121
Korean Circulation J 2006;36:121-125 ⓒ 2006, The Korean Society of Circulation
스텐트 내 재협착에 시행한 Sirolimus 약물 방출 스텐트 삽입의 임상적 결과: 관상동맥 조영술에 의한 정량적 연구
건양대학교 의과대학 심장내과학교실
유기현·배장호·김기영·현대우
Clinical Outcomes of Using Sirolimus-Eluting Stents for Treating In-Stent Restenosis: A Quantitative Coronary Angiography Study
Ki-Hyun Ryu, MD, Jang-Ho Bae, MD, Ki-Young Kim, MD and Dae-Woo Hyun, MD
Division of Cardiology, Heart Center, College of Medicine, Konyang University, Daejeon, Korea ABSTRACTBackground and Objectives:There is little clinical data on the results of using Sirolimus-Eluting Stent (SES) for treating In-Stent Restenosis (ISR). We performed this study to evaluate the clinical outcomes for implanting SES for treating ISR in a real world hospital environment. Subjects and Methods:A total of 30 patients with 32 ISRs (males: 73.3%, mean age: 60.2) (focal lesions: 21.9%, diffuse intra-stent lesions: 34.4%, proliferative lesions: 21.9%, total occlusions: 21.9%) were treated with SES after balloon predilation was performed. We eva- luated the clinical results and the performed coronary angiography after 6 months. Results:All the procedures were successful. The mean SES diameter and length were 3.0±0.3 mm and 27.1±5.5 mm, respectively, and the mean acute gain was 2.42±0.38 mm. No in-hospital major adverse cardiac events (MACE) were observed. Twenty five patients with 27 lesions (84.4%) underwent coronary angiography at their 6 month follow-up. The late loss and loss index were 0.41±0.56 mm and 0.18±0.22, respectively. The binary restenosis rate was 7.4% (2/27 le- sions). The rate of target lesion revascularization was 3.7% (1/27 lesion). The incidence of MACE at 6 months was 3.3% (1/30 patient). Conclusion:Treating ISR with SES is a safe and effective procedure for reducing ISR without the occurrence of acute or sub-acute thrombosis. (Korean Circulation J 2006;36:121-125)
KEY WORDS:
Coronary artery disease;Coronary restenosis;Stents.
서 론
관상동맥 스텐트 삽입술은 경피적 관상동맥 성형술(percu- taneous transluminal coronary angioplasty, PTCA)의 80%
이상에서 시행되고 있으며 이는 단순한 풍선확장술에 비해 임상적인 면이나 관상동맥 조영술상으로 재협착을 현저히 줄
여주고 있다.1) 관상동맥에 스텐트삽입 후 발생하는 재협착은 스텐트 내 재협착이 대부분을 차지하며 그 발생빈도는 약 20~40%정도로 보고되고 있다.2) 최근 약물 방출 스텐트의 등 장 이후 스텐트 내 재협착의 비율을 10% 미만으로 낮추고 있 으나 완전히 없애지는 못하고 있다.3-5) 스텐트 내 재협착에 대 한 치료로는 풍선성형술, cutting balloon 성형술, 죽상반 회 전절제술(rotational atherectomy) 및 방향절제술(directio- nal coronary atherectomy), 관상동맥 내 국소방사선 조사 요법, 단순 스텐트나 약물 방출 스텐트 재삽입 등의 다양한 방법이 사용된다. 그 동안의 무작위적 임상연구에 의하면 스 텐트 내 재협착의 치료는 관상동맥내 국소방사선 조사요법 (brachytherapy)이 효과적인 것으로 알려져 왔으나 치료에 있 어서 상당한 장비 및 방사물리학적 지원이 필요하고 우려할 논문접수일:2005년 17월 22일
수정논문접수일:2005년 9월 20일 심사완료일:2005년 12월 13일
교신저자:배장호, 302-718 대전광역시 서구 가수원동 685 건양대학교 의과대학 심장내과학교실
전화:(042) 600-6400·전송:(042) 600-6399 E-mail:jhbae@kyuh.co.kr
정도의 부작용이 관찰됨으로써 실제 임상적 치료에 있어 한 계를 가지고 있었다.6) 그에 비해 최근의 연구들은 스텐트 내 재협착에 대한 치료로써 Sirolimus, Paclitaxel 등의 약물 방 출 스텐트의 삽입을 그러한 국소 방사선 요법의 단점을 극복 하면서 스텐트 내 재협착에 대한 치료효과를 향상시킬 수 있 는 치료법으로 제시하고 있다. 본 연구는 스텐트 내 재협착 의 치료에 있어 Sirolimus 약물 방출 스텐트(Sirolimus Elu- ting Stent, SES)의 유용성과 안정성에 대해 정량적 관상동 맥 조영술 및 임상적 결과를 통해 평가 하였다.
대상 및 방법
본 연구의 대상은 일반금속스텐트를 이용한 관상동맥 성 형술 이후 QCA(quantitative coronary angiography)상 50%
이상의 스텐트 내 재협착이 발생한 환자 중 70% 이상의 재 협착이 관찰되어 재개통을 시행하여 성공적인 결과를 얻은 환자를 대상으로 하였다. 재개통시의 성공적인 결과는 시 술 직후 Thrombolysis In Myocardial Infarction(TIMI7)) grade 3 flow의 회복과 잔여협착이 30% 미만인 것으로 하 였다.
스텐트 내 재협착은 과거 스텐트를 삽입한 부위에 급성 혹 은 아급성의 혈전증이 없이 50% 이상의 내경감소가 정량적 관상동맥 조영술에 의해 관찰된 것으로 정의하였다.
정량적 관상동맥 조영술은 CAAS-I(Cardiovascular Angio- graphy Analysis System; Pie Medical Imaging, Nethe- rlands)를 이용하여 수행되었고, 국소 마취 후 우측 대퇴동 맥을 Seldinger씨 방법으로 천자하거나, 요골 동맥을 통하여 동맥 sheath를 삽입하였다. 관상동맥 조영술을 실시하여 70%
이상의 스텐트 내 재협착이 관찰되는 경우 Sirolimus 약물방 출 스텐트(Cypher®, Cordis, Miami, USA)를 삽입하였다. 목 표병변에 대한 관상동맥 성형술은 성형술 전 아스피린, clo- pidogrel을 경구투여 하고 헤파린을 정맥주사 하는 등 표준 적인 방법을 사용하였다. 이후 6개월 추적 관상동맥 조영술 을 시행하였다.
시술 전과 시술 후, 6개월 추적검사에서 최소 혈관직경 (minimal luminal diameter, MLD)과 기준 혈관직경(refe- rence diameter, RD), 협착 정도를 측정하였으며 직경의 기 록은 관상동맥 조영시 혈관 직경이 가장 좁아 보이는 방향을 기준으로 하여 기록하였다.
관상동맥 조영술상 성공적인 결과는 6개월 추적검사에서 스텐트 내 재협착이 50% 미만인 것으로 정의하였다. 임상적 으로 성공적인 결과는 관상동맥 조영술상 성공적인 결과와 함께 주요 심장사건(Major Adverse Cardiac Event)이 없는 것으로 정의하였고, 주요 심장사건이라 함은 사망, 급성 심 근경색증, 목표병변 재개통(TLR; Target Lesion Revascula- rization)을 시행한 경우로 정의하였다.
결 과
임상적 특성(Table 1)
총 30명의 환자를 대상으로 하였고, 평균 연령은 60.2±
9.4세였으며, 성별은 남자가 22명(73.3%)이었다. 위험인자로 고혈압을 가지고 있는 환자가 24명(80.0%), 당뇨 12명(40.0%), 흡연력 12명(40.0%), 이상지질혈증 23명(76.7%)이었다. 이 전 일반 스텐트 삽입시 급성 심근경색으로 진단을 받았던 환 자는 19명(63.3%)이었다. 스텐트 내 재협착 당시의 진단으로 안정형 협심증은 22명(73.3%), 불안정형 협심증은 4명(13.3%), 급성 심근경색증은 4명(13.3%)이었다.
검사실 소견
대상 환자들의 공복시 혈당은 176±121 mg/dL, 총 콜레스 테롤 148±31 mg/dL, 중성지방 165±80 mg/dL, 고밀도지 질단백 38.8±9.1 mg/dL, 저밀도지질단백 84.6±24.2 mg/
dL, 호모시스테인 9.8±3.6(mol/L, Hs-CRP 0.22±0.30 mg/dL였다. 초음파를 이용하여 측정한 좌심실 구혈률은 평 균 62.5±11.9%였다.
연구대상의 특성(Table 2)
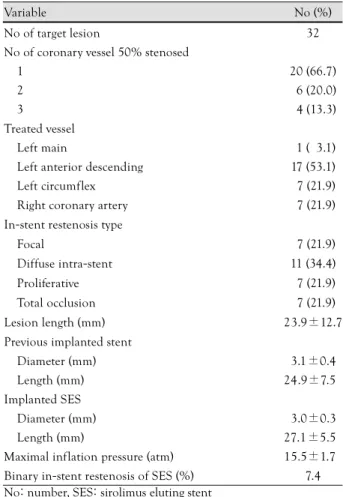
총 병변의 수는 32개였고 50% 이상의 협착이 보이는 병변 혈관의 숫자에 따라 단일 혈관질환 20예(66.7%), 두 혈관질 환 6예(20.0%), 세 혈관질환 4예(13.3%)이었다. 목표병변의 위치는 좌주간부 1예(3.1%), 좌전하행동맥 17예(53.1%), 좌 회선동맥 7예(21.9%), 우관상동맥 7예(21.9%)였다. Mehran 분류8)에 의한 재협착 병변은 Ⅰ형(focal) 7예(21.9%), Ⅱ형 (diffuse) 11예(34.4%), Ⅲ형(proliferative) 7예(21.9%), Ⅳ 형(total occlusion) 7예(21.9%)였다. 병변의 길이는 평균 23.9±12.7 mm였고, 목표병변 내에 1개의 스텐트를 삽입한 경우가 26예(81.3%), 2개의 스텐트를 삽입한 경우가 6예 (18.8%)이었다.
Table 1. Baseline clinical characteristics
Variable Number (%)
Patients 30
Age (years) 60.2±9.4
Male 22 (73.3)
Risk factors
Hypertension 24 (80.0)
Diabetes 12 (40.0)
Smoking 12 (40.0)
Dyslipidemia 23 (76.7)
Diagnosis
Stable angina 22 (73.3)
Unstable angina 04 (13.3)
Acute myocardial infarction 04 (13.3) Previous myocardial infarction 19 (63.3)
관상동맥 조영술 상 결과
재협착에 대한 스텐트 삽입시 총 병변 32부위에서 기준 혈 관내경이 2.90±0.40 mm, 최소 혈관내경이 0.32±0.25 mm, 이전에 사용한 일반 스텐트 삽입시의 스텐트 내경과 길이는 각각 3.1±0.4 mm, 24.9±7.5 mm였고, 병변길이는 23.9±
12.7 mm였다. 스텐트 내 재협착의 치료로 사용한 Sirolimus 약물방출 스텐트 직경과 길이는 각각 3.0±0.3 mm, 27.1±
5.5 mm였고, 최대 팽창압은 15.5±1.7기압이었고, 스텐트 중 복은 4예(12.5%)에서 시행 되었다.
스텐트 삽입 후 임상적으로 모든 환자를 추적관찰 하였고 6개월 후 시행한 관상동맥 조영술을 통한 추적관찰은 30명의 환자 중 25명에서 시행 되었고, 32개의 예 중 27예(84.4%) 에서 시행되었다. 기준 혈관직경은 시술직후 2.97±0.33 mm, 6개월 추적검사에서는 2.99±0.34 mm이었고, 최소 혈관직 경은 시술전 0.32±0.25 mm 시술직후 2.74±0.30 mm 이 였고 초기 획득(acute gain)은 2.42±0.38 mm였다. 6개월 추적검사시 2.32±0.66 mm였다. 6개월 추적 관상동맥 조영 술 후 측정한 최소 혈관 직경과 관상동맥 중재시술 후의 최 소 혈관 직경의 차이를 나타내는 후기 손실(late loss)은 0.41±
0.56 mm, 중재술 전후의 최소 혈관 직경의 차이(acute gain) 와 late loss사이 비율인 loss index의 값은 0.18±0.22이었 다(Table 3). 6개월 추적 관상동맥 조영술상 2예(7.4%)에서
재협착이 발생되었고, 그 중 1예에서는 관상동맥 조영술상 스 텐트 내 근위부 가장자리에 89%의 협착 소견을 보여 cutting balloon을 이용하여 재개통이 시행되었으며, 다른 1예에서는 55%의 스텐트 내 협착 소견을 보여 약물요법 시행 후 추적 관찰 중이다.
임상적 결과
모든 환자에서 성공적으로 SES를 시술하였으며 병원 내 임상 경과는 양호하였고 시술과 관련된 주요심장사건과 혈 관합병증은 없었다.
6개월간 임상적인 경과 관찰중 주요 심장사건은 사망이나 심근경색증은 발생하지 않았고. 1예(3.3%)에서 추적 관상동 맥 조영술 후 목표병변 재개통을 시행 하였다.
고 찰
본 연구는 그 동안 여러 연구에서 언급되어진 바와 같이 Sirolimus 약물 방출 스텐트가 스텐트 내 재협착 방지에 긍 정적인 작용을 한다는 이론에 근거하여 스텐트 내 재협착 병 변에 대한 치료에 있어서도 그 유용성과 안정성이 있음을 임 상연구에서 직접 확인하였다는데 그 의의가 있다. 몇몇 무작 위 연구에 의하여 스텐트 내 재협착 병변에 대한 치료로서 국소 방사선 조사 요법이 다시 발생하는 재협착을 억제하고, 주 요심장사건을 줄이는데 효과적인 것으로 알려져 있었지만,9)10) 후기 혈전증,11) 치유 지연,12) black hole 현상,13) geographic miss14) 등의 부작용이 관찰되었다. Saia 등15)은 43명의 관상 동맥 내 국소 방사선 조사 요법(Vascular Brachytherapy;
VBT) 시행군과 44명의 Sirolimus 약물방출 스텐트 삽입술 시행군을 9개월 동안 임상적으로 추적하였고 결과적으로 주 요심장사건 없이 생존할 확률은 두 군에서 큰 차이가 없었 으며(79.1% VBT vs. 81.5% SES), Sirolimus약물방출 스텐 트가 기술적인 면에서 간단하여 효용성이 더 높은 것으로 기술하였다. Sirolimus 또는 Rapamycin은 천연 macrocy- clic lactone으로 면역억제제 이며 이는 세포내 수용체 단백 질(FK506 결합단백 12)과 그 복합체에 결합하여 세포분화의 중요한 역할을 하는 mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)16)이라고 불리는 효소를 억제함으로써 세포분화를 후 기 G1기에 멈추게 하고 횡문근의 증식을 억제하게 된다.17)18)
Table 2. Lesion characteristics
Variable No (%)
No of target lesion 32
No of coronary vessel 50% stenosed
1 20 (66.7)
2 06 (20.0)
3 04 (13.3)
Treated vessel
Left main 01 (03.1)
Left anterior descending 17 (53.1)
Left circumflex 07 (21.9)
Right coronary artery 07 (21.9) In-stent restenosis type
Focal 07 (21.9)
Diffuse intra-stent 11 (34.4)
Proliferative 07 (21.9)
Total occlusion 07 (21.9)
Lesion length (mm) 23.9±12.7
Previous implanted stent
Diameter (mm) 03.1±0.40
Length (mm) 24.9±7.50
Implanted SES
Diameter (mm) 03.0±0.30
Length (mm) 27.1±5.50
Maximal inflation pressure (atm) 15.5±1.70 Binary in-stent restenosis of SES (%) 7.4 No: number, SES: sirolimus eluting stent
Table 3. Quantitative coronary angiographic analysis
Parameters Preprocedure Postprocudure Follow-up RD (mm) 02.90±0.400 2.97±0.33 02.99±0.340 MLD (mm) 00.32±0.250 2.74±0.30 02.32±0.660 DS (%) 88.72±8.990 7.42±7.92 22.70±19.38 Lesion length (mm) 023.9±12.73
Late loss (mm) 00.41±0.560
Loss index 00.18±0.220
RD: reference diameter, MLD: minimal luminal diameter, DS: dia- meter stenosis
Degertekin 등19)은 Sirolimus 약물방출 스텐트가 재협착을 예 방함에 있어 de novo 병변(n=45)과 스텐트 내 재협착 병변 (n=41)에 동일한 효과를 나타냄을 관상동맥 내 초음파 추적 검사를 통해 관찰하였다.
다른 약물 방출 스텐트로는 paclitaxel-eluting stents (TAXUS NIRxTM, Boston Scientific Corporation), QuaDS- QP2 stent(Quanum Medical Corporation), everolimus(Gui- dant Corporation), ABT-578(Abbott Vascular and Medtro- nic), and biolimus(Terumo and Biosensors)와 같은 것들 이 있다. Paclitaxel은 난소암이나 유방암에 사용되는 항암약 물로 혈관횡문근의 증식이나 이동을 억제하는 것으로 알려져
있다.20)21) TAXUS Ⅲ연구에서는 28명의 스텐트 내 재협착 환
자를 대상으로 paclitaxel 약물방출 스텐트를 삽입하여 6개 월 후 시행한 관상동맥 조영술 추적 관찰에서 16%의 재협착 병변을 관찰할 수 있었으며, 6개월에서 12개월 사이에 목표 병변 재개통은 21.4%에서 시행되었고, 주요 심장사건은 29%
에서 발생하였다.22) 그러나 paclitaxel 유도체인 7-hexanoyl- taxol(QP2)-eluting polymer stent system(QuaDS)의 경우 재협착에 대한 시술 후 6개월에 관상동맥 조영술 상 13.3%의 재협착률을 보였으나 12개월 추적 관찰시에는 61.5%로 증가 하는 양상을 보여 재협착에 대한 시술로 적합하지 않음을 보 여줬다.23)
과거의 연구를 보면 Rotterdam FIM(First In Man)연구 에서는 16명의 중증의 재발성 스텐트 내 재협착 환자를 대 상으로 1개 이상의 18-mm SES를 삽입하여 4개월 후 관상 동맥 조영술을 통해 추적 관찰하였는데, 추적중 1예에서 급 사하였으며, 나머지 15명의 인원 중 3예(20%)에서 재협착이 재발하였다.24) Sao Paulo FIM연구에서는 25명의 스텐트 내 재협착 환자를 대상으로 1개 이상의 18-mm SES삽입 하였고 12개월 후 관상동맥 조영술을 통한 추적 관찰 결과 1예(4%) 에서 스텐트 내 재협착이 발생하였다.25) 본 연구에서는 30 명의 환자를 대상으로 하여 1개 이상의 SES(길이 27.1±5.5 mm)를 삽입하였으며, 6개월 후 관상동맥 조영술 추적검사를 시행한 27예 중 2예(7.4%)에서 재협착이 발생하였고, 1예에 서 목표병변 재개통을 시행하였다.
본 연구는 그 동안의 연구에 비하여 비교적 적지 않은 환 자를 대상으로 약물 방출 스텐트 중 SES에 대해서만 연구가 행해졌으며, 비교적 높은 추적 관상동맥 조영술(84.4%)을 시 행한 것이 특징이다. 이 연구의 제한점은 목표병변 재협착 에 혈관 내 초음파검사가 시행되지 못하였고, 스텐트 내 재 협착(2예)이 적어 재협착에 영향을 주는 임상 양상과 관상동 맥 조영술 소견, 그리고 스텐트 삽입술에 관한 인자들26)27)에 대한 분석을 시행하지 않았다.
Sirolimus 약물방출 스텐트는 일반적인 경피적 관상동맥 성형술을 시행할 수 있는 시술 인력이나 장비만 있으면 쉽게 시행할 수 있는 장점을 가지고 있다. 그러나 이러한 SES 삽 입 후 발생하는 스텐트 내 재협착의 발생은 현재 de-novo
병변의 경우 2년,28)29) 스텐트 내 재협착 병변의 경우 1년30) 의 추적 관찰에 대한 연구들이 있는 상태이고, 기타 다른 약 물 방출 스텐트의 경우에 있어서도 그 이후에 발생할 수 있 는 후기 재협착에 대한 연구는 아직 없는 상태이므로 위에 서 기술한 7-hexanoyltaxol(QP2)-eluting polymer stent system처럼 장기적인 추적관찰 기간 동안 부정적인 결과를 보일 가능성을 배제하지는 못하는 상태이다.
요 약
배경 및 목적:
본 연구는 Sirolimus 약물방출 스텐트가 스텐트 내에 발 생하는 재협착을 억제한다는 것에 기초하여 스텐트 내 재협 착 병변에 대한 치료에 있어서도 그 유용성과 안정성이 있 는지를 확인하고자 하였다.
방 법:
과거 스텐트 내 재협착이 발생한 총 30명의 환자, 총 32개 의 병변을 대상으로 하였고 병변의 특성에 따라 적절한 길이 와 직경의 Sirolimus 약물 방출 스텐트를 삽입하였다. 이후 지속적인 임상적 추적 관찰을 하였고, 6개월 이후의 관상동 맥 조영술 추적검사를 통하여 기준 혈관직경, 최소 혈관 직 경, late loss, loss index 등을 측정하였다.
결 과:
총 27개의 예에서 6개월 추적 관상동맥 조영술상 late loss 는 평균 0.41±0.56 mm, loss index는 평균 0.18±0.22이 었고, 재협착 2예(7.4%)중 1예에 대해서 표적병변 재개통이 시행 되었다. 임상적 추적 관찰 결과 주요심장사건은 없었다.
결 론:
본 연구에서 보듯이 Sirolimus 약물방출 스텐트는 스텐트 내 재협착의 치료에 있어 유용성과 안정성이 있다고 볼 수 있다.
중심 단어:관상동맥질환;재협착;스텐트.
REFERENCES
1) Fischman DL, Leon MB, Baim DS, et al. A randomized compari- son of coronary-stent placement and balloon angioplasty in the treatment of coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 1994;331:
496-501.
2) Lowe HC, Oesterle SN, Khachigian LM. Coronary in-stent res- tenosis: current status and future strategies. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002;39:183-93.
3) Seung KB. Drug eluting stent and percutaneous coronary inter- vention. Korean Circ J 2003;33:857-60.
4) Moses JW, Leon MB, Popma JJ, et al. Sirolimus-eluting stents versus standard stents in patients with stenosis in a native coro- nary artery. N Engl J Med 2003;349:1315-23.
5) Stone GW, Ellis SG, Cox DA, et al. A polymer-based, paclitaxel eluting stent in patients with coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 2004;350:221-31.
6) Leon MB, Teirstein PS, Moses JW, et al. Localized intracoronary gamma-radiation therapy to inhibit the recurrence of restenosis
after stenting. N Engl J Med 2001;344:250-6.
7) TIMI Study Group. The Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infaction (TIMI) Trial. N Eng l J Med 1985;312:932-6.
8) Mehran R, Dangas G, Abizaid AS, et al. Angiographic patterns of in-stent restenosis: classification and implications for long-term outcome. Circulation 1999;100:1872-8.
9) Hong YJ, Jeong MH. Is debulking combined with brachytherapy a new therapeutic approach for diffuse coronary stent restenosis?
Korean Circ J 2004;34:927-9.
10) Waksman R, Cheneau E, Ajani AE, et al. Intracoronary radia- tion therapy improves the clinical and angiographic outcomes of diffuse in-stent restenotic lesions. Circulation 2003;107:1744-9.
11) Costa MA, Sabate M, van der Giessen WJ, et al. Late coronary occlusion after intracoronary brachytherapy. Circulation 1999;
100:789-92.
12) Kay IP, Sabate M, van Langerhove G, et al. Outcome from bal- loon induced coronary artery dissection after intracoronary beta radiation. Heart 2000;83:332-7.
13) Kay IP, Ligthart JM, Virmani R, et al. The black hole: echolucent tissue observed following intracoronary radiation. Int J Cardio- vasc Intervent 2003;5:137-42.
14) Sabate M, Costa MA, Kozuma K, et al. Geographic miss: a cause of treatment failure in radio-oncology applied to intracoronary radiation therapy. Circulation 2000;101:2467-71.
15) Saia F, Lemos PA, Hoye A, et al. Clinical outcomes for sirolimus eluting stent implantation and vascular brachytherapy for the treatment of in-stent restenosis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 2004;
62:283-8.
16) Heitman J, Movva NR, Hall MN. Targets for cell cycle arrest by the immunosuppressant rapamycin in yeast. Science 1991;253:
905-9.
17) Marx SO, Jayaraman T, Go LO, Marks AR. Rapamycin-FKBP inhibits cell cycle regulators of proliferation in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 1995;76:412-7.
18) Poon M, Marx SO, Gallo R, Badimon JJ, Taubman MB, Marks AR. Rapamycin inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell migration.
J Clin Invest 1996;98:2277-83.
19) Degertekin M, Lemos PA, Lee CH, at al. Intravascular ultrasound evaluation after sirolimus eluting stent implantation for de novo
and in-stent restenosis lesions. Eur Heart J 2004;25:32-8.
20) Axel DI, Kunert W, Goggelmann C, et al. Paclitaxel inhibits arte- rial smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration in vitro and in vivo using local drug delivery. Circulation 1997;96:636-45.
21) Hou D, Rogers PI, Toleikis PM, Hunter W, March KI. Intrape- ricardial paclitaxel delivery inhibits neointimal proliferation and promotes arterial enlargement after porcine coronary overstretch.
Circulation 2000;102:1575-81.
22) Tanabe K, Serruys PW, Grube E, et al. TAXUS III Trial: in-stent restenosis treated with stent-based delivery of paclitaxel incor- porated in a slow-release polymer formulation. Circulation 2003;
107:559-64.
23) Liistro F, Stankovic G, di Mario C, et al. First clinical experi- ence with a paclitaxel derivate-eluting polymer stent system im- plantation for in-stent restenosis: immediate and long-term clinical and angiographic outcome. Circulation 2002;105:1883-6.
24) Degertekin M, Regar E, Tanabe K, et al. Sirolimus-eluting stent for treatment of complex in-stent restenosis: the first clinical ex- perience. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003;41:184-9.
25) Sousa JE, Costa MA, Abizaid A, et al. Sirolimus-eluting stent for the treatment of in-stent restenosis: a quantitative coronary angio- graphy and three-dimensional intravascular ultrasound study.
Circulation 2003;107:24-7.
26) Yoon HJ, Kim KS, Park HS, et al. Clinical and angiographic factors affect on in-stent restenosis. Korean Circ J 2003;33:
1084-92.
27) Alfonso F, Azcona L, Perez-Vizcayno MJ, et al. Initial results and longterm clinical and angiographic implications of coronary sten- ting in elderly patients. Am J Cardiol 1999;83:1483-7.
28) Costa MA, Sabate M, van der Gibssen WJ, et al. Late coronary occlusion after intracoronary brachtherapy. Circulation 1999;100:
789-92.
29) Poon M, Marx SO, Gallo R, et al. Rapamycin inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell migration, J Clin Inves 1996;98:2277-83.
30) Sousa JE, Costa MA, Abizaid A, et al. Sirolimus-eluting stent for the treatment of in-stent restenosis: a quantitative coronary an- giography and three-dimensional intravascular ultrasound study.
Circulation 2003;107:24-7.