대한 두경부 종양 학회지 제 27 권 제 1 호 2011
Introduction
Head and neck cancer is the sixth most common type of
cancer, representing about 6% of all cancers and accounting for an estimated 650,000 new cancer cases and 350,000 can- cer deaths worldwide every year.
1)The 5-year survival of
교신저자 : 김철호, 443-751 경기도 수원시 영통구 원천동 산 5 아주대학교 의과대학 이비인후과학교실전화 : (031) 219-5269 · 전송 : (031) 219-5264 · E-mail : ostium@ajou.ac.kr
Expression and Clinical Significance of the N-myc Downstream Regulated Gene-1 in Hypopharyngeal Cancer
Inkyung Sohn, MD
1, Nam Soo Han, MD
1, Yoo Seob Shin, MD
1, Jang Hee Kim, MD
2, Chul-Ho Kim, MD
1Department of Otolaryngology
1and Pathology,
2Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea
하인두암에서의 N-myc Downstream Regulated Gene-1 발현의 임상적 의의
아주대학교 의과대학 이비인후과학교실,
1병리학교실
2손인경1·한남수1·신유섭1·김장희2·김철호1
= 국 문 초 록 =
목 적
두경부 암은 발생 순위에서 전체 6위에 해당하는 다빈도 암이나 최근 20여년 동안의 노력에도 불구하고 두경부 암의 독톡한 특성상 생존률에서 뚜렷한 향상을 보이지 못하고 있다. 특히, 하인두 암은 원발 부위의 점막하 침윤이 흔하며, 주변 림프절 전이와 원격 전이가 흔하고, 2차 원발 암종 발생이 흔하여 두경부 암 중에서도 가장 불량한 예 후를 보이고 있는 악성 종양이다. 최근에 이러한 암을 치료하고 진단하기 위한 방법으로 분자생물학적 접근법들이 많이 시도 되고 있으며, 그 중 하나로 N-myc downstream regulated gene-1(Ndrg-1)이라는 유전자가 유방, 전 립선, 방광 암 등의 타 악성 종양에서 종양의 전이 및 진행 양상과 관련되어 있다는 보고가 있었다. 이에 본 연구는 하인두 암에서의 Ndrg-1의 발현 양상을 살펴보고 이와 임상 양상과의 연관관계를 살펴보고자 하였다.
방 법
1996년부터 2003년까지 수술 받은 하인두 암 환자 56명을 대상으로 면역조직화학검사를 시행하여 Ndrg-1 발현 을 확인하였고, 3명의 신선 조직을 대상으로 RT-PCR, Western blot을 시행하였다.
결 과
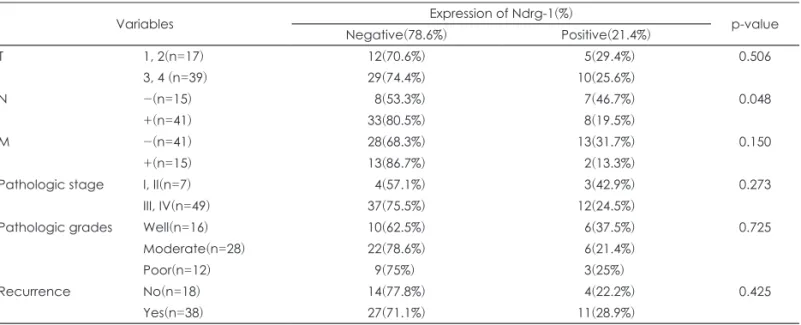
Ndrg-1은 RT-PCR에서 정상 조직과 악성종양 조직 모두에서 비슷한 수준으로 발현되었다. 그러나 Western blot 에서는 정상 조직에서 뚜렷한 증가 양상을 보여 타 연구와 동일한 결과를 보였고, 이는 불필요하며 비효율적인 mRNA수준에서의 발현이 있지만 최종적인 단백 산물 발현에서는 암종의 진행과 연계되어 악성 종양 진행군에서 발현 이 억제되는 결과로 해석된다. 면역조직화학검사에서는 정상 상피조직에서 Ndrg-1 발현이 확인되었으며, 통계적으 로 유의하지는 않으나 불량한 예후를 가진 그룹에서 대체로 발현이 억제되는 악성 종양과의 역 연관 관계를 확인할 수 있었고, 특히 림프절 전이를 보인 그룹과 그렇지 않은 그룹 사이에서는 통계적으로 유의미한 결과가 확인되었다.
결 론
즉, 림프절 전이가 없는 그룹에서 Ndrg-1이 종양의 전이에 관여할 것이라는 타 연구와 일관된 결과로 하인두 암에서도 그 역할이 있음을 나타내는 결과라 할 수 있다.
중심 단어
:Ndrg-1ㆍ하인두암ㆍ경부전이.online©MLComm