Physiologic Evaluation of Microvascular Damage in Culprit Vessel After Successful Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention for ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction Patients JLA
전체 글
수치
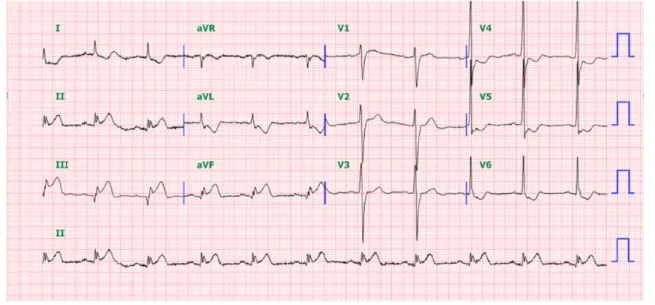
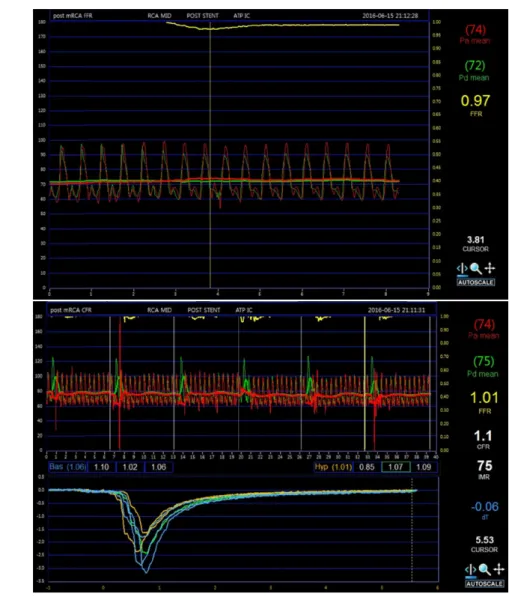
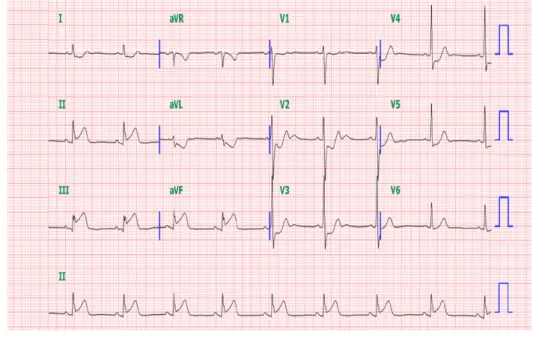
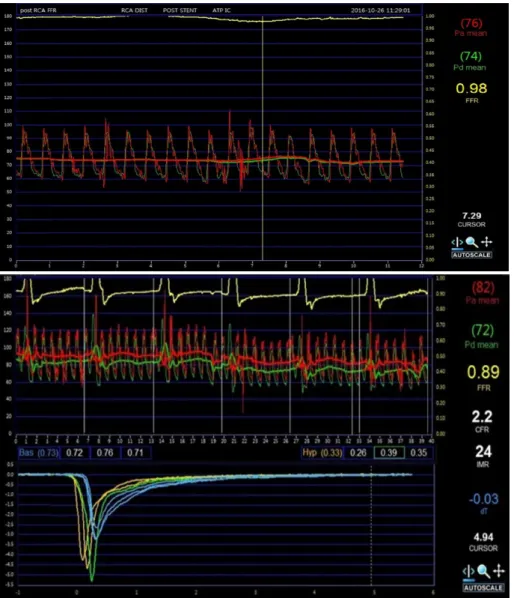
관련 문서
• Heat conduction with a electrical heat source, a nuclear heat source, a viscous heat source, and a chemical heat source.. • Heat conduction
• Theory can extent to molten polymers and concentrated solutions.. The single-molecule bead spring models.. a)
• Diffusion Equation for fluid flow in porous media... Fluid flow
Aerodynamic noise noise noise that noise that that that happen happen happen happen in in in in unsteady unsteady unsteady flow unsteady flow flow flow of
Therefore, cTnT is a recommended biomarker for use in the detection of myocardial infarction (MI) and in acute coronary syndromes.[8] Indeed, several authors
Logically AND the pending interrupt field (Cause register) and the interrupt mask field (Status register) to see which enabled interrupt could be the culprit.. Copies are
- Derive Bernoulli equation for irrotational motion and frictionless flow - Study solutions for vortex motions.. can be obtained by integrating Navier-Stokes equation for
1) Zone of viscous action (boundary layer): frictional effects cannot be neglected. 2) Flow in the reservoir and central core of the tube: primary forces are pressure
