대한소화기학회지 2006;47:291-294
□ REVIEW □
서 론
1930년 Dukes의 직장암 침윤 정도와 예후의 연관성에 관 한 연구 이후 Dukes 병기가 직장암 병기로 대장항문 외과 의사들에게 널리 이용되었다. 1944년 Dukes 병기는 C1 병기 (국소 림프절 전이는 있으나, 결찰동맥 주변 림프절 전이가 없는 경우), C2 병기(국소 림프절 전이가 있으며, 결찰동맥 주변의 림프절 전이도 있는 경우)로 세분되었으며, 1954년 Astler-Coller modification에 의해 B1 병기(종양 침윤이 직장 벽 내에 국한된 경우)와 B2 병기(종양 침윤이 직장벽을 전 층 침범하여 직장 주변 지방조직에 침윤한 경우), C1 병기
(종양 침윤이 직장벽에 국한되어 있으나 림프절 전이가 있 는 경우)와 C2 병기(종양 침윤이 직장의 전 층을 넘어 직장 주변 지방층까지 침윤하였으며 림프절 전이가 있는 경우)로 다시 세분화하여 사용하였다. 이러한 병기 구분은 때때로 병기 비교에 혼란을 초래하기도 하였으며, 병기 표기가 불 분명한 경우가 발생하기도 하였다. 최근 들어 직장암에서도 TNM 병기를 이용하는 것이 일반적이다. 그러므로 본문에 서는 2002년 개정된 American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC)/International Union Against Cancer (UICC) TNM 병기 (6th edition)를 중심으로 표기하고자 한다.1
직장암의 TNM 및 분자생물학 병기와 예후
경희대학교 의과대학 외과학교실
이 석 환
TNM Staging, Molecular Staging and Prognostic Factors of Rectal Cancer
Suk Hwan Lee, M.D.Department of Surgery, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
Pathologic evaluation of the resected specimen is a critical component when managing the patients with rectal cancer, from initial diagnosis through definitive treatment. The best estimation of prognosis in rectal cancer is related to the anatomic extent of disease determined by pathology. Although a large number of staging system has been developed for rectal cancer over the years, use of TNM staging system of the AJCC (American Joint Committee on Cancer) and the UICC (International Union Against Cancer) are gaining popularity among the colorectal surgeons. Multiple genetic alterations are the prerequisite for carcinogenesis including rectal cancer. Although numerous molecular markers are investigated in relation to prognosis or response to therapy of rectal cancer, those molecular markers could not provide sufficient evidence for the incorporation of available prognostic biomarkers into clinical practice.
In this article, the evolution of staging system of rectal cancer and its prognostic relevance are reviewed com- prehensively. (Korean J Gastroenterol 2006;47:291-294)
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ
Key Words: Rectal cancer; TNM stage; Prognosis
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ
연락처: 이석환, 130-702, 서울시 동대문구 회기동 1번지 경희대학교 의과대학 외과학교실
Tel: (02) 958-8266, Fax: (02) 966-9366 E-mail: leeshdr@khu.ac.kr
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ Correspondence to: Suk Hwan Lee, M.D.
Department of Surgery, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine 1 Hoegi-dong, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul 130-702, Korea
Tel: +82-2-958-8266, Fax: +82-2-966-9366 E-mail: leeshdr@khu.ac.kr
292 대한소화기학회지: 제47권 제4호, 2006
본 론
1. TNM 병기
1) TNM 병기 결정
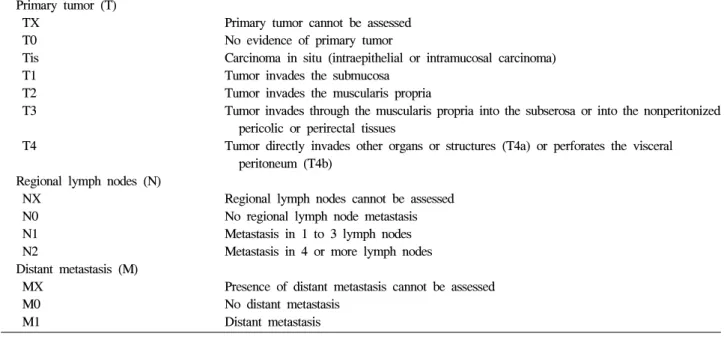
AJCC와 UICC는 고형암 병기를 tumor (T), node (N), met- astasis (M)의 유무에 따라 분류하는 통일된 표기 방식을 제 공함으로써 예후를 객관적으로 예측하고 각 연구기관들의 임상연구 비교를 가능케 하여 임상연구 발전을 모색하고자 하였다. AJCC와 UICC는 1987년부터 통합된 암 병기 규약 을 발간하였으며, 2002년 제6판 암 병기 규약이 출판되었 다.1 직장암의 병기는 결장암과 따로 분리되어 있지 않으나 국소 림프절의 범위를 표시하고 있다(Table 1). 직장의 국소 림프절은 perirectal, sigmoid mesenteric, inferior mesenteric, lateral sacral, presacral, internal iliac, sacral promontory, sup- erior rectal, middle rectal, inferior rectal 림프절을 포함한다.
림프절 전이 여부를 정확히 판정하기 위해서는 절제 조직에 서 충분한 림프절을 검사하는 것이 필요하다. Canessa 등2의 보고에 의하면 상직장동맥의 분지점 하방에서 수집된 림프 절의 평균 개수가 8.2개라고 한다. 림프절의 수집 방법과 림 프절 전이 진단 방법에 따라서도 직장암 병기에 영향을 미 칠 수 있다.3-5 직장암의 정확한 병기 결정과 림프절 전이 여 부를 정확하게 평가하기 위해 1990년 The Working Party Report to the World Congress of Gastroenterology에서는 절제 된 조직에서 최소한 12개의 림프절을 병리 검사해야 한다고 권고하였으며,6 AJCC TNM 제6차 개정판에서는 7-14개의 림프절 검사가 필요하다고 하였다.1
2) TNM 병기의 표기
직장암의 예후 예측과 치료 방법 결정에는 병리조직 검사 에 의거한 TNM 병기를 사용해야 하지만 술 전 방사선항암 요법을 시행하는 직장암의 경우에는 임상 병기(clinical sta- ging)를 이용하기도 한다. 또한 술 전 방사선항암요법을 시 행 받은 경우의 병기는 치료 전 병기와 다르게 나타날 수 있으므로 표기를 달리해야 한다. 이를 위해 TNM 병기의 표 기 방법이 제시되었다. 수술 전 방사선검사에 의한 임상 병 기 결정인 경우에는 소문자 c를 TNM 병기에 표기하도록 하였으며, 병리조직 병기인 경우에는 소문자 p를 표기한다.
술 전 방사선항암요법을 시행한 경우에는 소문자 y를 표기 한다. 또한 재발암의 병기인 경우에는 소문자 r을 표기한다.
예를 들어 ypT1N0M0라면 술 전 방사선화학요법을 받은 환 자의 술 후 병리조직 병기를 표기한 것이다. 한편 술 전 방 사선항암화학요법을 받은 경우에는 술 후 병리조직 병기와 예후와의 연관성에 대한 논란이 많으며, 치료 방향 결정 역 시 술 전 임상 병기를 기준으로 시행하는 추세이다.7,8
2. 병리조직 예후 인자
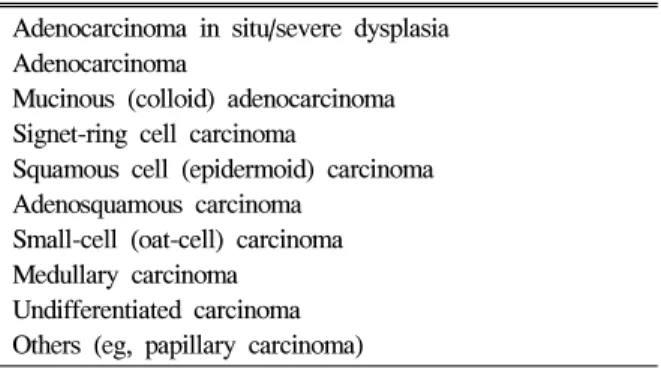
1) 직장암의 조직 분류
World Health Organization (WHO)가 제안하는 조직 분류 가 병리조직검사 결과로 보고되고 있다(Table 2). 2000년에 수질암(medullary carcinoma)이 추가되었는데 과거에는 미분 화세포암(undifferentiated carcinoma)으로 분류되었으나, 현미 부수체 불안정성(microsatellite instability, MSI)을 나타내는 종양 또는 유전비용종대장암(hereditary nonpolyposis colore- ctal cancer)에서 흔히 관찰되는 종양침윤림프구(tumor infil-
Table 1. AJCC TNM Definition for Colorectal Cancer Primary tumor (T)
TX T0 Tis T1 T2 T3
T4
Regional lymph nodes (N) NX
N0 N1 N2
Distant metastasis (M) MX
M0 M1
Primary tumor cannot be assessed No evidence of primary tumor
Carcinoma in situ (intraepithelial or intramucosal carcinoma) Tumor invades the submucosa
Tumor invades the muscularis propria
Tumor invades through the muscularis propria into the subserosa or into the nonperitonized pericolic or perirectal tissues
Tumor directly invades other organs or structures (T4a) or perforates the visceral peritoneum (T4b)
Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed No regional lymph node metastasis Metastasis in 1 to 3 lymph nodes Metastasis in 4 or more lymph nodes
Presence of distant metastasis cannot be assessed No distant metastasis
Distant metastasis
이석환. 직장암의 TNM 및 분자생물학 병기와 예후 293
trating lymphocyte)의 침윤이 특징이다.
일반적으로 직장암의 조직 분류는 예후와 연관성이 없으 나 몇 가지 예외의 경우가 있다. 상기한 수질암의 경우 예 후가 매우 양호하며, 인환세포암(signet- ring cell carcinoma) 과 소세포암(small cell carcinoma)의 예후는 매우 불량하다.
점액암(mucinous carcinoma)의 경우에는 예후에 대한 논란이 많으나 45세 이하의 약년층에서 발생한 경우와 직장에 발생 한 경우 예후가 불량하다.
2) 종양세포 분화도
종양세포 분화도는 주로 선 형성(gland-formation) 정도에 따라 분류하지만 주관적인 경우가 많다. TNM 병기는 G1- G4까지 4단계로 분류하나 관찰자 간의 차이가 많으므로 1999년 전미병리학회의 권고에 따라 고분화암(G1-G2)과 미 분화암(G3-G4)으로 분류한다.
3) 종양 절단면의 중요성
직장암 절제 조직의 절단면 검사는 직장암의 국소재발에 매우 중요한 영향을 미치는 요소이다. 일반적으로 근위절단 면, 원위절단면과 circumferential resection margin (CRM)을 검사하며, 특히 원위절단면과 CRM이 중요하다. 원위절단면 은 소화기 암에서는 5 cm 이상으로 정의하고 있으나 하부 직장암의 경우 5 cm 원위절단면을 확보하려면 항문기능을 살릴 수 없는 경우가 생기며, Williams 등9의 연구 결과 2 cm 원위절단면만으로도 종양세포 침윤이 없음을 확인하여 하부직장암 수술에 적용하고 있다. CRM은 직장암 수술에 서 전직장간막절제술(total mesorectal excision, TME)의 개념 이 도입된 후 더욱 중요하다. 전체 직장암 수술 조직의 약 25%에서 종양 세포가 CRM을 침범하고 있으며, CRM에 종 양세포 침윤이 있는 경우 국소재발률 78%, 5년 생존율이 24%였으며 CRM에 종양세포 침윤이 없는 경우는 국소재발 률 10%, 5년 생존율 76%였다.10 또한 다른 연구에서도 직장 암 수술 후 예후에 미치는 영향에 대한 다변량분석 결과
CRM의 종양세포 침윤 여부가 가장 중요한 예후인자였다.
CRM에서 1 mm 이내에 종양세포 침윤이 있는 경우 CRM 양성으로 간주한다.11
3. 분자생물학 병기와 예후인자
1) 림프절 미세전이
현재, 유방암의 경우, 림프절 미세전이 여부를 TNM 병기 분류에 사용하고 있지만 림프절 전이 여부 결정에는 아직까 지 영향을 주지 않으며 향후 지속적인 연구가 필요하다. 림 프절 미세전이는 크게 isolated tumor cells (ITCs)과 미세전이 (micrometastasis)로 구분하는데 ITCs는 0.2 mm 이하의 암세 포로, 미세전이는 0.2 mm 이상 2.0 mm 이하의 암세포로 정 의한다. 유방암의 경우 ITCs의 경우에는 면역조직화학염색 의 결과에 따라 pN0 (i-), pN0 (i+)로 표기하지만, 미세전 이인 경우에는 pN1mi로 표시하며 면역조직화학염색의 결과 에 따라 pN1mi (i+)로 표기한다. 그러나 아직까지 pN1mi을 pN1으로 분류해야 하는지에 대해서는 논란이 많으며 미국 병리학회에서는 pN1mi+에 대해서 반드시 H&E 염색을 할 것을 권장하고 있다. 직장암의 경우 대부분의 연구들이 결 장암과 직장암의 구별 없이 연구가 되어 있으므로 아직까지 는 예후에 영향을 미치는 중요한 인자로 인정되지는 않으며 미세전이 양성인 경우에도 pN0로 표기하여야 한다.12-14
2) 분자생물학 예후인자
분자생물학 연구 기법의 발달과 암 발생의 다단계 모델이 발표된 이후 여러 종류의 분자생물학 예후인자들이 연구되 었으며 그 결과 또한 다양하다. 분자생물학 예후인자들은 크게 다음과 같이 분류할 수 있다.
i. Cell proliferation indices (Ki-67, Mib-1, proliferating cell nuclear antigen [PCNA])
ii. Oncogene/tumor suppressor genes (p53, K-ras, deleted in colorectal cancer [DCC], Bcl-2, c-erbB2)
iii. DNA repair (microsatellite instability [MSI])
iv. Markers of angiogenesis (vascular count, vascular endo- thelial growth factor)
v. Markers of invasion/metastasis (plasminogen-related mo- lecules, matrix metalloproteinase)
vi. Biochemical markers (thymidylate synthase [TS], dihyd- ropyrimidine dehydrogenase [DPD])
이들 분자생물학 예후인자들은 독립적으로 또는 다른 인 자와 연관성을 가지며 예후에 영향을 미치는 것으로 보고되 지만 연구에서 결장암과 직장암의 구별이 없으며, 연구 방 법의 표준화가 이루어지지 않아 결과가 상이한 경우가 많 다. 또한 분자생물학 연구 기법은 시간이 많이 필요하며 검 사 방법이 복잡하여 임상에 적용하기에는 어려움이 있다.
Table 2. World Health Organization Classification of Colo- rectal Cancer (Epithelial Tumor)
Adenocarcinoma in situ/severe dysplasia Adenocarcinoma
Mucinous (colloid) adenocarcinoma Signet-ring cell carcinoma
Squamous cell (epidermoid) carcinoma Adenosquamous carcinoma
Small-cell (oat-cell) carcinoma Medullary carcinoma
Undifferentiated carcinoma Others (eg, papillary carcinoma)
294 The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology: Vol. 47, No. 4, 2006
최근에는 이들 분자생물학 예후인자들을 림프절 전이가 없는 TNM stage II 환자들의 항암화학요법 환자군 선택을 위한 표지자를 찾기 위한 방향으로 연구가 활발하게 진행되 고 있다. 메타분석을 이용한 몇몇 연구에서는 p53, K-ras, DCC, TS, MSI 등의 표지자들이 환자군 선택에 기여할 것이 라고 한다.15-18
참고문헌
1. Greene FL, Balch CM, Page DL, et al. AJCC cancer staging manual. 6th ed. New York: Springer-Verlag, 2002.
2. Canessa CE, Badia F, Fierro S, Fiol V, Hayek G. Anatomic study of the lymph nodes of the mesorectum. Dis Colon Rectum 2001;44:1333-1336.
3. Cawthorn SJ, Gibbs NM, Marks CG. Clearance technique for the detection of lymph nodes in colorectal cancer. Br J Surg 1986;73:58-60.
4. Crucitti F, Doglietto GB, Bellantone R, et al. Accurate speci- men preparation and examination is mandatory to detect lymph nodes and avoid understaging in colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol 1992;51:153-157.
5. Scott KW, Grace RH. Detection of lymph node metastases in colorectal carcinoma before and after fat clearance. Br J Surg 1989;76:1165-1167.
6. Fielding LP, Arsenault PA, Chapuis PH, et al. Clinicopath- ological staging for colorectal cancer: an International Docu- mentation System (IDS) and an International Comprehensive Anatomical Terminology (ICAT). J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1991;6:325-344.
7. Compton C, Fenoglio-Preiser CM, Pettigrew N, Fielding LP.
American Joint Committee on Cancer Prognostic Factors Consensus Conference: Colorectal Working Group. Cancer 2000;88:1739-1757.
8. Garcia-Aguilar J, Hernandez de Anda E, Sirivongs P, Lee SH, Madoff RD, Rothenberger DA. A pathologic complete response to preoperative chemoradiation is associated with lower local recurrence and improved survival in rectal cancer
patients treated by mesorectal excision. Dis Colon Rectum 2003;46:298-304.
9. Williams NS, Dixon MF, Johnston D. Reappraisal of the 5 centimetre rule of distal excision for carcinoma of the rectum:
a study of distal intramural spread and of patients' survival.
Br J Surg 1983;70:150-154.
10. Adam IJ, Mohamdee MO, Martin IG, et al. Role of cir- cumferential margin involvement in the local recurrence of rectal cancer. Lancet 1994;344:707-711.
11. Quirke P, Durdey P, Dixon MF, Williams NS. Local recur- rence of rectal adenocarcinoma due to inadequate surgical resection. Histopathological study of lateral tumour spread and surgical excision. Lancet 1986;2:996-999.
12. Davidson BR, Sams VR, Styles J, Deane C, Boulos PB.
Detection of occult nodal metastases in patients with colo- rectal carcinoma. Cancer 1990;65:967-970.
13. Greenson JK, Isenhart CE, Rice R, et al. Identification of occult micrometastases in pericolic lymph nodes of Duke's B colorectal cancer patients using monoclonal antibodies against cytokeratin and CC49. Correlation with long-term survival.
Cancer 1994;73:563-569.
14. Lee SH, Kim TY, Km YW, et al. Clinical significance of occult micrometastases in colorectal cancer. J Korean Soc Coloproctol 2000;16:78-86.
15. Graziano F, Cascinu S. Prognostic molecular markers for planning adjuvant chemotherapy trials in Dukes' B colorectal cancer patients: how much evidence is enough? Ann Oncol 2003;14:1026-1038.
16. Houlston RS. What we could do now: molecular pathology of colorectal cancer. Mol Pathol 2001;54:206-214.
17. Klump B, Nehls O, Okech T, et al. Molecular lesions in colorectal cancer: impact on prognosis? Original data and review of the literature. Int J Colorectal Dis 2004;19:23-42.
18. Vincenzi B, Cesa AL, Santini D, et al. Predictive factors for response to chemotherapy in colorectal cancer patients. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2004;52:45-60.