의학
의학
의학
의학 석사학위
석사학위
석사학위 논문
석사학위
논문
논문
논문
ATTICOSINOPLASTY
ATTICOSINOPLASTY
ATTICOSINOPLASTY
ATTICOSINOPLASTY
를
를
를
를
이용한
이용한
이용한
이용한 초기
초기
초기
초기 중이
중이
중이
중이 진주종의
진주종의
진주종의
진주종의 치료
치료
치료
치료
아
아
아
아 주
주
주 대
주
대
대 학
대
학
학
학 교
교 대
교
교
대
대 학
대
학
학
학 원
원
원
원
의
의
의
의 학
학
학
학 과
과
과
과
박
박
박
박 승
승
승
승 구
구
구
구
ATTICOSINOPLASTY
ATTICOSINOPLASTY
ATTICOSINOPLASTY
ATTICOSINOPLASTY
를
를
를
를
이용한
이용한
이용한
이용한 초기
초기
초기
초기 중이
중이
중이
중이 진주종의
진주종의
진주종의
진주종의 치료
치료
치료
치료
지도교수
지도교수
지도교수
지도교수 박
박
박
박 기
기
기 현
기
현
현
현
이
이
이
이 논문을
논문을
논문을 의학
논문을
의학
의학
의학 석사학위
석사학위
석사학위 논문으로
석사학위
논문으로
논문으로
논문으로 제출함
제출함
제출함....
제출함
2008
2008
2008
2008
년
년
년
년 2
2
2
2
월
월
월
월
아
아
아
아 주
주
주 대
주
대
대 학
대
학
학
학 교
교 대
교
교
대
대 학
대
학
학
학 원
원
원
원
의
의
의
의 학
학
학
학 과
과
과
과
박
박
박
박 승
승
승
승 구
구
구
구
박승구의
박승구의
박승구의
박승구의 의학
의학
의학 석사학위
의학
석사학위
석사학위
석사학위 논문을
논문을 인준함
논문을
논문을
인준함
인준함
인준함
.
.
.
.
심사위원장
심사위원장
심사위원장
심사위원장
박
박 기
박
박
기
기
기 현
현
현
현 인
인
인
인
심 사 위 원
심 사 위 원
심 사 위 원
심 사 위 원 정
정
정 연
정
연
연 훈
연
훈
훈 인
훈
인
인
인
심 사 위 원
심 사 위 원
심 사 위 원
심 사 위 원
김
김 철
김
김
철
철
철 호
호
호
호 인
인
인
인
아
아
아
아 주
주
주 대
주
대
대 학
대
학
학
학 교
교 대
교
교
대
대 학
대
학
학
학 원
원
원
원
2007
2007
2007
2007
년
년 12
년
년
12
12
12
월 21
월
월
월
21
21
21
일
일
일
일
-국문요약
-Atticosinoplasty
Atticosinoplasty
Atticosinoplasty
Atticosinoplasty를
를
를 이용한
를
이용한
이용한
이용한 초기
초기 중이
초기
초기
중이
중이
중이 진주종의
진주종의
진주종의 치료
진주종의
치료
치료
치료
연구목적 : 진주종성 중이염의 치료의 목적은 수술적 치료를 통해 중이강 내의 병소를 완전히 제거한 후 유양동과 중이강 구조를 변화시켜 재발을 막고 고막과 이소골의 재건을 통해 청력 호전을 꾀하는 것이다. 다른 많은 임상의학의 발달과 마찬가지로 진주종성 중이염의 수술적 치료도 많은 시행착오와 획기적인 전환을 반복하면서 발전을 거듭해오고 있으며 지금도 새로운 수술술기를 비롯한 임상적 연구 업적이 계속 등장하고 있다. 하지만 이런 지속적인 발전과 노력에도 불구하 고 아직 중이수술에 있어 체계적인 치료의 접근과 방법에서 적지 않은 논란과 이견이 있어 온 것도 사실이다. 이러한 현실적인 문제들은 그 난해함과 어려움에 도 불구하고 궁극적으로는 극복되어지고 지속적인 발전을 거듭할 것으로 예견된 다. 향후 중이 수술은 초기 중이 진주종이나 과거에 시행했던 중이수술에 대한 재수술의 비중이 높아질 것으로 예상된다. 차제에 빈도나 비중이 높아지게 될 것 으로 예상되어지는 초기 중이 진주종의 치료에서 atticosinoplasty가 어느 정도 의 적합성과 합리성을 갖고 적용될 수 있는가를 정리해보고, 아울러 유양동폐쇄 술이나 개방공동 유양동삭개술 등의 다른 술기와 비교하여 청력개선 효과를 가 늠해 보고자 하였다. 연구대상 및 방법 : 1995년 3월부터 2007년 2월까지 약 12년 간 아주대학교 병원 이비인후과에서 atticosinoplasty를 시행한 173예에서 추적관찰기간이 6개 월 이상 가능했던 156예 중에서 측두골 단층촬영 상 진주종의 병변이 크지 않은 비교적 초기 중이 진주종으로 진단된 120예와 같은 기간 중 atticosinoplasty를 시행하려다 여의치 못해 시행된 유양동폐쇄술 35예, 개방공동 유양동삭개술 110예에 대하여 청력개선 효과를 비교분석 하였으며, atticosinoplasty를 시행한 환자에 있어 수술 후 각 진주종의 종류와 이소골 재건재료에 따른 수술결과도알아보았다. 또한 수술 전 기도청력이 30 dB이내인 환자를 near-normal hearing을 가진 환자로 정의하고 atticosinoplasty를 시행한 near-normal hearing을 가진 40예에 있어서도 역시 수술 후 진주종의 종류와 이소골 재건재 료에 따른 수술결과를 알아보았다. 결과 : atticosinoplasty를 시행한 초기 중이 진주종 120예를 유양동폐쇄술 35예, 개방공동 유양동삭개술 110예와 청력개선 효과를 비교해 보았을 때 atticosinoplasty를 시행한 환자들에서 수술결과가 의미있게 좋아진 것으로 확인 되었다. 진주종의 종류에 따른 분석에서는 상고실진주종에서, 이소골 재건재료에 따른 비교에서는 malleus stapes strut를 시행한 환자에서 상대적으로 좋은 결 과가 있었음을 확인할 수 있었다. near-normal hearing군에 있어서는 수술 후 이소골재건술을 시행한 경우나 하지 않은 경우 모두 청력보존이 잘 이뤄졌다. 진 주종의 종류에 따른 분석에서도 역시 상고실진주종에서 비교적 청력보존이 잘 이뤄졌으며 이소골 재건재료에 따른 비교에서는 거의 모든 환자에서 있어 좋은 결과가 있었음을 볼 수 있었다. 이소골이 유지되거나 유지되지 않은 경우에는 서 로간에 청력유지에 큰 차이가 없었으나 유지되지 않은 경우 등골이 유지된 경우 가 의미있게 결과가 좋았다. 결론 : 초기 중이 진주종의 치료를 위한 수술법으로서의 atticosinoplasty는 청 력개선에 효과가 있었으며 합병증은 미미하였다. 이는 초기 중이 진주종의 치료 의 효율적이고 체계적인 접근이나 선택에 있어 atticosinoplasty가 유용성을 가 지고 있음을 보여준다.
핵심어 : atticosinoplasty, 초기 중이 진주종, 유양동폐쇄술, 개방공동 유양동삭 개술, 이소골재건술, 상고실진주종
차
차
차
차 례
례
례
례
국문요약 ··· i 차례 ··· iii 그림 차례 ··· iv 표 차례 ··· v 약어 ··· vii Ⅰ. 서론 ··· 1 Ⅱ. 연구대상 및 방법 ··· 3 A. 연구대상 ··· 3 B. atticosinoplasty의 시술방법 ··· 3 C. 통계방법 ··· 5 Ⅲ. 결과 ··· 6 Ⅳ. 고찰 ··· 12 Ⅴ. 결론 ··· 16 참고문헌 ··· 17 ABSTRACT ··· 23LIST
LIST
LIST
LIST OF
OF
OF
OF FIGURE
FIGURE
FIGURE
FIGURE
LIST
LIST
LIST
LIST OF
OF
OF
OF TABLES
TABLES
TABLES
TABLES
Table 1. Pure tone average before & after atticosinoplasty ··· 6
Table 2. Hearing results before & after atticosinoplasty ··· 6
Table 3. Successful hearing results according to preoperative
diagnosis ··· 7
Table 4. Successful hearing results according to the type of
cholesteatoma ··· 7
Table 5. Successful hearing results according to the type of surgery in early middle ear cholesteatoma ··· 8
Table 6. Successful hearing results according to ossiculoplastic
materials ··· 8
Table 7. Hearing results according to the type of cholesteatoma in cases with near-normal hearing ··· 9
Table 8. Hearing results according to ossiculoplastic materials
in cases with near-normal hearing ···10
Table 9. Hearing results according to the status of ossicular
Table 10. Complications of atticosinoplasty ··· 11
ABBREVIATION
ABBREVIATION
ABBREVIATION
ABBREVIATION
OM, otitis media ; SNHL, sensorineural hearing loss ; OCR, ossicular chain reconstruction ; TORP, total ossicular replacement prosthesis ; PORP, partial ossicular replacement prosthesis ; MSS, malleus stapes strut ; ABG, air-bone gap ; HRCT, high resolution computed tomography
Ⅰ
Ⅰ
Ⅰ
Ⅰ.
.
.
. 서론
서론
서론
서론
중이 진주종은 상피조직의 과증식, 과분화를 특징으로 하는 질환으로, 중이수 술 원인의 상당부분을 차지하고 있다. 중이 진주종의 수술적 치료의 목적은 중이 강내의 병소를 완전히 제거한 후 유양동과 중이강 구조를 가급적 보존시켜 재발 을 막고 고막과 이소골의 재건을 통해 청력 호전을 꾀하는 것이다. 근치적 수술로 이루어졌던 중이 수술이 1950년대에 이후 Wullstein(Wullstein, 1956)에 의해 고실성형술(tympanoplasty)의 이론이 정 립되고, Shambaugh에 의해 측두골 해부학의 이해와 더불어 수술현미경의 개발 및 수술 소독의 발달이 중이 진주종의 수술에 큰 변화를 가져왔다. 1960년대에 들어오면서 독일의 Jansen(Jansen, 1967)에 의해 폐쇄공동 유양동삭개술 (intact canal wall mastoidectomy)의 개념이 도입되면서 보전적 중이 수술의 술기가 소개되기도 하였으나 이러한 폐쇄공동 유양동삭개술는 외이도의 형태유 지에 도움이 되는 반면 진주종성 중이염 수술 이후 병변의 제거가 완전하지 못 할 수 있어 진주종이 남아있을 가능성 문제가 제기되었고, 1970년대 초까지 Sheehy 등(Sheehy와 Patterson, 1967)에 의해서 수술 후 일정 기간 후에 이 차 수술을 하는 단계적 수술방법으로 극복하려는 노력이 있어왔으나 진주종에 의해 외이도 후벽의 결손이 심해지거나 작아진 유양동에서의 후고실 및 상고실 의 진주종의 제거는 용이하지 못한 제약이 따랐다. 1970년대 말 이후 중이 수술 의 쟁점은 신소재의 개발과 더불어 시작된 이소골재건술(ossiculoplasty)의 재 료와 성적 결과에 대한 보고였고, 보존적인 중이 수술과 이소골재건술의 결과는 결국 이관기능부전이라는 근원적인 문제에서 한계점을 드러내게 되었다. 많은 임 상의학의 발달과 마찬가지로 중이 진주종의 수술적 치료도 많은 시행착오와 획 기적인 전환을 반복하면서 발전을 거듭해왔으며 지금도 새로운 수술술기를 비롯 한 임상적 연구 업적이 계속 등장하고 있는 실정이다.최근 고해상도 컴퓨터 단층촬영(high resolution computed tomography: HRCT)의 보편적인 사용과 국민들의 원활한 의료 이용으로 인해 비교적 초기
진주종의 발견이 증가하고 있으며, 이는 앞으로의 중이 수술의 하나의 초점이 될 것이다. 초기 진주종의 치료는 보존적이어야 하고 비침습적이어야 하며 경우에 따라서는 내시경 수술을 겸해야하는 기능적 수술의 개념이 도입 되어야 한다. 기능적 중이 수술의 개념은 진주종의 완전한 제거와 더불어 점막의 보존, 적절한 환기, 고막함몰의 예방이 필수적으로 이루어져야 함을 내포하고 있다.
초기진주종의 수술 술기로써 “atticosinoplasty"는 atticotomy, posterior sinusectomy, scutumplasty, annuloplasty의 4단어의 합성이라고 볼 수 있으 며, 그 선행조건으로는 수술 당시 염증소견이 없어야 하고 상고실과 후고실에 있 는 진주종 병변이 완전히 제거되어야 하며, 수술시야에서 이관 주위의 점막이 정 상이어야 하며, 상이관와(supratubal recess)를 통한 환기 확보를 위해 침골 (incus)과 추골두(malleus head)를 제거해야 하며, 아울러 전상고실골판 (anterior attic bony plate : cog)도 경우에 따라서 제거해야 함을 전제로 하고 있다(Park, 2002). 이러한 조건을 만족시키면서 초기 중이 진주종의 치료에 있 어 atticosinoplasty가 어느 정도의 적합성과 합리성을 갖고 적용될 수 있는가 를 정리해보고, 아울러 유양동폐쇄술(mastoid obliteration)이나 개방공동 유양 동삭개술 등의 다른 술기에 비교하여 차지할 수 있는 위치를 가늠해 보는 것이 필요하다고 판단되어지지만 아직까지 이에 대한 연구결과는 매우 부족한 실정이 다. 본 연구는 atticosinoplasty의 치료 결과를 비교분석하여 초기 중이 진주종 의 수술적 술기로써의 atticosinoplasty의 유용성에 대해 알아보고자 하였다.
Ⅱ
Ⅱ
Ⅱ
Ⅱ.
.
.
. 연구대상
연구대상
연구대상 및
연구대상
및
및
및 방법
방법
방법
방법
A. 연구대상 1995년 3월부터 2007년 2월까지 약12년 간 아주대학교병원 이비인후과에서 atticosinoplasty를 시행한 173예 중에서 추적관찰 기간이 6개월 이상 가능했던 156예 중에서 측두골 단층 촬영 상 진주종의 병변이 크지 않은 비교적 초기 중 이 진주종으로 진단된 120예와 atticosinoplasty를 시행하려다 여의치 않아 시 행한 유양동폐쇄술 35예, 개방공동 유양동삭개술 110예를 비교분석 하였다. atticosinoplasty를 시행한 환자는 남성이 49명, 여성이 107명이고 연령은 14~65세로 평균나이는 37.7세였으며, 14~19세가 8명(5.5%), 20~29세가 23 명(14.7%), 30~39세가 58명(37.2%), 40~49세가 47명(30.1%), 50~59세가 14명(9%), 60세 이상이 6명(3.8%)으로 30대에서 가장 많았고 추적관찰 기간 은 6 ~ 130 개월이었다. 유양동폐쇄술을 시행한 환자는 남성이 18명, 여성이 17명이고 연령은 16~56세로 평균나이는 34.7세였으며 추적관찰 기간은 15 ~ 71 개월이었다. 그리고 개방공동 유양동삭개술을 시행한 환자는 남성이 53명, 여성이 57명으로 연령은 17~59세에 평균나이는 32.3세였으며 추적관찰 기간 은 6~72 개월이었다. 수술 전 기도청력이 30 dB이내인 환자를 near-normal hearing을 가진 환자 로 정의할 때 atticosinoplasty를 시행한 156예 중에서 모두 40예가 수술 전 near-normal hearing을 가진 환자였으며 평균나이는 31.9세였다. 이 중 남자 는 17명으로 평균나이는 30.9세이고, 여자는 23명으로 평균나이는 32.6세였다. B. atticosinuplasty의 시술방법전신마취하에 먼저 이내절개(endoaural incision)를 넣어 외이도 후벽의 skin flap을 만든 후 이개후 접근을 하여 측두골을 노출시킨다. 뒤쪽 고막을 들어 올 리고 후방 중고실(posterior mesotympanum)을 확인하면서 이관주위 점막을 확인하고 이관 주위 점막에 염증이 있고 좋지 않으면 바로 개방공동 유양동삭개
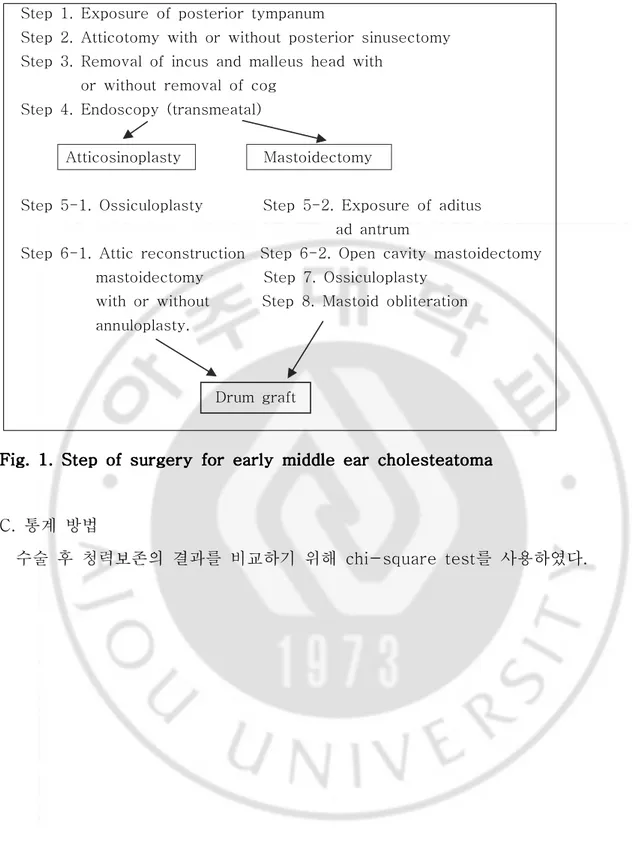
술을 시행한다. 이관주위 점막의 상태가 양호하면 상고실개방술(atticotomy)을 시행하여 진주종을 제거하고 침골을 빼내고 추골두를 자른 후 상고실의 잔존 병 변을 확인한다. 경우에 따라 전상고실골판이 돌출된 경우에는 상이관와를 통한 환기를 위해서 제거하여야 한다. 고실동(tympanic sinus)과 후고실강(posterior attic space)의 병변 확인을 위해서 posterior sinusectomy를 시행하고, 고실동 이 깨끗한 순수 상고실 진주종이면 posterior sinusectomy는 할 필요가 없다. 상고실개방술과 posterior sinusectomy 후 진주종을 제거한 뒤, 70˚ 내시경을 통하여 유양동구(mastoid ad antrum)을 통하여 유양동내 병변을 확인하여야 한 다. 잔존병변이 없다는 확신이 들면 이내절개 부위를 통하여 가급적 크게 이주연 골을 취득한다. 연골막은 벗겨서 고막이식조직으로 사용하고 연골은 상고실 결손 과 후윤상골(posterior annular bone)의 결손을 막아주는데 사용한다. scutumplasty와 annuloplasty를 하기 전에 이소골성형술을 시행하는데 가급적 남아있는 추골병을 이용한다. 대부분의 초기 진주종은 등골의 상부구조가 있는 경우가 많기 때문에 malleus stapes strut을 이용하는 경우가 많았다. 만약 진 주종의 잔존병변이 남아있고 제거가 불가능하면 개방공동 유양동삭개술을 시행 하였으며 이 경우 유양동내 병변이 심하지 않고 비교적 건강한 점막과 함기세포 가 유지되면 과대 유양동 문제(cavity problem)를 줄이기 위해 후부벽 (posterior buttress)의 받침(bridge)을 가능한 높게 유지하고 유양동은 골편 (bone chip)이나 glass ionomer cement로 유양동폐쇄술을 시행하였다(Fig. 1).
Step 1. Exposure of posterior tympanum
Step 2. Atticotomy with or without posterior sinusectomy Step 3. Removal of incus and malleus head with
or without removal of cog Step 4. Endoscopy (transmeatal)
Atticosinoplasty Mastoidectomy
Step 5-1. Ossiculoplasty Step 5-2. Exposure of aditus ad antrum
Step 6-1. Attic reconstruction Step 6-2. Open cavity mastoidectomy mastoidectomy Step 7. Ossiculoplasty
with or without Step 8. Mastoid obliteration annuloplasty. Drum graft Fig. Fig. Fig.
Fig. 1. 1. 1. Step 1. Step Step Step of of of of surgery surgery surgery surgery for for early for for early early early middle middle middle ear middle ear ear cholesteatomaear cholesteatomacholesteatomacholesteatoma
C. 통계 방법
수술 후 청력보존의 결과를 비교하기 위해 chi-square test를 사용하였다.
Ⅲ
Ⅲ
Ⅲ
Ⅲ.
.
.
. 결과
결과
결과
결과
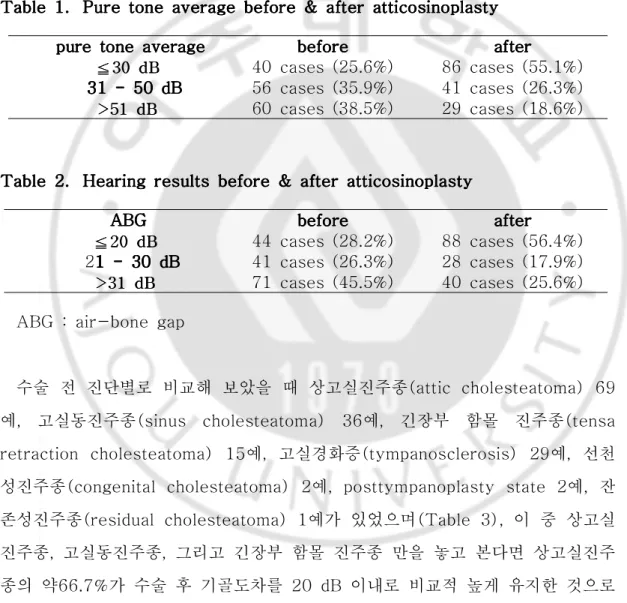
atticosinoplasty를 시행한 156예의 수술 전 순음평균역치(pure tone average)는 44.8 dB이었고, 수술 후 순음평균역치는 40.0 dB였다. 수술 후 기 도역치가 30 dB보다 작은 경우는 모두 86예(55.1%)로 수술 전 40예(25.6%) 보다 높아졌고(Table 1), 기골도차가 20 dB 이내에서 보존된 경우도 수술 전 44예에서 88예(56.4%)로 높아졌음을 볼 수 있었다(Table 2). Table Table Table
Table 1.1.1.1. Pure Pure Pure Pure tone tone tone tone average average before average average before before & before & & & after after after after atticosinoplastyatticosinoplastyatticosinoplasty atticosinoplasty
ppure ppure ure ure tone tone tone tone averageaverage averageaverage beforebeforebeforebefore afterafterafterafter
≦≦≦333000dddBBB 40 cases (25.6%) 86 cases (55.1%) 31 31 31 - 31 - - 50 - 50 50 50 dBdBdBdB 56 cases (35.9%) 41 cases (26.3%) > > >555111dddBBB 60 cases (38.5%) 29 cases (18.6%) Table Table Table
Table 2.2.2. Hearing 2. Hearing Hearing Hearing results results results before results before & before before & & & after after after after atticosinoplastyatticosinoplastyatticosinoplastyatticosinoplasty
ABGABGABGABG beforebeforebeforebefore afterafterafterafter
≦≦≦222000dddBBB 44 cases (28.2%) 88 cases (56.4%) 21 1 1 1 - - - 30 - 30 30 30 dBdBdBdB 41 cases (26.3%) 28 cases (17.9%) > > >333111dddBBB 71 cases (45.5%) 40 cases (25.6%)
ABG : air-bone gap
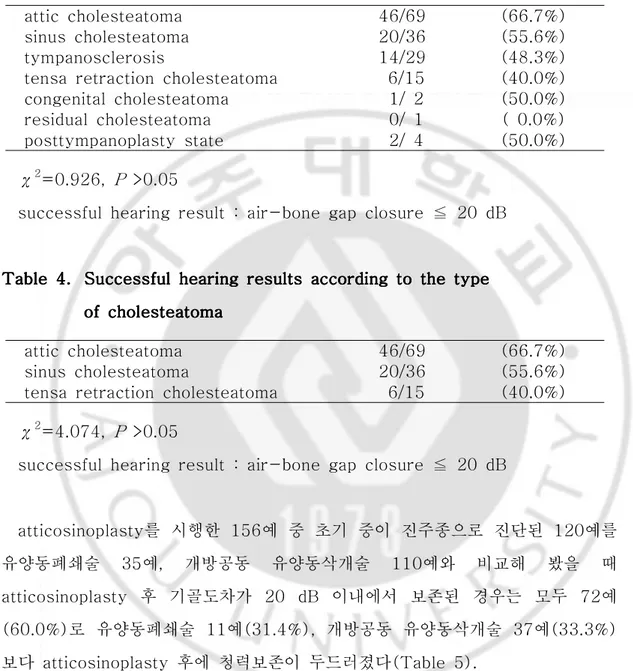
수술 전 진단별로 비교해 보았을 때 상고실진주종(attic cholesteatoma) 69 예, 고실동진주종(sinus cholesteatoma) 36예, 긴장부 함몰 진주종(tensa retraction cholesteatoma) 15예, 고실경화증(tympanosclerosis) 29예, 선천 성진주종(congenital cholesteatoma) 2예, posttympanoplasty state 2예, 잔 존성진주종(residual cholesteatoma) 1예가 있었으며(Table 3), 이 중 상고실 진주종, 고실동진주종, 그리고 긴장부 함몰 진주종 만을 놓고 본다면 상고실진주 종의 약66.7%가 수술 후 기골도차를 20 dB 이내로 비교적 높게 유지한 것으로
나왔으나 다른 종류와 비교해 볼 때 유의할만한 수치는 되지 못하였다(by χ2,
P >0.05)(Table 4).
Table Table Table
Table 3.3.3.3. Successful Successful Successful Successful hearing hearing hearing hearing results results according results results according according according to to to preoperative to preoperative preoperative diagnosispreoperative diagnosisdiagnosisdiagnosis
attic cholesteatoma 46/69 (66.7%) sinus cholesteatoma 20/36 (55.6%) tympanosclerosis 14/29 (48.3%) tensa retraction cholesteatoma 6/15 (40.0%) congenital cholesteatoma 1/ 2 (50.0%) residual cholesteatoma 0/ 1 ( 0.0%) posttympanoplasty state 2/ 4 (50.0%) χ2=0.926, P >0.05
successful hearing result : air-bone gap closure ≦ 20 dB
Table Table Table
Table 4.4.4.4. Successful Successful Successful Successful hearing hearing hearing hearing results results according results results according according according to to to the to the the type the type type type
of of of of cholesteatomacholesteatomacholesteatomacholesteatoma
attic cholesteatoma 46/69 (66.7%) sinus cholesteatoma 20/36 (55.6%) tensa retraction cholesteatoma 6/15 (40.0%)
χ2=4.074, P >0.05
successful hearing result : air-bone gap closure ≦ 20 dB
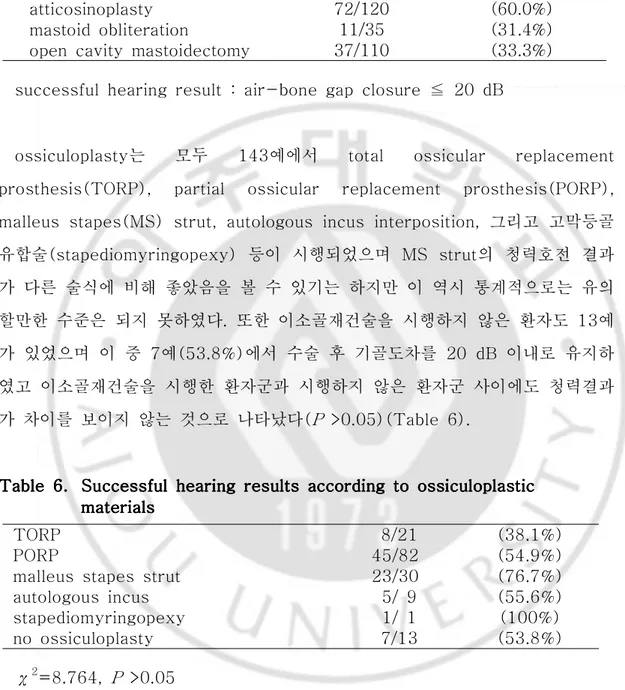
atticosinoplasty를 시행한 156예 중 초기 중이 진주종으로 진단된 120예를 유양동폐쇄술 35예, 개방공동 유양동삭개술 110예와 비교해 봤을 때 atticosinoplasty 후 기골도차가 20 dB 이내에서 보존된 경우는 모두 72예 (60.0%)로 유양동폐쇄술 11예(31.4%), 개방공동 유양동삭개술 37예(33.3%) 보다 atticosinoplasty 후에 청력보존이 두드러졌다(Table 5).
Table Table Table
Table 5.5. Successful 5.5. Successful Successful Successful hearing hearing hearing hearing results results results results according according according according to to the to to the the type the type type type of of of of surgery surgery surgery surgery in in in in
early early early early middle middle middle middle ear ear ear cholesteatomaear cholesteatomacholesteatomacholesteatoma
atticosinoplasty 72/120 (60.0%) mastoid obliteration 11/35 (31.4%) open cavity mastoidectomy 37/110 (33.3%)
successful hearing result : air-bone gap closure ≦ 20 dB
ossiculoplasty는 모두 143예에서 total ossicular replacement prosthesis(TORP), partial ossicular replacement prosthesis(PORP), malleus stapes(MS) strut, autologous incus interposition, 그리고 고막등골 유합술(stapediomyringopexy) 등이 시행되었으며 MS strut의 청력호전 결과 가 다른 술식에 비해 좋았음을 볼 수 있기는 하지만 이 역시 통계적으로는 유의 할만한 수준은 되지 못하였다. 또한 이소골재건술을 시행하지 않은 환자도 13예 가 있었으며 이 중 7예(53.8%)에서 수술 후 기골도차를 20 dB 이내로 유지하 였고 이소골재건술을 시행한 환자군과 시행하지 않은 환자군 사이에도 청력결과 가 차이를 보이지 않는 것으로 나타났다(P >0.05)(Table 6). Table Table Table
Table 6.6.6.6. Successful Successful Successful Successful hearing hearing hearing hearing results results according results results according according according to to to ossiculoplasticto ossiculoplasticossiculoplasticossiculoplastic
materialsmaterialsmaterialsmaterials
TORP 8/21 (38.1%)
PORP 45/82 (54.9%)
malleus stapes strut 23/30 (76.7%) autologous incus 5/ 9 (55.6%) stapediomyringopexy 1/ 1 (100%) no ossiculoplasty 7/13 (53.8%) χ2=8.764, P >0.05
수술 전 기도청력 수치가 30 dB이내였던 환자 40예 중에서 고실경화증 1예와 posttympanoplasty state 1예를 제외하면 상고실진주종, 고실동진주종, 그리고 긴장부 함몰 진주종 환자는 모두 38예로 그 중 상고실진주종 환자에서 비교적 청력보존이 잘 이루어지고는 있으나 이 역시 유의할만한 수준은 아니었다(P >0.05)(Table 7). Table Table Table
Table 7. 7. 7. 7. Hearing Hearing Hearing Hearing results results results results according according according to according to the to to the the type the type type of type of cholesteatoma of of cholesteatoma cholesteatoma cholesteatoma in in in in cases
cases cases
cases with with with with near-normal near-normal near-normal hearing near-normal hearing hearing hearing
c c chhhaaannngggeeeiiinnnPPPTTTAAA aaatcchchohttttitooliiccclleeesststteeeaaatttoomomamaa sccchssihhoiinnnuoolusulleessesststteeeaaatttooommmaaa cctttechenehhonsnoolssaleleseaarstsrtetreeaeeteatattrrratotomoaacmamccttitiaaioononn ≦ ≦≦111000dddBBB 23/27(85.2%) 6/9(66.7%) 1/2(50.0%) >>>111000ddBdBB 4/27(14.8%) 3/9(33.3%) 1/2(50.0%) χ2=1.873, P >0.05
near-normal hearing : air conduction threshold ≦ 30 dB
이소골재건술을 시행한 34예 중에서는 TORP를 시행한 5예에서 80%의 높은 청력보존을 보이기는 하였으나 유의있는 결과가 아니었으며, 이소골재건술을 시 행하지 않은 6예에서는 모두 청력이 보존되었음을 보여주고 있으나 이는 이소골 재건술을 시행한 34예와 비교해 보았을 때 역시 청력보존에 있어 큰 차이는 없 었다(P >0.05) (Table 8).
Table Table Table
Table 8. 8. 8. 8. Hearing Hearing Hearing Hearing results results results according results according according according to to ossiculoplastic to to ossiculoplastic ossiculoplastic ossiculoplastic materials materials materials in materials in in in cases cases cases cases with
with with
with near-normal near-normal near-normal near-normal hearing hearing hearing hearing
mmmaaattteeerrriiaiaalllsss ≦≦≦11100d0ccchddBhhaBBanangnggeeeiiinnPnPTP>TAT>>1110AA00dddBBB TORP 4/5 (80.0%) 1/5(20.0%) PORP 11/15(73.3%) 4/15(26.7%) malleus strut 8/11(72.2%) 3/11(21.8%) autologous incus 0/2 (0.0%) 2/2(100.0%) stapediomyringopexy 1/1(100.0%) 0/1 (0.0%) no ossiculoplasty 6/6(100.0%) 0/6 (0.0%) χ2=5.942, P >0.05
between ossiculoplasty and no ossiculoplasty : χ2=1.246, P >0.05 near-normal hearing : air conduction threshold ≦ 30 dB
수술 전 기도청력 수치가 30 dB이내였던 환자 중에서 이소골재건술을 시행한 환자 34예 중 이소골 연쇄가 정상인 경우는 9예, 이소골 연쇄가 정상이지 않은 경우는 25예가 있었고 전반적으로 청력보존이 잘되어 두 그룹간에 유의할만한 차이를 보이지는 않았다(P >0.05). 하지만 이소골 연쇄가 정상이지 않은 경우에 서 등골이 정상인 경우가 18예, 등골이 정상이지 않은 경우가 7예였으며 두 경 우에서는 등골이 정상인 경우에서 청력보존이 유의할 만하게 좋아졌음을 볼 수 있었다(P ≦0.05)(Table 9). Table Table Table
Table 9. 9. 9. 9. Hearing Hearing Hearing results Hearing results according results results according according to according to to the to the status the the status status of status of of ossicular of ossicular ossicular ossicular chain chain chain chain in in in in cases
cases cases
cases with with with with near-normal near-normal near-normal hearingnear-normal hearinghearinghearing
ooossssssiiicccuulullaaarrrccchhhaaaiiinnn ≦≦≦11010d0dBdBBchcchhaaannnggegeeiiinPnnPTPTTAAA>>>111000dddBBB i i innntttaaacccttt 7/9 (77.8%) 2/9(22.2%)
not not not intactnot intactintactintact 21/25(84.0%) 4/25(16.0%) intact stapes 17/18(94.4%) 1/18(6.6%) not intact stapes 4/7 (57.1%) 3/7(42.9%)
between cases with intact stapes and cases without intact stapes : χ2=5.218, P ≦0.05
between intact and not intact ossicular chain : χ2=5.002, P >0.05 near-normal hearing : air conduction threshold ≦ 30 dB
추적관찰 중 나타난 수술 후 합병증으로는 고막 천공 4예, 상고실 함몰 2예, 중이 삼출 1예, prosthesis extrusion 2예, recidivisional cholesteatoma 2예, 감각신경성 난청 1예 등(Table 10)이었고, 이중 재수술을 시행한 환자는 4예로 각각의 원인은 고막 천공 1예, prosthesis extrusion 1예, recidivisional cholesteatoma 2예 등이었다.
Table Table Table
Table 10. 10. 10. 10. Complications Complications Complications of Complications of of atticosinoplastyof atticosinoplastyatticosinoplastyatticosinoplasty
drum perforation prosthesis extrusion
recidivisional cholesteatoma attic retraction
middle ear effusion
sensorineural hearing loss
4 cases 3 cases 2 cases 2 cases 1 case 1 case
Ⅳ
Ⅳ
Ⅳ
Ⅳ.
.
.
. 고찰
고찰
고찰
고찰
진주종을 포함한 만성중이염 환자의 치료에 있어서 질병을 완벽하게 제거하고 수술 술기가 간편하면서도 수술 후에 환자의 불편을 최소화하도록 하기위해 환 자의 질병상태 및 사회적 여건이나 술자의 경험 등 많은 변수와 함께 어떤 치료 방법이나 수술방법을 선택하는 것이 좋을 것인가에 대해서 지금까지 많은 성과 가 있었지만 아직까지 뚜렷한 해답을 찾아내지는 못하고 논의를 거듭하고 있는 것이 사실이다. 더욱이 고해상도 측두골 단층촬영의 보편적 이용과 의료 접근성 의 증가로 인해 초기 진주종의 진단이 증가하고 있는 추세이기는 하나, 이에 대 한 명확한 수술적 치료 방침에 대해서도 역시 지금도 많은 논의가 진행 중인 상 태이다. Tos(Tos 등, 1981 ; Tos, 1993과 1997)는 후천성 중이 진주종을 상고실진 주종, 고실동진주종, 긴장부 함몰 진주종로 분류한 바 있으며 이는 임상적인 측 면에서 상당히 합리적이고, 객관성이 있다고 할 수 있다. 상고실 진주종은 고막 이완부 함몰이나 천공으로 정의되는데 진주종이 상고실 함요(prussack's space)에서 상고실, 유돌동구(aditus ad antrum)를 통하여 유양동으로 진행되 고, 고실동진주종은 고막 긴장부의 후상방 부위의 함몰이나 천공으로 정의되는데 진주종이 고실동(sinus tympani)과 후고실(posterior tympanum)에서 시작하 여 침골의 내측을 통하여 상고실, 유돌동구, 유양동으로 진행되며, 긴장부 함몰 진주종은 고막긴장부가 전체적으로 함몰되어 이관입구, 추골, 침골 내측을 통하 여 상고실, 유돌동구, 유양동으로 진행되는 것을 말한다. 그래서 상고실진주종은 일명 외측 상고실진주종(lateral attic cholesteatoma)이라 할 수 있으며, 고실 동진주종과 긴장부 함몰 진주종은 내측 상고실진주종(medial attic cholesteatoma) 이라 명명하기도 한다(Chun 등, 1998). 이렇게 Tos에 의해서 분류된 세 가지 진주종은 초기 진주종일 때 그 분류가 명확해지며 유양동까지명확해 질 수 없다. “atticosinopiasty"의 개념은 Tos의 분류에 의한 세가지 형 태의 중이 진주종의 초기 치료를 포괄한다고 할 수 있다.
초기 상고실진주종의 수술은 상고실개방술과 상고실재건술(attic reconstruction)으로 이루어지고, 초기 고실동진주종은 posterior sinusectomy 와 annuloplasty로 이루어지며, 초기 긴장부 함몰 진주종은 상고실개방술과 posterior sinusectomy 후 scutumplasty와 annuloplasty로 이루어진다고 볼 수 있다. 이와 더불어 atticosinoplasty에서 침골과 추골두를 제거하고 전상고실 골판을 제거하는데, 이는 특히 이소골에 얇게 붙어 있는 병변을 제거하는 것뿐만 아니라, 상이관와를 통한 상고실 환기 통로의 확보 때문이다(Park, 2002). 중이열(middle ear cleft)의 형태 기능적인 구분은 고실격막(tympanic diaphragm)에 의해(Chatellier와 Lemoine, 1946 : Proctor, 1964) 전하부 (anteroinferior compartment)와 후상부(posterosuperior compartment)로 이 루어지는데 전하부는 중고실(mesotympanum), 하고실(hypotympanum), 전구 고실(protympanum)로 구성되고, 후상부는 상고실, 유돌동구, 유양동 및 유돌봉 소조직으로 구성된다. 전하부의 형태 기능적인 역할은 주로 점액 섬모기능이고 후상부는 중이열과 혈관사이의 가스 교환 기능이다. 중이열 점막의 염증반응은 이러한 가스 교환의 문제를 초래하고 중이열 내의 음압을 유발하고 이렇게 생성 된 음압은 고막의 상피층의 기능부전과 상피하 고유층의 위축과 더불어 고막의 함몰과 진주종을 유도하게 된다(Ars, 1999). 중이열 후상부와 전하부의 유일한 통로는 고실격막(tympanic diaphragm)내의 고실협부(tympanic isthmus)이며 후상부의 환기는 전적으로 고실협부의 상태에 달려있다. 고실협부의 폐쇄요인은 점막부종, 육아조직 혹은 고막 후상부의 함몰을 들 수 있는데(Aimi, 1978), 후 자의 경우 고막후상부의 함몰이 고실협부를 폐쇄함으로써 상고실의 가스 흡수가 일어나고 이차적으로 고막이완부의 함몰을 일으킴으로써 고막 후상부 함몰과 고 막 이완부 함몰 진주종이 동시에 일어 날 수 있는 가능성을 설명할 수 있다 (Yoon 등, 1990). 이렇듯 중이열 내의 후상부와 전하부의 형태 기능적인 차이 는 이관기능이 정상으로 되어도 상고실내의 진주종이 계속 진행 될 수 있는 요
인이 될 수 있다. 실제로 초기 진주종의 수술시 많은 예에서 이관 주위의 점막이 깨끗하고 정상적인 이관 개구부를 관찰 할 수 있다. 이런 관점에서 "atticosinoplasty"의 초기 진주종의 수술은 상고실 병변의 제거와 더불어 중이 열 후상부의 환기 통로를 조기에 확보하는데 유용하게 접근할 수 있다. 본 연구에서 atticosinoplasty를 시행한 156례 중 88례(56.4%)에서 술 후 골 기도차가 20dB 이내의 청력보존을 볼 수 있었다. 성공적인 청력보존율을 수술 후 골기도차가 20dB 이내 인 것으로 정의할 때, 이 결과는 같은 시기에 시행한 유양동폐쇄술(31.4%)이나 개방공동 유양동삭개술(33.3%)의 청력보존율보다 atticosinoplasty의 청력보존율이 의미있게 높다는 것을 보여준다. 이러한 결과 는 초기 진주종의 치료에 있어서 청력보존의 관점에서 atticosinoplasty의 유용 성을 보여주며, 또한 156례중 단지 2례에서만 재발이 확인됨으로써 초기 진주종 에 있어서 진주종의 완전 제거의 관점에 있어서도 atticosinoplasty의 유용성을 확인할 수 있었다. 진주종의 유형에 따라 분류해 보면, 상고실진주종의 청력보존율이 66.7%, 고 실동진주종이 55.6%, 긴장부 함몰 진주종이 40.0%로서 상고실진주종의 청력보 존율이 상대적으로 높았는데 이는 상고실진주종은 상고실의 외측으로 진행되어 상고실의 내측으로 진행하는 고실동진주종, 긴장부 함몰 진주종보다 진주종의 제 거가 상대적으로 용이했던 점이 영향을 미친 것으로 생각된다. 수술 전 기도청력이 30dB이내인 40명을 대상으로 하였을 때, 이소골재건술을 시행한 34례중 28례(82.4%)에서 10dB 내에서 청력보존이 가능하였다. 이는 비교적 청력저하가 미미하더라도 진주종의 제거를 위해 조기에 수술을 시행할 수 있는 하나의 근거가 될 수 있다. 게다가 atticosinoplasty의 수술의 특이할만한 점은 유양동내의 점막을 보존 시켜 가스 교환이 문제되지 않는다는 점이다. 중이 점막의 염증반응이 가스 교 환의 문제를 초래하여 중이열 내의 음압을 유발한 후 고막 상피층의 기능부전과 상피하 고유층의 위축과 더불어 고막의 함몰과 진주종을 유도하게 된다고 볼 때 초기 중이 진주종의 수술 후 유양동내의 점막이 보존됨으로 인해 가스 교환의
문제가 생길 가능성이 현저히 줄어들게 되어 수술 후 예후에 있어서도 긍정적인 영향을 미치리라 예상된다. 이러한 결과들을 종합하여 보면, 비교적 초기 중이 진주종에 있어서 atticosinoplasty를 시행하면서 그 자체로도 비교적 좋은 결과를 기대할 수 있으 면서 병변의 정도와 상황에 따라서는 다른 술식으로의 전환 등을 통해 병변의 제거와 청력보존의 관점에서 성공적인 결과를 얻을 수 있다는 것을 알 수 있다 (Park, 2002).
Ⅴ
Ⅴ
Ⅴ
Ⅴ.
.
.
. 결론
결론
결론
결론
초기 중이 진주종의 치료를 위한 수술법으로서의 atticosinoplasty는 청력개선 에 효과가 있었으며 합병증은 미미하였다. 향후 초기 중이 진주종의 수술적 처치 에 일관된 개념이 도입이 향후 진주종성 중이염의 치료에 있어 비약적인 발전을 이끌어 낼 수 있을 것으로 기대되며, 본 연구의 결과는 초기 중이 진주종의 치료 에 있어서 atticosinoplasty의 유용성을 보여주고 있다. 이는 초기 중이 진주종 의 치료의 효율적이고 체계적인 접근이나 선택에 있어서 atticosinoplasty가 의 미있는 방법임을 보여준다.REFERENCES
REFERENCES
REFERENCES
REFERENCES
1. Aimi K. The tympanic isthmus: its anatomy and clinical significance. Laryngoscope 88: 1067-1081, 1978
2. Ars B. Pathogenesis of acquired cholesteatoma. In: Pathogenesis in cholesteatoma. Ars B(ed). Hague. Kugler publications 1-18, 1999
3. Baba S, Fujikura T, Pawankar R, Yagi T. Subjective evaluation of post-tympanoplasty hearing in relation to the pure tone threshold. Auris Nasus Larynx 31: 347-351, 2004
4. Brown JS. A ten year statistical follow-up of 1142 consecutive cases of cholesteatoma: The closed vs. the open technique. Laryngoscope 92: 390-396, 1982
5. Browning GG, Gatehouse S, Swan IR. The Glasgow Benefit Plot: A new method for reporting benefits from middle ear surgery. Laryngoscope 101: 180-185, 1991
6. Chatellier HP, Lemoine J, Le diaphragme inter-attico-tympanique du nouveau-ne'; description de sa morphologie: considerations sur son role pathogenique dans les oto-mastoidites cloisonnees du nourrisson. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac 13: 534-566, 1946
7. Cho HH. Reconstruction of the posterior canal wall with silastic in chronic otitis media surgery. Korean J Otolaryngol 48(12): 1442-1446, 2005
8. Chun YM. Park K. Shin SJ. Kim BH. Clnical appearances on the extension of attic cholesteatoma. Korean J Otolaryngol 41: 32-36, 1998
9. Cody DT, McDonald TJ. Mastoidectomy for acquired cholesteatoma: Follow-up to 20 years. Laryngoscope 94: 1027-1029, 1984
10. Committee on hearing and equilibrium guidelines for the evaluation of results of treatment of conductive hearing loss. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 13: 186-187, 1995
11. Dornhoffer J. Cartilage tympanoplasty: Indications, techniques and outcomes in a 1,000-patient series. Laryngoscope 13: 1844-1856, 2003
12. Dornhoffer JL. Retrograde mastoidectomy with canal wall reconstruction: A follow-up report. Otol Neurotol 25: 653-660, 2004
13. El-Meselaty K, Badr-El-Dine M, Mandour M, Mourad M, Darweesh R. Endoscope affects decision making in cholesteatoma surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 129: 490-496, 2003
14. Farrier JB. The anterior attico-tympanotomy. Laryngoscope 76; 768-779, 1968
15. Farrior JB, Nichols SW. Long-term results using ossicular grafts. Am J Otol 17: 386-392, 1996
16. Fisch U. Closed mastoido-epitympanectomy with tympanoplasty. In; Tympanoplasty. mastoidectomy and stapes surgery. Stuttgart. Thieme 154-163, 1994
17. Jansen C, Posteriore Tympanotomie: Zugang zum Mittelohrmit
Erhaltung des ausseren Gehoergangs. Arch Otolaryngol 188: 2-6, 1967
epitympanoplasty with mastoid obliteration technique. Korean J Otolaryngol 44: 476-484, 2001
19. Kang MK. Epitympanoplasty with mastoid obliteration technique : 38
months follow-up results of 283 cases. Korean J Otolaryngol 48(8): 975-980, 2005
20. Kim HJ. Classification and hearing results reporting guideline in chronic otitis media surgery. Korean J Otolaryngo 49(1): 2-6, 2006
21. Lee WS. Correlation between the pure tone audiometry results and the subjective hearing benefit of tympanoplasty. Korean J Otolaryngol 50(5): 399-403, 2007
22. Meuser W. The exenterated mastoid: A problem of ear srgery. Am J Otol 6: 323-325, 1985
23. Morimitzu T. Matsumoto I, Nagai T. Nagai M, Ide M, Mgkino K. et al. pathogeneis of cholesteatoma based on clinical results of anterior tympanotomy. Auris Nasus Larynx (Tokyo) 16(suppl 1): 9-14, 1989
24. Palva T. Operative technique in mastoid obliteration. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 75: 289-290, 1973
25. Park KH. Management of early cholesteatoma. J Clinical Otolaryngol 5: 13-19, 2002
26. Pfleiderer AG, Ghosh S, Kairinos N, Chaudhri F. A study of recurrence of retraction pockets after various methods of primary reconstruction of attic and mesotympanic defects in combined approach tympanoplasty. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 28: 548-551, 2003
27. Portmann M. the choice of techniques of the surgery of chronic otitis media with cholesteatoma. J Laryngol Otol 89: 533-547, 1985
28. Proctor B, The development of the middle ear spaces and their surgical significance. J Laryngol Otol 78: 631-648, 1964
29. Proctor B. Surgical anatomy of the ear and temporal bone. New York, Theieme 83-84, 1989
30. Roger G, Denoyelle F, Chauvin P, Schlegel-Stuhl N, Garabedian EN. Predictive risk factors of residual cholesteatoma in children: A study of 256 cases. Am J Otol 18: 550-558, 1997
31. Sakai M, Shinkawa A, Miyake H, Fujii K. Reconstruction of scutum
defects (scutumplasty) for attic cholesteatoma. Am J Otol 7: 188-192, 1986
32. Sanna M, Zini C, Gamoletti R, Delogu P, Scandellari R, Russo A, et al. Prevention of recurrent cholesteatoma in closed tympanoplasty. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 96: 273-275, 1987
33. Sheehy JL, Patterson ME, Intact canal wall tympanoplasty with mastoidectomy. Laryngosope 77: 1502-1542, 1967
34. Sheehy JL. Acquired cholesteatoma in adults. Otolaryngol Clin Nor Am 22: 1041-1053, 1989
35. Smyth GD, Patterson CC. Results of middle ear reconstruction: Do patients and surgeons agree? Am J Otol 6(3): 276-279, 1985
36. Smyth GD. Postoperative cholesteatoma in combined approach tympanoplasty. J Laryngol Otol 90: 597-621, 1976
canal wall. Laryngoscope 13: 443-448, 2003
38. Tos M. Holm-Jensen S. Sorensen CH. Changes in prevalence of secretory otitis from summer to winter in four-year old children, Am J Otol 2: 324-327, 1981
39. Tos M. Modification of combined approach tympanoplasty in attic cholesteatoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 108: 772-778, 1982
40. Tos M. Pathogenesis of sinus and tensa retraction cholesteatoma. In;
Cholesteatoma and mastoid surgery. Proceedings of the 5th International conference. Sanna et al. (eds). Rome CIC Edizioni Internazionali 3-8, 1997
41. Tos M. Sequelae after secetory otitis and pathogenesis of attic cholesteatoma in: Cholesteatoma and mastoid surgery. proceedings of the 4th International conference. Nakono et al. (eds), Amsterdam, Kugler Publications 289-294, 1993
42. Weber PC, Gantz BJ. Cartilage reconstruction of the scutum defects in canal wall up mastoidecomies. Am J Otolaryngol 19: 178-182,
1998
43. Wullstein H. Theory and practice of tympanoplasty, Laryngoscope 66: 1076-1093, 1956
44. Wullstein SR. Osteoplastic epitympanotomy. Am Otol Rhinol Laryngol 84: 663-668, 1974
45. Yoon TH, Paparella MM, Aeppli DM. Pathology and pathogeneis of tympanic retraction. Am J Otolaryngol 11: 10-17, 1990
audiogram results and hearing benefit of tympanoplasty for chronic suppurative otitis media. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 109(4): 381-384, 2000
47. Zanetti D, Nassif N, Antonelli AR. Surgical repair of bone defects of the ear canal wall with flexible hydroxylapatite sheets : A pilot study. Otol Neurotol 22: 745-753, 2001
48. Zini C, Bacciu S, Sandellari R, Pasanisi E, Intraoperative management
of the osseous eustachian tube; technique and results. In; Cholesteatoma and mastoid surgery. Proceedings of 3th International
conference. Tas M. et al. (eds). Amsterdam. Kugler and Ghedini 533-541, 1989
- - -
- ABSTRACT ABSTRACT ABSTRACT -ABSTRACT --
Treatment
Treatment
Treatment
Treatment of
of
of
of early
early middle
early
early
middle
middle ear
middle
ear
ear cholesteatoma
ear
cholesteatoma
cholesteatoma
cholesteatoma
by
by
by
by atticosinoplasty
atticosinoplasty
atticosinoplasty
atticosinoplasty
Seung Ku Park
Department of Medical Sciences The Graduate School, Ajou University
(Supervised by Professor Keehyun Park)
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES : Treatment of early cholesteatoma usually involves surgical modification of mastoid antrum and tympanum to prevent recurrence. Reconstruction of ossicular chain and the ear drum after complete elimination of cholesteatoma in tympanum improves hearing greatly. However, like in other fields of clinical medicine, treatment of early cholesteatoma is advancing through trial and errors, and many new surgical techniques are still being published until this time. Despite of continuing achievement and effort, there have been considerable controversies upon systematic approach and treatment method in middle ear surgery. These difficulties, however, will be overcome and development of such treatment methods will eventually increase operation of early cholesteatoma and revisional ear surgery. With its increasing importance, it will be meaningful to evaluate the role of atticosinoplasty in the treatment of early cholesteatoma, and to
compare its effect in improving hearing with other techniques like mastoid obliteration and open cavity mastoidectomy.
METHODS : Retrospective review was performed for 173 cases treated by atticosinoplasty in the period of 12 years between Mar 1995 and Feb 2007 in Department of Otolaryngology of Ajou University Medical Center. Of 156 cases with more than 6 months of follow up period, 120 cases of relatively small cholesteatoma on temporal bone tomography were comparatively analysed for hearing improvement with 35 cases of mastoid obliteration and 110 cases of open cavity mastoidectomy. We analysed results according to the type of cholesteatoma and ossiculoplastic materials. We also compared 40 cases with near-normal hearing before surgery in terms of types of cholesteatoma and ossiculoplastic materials.
RESULT : When 120 cases of atticosinoplasty for early cholesteatoma were compared for hearing improvement with 35 cases of mastoid obliteration and 110 cases of open cavity mastoidectomy, patients treated by atticosinoplasty had significantly better results. In analysis by type of cholesteatoma, attic cholesteatoma had relatively better results. Comparison among ossiculoplastic materials showed malleus stapes strut gave relatively good results. In the cases of near-normal hearing group, better maintenance of hearing acuity was shown when ossiculoplasty was not performed. Analysis according to type of cholesteatoma showed better results in attic cholesteatoma. There were good results regardless of ossiculoplastic material used.
CONCLUSION : Atticosinoplasty as an initial treatment choice for early cholesteatoma was certainly effective in improving hearing acuity with minimal complications. In the future, when a universal concept is introduced to surgical treatment of early cholesteatoma, atticosinoplasty will be a useful option in the systematic approach.
key key key key wordswordswords : atticosinoplasty, cholesteatoma, open cavity mastoidectomy, words mastoid obliteration, ossiculoplasty