1035 서 론
상부요로상피종양은 비교적 드문 질환으로 신우종양은 모든 신종양의 약 10%를 차지하고 전체 요로상피종양의 5%를 차지한다.1 요관종양은 더욱 드물어 신우종양의 1/4 정도로 발병한다.2 그러나 최근 진단방법의 발달과 인구의 고령화로 상부요로상피종양의 발생빈도가 증가하는 추세
이다.3
상부요로상피종양은 병리소견, 병인, 임상증상 및 자연경 로 등이 방광종양과 유사하며 요로의 다른 부위로의 재발 이 흔하고, 특히 15-40%에서 방광에 재발한다.2,4-6 그러나 방광종양의 재발에 관련된 인자에 대해서는 술 전 요세포 검사, 종양의 다발성, 병기, 분화도 및 수술방법 등 다양한 인자들이 보고7-9되고 있으나 아직까지 논란이 있다.
이에 저자들은 본원에서 상부요로상피종양으로 근치적
인자
Risk Factors for Subsequent Bladder Cancer Recurrence following Radical Surgery for Upper Urinary Tract Urothelial Cancer
Deok Hyun Cho, Jae Soo Kim, Hyun Tae Kim, Eun Sang Yoo, Tae Gyun Kwon, Bup Wan Kim
From the Department of Urology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to determine the clinical and pathological risk factors for subsequent bladder recurrence for the patients suffering with transitional cell carcinoma in the upper urinary tract (UUT-TCC) following radical surgery, and these factors should allow more accurate prediction of the disease outcome.
Materials and Methods: Between 1995 and 2004, a total of 71 patients underwent total nephroureterectomy for UUT-TCC. Patients with con- comitant or previous bladder tumor or a follow-up period of less than 1 year were excluded in this study. Univarariate and multivariate analysis by Cox's proportional hazards model was used to determine the inde- pendent risk factors for intravesical tumor recurrence.
Results: Fifteen out of 71 patients (21.1%) experienced subsequent intra- vesical tumor recurrence during a mean follow-up period of 16.5 months (range: 3-28). On univariate analysis, tumor size, multiplicity, stage and grade were significantly correlated with subsequent intravesical tumor recurrence. On the multivariate analysis, tumor stage and multiplicity had a statistically significant impact on the risk of subsequent intravesical tumor recurrence.
Conclusions: Tumor stage and multiplicity are important factors for subsequent intravesical tumor recurrence in the patients who suffer with UUT-TCC following surgery. Therefore, closer follow-up might necessary for patients with multiple foci and high stage UUT-TCC for the early detection of subsequent intravesical tumor recurrences. (Korean J Urol 2006;47:1035-1040)
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ
Key Words: Urinary tract, Transitional cell carcinoma, Bladder, Recur- rence, Risk factors
대한비뇨기과학회지 제 47 권 제 10 호 2006
경북대학교 의과대학 비뇨기과학교실
조덕현․김재수․김현태 유은상․권태균․김법완
접수일자:2006년 5월 24일 채택일자:2006년 7월 26일
교신저자: 권태균
경북대학교병원 비뇨기과 대구광역시 중구 삼덕 2가 50번지
ꂕ 700-721 TEL: 053-420-5855 FAX: 053-421-9618 E-mail: tgkwon@mail.
knu.ac.kr
수술을 시행한 환자를 대상으로 방광으로의 종양재발에 영 향을 미치는 인자에 대해 알아봄으로써 상부요로상피종양 환자의 치료와 추적에 도움이 되고자 한다.
대상 및 방법
1995년부터 2004년까지 상부요로상피종양으로 근치적 수술을 시행한 후 1년 이상 추적이 가능했던 환자 중 요로 상피종양의 과거력이 있거나, 진단과 수술 시에 방광종양 이 동반된 경우, 림프선이나 원격전이된 경우를 제외한 71 례를 대상으로 하였다. 임상병리학적 소견은 후향적으로 분석하였다.
평균 추적기간은 33.9개월 (12-101)이었으며, 추적관찰은 방광내시경과 요세포검사를 첫 2년 동안 3개월마다, 그 후 2년 동안 6개월마다, 그 후로는 매년 시행하였고, 배설성요 로조영술, 복부초음파검사나 전산화단층촬영은 1년마다 시 행하였다.
연령은 65세를 기준으로 그 이상과 미만군으로, 종양의 위치에 따라 신우, 요관으로 나누었으며, 종양의 수는 단발 성과 다발성으로 분류하였다. 종양의 크기는 장경 3cm를 기준으로 나누었고, 모양은 유두상과 비유두상군으로 분류 하였다. 술 전 요세포검사는 양성과 음성군으로, 종양의 병 기는 1997년 TNM 병기에 따라 pT1 이하인 경우와 pT2-T4 로 나누었고, 세포분화도는 WHO의 분류를 사용하여 grade 1, 2, 3으로 분류하였다. 수술방법에 따라서 고식적 개복술 군과 복강경수술군 및 요관구주위방광점막절제술을 시행 한 군과 시행하지 않은 군으로 분류하였다. 또한 술 후 보조 적 항암화학요법을 시행한 29례에 대하여 methotrexate, vin- blastine, adriamycin and cisplatin (M-VAC)군 16례와 gem- citabine and cisplatin (GC)군 13례로 분류하였다.
각각의 위험인자가 방광종양 재발에 미치는 영향을 분석 하기 위해 Kaplan-Meier 방법을 이용하여 생존율 및 disease free rate를 구하였고, 위험인자로 설정한 성별, 연령, 주증상 및 혈뇨의 유무, 술 전 요세포검사 결과, 좌우와 위치, 크기, 다발성, 모양, 조직학적 병기와 분화도, 수술방법, 요관구주 위방광점막절제술 유무와 종양과 절제면과의 거리, 수술 후 보조적 항암화학요법 등에 따른 유의성은 log rank test로 검증하였다. Cox proportional hazard model을 사용하여 방광 재발에 대한 상대적 위험도를 구하였으며 p값이 0.05 미만 일 때 통계학적으로 유의하다고 판정하였다.
결 과
전체 대상 환자 71례 중 15례 (21.1%)에서 방광재발이 있
었다. 재발에 걸린 시간은 16.5±7.5개월이었으며 28개월에 재발하였던 1례를 제외한 14례 (93%)에서 2년 내에 재발하 였다. 재발에 영향을 미치는 인자에 대한 단변량 및 다변량 분석결과는 다음과 같다.
Table 1. Clinical characteristics
ꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚ Cases Recurrence
No. of free
Variables of bladder survival p-value
patients recur- time rence (months)
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ
Sex 0.498
Male 48 11 33.28±2.41
Female 23 4 30.57±3.22
Age 0.080
<65 36 8 35.32±2.88
≥65 35 7 29.27±2.45
Chief complaint 0.849
Gross hematuria 44 10 32.47±2.21
Flank pain 23 5 31.44±3.82
Other 4 0 35.50±10.57
Gross hematuria 0.616
Negative 17 3 34.11±4.36
Positive 54 12 31.69±2.13
Microscopic hematuria 0.947
Negative 6 0 32.17±6.31
Positive 65 15 32.34±2.05
Preoperative cytology 0.729
Negative 56 12 32.49±2.20
Positive 15 3 31.69±4.04
Location 0.784
Pelvis 34 6 33.81±2.68
Ureter 33 9 31.09±2.79
Pelvis+ureter 4 0 27.00±11.00
Laterality 0.776
Right 26 6 31.73±3.30
Left 45 9 32.54±2.40
Surgical modality 0.141
Open 54 13 34.08±2.14
Laparoscopy 17 2 27.20±4.06
Bladder cuff resection 0.095
No 16 1 26.97±3.98
Yes 55 14 34.13±2.15
Adjuvant chemotherapy 0.437
GC 16 7 28.85±3.60
M-VAC 13 2 36.39±5.85
None 42 6 32.83±2.47
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ GC: gemcitabine and cisplatin, M-VAC: methotrexate, vinblastine, adriamycin and cisplatin
1. 단변량 분석 (Table 1, 2)
1) 환자의 성별 및 연령, 주증상 및 혈뇨의 유무, 수술 전
요세포검사, 좌우와 위치에 따른 방광재발기간에 유의한 차이는 없었다 (p>0.05).
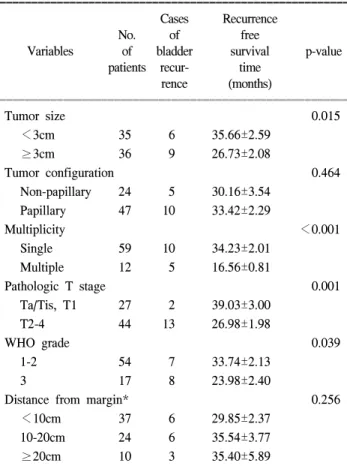
2) 종양의 크기: 종양의 장경이 3cm 미만인 환자 35례 중 6례, 3cm 이상인 경우 36례 중 9례에서 방광재발이 있었고, 생존곡선 분석결과 종양의 크기가 큰 경우에 방광재발기간 이 유의하게 짧았다 (p=0.015).
3) 종양의 다발성: 요관 내 종양이 단일병소였던 59례 중 10례, 다발병소 12례 중 5례에서 방광재발을 보였으며, 생 존곡선 분석결과에서 다발성 유무에 따른 방광재발기간에 통계적으로 유의한 차이를 보였다 (p<0.001, Fig. 1).
4) 종양의 모양: 종양의 모양이 유두상인 47례 중 10례, 비유두상 24례 중 5례에서 방광재발이 있었고, 종양의 모양 에 따른 방광재발기간의 차이는 없었다 (p=0.464).
5) 조직학적 병기: pTa/Tis 또는 pT1 병기 27례 중 2례, pT2-4병기 44례 중 13례에서 방광재발이 발생하였고, 생존 곡선 분석결과 종양의 병기와 재발기간은 통계적 유의한 차이를 보였다 (p=0.001, Fig. 1).
6) 분화도: Grade 1-2인 54례 중 7례, grade 3인 17례 중 8례에서 방광재발이 발생하였고, 분화도가 높을수록 방광 재발이 더 일찍 일어났다 (p=0.039).
7) 수술방법: 개복수술을 시행한 54례 중 13례, 복강경수 술을 시행한 17례 중 2례에서 방광재발이 있었으며, 두 군 간에 방광재발기간의 유의한 차이는 없었다 (p=0.141).
8) 요관구주위방광점막절제술 유무와 종양과 절제면과 의 거리: 요관구주위방광점막절제술을 시행한 55례 중 14 례, 요관구주위방광점막절제술을 시행하지 않은 17례 중 1 례에서 방광재발이 관찰되었으며, 요관구주위방광점막절 제술을 시행한 군에서 방광재발기간이 길었으나 통계학적 유의성은 없었다 (p=0.095). 수술절제면과 종양과의 간격이
Fig. 1. The Kaplan-Meier curve shows the bladder tumor recurrence according to (A) multiplicity and (B) pathologic T stage (p<0.001 and p=0.001, respectively).
Table 2. Pathologic characteristics
ꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚ Cases Recurrence
No. of free
Variables of bladder survival p-value
patients recur- time rence (months)
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ
Tumor size 0.015
<3cm 35 6 35.66±2.59
≥3cm 36 9 26.73±2.08
Tumor configuration 0.464
Non-papillary 24 5 30.16±3.54
Papillary 47 10 33.42±2.29
Multiplicity <0.001
Single 59 10 34.23±2.01
Multiple 12 5 16.56±0.81
Pathologic T stage 0.001
Ta/Tis, T1 27 2 39.03±3.00
T2-4 44 13 26.98±1.98
WHO grade 0.039
1-2 54 7 33.74±2.13
3 17 8 23.98±2.40
Distance from margin* 0.256
<10cm 37 6 29.85±2.37
10-20cm 24 6 35.54±3.77
≥20cm 10 3 35.40±5.89
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ Tis: carcinoma in situ, *: distance between tumor focus and distal resection margin
10cm 미만인 37례 중 6례, 10-20cm였던 24례 중 6례, 20cm 이상인 10례 중 3례에서 방광재발이 있었으며, 종양과 수술 절제면과의 간격에 따른 방광재발기간의 유의한 차이는 없 었다 (p=0.256).
9) 수술 후 보조적 항암화학요법: 전체 71례 중 29례에서 항암화학요법을 시행하였으며 16례에서 GC를, 13례에서 M-VAC을 시행하였다. 그 결과 GC군 7례, M-VAC군 2례에 서 방광재발이 관찰되었으며, 항암화학요법을 시행하지 않 은 42례 중 6례에서 방광재발이 관찰되었다. M-VAC군에서 더 긴 방광재발기간을 보였으나 생존곡선 분석에서 통계학 적으로 유의한 차이를 보이지 않았다 (p=0.437).
2. 다변량 분석 (Table 3)
Cox proportional model을 이용한 다변량 분석에서 종양의 병기 및 다발성이 방광재발기간과 관련이 있었으며 (p=
0.025, p=0.016), 나머지 인자들은 통계적 유의성이 없었다 (p>0.05).
3. 방광재발이 생존율에 미치는 영향 (Fig. 2)
평균 33.9개월의 추적 기간 동안 방광재발이 있었던 15례 중 12례가 생존하였고, 재발이 없었던 56례 중 46례에서 생 존하였으며 생존곡선 분석결과 방광재발여부와 생존율은 유의한 상관관계가 없었다 (p=0.649).
고 찰
상부요로상피종양은 동측 요로상피에서 다발성으로 발 생하는 경우가 흔하여 (27-36%) 신요관전적출술과 요관구 주위방광점막절제술이 표준적인 치료방법이다. 실제로 방 광종양의 치료 후 병발 또는 재발되는 상부요로상피종양은 1% 전후로 알려져 있으나 상부요로상피종양의 경우에는
30-60%에서 방광종양이 동반되며 수술 후 15-40%에서 방 광재발이 일어난다.10 상부요로상피종양에서 방광종양이 병발 또는 재발되는 기전은 field change에 의한 multicen- tricity와 tumor cell implantation으로 설명되며 상부요로상피 종양에서 방광종양으로 재발되는 기간이 방광종양에서 상 부요로상피종양으로 재발되는 기간의 절반 정도이다.11,12 그러나 이처럼 수술 후 방광재발이 흔함에도 불구하고 재 발에 관여하는 위험인자에 대해서는 여전히 논란이 많다.
상부요로상피종양의 방광재발에 관여하는 위험인자에 대한 지금까지의 연구에서는 대체로 병리조직학적 소견이 중요한 인자로 인정되고 있다. 종양의 크기와 관련하여 Hisataki 등9과 Koga 등13은 종양의 크기가 방광재발에 영향 을 미치지 않는다고 하였으나, Raman 등14은 단변량 분석에 서는 크기가 큰 종양에서 더 많은 방광재발을 보였으나, 다 변량 분석결과 유의한 차이를 보이지 않았다고 하였고, 저 자들의 경우에도 같은 결과를 보였다. 종양의 다발성과 관 련하여 Kim 등7과 Kim 등8은 다발성 병소를 보이는 경우 방광종양의 재발에 영향을 미치지 않는다고 보고하였으나, Hisataki 등9, Matsui 등15과 Kang 등16은 저자들의 경우와 마 찬가지로 다발성 병소를 보이는 경우 방광재발과 관련이 있다. 종양의 병기 및 분화도와 관련하여 Hall 등17은 252례 의 상부요로상피종양 환자에서 종양의 분화도와 병기가 술 후 방광종양의 재발에 영향을 미친다고 하였고, Badala- ment 등18과 Cozad 등19도 유사한 결과를 보고하였으나 다변 량 분석에서 종양의 병기만이 영향을 미친다고 주장하였 다. 또한 Hisataki 등9은 pTa-1 병기보다 pT2-4에서 더 높은 방광재발을 보였다고 하였다. Morioka 등20은 상부요로상피 종양 환자의 생존에 영향을 주는 인자가 pT 병기라고 하였 Table 3. Multivariate analysis for intravesical recurrence by Cox's
proportional hazards model
ꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚ Standard
Variables Hazard ratio 95% CI p-value
error
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ
Age 1.656 0.864-3.175 0.332 0.129
Cuff resection 0.872 0.430-1.767 0.360 0.704 Pathologic T stage 2.180 1.104-4.304 0.347 0.025 Multiplicity 3.539 1.260-9.939 0.527 0.016
WHO grade 1.473 0.631-3.437 0.432 0.371
Size 1.590 0.803-3.147 0.349 0.184
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ CI: confidence interval
Fig. 2. The Kaplan-Meier curve shows the overall survival of patients with upper tract urothelial tumor who are with and without subsequent bladder tumor: there is no statistically significant dif- ference between the two groups (p=0.649).
으며 방광재발에는 특별한 인자를 발견하지 못하였으나, 분화도가 높으면 침윤성 방광종양 재발에 영향을 준다고 보고하였다. Kim 등8은 단변량 분석에서 종양의 병기와 분 화도가 방광재발에 영향을 주었으나 다변량 분석에서는 종 양의 병기만이 유의하다고 하였다. 저자들의 경우에도 단 변량 분석에서는 병기와 분화도가 유의한 결과를 보였으나 다변량 분석에서는 분화도는 유의하지 않고 병기만 유의한 결과를 보였다. 종양의 형태와 관련하여서는 Hisataki 등9과 Matsui 등15은 본 연구와 같이 종양의 형태가 방광종양의 재 발과 관련이 없다고 보고하였다.
상부요로상피종양의 방광재발과 관련하여 술 전 인자들 은 대체로 방광재발에 연관이 없다고 알려져 있다. 먼저 환 자의 성별과 연령은 대체로 방광재발과 관련이 없으 며,12,15,21,27
육안적 혈뇨 유무도 방광재발에 관련이 없다.16 술 전 요세포검사가 환자의 예후나 방광재발에 영향을 미 치는지에 대해서는 논란이 있어 더 많은 연구가 필요하다.
Koga 등13은 술 전 요세포검사가 방광재발에 영향을 미치지 않는다고 보고하였으나 Kim 등7은 수술 전 요세포검사가 술 후 방광종양 재발의 유일한 예후인자로 보고하였고 저 자들의 경우 술 전 요세포검사 결과는 방광재발에 영향을 미치지 않았다.
수술방법에 따른 종양의 재발에 대한 연구들도 논란이 있는데 Strong과 Pearse22는 상부요로상피종양에서 근치적 신적출술, 신적출술과 부분요관절제술, 신요관전적출술, 신 요관전적출술과 요관구주위방광점막절제술을 시행한 경우 잔여 요관에서 재발률은 각각 42%, 25%, 22%, 0%로 보고하 면서 잔여 요관의 길이가 종양의 재발과 연관이 있다고 주 장하였다. 그러나 Stoller 등23은 예후는 수술방법보다 종양 의 악성도와 병기에 더욱 관계가 있다고 하였으며, Wallace 등24은 신절제술만 시행한 군과 신요관절제술을 시행한 군 사이의 예후에 별다른 차이가 없다고 보고하였다. 국내에 서는 Jeong 등5과 Kim 등8이 요관구주위방광점막절제술을 시행 유무에 따른 방광 재발에 유의한 차이가 없다고 보고 하였고, 저자들의 경우에도 요관구주위방광점막절제술과 종양과 절제면 간의 거리는 방광재발에 영향을 미치지 않 았다. 최근 복강경 술기의 발달로 인해 상부요로상피종양 에서도 복강경 술기가 널리 이용되고 있는데 복강경수술 후의 방광재발이나 예후는 대부분 보고에서 본 연구결과와 마찬가지로 개복술과 대등하였다.13,25,26
또한 상부요로상피종양의 술 후 병리조직검사에서 종양 의 병기가 높거나 절제면 양성인 경우 국소재발과 전이를 방지하기 위하여 보조적인 항암화학요법을 시행하는데 이 러한 항암요법이 방광재발을 줄일 수 있는지에 대해서도 논란이 있다. 예를 들면 Hisataki 등9은 69례의 상부요로상피
종양 환자에 대한 근치적 수술 후 43.5%에서 항암요법을 시행한 결과 항암요법이 방광종양 재발에 영향을 미치지는 않는다고 하였고, Igawa 등27도 요로상피종양 환자에 대한 M-VAC 항암화학요법이 방광종양의 속발에 영향을 미치지 않는다고 하였다. 한편 Maase 등28과 Koga와 Naito29는 이행 상피세포암에서 M-VAC과 GC 항암요법은 방광재발을 포 함한 효과면에서 차이는 없고, GC가 부작용이 적다고 하였 다. 저자들의 경우에도 M-VAC군과 GC군 간에 방광재발률 의 차이는 없었다.
한편, 방광재발이 환자의 생존에는 영향이 없다고 보고 되었는데 그 이유는 수술 후 철저한 방광경 검사로 방광암 이 조기에 발견되고 치료되기 때문이라고 하였다.6,30 저자 들의 경우에도 방광재발 유무는 생존에 영향을 주지 않았 다.
결 론
상부요로상피종양에서 근치적 수술 후 방광재발과 관련 된 단변량 분석에서 종양의 크기, 다발성, 병기, 분화도가 중요한 인자로 나타났고, 다변량 분석에서는 종양의 다발 성과 병기가 방광종양의 재발에 독립적인 인자로 나타났 다. 따라서 처음 진단 시 병기가 높거나 다발성 병소를 보이 는 상부요로상피종양 환자들은 술 후 방광재발에 대한 적 극적인 추적 검사가 필요하다고 생각한다.
REFERENCES
1. Fraley EE. Cancer of the renal pelvis. In: Skinner DG, deKernion JB, editors. Genitourinary Cancer. Philadelphia:
Saunders; 1978;134
2. Huben RP, Mounzer AM, Murphy GP. Tumor grade and stage as prognostic variables in upper tract urothelial tumors. Cancer 1988;62:2016-20
3. Resseguie LJ, Nobrega FT, Farrow GM, Timmons JW, Worobec TG. Epidemiology of renal and ureteral cancer in Rochester, Minnesota, 1950-1974, with special reference to clinical and pathologic features. Mayo Clin Proc 1978;53:
503-10
4. Sakamoto N, Naito S, Kotoh S, Nasashima M, Nakamura M, Ueda T, et al. Recurrence following surgery for primary renal pelvic and ureter cancer-clinicopathologic analysis of distant metastasis. Nippon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi 1992;83:658-63 5. Jeong IG, Kwak C, Jeong H, Lee ES, Lee CW, Lee SE.
Carcinoma of the upper urinary tract: clinical analysis on patients during recent 10 years. Korean J Urol 2003;44:22-7 6. Park SC, Hong BS, Kim YJ, Kim CS, Ahn HJ. Prognostic
factors for survival in the transitional cell carcinoma of the
upper urinary tract. Korean J Urol 2003;44:1087-92 7. Kim GP, Kim HH, Oh BR, Kim HJ, Ryu SB, Park YK, et
al. Risk factors for subsequent bladder tumor in upper tract urothelial tumor. Korean J Urol 2001;42:1258-64
8. Kim KH, Park JS, Kim CI, Lee KS. Risk factors for the development of bladder transitional cell carcinoma following surgery for transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. Korean J Urol 2005;46:229-33
9. Hisataki T, Miyao N, Masumori N, Takahashi A, Yanase M, Itoh N, et al. Risk factors for multiple intravesical recurrences of superficial bladder cancer. Urology 2001;58:935-9 10. Miyake H, Hara I, Arakawa S, Kamidono S. A clinico-
pathological study of bladder cancer associated with upper urinary tract cancer. BJU Int 2000;85:37-41
11. Wolf H, Hojgaard K. Prognostic factors in local surgical treatment of invasive bladder cancer, with special reference to the presence of urothelial dysplasia. Cancer 1983;51:1710-5 12. Mahadevia PS, Karwa GL, Koss LG. Mapping of urothelium
in carcinomas of the renal pelvis and ureter. A report of nine cases. Cancer 1983;51:890-7
13. Koga F, Nagamatsu H, Ishimaru H, Mizuo T, Yoshida K. Risk factors for the development of bladder transitional cell carcinoma following surgery for transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. Urol Int 2001;67:135-41
14. Raman JD, Ng CK, Boorjian SA, Vaughan ED Jr, Sosa RE, Scherr DS. Bladder cancer after managing upper urinary tract transitional cell carcinoma: predictive factors and pathology.
BJU Int 2005;96:1031-5
15. Matsui Y, Utsunomiya N, Ichioka K, Ueda N, Yoshimura K, Terai A, et al. Risk factors for subsequent development of bladder cancer after primary transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. Urology 2005;65:279-83
16. Kang CH, Yu TJ, Hsieh HH, Yang JW, Shu K, Huang CC, et al. The development of bladder tumors and contralateral upper urinary tract tumors after primary transitional cell car- cinoma of the upper urinary tract. Cancer 2003;98:1620-6 17. Hall MC, Womack S, Sagalowsky AI, Carmody T, Erickstad
MD, Roehrborn CG. Prognostic factors, recurrence, and sur- vival in transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract:
a 30-year experience in 252 patients. Urology 1998;52:594- 601
18. Badalament RA, O'Toole RV, Kenworthy P, Young DC, Keyhani-Rofagha S, Simon J, et al. Prognostic factors in
patients with primary transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. J Urol 1990;144:859-63
19. Cozad SC, Smalley SR, Austenfeld M, Noble M, Jennings S, Raymond R. Transitional cell carcinoma of the renal pelvis or ureter: patterns of failure. Urology 1995;46:796-800 20. Morioka M, Jo Y, Furukawa Y, Kinugawa K, Sone A, Matsuki
T, et al. Prognostic factors for survival and bladder recurrence in transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. Int J Urol 2001;8:366-73
21. Anderstrom C, Johansson SL, Pettersson S, Wahlqvist L.
Carcinoma of the ureter: a clinicopathologic study of 49 cases.
J Urol 1989;142:280-3
22. Strong DW, Pearse HD. Recurrent urothelial tumors following surgery for transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. Cancer 1976;38:2173-83
23. Stoller ML, Gentle DL, McDonald MW, Reese JH, Tacker JR, Carroll PR, et al. Endoscopic management of upper tract urothelial tumors. Tech Urol 1997;3:152-7
24. Wallace DM, Whitfield HN, Hendry WF, Wickham JE. The late results of conservative surgery for upper tract urothelial carcinomas. Br J Urol 1981;53:537-41
25. El Fettouh HA, Rassweiler JJ, Schulze M, Salomon L, Allan J, Ramakumar S, et al. Laparoscopic radical nephroureterec- tomy: results of an international multicenter study. Eur Urol 2002;42:447-52
26. Tsujihata M, Nonomura N, Tsujimura A, Yoshimura K, Miyagawa Y, Okuyama A. Laparoscopic nephroureterectomy for upper tract transitional cell carcinoma: comparison of la- paroscopic and open surgery. Eur Urol 2006;49:332-6 27. Igawa M, Urakami S, Shiina H, Ishibe T, Kadena H, Usui T.
Long-term results with M-VAC for advanced urothelial cancer:
high relapse rate and low survival in patients with a complete response. Br J Urol 1995;76:321-4
28. Von der Maase H, Sengelov L, Roberts JT, Ricci S, Dogliotti L, Oliver T, et al. Long-term survival results of a randomized trial comparing gemcitabine plus cisplatin, with methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, plus cisplatin in patients with bladder cancer. J Clin Oncol 2005;23:4602-8
29. Koga H, Naito S. Recent progress in the treatment for urothelial cancer. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 2006;33:164-70 30. Son YW, Lee JJ, Woo YN. Prognostic factors in transitional
cell carcinoma of the renal pelvis: multivariate analysis.
Korean J Urol 2002;43:202-7