Vol. 12, No. 2, November, 1998 □ 원 저 □
신이식 초기에 있어서 착상신생검과 급성거부반응과의 상관관계
한림대학교 의과대학, 강동성심병원 외과학교실 및 1해부병리과학교실
이필립・구대진・이삼열・김주섭 남은숙1・김수태・최창식
= Abstract =
Relationship of Renal Implantation Biopsies and Acute Rejection during Immediate Posttransplantation Period
Philip Lee, M.D., Dae Jin Koo, M.D., Samuel Lee, M.D.
Joo Seop Kim, M.D., Eun Sook Nam, M.D.1, Soo Tae Kim, M.D.
and Chang Sig Choi, M.D.
Department of Surgery and 1Pathology, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University
Many factors can be recognized for the acute rejection such as: degree of HLA mismatching, cytokine gene expression, ischemic time, etc. Some authors have suggested the importance of early routine biopsy of renal allograft to predict acute rejection. This prospective study on renal implantation biopsies was performed to evaluate the relationship between the implantation biopsies and the acute rejection during the immediate post-transplantation period.
From December 1996 to February 1998 implantation biopsies were performed on 46 renal allografts within 40~60 minutes after vascular anastomosis using tru-cut needle (18G). Two samples were obtained from transplanted kidney in each patient. Serial sections were stained for the light microscopic examination. The slides were evaluated for histologic features such as interstitial cellular infiltration, nephrosclerosis, tubular damage, glomerular neutrophil count (GL-PMN), and peritubular neutrophil count (PTC-PMN). Forty six biopsies were grouped into acute rejection group (R group, n=10) and non-rejection group (N group, n=36) during immediate posttransplantation period (1 month). Acute rejections were confirmed by ultrasonography guided biopsy. Histologic findings were classified according to Banff schema. The statistical analysis was performed by using Chi-Square Test and Spearman Rank Sum Test.
During the immediate post-transplantation period, acute rejection developed in 10 cases (21.7%) of which 9 cases were the biopsy-proven rejection. The male to female ratio was 21:25. Recipients were ranged from 22 to 54 years old with a mean age of 38.2 9.1. Original disease of recipient were chronic glomerulonephritis in 15 cases (32.6%), hypertension in 8 cases, diabetes mellitus in 3 cases, RPGN in 2 cases. Fifteen cases (32.6%) were of unknown etiology. The mean number of HLA mismatches was 4.6 0.9 in R group, 4.7 1.2 in N group, and the mean number of HLA-B & DR mismatches was 2.2 0.4 in R group, 2.3 0.7 in N group. The ratio of the living vs. cadaveric donors was 34:12.
No statistical difference was observed between two groups in interstitial cellular infiltration, nephrosclerosis and tubular damage. The GL-PMN was 0.6 0.9 in R group, while 0.1 0.4 in N group.
275
서 론
신장이식후 거부반응은 이식신의 예후에 많은 영 향을 미치며, 이에는 초급성, 가속성, 급성, 만성 거 부반응 등이 있다. 이들은 각기 특징적인 병리조직 학적 소견과 면역학적인 기전을 나타내고 있다. 거 부반응의 진단에는 임상적인 경과, 혈청학적 검사, 소변검사, 도플러 초음파 및 이식신의 조직생검 등 이 사용된다. 거부반응중 초급성이나 만성거부반응 은 일단 발생하면 거의 치료가 불가능하여, 거부반 응치료약제에 가역적으로 반응하는 급성거부반응과 구별된다. 현재 다양한 면역억제제의 개발로 인하여 거부반응의 발생빈도 감소 및 이식신의 장기 생존 율이 증가되고 있으나, 거부반응의 발생 자체를 예 방하지는 못하고 있는 실정이다.
신장이식후 급성거부반응은 대개 수술후 1~3개
월사이에 일어나며, 급성거부반응은 수술후 이식편 의 예후를 결정하는 가장 중요한 요소중 하나이다.
따라서, 신이식후 급성거부반응을 예측하기 위한 노 력이 계속되어 왔으며, 그 예로서 인체백혈구항원 (human leukocyte antigen, HLA)의 비적합성, cytokine 유전자 발현,1) 허혈손상 등에 관한 많은 연구들이 있다. 또한 여러 연구자에 의해 조기 신이식편 생검 이 급성거부반응을 예측하는데 중요하다고 보고되 고 있다.2~10) 특히 신이식수술중 혈관문합완료후 시 행한 착상신생검소견과 급성거부반응과의 관계에 대한 연구들이 많이 보고되고 있다.2,4,11) 저자들은 전향적인 연구를 통하여 수술중 이식편의 착상신생 검 소견이 수술후 초기 기간중 급성거부반응과 어 떠한 관계가 있는지 살펴보고자 하였다.
대상 및 방법
1996년 12월부터 1998년 2월까지 한림의료원 강 The PTC-PMN was 5.3 3.3 in R group and 0.3 1.1 in N group (p<0.05). The presence of more than five PTC-PMN count was related with the occurrence of acute rejection (p<0.01). In conclusion, the PTC-PMN of renal implantation biopsies is a possible predicting factor for acute rejection in this preliminary report.
Key Words: Renal implantation biopsy, Acute rejection
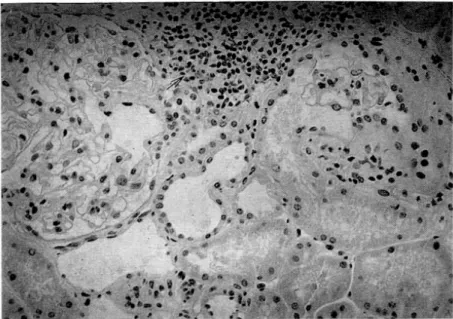
Fig. 1. Interstitial cellular infiltration (grade I); Focal periglomerular lymphocyte infiltration(arrow)., 200. H&E stain.
동성심병원에서 시행한 신장이식중 신이식편의 착 상생검을 시행한 51예 중에서 생검조직양이 불충분 하거나 고정에 실패했던 5예를 제외한 46예를 대상 으로 하였다. 이식된 신장의 착상생검은 혈관문합완 료후 40~60분 이내에 시행하였으며 18G의 tru-cut
needle을 이용하여 이식편의 상극부에서 2회 시행하 였다. 생검조직은 Dubosque-Brazil 용액에 고정하고, hematoxylin-eosin, periodic acid-Schiff, Masson' s tri- chrome, Jones' silver 등의 염색법으로 광학 현미경 하에서 다음의 조직학적 변화를 관찰하고 정도에
Fig. 2. Nephrosclerosis (grade II); Prominent fibrosis of the media of interlobular arteries(arrow) and arterioles(small arrows)., 200. Masson' s trichrome stain.
Fig. 3. Tubular damage (grade II); There are loss of brush borders, flattening and dilatation of tubular epithelial cells., 400. Masson' s trichrome stain.
따라 다음과 같이 분류하였다.
1) 간질세포침윤(interstitial cellular infiltration)
grade 1; 경도의 국소적 사구체주위 또는 혈관주 위 침윤(Fig. 1)
grade 2; 경도 내지 중등도의 미만성침윤 또는 중 등도의 국소적 침윤
2) 신경화증(nephrosclerosis)
grade 1; 혈관 중막을 넘지않는 내막비후 grade 2; 혈관 중막을 넘는 내막비후(Fig. 2)
3) 세뇨관 손상(tubular damage)
grade 1; 쇄자연 (brush border)이 소실된 세뇨관 확장
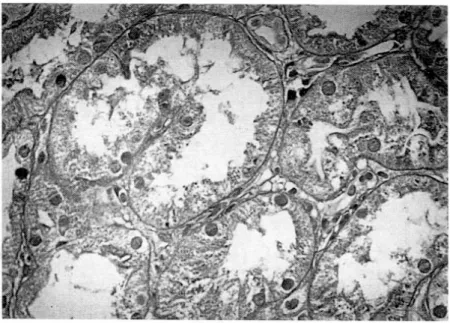
Fig. 4. Glomerular neutrophil count; Glomerular capillaries contains neutrophils(arrows)., 400. H&E stain.
Fig. 5. Peritubular neutrophil count; Dilated peritubular capillaries contains neutrophils(arrow)., 400.
H&E stain.
grade 2; 세뇨관 상피세포손실과 기저막의 탈락 (Fig. 3)
4) 사구체 호중구치(glomerular neutrophil count)
전사구체내에서 관찰된 호중구치를 관찰한 사구 체 개수로 나눈 평균치(Fig. 4)
5) 세뇨관주위 호중구치(peritubular neutrophil count)
연속된 10개의 고배율시야(400배)에서 관찰된 세 뇨관주위 호중구치의 전체 개수(Fig. 5)
수여자의 급성거부반응 관찰기간은 이식후 1개월 간이었으며, 임상적으로 거부반응이 의심되면 steroid 충격요법을 시작하기전, 초음파를 이용한 신생검을 시행하였고, 조직학적 진단은 Banff 분류법12)을 따랐 다. 수여자의 만성신부전의 원인질병, 공여자와 수 여자 간의 HLA 부적합성, HLA B, DR항원의 부적 합성, ABO 혈액형 적합성, 공여자와 수여자의 성별 조합, 혈연관계, 수술후 2일째 혈청 creatinine 수치등 을 조사하고, 이들 각 인자들이 이식술후 1개월내 거부반응과 관계있는지 여부를 함께 분석하였다.
급성거부반응과 각 변수의 상관관계에 대한 통계 학적 분석은 chi-square test 및 Spearman rank sum test를 시행하였다.
결 과
연구기간중 대상환자 46예 중에서 신이식술후 1 개월내에 급성거부반응이 발생한 경우는 10예(21.7%) 이었으며, 이중 1예를 제외한 9예에서 초음파 검사 유도하에 신생검을 시행하여 조직학적으로 급성거 부반응을 진단하였다. 신이식술후 1개월내에 급성거
부반응이 발생하였던 10예(21.7%)를 R군, 거부반응 이 없었던 나머지 36예(88.3%)를 N군으로 분류하였 다(Table 1).
만성신부전의 원인 질병은 만성사구체신염이 15 예(32.6%)로 가장 많았으며, 그밖에 고혈압이 8예, 당뇨병 3예, 급속진행성 사구체신염 2예, 다낭신 1 예, 통풍성 신염 1예, Alport 증후군 1예 등이었고, 원인 불명인 경우가 15예 (32.6%)이었다.
1) 수여자의 연령 및 성별 분포
대상 환자는 남자와 여자가 각각 21, 25명이었고 연려운포는 24세에서 54세까지로서 평균연령은 38.2 세였다. 그 중 R군과 N군의 평균 연령은 36.8 9.4 세, 38.6 9.2세로서 두군간의 통계학적 유의한 차이 는 없었다. R군과 N군의 남녀비는 각각 19:2, 18:
7로서 여자에서 거부반응이 적은 경향을 보였으나 통계학적인 의미는 없었다.
Table 1. Comparison between patients with rejection and non-rejection group HLA HLA B & DR
Age GM-PMN* PTC-PMN**
mismatches mismatches
Non-rejection 38.5 9.2 4.7 1.2 2.3 0.7 0.14 0.38 0.3 1.6 Rejection 36.8 9.4 4.6 0.9 2.2 0.4 0.64 0.85 5.2 3.3
All 38.2 9.1 4.7 1.1 2.3 0.6 2.8 2.3
p-value NS† NS† NS† NS† 0.0021
*GL-PMN; glomerular neutrophil count, †NS; not significant, **PTC-PMN; peritubular neutrophil count Fig. 6. ABO incompatibility.
2) 공여자와 수여자의 HLA 적합성과 ABO 적 합성
전체 HLA 비적합 항원수는 R군에서 4.6 0.9, N 군에서 4.7 1.2이었고, HLA-B 및 DR의 비적합 항 원수는 R군과 N군이 각각 2.2 0.4, 2.3 0.7로서 유 의한 차이는 없었다. 공여자와 수여자간 ABO 혈액형 적합성은 완전일치와 적합이 각각 38예(82.6%), 8예였 으며 R군과 N군간의 유의한 차이는 없었다(Fig. 6).
3) 공여자와 수여자 사이의 성별 조합
공여자의 성별에 상관없이 수여자가 남자인 경우 거부반응이 25예 중 8예(32%)에서 발생한데 비하여 수여자가 여자인 경우 급성거부반응이 21예 중 2예 (9.5%)로 적게 발생한 경향을 보였으나 통계학적인 유의한 차이는 관찰되지 않았다(p=0.065, Fig. 7).
4) 혈연관계
생체이식과 사체 이식은 각각 34예(73.9%)와 12예 (26.1%)였으며, 생체이식 중 형제간 이식이 7예, 부 모-자식간 이식이 3예로서 혈연간생체이식은 모두 10예였고, 비혈연생체이식은 24예였다. 각각의 혈연 관계와 거부반응의 발생빈도간에 특별한 상관관계 가 없었다(Fig. 8).
5) 이식수술후 2일째 혈청 creatinine
이식수술 2일후 혈청 creatinine이 2.0 mg/dl 이하 인 경우가 11예(23.9%)였으며, 2.0 이상인 경우가 35 예(76.1%)였는데, 거부반응의 유무와 상관관계는 없 었다(Fig. 9).
6) 착상신생검
(1) 간질세포침윤: R군의 grade 0,1 간질세포침윤 Fig. 7. Donor to recipient sex relation.
Fig. 8. Relation between donor and recipient.
Fig. 9. Creatinine below 2 mg/dl after posttransplantation day 2.
Fig. 10. Interstitial cellular infiltration.
은 각각 9예(90%), 1예(10%)였고, N군은 각각 29예 (80.6%), 7예(19.4%)였다(Fig. 10).
(2) 신경화증: R군에서 grade 0, 1, 2의 신경화증은 각각 5(50%), 2(20%), 3(30%)예였고, N군에서 grade 0, 1, 2의 신경화증은 각각 20(55.6%), 11 (30.6%), 5예 (13.8%)였으며, 양군간의 통계학적인 유의한 차이는 관찰되지 않았다(Fig. 11).
(3) 세뇨관 손상: R군의 grade 0, 1, 2의 세뇨관 손 상은 각각 8(80%), 2(20%), 0예였고, N군은 각각 27(75%), 7(19.4%), 2(5.6%)예였으며 양군간의 통계학 적으로 유의한 차이는 관찰되지 않았다(Fig. 12).
(4) 사구체 호중구치: 사구체내 침윤된 호중구수의 평균치는 R 군이 0.6 0.9로서 N군의 0.1 0.4에 비 해 많은 경향을 보였으나, 생검조직에서 관찰이 가 능한 사구체의 절대수가 1개에서 14개로 일정하지 않아 통계학적인 비교가 불가능하였다.
(5) 세뇨관주위 호중구치: 세뇨관주위에 침윤된 호
중구수의 평균치는 R군이 5.3 3.3, N군이 0.3 1.1 로서 통계적인 유의한 차이가 있었으며(p<0.05), 호 중구수의 cut-off value를 5 이상으로 정하였을 때 가 장 뚜렸한 차이가 관찰 되었다(p<0.01, Fig. 13).
고 찰
과거에는 거부반응을 발생 시기에 따라 분류하였 으나, 현재는 거부 반응의 발생시기에 따른 분류는 의미가 없는 것으로 되어 있으며, 실제로 신이식후 1년 이상 경과한후에도 급성거부반응이 발생하는 경우를 볼 수 있다. 이식후 거부반응의 발생시기에 대해, Gulanikar등13)은 이식후 1개월동안 35%에서 최 초 급성거부반응이 발생하고, 3개월까지 50%에서 급성거부반응이 일어나며, 3개월 이후에는 시간 경 과에 따라 급성거부반응의 발생빈도가 점차 감소한 다고 하였다. 그러나 Rao등14)은 신이식후 10년 이상 경과한 환자중 22%에서 만발성(delayed onset acute rejection) 거부반응이 발생했다고 보고하여, 거부반 응의 발생시기별 분류는 큰 의미가 없다고 하였다.
다양한 거부반응중 실제로 치료에 가역적인 반응을 보이는 것은 급성거부반응 뿐이며, 초급성 또는 만 성 거부반응은 치료가 불가능하여 이식신의 소실을 초래한다. 신이식후 초기에 있어서 이식신 기능부전 을 동반한 급성 거부반응이 발생하였을 경우, 이식 신의 생존율이 불량하다고 보고되고 있다.15) Leggat 등16)은, 사체 신이식후 1년동안 신기능이 유지된 31,600예의 환자에서 급성 거부반응이 일어난 시점 에 따른 이식신의 장기생존율을 보고하였는데, 1년 동안 거부반응 비발생군에서는 78%의 4년 생존율을 Fig. 11. Nephrosclerosis.
Fig. 12. Tubular damage.
Fig. 13. Peritubular neutrophil count.
보인데 반해, 1개월, 2~6개월, 7~12개월사이의 거 부반응군의 생존율이 각각 72%, 69%, 54%로 현저 한 차이가 있다고 하였다.
신이식수술중 혈관 문합이 끝나고 재혈류가 시작 된 직후 시행하는 착상신생검이 이식수술후 초기에 급성거부반응의 발생을 예측할 수 있는지에 대한 많은 연구가 있었는데,2,4,11) Balch등17)은 간질세포침 윤이 휴지기 동안 선행하며, 이 때 세포침윤의 표현 형은 거부반응의 발생을 결정하는데 중요하다고했 다.2,18) 신경화증은 고령 공여자의 신장에서 흔히 보 는 소견이며, 그 정도가 높으면 급성거부반응이 일 어날 가능성이 높다. Gaber등19)에 의하면, 신경화증 의 표지자로서 사구체경화증이 20% 이상인 군에서 이식신의 조기 소실 위험도가 증가하며, 6개월 및 12개월에서의 이식신기능 저하가 관찰된다고 하였 고, 이로 인해 장기적출전 혈중 creatinine 수치가 정 상범위라 할지라도, 50세 이상의 고령 공여자 및 비 외상성 뇌졸중 공여자에서 신생검을 시행하여야 한 다고 하였다. 또 착상신생검에서 세뇨관 주위 모세 혈관에서 호중구치가 7개 이상인 경우, 급성 거부반 응을 예측할 수 있고, 평균 사구체주위 호중구치는 이식신의 허혈성 손상 및 이식신 소실과 관련이 있 으며, 현격히 높은 평균 사구체주위 호중구치는, 높 은 세뇨관주위 호중구치를 동반할 경우, 초급성 거 부반응과 밀접한 관련이 있다고 하였다.4) 본 연구에 서는 사구체내 호중구침윤은 관찰대상인 사구체의 수가 매우 다양하여 비교의 의미가 없었으며, 이는 착상생검시 충분한 신피질 조직을 얻는데 실패하였 기 때문인 것으로 사료된다. 이에 반해 세뇨관주위 호중구침윤은 거부반응이 일어난 군에서 유의하게 증가하였으며, 호중구치 5개 이상인 경우, 1개월내 급성 거부반응의 발생과 밀접한 관련이 있음을 알 수 있었다. 급성거부반응이 발생했을 때 사구체와 세뇨관주위 모세혈관에서 호중구 침윤이 차이가 있 는 것은 두 조직의 내막의 혈관내막세포(vascular endothelial cell) 항원발현에 차이가 있기 때문인 것 으로 여겨진다.20,21) 즉 혈관내막세포 항원은 사구체 주위 모세혈관내막에 비해 세뇨관주위 모세관 내막 에 더 높은 빈도로 발현되며 이로 인해 호중구 침 윤이 세뇨관주위 모세혈관에 증가하게 되는 것이다.
결 론
본 연구를 통해서 세뇨관주위 모세혈관내 호중구 치는 거부반응발생군과 비발생군간에 유의한 차이 를 보였으며, 호중구치가 5 이상일 때 가장 뚜렷한 차이가 관찰되었다(p<0.01). 따라서 신이식시 착상 신생검은 술후 1개월내의 급성거부반응의 발생을 예측하는데 있어서 유용한 지표로 여겨진다.
REFERENCES
1) McLean AG, Hughes D, Welsh KI, et al: Patterns of graft infiltration and cytokine gene expression during the first 10days of kidney transplantation. Trans- plantation 63: 374, 1997
2) Burdick JF, Beschorner WE, Smith WJ, McGraw D, Bender WL, Williams GM, Solez K: Characteristics of early routine renal allograft biopsies. Transplan- tation 38: 679, 1984
3) Cahen R, Dijoud F, Couchoud C, Devonec M, Trolliet P, Adeleine P, Fendler JP, Joubert P, Perrin P, Francois B: Evaluation of renal grafts by pretransplant biopsy. Transplant Proc 27: 2470, 1995
4) Gaber LW, Gaber AO, Tolley EA, Hathaway DK:
Prediction by postrevascularization biopsies of cad- averic kidney allografts of rejection, graft loss, and preservation nephropathy. Transplantation 53: 1219, 1992
5) Kon SP, Templar J, Dodd SM, Rudge CJ, Raftery MJ:
Diagnostic contribution of renal allograft biopsies at various intervals after transplantation. Transplantation 63: 547, 1997
6) Rush DN, Henry SF, Jeffery JR, Schroeder TJ, Gough J: Histological findings in early routine biopsies of stable renal allograft recipients. Transplantation 57:
208, 1994
7) Rush DN, Jeffery JR, Gough J: Protocol biopsies in stable renal transplant patients under triple immuno- suppression: results at 6 months. Transplant Proc 26:
2756, 1994
8) Rush DN, Jeffery JR, Gough J: Sequential protocol biopsies in renal transplant patients: repeated inflam- mation is associated with impaired graft function at 1 year. Transplant Proc 27: 1017, 1995
9) Rush DN, Jeffery JR, Gough J: Sequential protocol biopsies in renal transplant patients: clinico-path-
ological correlations using Banff schema. Transplanta- tion 59: 511, 1995
10) Seron D, Moreso F, Bover J, Condon E, Gil-Vernet S, Canas C, Fulladosa X, Torras J, Carrera M, Grinyo JM, Alsina J: Early protocol renal allograft biopsies and graft outcome. Kindey Int 51: 310, 1997 11) Vazquez MC, Schiavelli RO, Sabbatiello R, Casti-
glioni T, Pattin M: Intraoperative renal biopsy and its relation to renal function at the end of the first year posttransplantation. Transplant Proc 28: 372, 1996 12) Solez K, Benediktsson H, Marcussen N, Olsen S, Ra-
cussen LC, et al: International standardization of cri- teria for the histologic diagnosis of renal allograft rejection: The Banff working classification of kidney transplant pathology. Kidney International 44: 411, 1993
13) Gulanikar AC, Macdonald AS, Sungurtekin U, et al:
The incidence and impact of early rejection episodes on graft outcome in recipients of first cadaver kidney transplants. Transplantation 53: 323, 1992
14) Rao KV, Kasiske BL, Bloom PM: Acute graft re- jection in the late survivors of renal transplantation.
Transplantation 47: 290, 1989.
15) Cosio FG, Pelletier RP, Falkenhain ME, Henry ML, Elkhammas EA, Davies EA, Bumgardner GL, Fer- guson RM: Impact of acute rejection and early al- lograft function on renal allograft survival. Trans-
plantation 63: 1611, 1997.
16) Leggat JE Jr, Ojo AO, Leichtman AB, Port FK, Wolfe RA, Turenne MN, Held PJ: Long-term renal allograft survival: prognostic implication of the timing od acute rejection episodes. Transplantation 63: 1268, 1997 17) Balch CM, Wilson CB, LEE S, Feldman JD: Thymus-
dependent lymphocytes in tissue sections of rejecting rat renal allograft. J Exp Med 138: 1584, 1973 18) Seron D, Moreso F, Condom E, Carrera M, Canas C,
Cruzado JM, Soto K, Gil-Vernet S, Torras J, Castelao AM, Grinyo JM, Alsina J: Evaluation of interstitial lesions in well-functioning renal allografts. Transplnat Proc 27: 2213, 1995
19) Gaber LW, Moore LW, Alloway RR, Amiri MH, Vera SR, Gaber AO: Glomerulosclerosis as a determinant of posttransplant function of older donor renal al- lografts. Transplantation 60: 334, 1995
20) Baldwin WM III, Class FHJ, VanEs LA, Van Rood JJ: Distribution of endothelial-monocytes and HLA antigens on renal vascular endothelium. Transplant Proc 13: 103, 1981
21) Morozumi K, Oikawa T, Fukuda M, Sugito K, Take- uchi O, Oda A, Fujinami T, Takeda A, Uchida K:
Diagnosis of chronic rejection using peritubular and glomerular capillary lesions. Transplant Proc 28: 508, 1996