불안정성과 불 유합과 관련이 있다고 알려져 있다. Itoh는 골 유합에서 골밀도 값 과 요골 길이의 감소 사이의 연관성을 기술하였으며,17) Clayton은 골밀도와 골절의 불유합, 초기 및 후기 불안정성 사이의 반비례 관계를 보고하였다.18) Mackenney는 환자의 나이가 요골 원위부 Table 1. Results according to the Radiographic Evaluation
Immediate posteropative
Postoperative
1 year p-value
Radial inclination (o) 22±3.1o 22±2.3o 0.71 Volar angluation (o) 4.5±3.0o 4.3±2.3o 0.77 Ulnar variance (o) 0.4±2.4o 0.7±2.4o 0.28 Step off (mm) 0.45±0.5 0.47±0.6 0.25Table 2. Correlation between Patient Age, and Changes in the Four Radiographic Parameters over the 1st Postoperative Year
Factors Correlation coefficient p-value
Association with change of radial inclinationPatients age 0.16 0.41
Association with change of volar angluation
Patients age 0.11 0.70
Association with change of ulnar variance
Patients age 0.15 0.49
Association with change of step off
Patients age 0.18 0.36
Table 3. Correlation between Patient BMD and Changes in the Four Radiographic Parameters over the 1st Postoperative Year
Factors Correlation
coefficient p-value
Association with change of radial inclinationBMD 0.11 0.86
Association with change of volar angluation
BMD 0.18 0.35
Association with change of ulnar variance
BMD 0.19 0.34
Association with change of step off
BMD 0.16 0.42
Table 4. The Wrist Functional Outcomes at Each Visit
3 months 6 months 1 year p-value
Flexion 79±8 86±12 91±14 0.04 Extension 77±9 86±13 88±23 0.02 Pronation 93±8 97±9 97±16 0.23 Supination 91±11 95±12 95±8 0.24 Grip strength 81±10 89±16 98±18 0.01 DASH 23±17 16±11 10±10 0.03 MMWS 72±13 83±20 88±9 0.01 VAS score 2.8±1.9 1.4±1.2 0.8±1.8 0.01 DASH, disability of arm, shoulder, and hand; MMWS, modified Mayo wrist score; VAS, visual analogue pain scale.골절의 불안정성과 불유합의 가장 유의한 예측인자라고 주장하 였다.11) 그러나 저자들은 본 연구를 통해 수술 후 골유합이 될 때 까지 나이의 증가와 골밀도의 감소가 영상학적 지표와의 관련이 없음을 알 수 있었다.
다만 골절 유형에 따른 영상학적 결과들을 세부적으로 분석하 지 못하였다는 점에 대해서는 추후 보다 자세한 연구가 필요할 것으로 생각된다.
결 론
수장 잠김 금속판은 고령 환자에서 불안정성 요골 원위부 골절의 효과적인 치료 방법으로 사료되며, 환자의 나이와 골밀도는 골절 의 정복과 영상학적 지표들의 변화와 상관성이 없음을 알 수 있 었다.
참고문헌
1. Makhni EC, Ewald TJ, Kelly S, Day CS. Eff ect of patient age on the radiographic outcomes of distal radius fractures subject to nonoperative treatment. J Hand Surg Am. 2008;33:1301-8.
2. Ring D, Jupiter JB. Treatment of osteoporotic distal radius fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16 Suppl 2:S80-4.
3. Orbay JL, Fernandez DL. Volar fi xed-angle plate fi xation for unstable distal radius fractures in the elderly patient. J Hand Surg Am. 2004;29:96-102.
4. Ring D. Treatment of the neglected distal radius fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;431:85-92.
5. Chung KC, Shauver MJ, Birkmeyer JD. Trends in the United States in the treatment of distal radial fractures in the elderly. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:1868-73.
6. Goldfarb CA, Yin Y, Gilula LA, Fisher AJ, Boyer MI. Wrist fractures: what the clinician wants to know. Radiology.
2001;219:11-28.
7. Medoff RJ. Essential radiographic evaluation for distal radius fractures. Hand Clin. 2005;21:279-88.
8. Cooney WP, Linscheid RL, Dobyns JH. Triangular fi brocarti- lage tears. J Hand Surg Am. 1994;19:143-54.
9. Hudak PL, Amadio PC, Bombardier C. Development of an upper extremity outcome measure: the DASH (disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand) [corrected]. Th e Upper Extremi- ty Collaborative Group (UECG). Am J Ind Med. 1996;29:602- 8.
10. Chung KC, Squitieri L, Kim HM. Comparative outcomes study using the volar locking plating system for distal radius fractures in both young adults and adults older than 60 years.
J Hand Surg Am. 2008;33:809-19.
11. Mackenney PJ, McQueen MM, Elton R. Prediction of in- stability in distal radial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am.
2006;88:1944-51.
12. Aro HT, Koivunen T. Minor axial shortening of the radius af- fects outcome of Colles' fracture treatment. J Hand Surg Am.
1991;16:392-8.
13. Gehrmann SV, Windolf J, Kaufmann RA. Distal radius frac- ture management in elderly patients: a literature review. J Hand Surg Am. 2008;33:421-9.
14. Slutsky DJ. Predicting the outcome of distal radius fractures.
Hand Clin. 2005;21:289-94.
15. Jupiter JB, Ring D, Weitzel PP. Surgical treatment of redis- placed fractures of the distal radius in patients older than 60 years. J Hand Surg Am. 2002;27:714-23.
16. Chen NC, Jupiter JB. Management of distal radial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:2051-62.
17. Itoh S, Tomioka H, Tanaka J, Shinomiya K. Relationship be- tween bone mineral density of the distal radius and ulna and fracture characteristics. J Hand Surg Am. 2004;29:123-30.
18. Clayton RA, Gaston MS, Ralston SH, Court-Brown CM, McQueen MM. Association between decreased bone mineral density and severity of distal radial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:613-9.
The Results of Unstable Distal Radius Fracture Following Volar Locking Plate Fixation in Elderly Patients
Jae Kwang Kim, M.D., Ph.D., and Seung Jun Rhee, M.D.
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea
Purpose: The purposes of this prospective study were to fi nd out whether the reduction is maintained 1 year after the volar locking
plate fi xation of unstable distal radius fracture in elderly patients, and to evaluate the effect of the patient’s age and bone mineral density (BMD) on the maintenance of radiographic reduction.Materials and Methods: Thirty-eight patients aged 65 years or older, with an unstable distal radius fracture were treated by open
reduction and internal fi xation with the volar locking plate system. Plain radiographs of the wrist, obtained immediately after surgery, were compared with those taken 1 year postoperatively. The evaluated radiographic parameters included radial inclination, volar tilt, ulnar variance and step off. The authors also evaluated correlations between patient factors of age and BMD and the postoperative changes of the four radiographic parameters.Results: Initial surgical reduction of unstable distal radius fractures was maintained in all 38 patients for 1 year after surgery. No
signifi cant correlation was found between patient factors of age, and BMD and the postoperative changes of radiographic parameters during the fi rst year after surgery.Conclusion: Using volar locking plate for initial reduction was maintained until bony union in elderly patients and showed
satisfactory outcome. Also, there was no correlation found in between postoperative changes of radiographic parameters, and the age of patients and BMD until the fi nal bony union.Key words: elderly, distal radius fracture, volar locking plate
Received June 15, 2010 Accepted May 31, 2011 Correspondence to: Jae Kwang Kim, M.D., Ph.D.
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Ewha Womans Mokdong Hospital, 911-1, Mok-6-dong, Yangcheon-gu, Seoul 158- 710, Korea