大짧放 9‘f 짧뽑!$~ 11" 1tt. 第 24 !{f
m
5 빠 pp. 687 - 691, 1988 Journal of Korean Radiological Society, 24(5) 687-691, 1988급성 백혈병 환자에서 항암제 투여 후 뇌 CT 소견
가툴릭 대 학 의 학부 방사선과학교실
임 준·박석희·김춘열·박용휘 - Abstract-
CT Findings of Brain Atrophy after Chemotheraphy in Acute Leukemia
Lim Jun, M.D., Seog Hee Park, M.D., Choon Yul Kim, M.D., Yong Whee Bahk, M.D.
Department of Radiologκ Catholic University Medical College, Seoul, Korea
A study was performed to evaluate the atrophic changes 01 the central nerve system alter chemotheraphy in the patients with acute leukemia.
The computed tomographic lindings and medical records 01 20 proven acute leukemia patients under 35 years-old who developed various CNS symptoms and signs during and/or alter 2 courses 01 chemotheraphy were reviewed
The results were as lollows
1. Age distribution was lrom 14 to 35 years (mean was 26 years). Male was 15.
2. Presenting clinical symptoms and signs were headache (16/20), nausea and vomiting (11/2이 and loss 01 con sciousness (5/20)
3. Brain atrophy was noted in 16 patients including cortical and subcortical atrophy 15 cases and subcortical atrophy 1 case
4. Two cases 01 hemorrhage, one each 01 intracranial hematoma and chronic subdural hematoma were lound in addition to brain atrophy. -
This showed that chemotherapeutic agents cause brain atrophy in a considerable number 01 the patients with symptomatic acute leukemia.
1. 서 론
뇌 위축은 노인성변화, 파컨슨영 및 대사성질환 둥 1)에 서 흔히 판찰되 며 Dilantin과 같은 약물의 장기 복 용에 의해서 발생될 수 있다2,3) 뿐얀 아니라 Methotrexte( 야하 MTX로 함)를 포함한 항암제에 의 해서도 발생되는 것으로 보고4 , 5) 되었마. 따라서 MTX를 포함한 항암 화학요엽 을 받은 환자에 서 뇌 전 본 논문은 1988 년도 가툴럭중앙의료원 연구보조바로 이 루어진 것임.
이 논문은 1988년 8월 31일에 정수하여 1988년 9월 23 일 에 채택되었음
산화 단층촬영 (이하 CT로 함)에서 뇌 위축소견을 예 상할수가 있마. 과거 항암요법을 받은급성 백혈영환 자에서 뇌백질 변화에 대한 조직뱅리학적 연쿠6,7)는 있었지만, CT를통한뇌위축소견에 대한분석은없었 다.
이에 저자들은 1986년 1월 1일부터 1988년 4월 15 일 까지 가올럭의대 부속성모뱅원을내원하여 급성 백혈 병우로 진단받고, 2회 이 상 MTX를 포함한 항암 화학 요볍을 받은 환자들 중, 두통, 쿠토 등 신경계 임상증 상이 있어 CT를 시행한 35세 이하 20 영을 분석하였 다.
- 687-
大韓放射線훌훌學會註、 : 第 24 卷 第 5 號 1988
II.
대상 및 방법대상은 1986 년 l 월부터 1988년 4월까지 가롤릭대학 부속 성모영원을 내원하여 급성백혈명으로 진단받고,
2회 이상화학요뱀을받은환자들중두통, 구토둥임
이었다.
임상석 증상은 두통(1 6예 ), 오심 및 쿠로 (11 예 ), 의 식소살(5예 ) 둥이 주된 증상이 었다(T able 2).
사용된 약제는 MTX(l2 mg), Prednisolon (60 mg/m2), Vincristine(2. 0 mg) 파 Daunorubicin (40 mg/m2) 이었다.
상증상이 있어 CT를 시행한 35세 이하를 선택 하였고 Table 2. Presenting Syr매toms and Signs 이 중 방사선 뇌조사, 척수강내 MTX 치료를 받은환
자를 제외한 20 명을 분석하였다. 이중 35세 야하를 선 택한 것은, 35세 이상에서는 자연 노화에 따른 생리적 인 뇌위축과8) 화학요법에 의한 헝석 뇌위축이 CT상 감벨이 어려울 것으로 예상되었기 해문이마.
사용한 전산화단층촬영 기 는 Siemens Somatom 2 scanner이었고, 8mm 절펀 두께로 단충촬영을 시행하 였다.
뇌 위축은 뇌피질파 뇌피잘하부로 나누아 측정하였 고, 뇌파질 위축은 전두부에서 대뇌반쿠간열의 간격 (AIF) 과 파질부 최대깐격 (FCS) , 또한 전둔부를 제 외한 대뇌반구 피질구의 최대간격 (CS) 를 측정하였으 여, 두께가 5mm 이상인 경우를 양성으로 보았다9,
뇌피질하부 위축은 양전우부지수 (bifrontal index), 양미상핵지수 (bicaudate index), Evans 지수를 측정 하였고, 각각 0.4, 0.22, 0.32 이상인 경우에 의의를
두었다9.11 , 12)
m.
성 적20영의 급성백혈영 환자 중 남자 15 명, 여자 5 영으 로 연령분포는 Table 1 파 같고 이 중 최연소자는 14세
Table 1. Age Distribution
Symptoms & Signs Headache
Nausea & Vomiting Loss of Consciousness Gait Disturbance Hemiplegia ( )percentage
No. of Patients 16(80) 11(55) 5(25) 3(15) 1( 5)
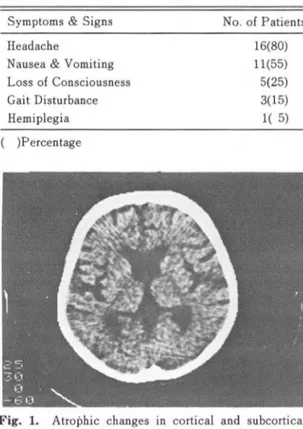
Fig. 1. Atroþhic changes in cortical and subcortical area
CT 소견상 총 20명 중 16 명에서 뇌위축소견을 보였 고,이 중 뇌파질 및 뇌파질하부 위축이 함께 있는 경 우는 10예(Fig. 1), 뇌파잘 위축만 있는 경우는 5예
Age Under 10 11- 15 16-20 21-25 26- 30 31-35
Number of Patients (Fig. 2),
뇌피질 하부 위축만 보이는 것은 1예
(FigTotal )Percentage
0(0) 2(10) 4(20) 3(15) 8(40) 3(15) 20(100)
3) 이었으며, 위축이 동안되지 않은 경우는 4예이었다 (Table 3).
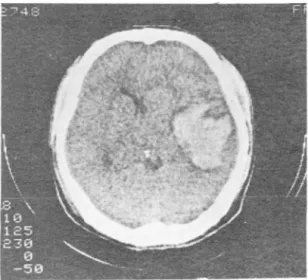
이 외 우연히 대 뇌 혈종 (Fig.4) 및 만성 경 악하혈종 (Fig. 5) 이 2예에서 판찰되었다.
N.
고 찰저자들의 CT 소견 분석결파 20예중 16예(80% )에
- 영 준 외 : 급성 백혈병 환자에서 항암제 투여 후 뇌 CT 소견 -
Fig. 2. Atrophic changes in cortical area
Fig. 3. Atrophic changes in subcortical area
Table 3. Prevalance of Atrophy
L。 cationof Atrophy
Cortical &
Subcortical atrophy Cortical atrophy Subcortical atrophy Without atrophy Total
( )percentage
No. of Patients 10(50)
5(25) 1( 5) 4(20)
20(1 00)
서 뇌피질과 뇌피질하부 뇌위축소견을 나타냈다.
CT에서는 뇌척수액이 저음영으로 나타냐 뇌피질과 뇌조의 영상이 쉽게 판찰되므로 13.14) 가뇌술같은 침습 적인 방엽이 아니더라도 뇌위축의 진단이 용이하마.
헨재까지 CT를 이용한 뇌위혹의 측정방엽은 여러 학
자들에 의해 연구 발표되 었다9.11.15)
뇌위축의 원인은 여러가지가 있으며 1) 이 중 항암 제를 포함한 약물에 의한 뇌위축은 정상인의 노인성 뇌위축파 같은 형태를 취하게 된다고 한다16.17) 이러 한소견은 CT상 뇌펴질 위축을 나타내는 양측 실비안 열파 전두부옐 및 양두부열의 지주막하공간의 확장과 뇌파질하위축소견인 뇌실강의 크기가 커지는 현상무 로 나타난다.
이제까지 급성백혈뱅 환자에서 항암제투여 후 뇌백 질의 변화에 관한 CT 소견을 발표되 었지 만 CT상 뇌 위축 소견에 판한 체계적연구는 없었마 18)
MTX를 포함한 항암제 투여후에 뇌위축이 딸생하판 정확한기전에 대해서는아직 밝혀지지 않았지만뇌말 초혈관에서 확산되어 냐온 약물성분에 의한화학적 뇌
Fig. 4. A case of intracerebral hematoma
Fig. 5. A case of chronïc subdural hematoma
- 689-
- 大韓放射線醫學會誌 第 24 卷 第 5 號 1988 -
지주악염, 화학적 말초 혈판염에 의한 주변조직 허탈 및 그에 이은 조직괴사에 의한 용적감소로 추정하고 있마19, 20, 21 , 22) 이 중 뇌파질 위축은 총 20여l 중 15예 에서 나타나 매우 의의있게 냐타났으며, 특히 뇌피잘 하 위축은 뇌피질 위축파의 판계는 분명하지 않지만 단독으로 온 것은 l예로 드물었마. 즉 항암제 투여 결 과로 위에 기술한 기전에 의해 주로 뇌파질 신경세포 수의 철대적인 강소가오여 부수적 ξ로뇌펴절하세포 수의 감소가 오는 것으로 추정 된다. 한펀 뇌위 축소견 이 없는 4예는 약물에 대한개인적인 감수성에 기인한 것으로 생각된다.
한펀 저자들의 20예중 16예가 뇌위축소견을 나타냈 지만 이는 2회 이상의 화학요뱅중 이거나치료후에 신 경계 증상이 있어서 CT촬영을 얻은 예만을 후향척으 로조사한것이기 때문에 실제석으로화학요법을받은 환자의 맺 %에서 뇌위축소견을 냐타낼 것인지와 이렇 게 위축된 뇌와 뇌기능파의 판계에 대하여는 전향적 (prospective) 으로 연구를 하여야 할 것 A로 생각된 마.
또한 백혈병 이외 마릎 원인으로 장기간 항암제 치 료를 받은환자도 역시 뇌위축이 초래될 수 있음이 자 명하으로 향후 항암제 치료후에 뇌 CT 스캔 영상을 얻은 것이 기본적인 조건으로제시하여야할것인가에 대하여서도 보다 연구가 진행되어야 하겠다.
20예 중 l예에서 우연히 대뇌출혈이 말견되었는데 급성백형명에서 출혈은 주요 사망원인 중의 하나이 며, 이것은 혈소판 수의 철대석인 감소와 이에따른 응 고 기능장애로 설명되어 왔다23) 주로 위장판점막 및 피부에 발생하며 드물게 대뇌출혈도 보인마24 , 25)
최근에는 핵자기 공영 영상법이 개발되어 뇌의 생러 석 생화학적 정보를 보마 많이 제공하으로 이를 통한 항암제 치료후 뇌변화에 대한 연구가 이루어져야 할 것£로 생각된마.
3. McCrea ES, Rao KCUG, Diaconis ]N: Roentgenog- raphic changes during longterm diphenylhydentoin therapy. South Med ] 73(3):310-311, 1980 4. Allen ]C: The effects of cancer therapy on the
nervous system. ] Pediatr 93:903-909, 1978 5. Moss HA, Nannis ED, Poplack DG: The effects of
prophylatic treatment of CNS on the intellectual functioning of children with acute lymphocytic leukemia. Amer ] Med 71:47-52, 1981
6. Kay HEM, Knapton P], 0’Sullivan ]P, et a1: En- cephalopathy in acute leukemia associated with MTX therapy. Arch. Dis. Child. 47:344-354, 1972 7. Robert A, Price RA, Pamela A]: The central ner- vous system in cildhood leukemia: II. Subacute leukoencephalopathy, Cancer 35:306-318, 1975 8 깅용찬, 김춘열 : 전산화 단층촬영상에서 뇌실, 뇌
연석"1. 가폴릭대학 의학부 논운집 Vol. 36, No. 3, p.687-692
9. Gomori ]M, Steiner 1, MelamedE, et al: The assess- ment of changes in brain volume using combined linear measurements. NeuIOradiology 26:21-24,
1984
10. Huckman MS, Fox J, Topel ], et a1: The validity of criteria of cerebral atrophy by CT. Radiology 116:85-92, 1975
11. Francis ]Y , Kwan R: FIOntal ventricular dimen sions on nOI1Ìlal computed tomography. Radiology 126:593-596, 1976
12 김웅진, 장기현, 한만청 : 한국정상인의 뇌 전산화단 층촬영에 의한 고찰. 대한방사선의학회지 17 (1) : 46 -53, 1983.
13. Baker HL, Compbell ]K, Houser 0, et a1: Computer assisted tomography of the head. Mayo Clin Proc 49:17-27, ]an. 1974
14. New PE], Scott WR, Schnur ]A, et al: Compu- terized axial tomography with the BMI scanner, Radiology 110:109-123, ]an. 1974
REFERENCES 15. Charles PH, Mohktav G: Computed tomography and agiilg of the brain. Radiology 139:391-396, 1. Lee, S.H., Krishna C.V.G. Rao: Cranial computed 1981
tomography: hydrocephalus and atrophy. 2nd Ed 16. Bentson J, Reza M, Winter ], et al: Steroids and p.244, 1νcGraw-Hill Book Company, Baltimore. apparent cerebral atrophy on computed tomography 2. Ghatak NR, Santoso RA, McKinney WM: Cerebel- scans. ] Comput Assist Tomogr 2:16, 1978
lar degeneration foJlowing long-term phenytoin 17. Rumbaugh CL, Fang HCH, Wilson GH, et al: Cere therapy. Neurology 26:818-820, 1976. bral CT findings in drug abuse: clinical and ex
임 준 외 : 급성 백혈명 환자에서 항암제 투여 후 뇌 CT 소견 -
perimental observation. ] Comput Assist Tomogr 4:330, 1980
18. Peylan RN, Poplack DG, Pizzo PA, et al: Abnor- mal CT scans of the brain in asymptomatic children with acute lymphocytic leukemia after prophylactic treatment of the CN5. N Engl ] Med 298:815, 1978
19. Crosley C], Rorke LB, Evans A, et al: Central nervous system lesions in childhood leukemia.
Neurology 28:678, 1978
20. Price RA, Birdwell DA: The central nerve system in childhood leukemia III. Cancer 42:171. 1978
21. Lampert P, 0’Brien J. Garrett R: Hexachlorophene encephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol 23:325, 1973 22. Holland ]F, Glidewell 0: Chemotheray of acute
lymphocytic leukeinia of childhood. Cancer 30:1480, 1972.
23. Gaydos LA, Freireich E], Manted N: The quanti- tave relation between platelet count and hemor- rhage in patients with acute leukemia. N Engl ] Med 266205, 1962.
24. Ray A], ]affe N, Djerassi 1. Prophylactic platelet transfusions in children with acute leukemia: A dose response study. Transfusion 13:283, 1973
- 691-