대 한 수 부 외 과 학 회 지 제 14 권 제 2 호 The Journal of the Korean Society for Surgery of the Hand VOLUME 14, NUMBER 2, June 2009
– 74 –
Clinical Results of Carpal Tunnel Release with Open Minimal Incision
Hyun-Dae Shin, MD, PhD, Kyung-Cheon Kim, MD, PhD, Jae-Hoon Yang, MD, Bo-Kun Kim, MD
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, School of Medicine,Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea
Purpose: To find out the clinical usefulness of carpal tunnel release with open minimal incision
Materials and Methods: We studied 149 patients (152 carpal tunnel) who were able to follow up for more than 6 months after being treated with carpal tunnel release with open minimal incision from January 2000 to January 2006. We compared the clinical results of this procedure using recovery time, the disappearance of symptoms, the presence of the kelloid and the scar ten- derness and analyzed preoperative and postoperative VAS score of tingling sensation, dull sensation, inappro- priate hand movement, muscle weakness, edema, palmar pain as subjective satisfaction. We used the independent t-test for the statistical significance.
Results: All cases had complete disappearance or marked improvement in symptoms, and there was no kelloid formation. Residual symptoms and tenderness of the scar was found in 8 cases (5.4%), but gradually dis- appeared. In last follow up, tingling sensation decreased
from 7.8 to 1.0 and dull sensation from 7.0 to 1.5, inap- propriate hand movement from 4.8 to 1.1, muscle weak- ness from 5.9 to 0.8, edema from 2.0 to 0.5, palmar pain from 2.1 to 0.2 in preoperative and postoperative VAS score, all were significantly improved statistically (P<0.05).
Conclusions: We think that carpal tunnel release with open minimal incision has little complication and is a safe and effective operation method having similar effect with endoscopic surgery or conventional open surgery.
(J Korean Soc Hand Surg 2009;14:74-7)
Key Words: Carpal tunnel syndrome, Open minimal incision
서 론
수근관 증후군은 말초신경의 포착 증후군 중 가장 흔한 질환으로서 정중 신경 분포부위를 따라서 통증과 이상감각을 특징으로 한다. 이 질환의 치료법으로 긴 절개를 통한 개방적 수술방법과 최근 많이 시행되는 내시경적 수술, 1993년 Biyani 등1, 1994년 Broomley2에 의해 소개된 개방적 최소 절개술이 있 다. 그 중 개방적 최소 절개술은 수술 후 작은 반흔, 낮은 합병증 등의 측면에서 각각 개방적 수술방법과 내시경적 수술 방법에 비하여 장점을 가지고 있어, 본 논문은 개방적 최소 절개를 이용한 수근관 감압술의 임상적 결과를 통하여 그 유용성을 평가하고자 한다.
연구 대상 및 방법
1. 연구 대상
2000년 1월에서부터 2006년 1월까지 본원에서 수근 관 증후군 진단 하에 최소 절개법으로 수술을 받고 최
개
개방 방적 적 최 최소 소 절 절개 개를 를 이 이용 용한 한 수 수근 근관 관 감 감압 압술 술의 의 임 임상 상적 적 결 결과 과
충남대학교 의과대학 정형외과학교실 신현대∙김경천∙양재훈∙김보건
Address reprint requests to: HHyyuunn--DDaaee SShhiinn,, MMDD,, PPhhDD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, 33, Munhwa-Ro, Jung-gu, Daejeon 301-721, Korea
TEL: 042-280-7349, FAX: 042-252-7098 E-mail: hyunsd@cnu.ac.kr
소 6개월 이상 추시가 가능하였던 환자 149명을 대상 으로 하였다. 연령은 평균 54(26~82)세였으며 남자 가 18예, 여자가 131예였다. 수술전과 수술후 6개월 에 저린 감각(Tingling sensation), 감각 둔화 (Numbness), 수부 운동 부적절성(Clumbsiness), 근 력 약화(Weakness), 부종(edema), 수장부 통증 (Pillar pain)과 같은 6가지 주 증상에 대하여 VAS(Visual analog scale)에 따라 조사한 후 inde- pendent t-test를 통하여 분석하였다. VAS는 환자 이 해를 돕기 위하여 국문으로 보조 설명하였다(Table 1).
2. 수술 방법
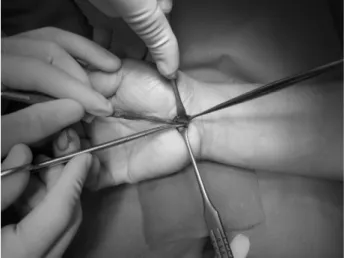
횡 수근 인대부위에서 원위부 손목 피부선을 향하여 척굴측으로 무지구 피부선을 따라 약 1.5 cm의 곡선 형 절개를 가한다(Fig.1). 수장부 건막과 피하 지방 을 박리한 후에 횡 수근 인대를 확인한다(Fig.2). 정 중신경에 손상을 주지 않기 위해 횡수근 인대를 확인 한 후 원위부를 직접 보면서 횡수근 인대에 부분적으 로 절개를 가하고 정중신경을 확인한다. 절개 부위보 다 근위부의 횡수근 인대와 전완부의 근막을 박리 시 에는 손목을 배측 굴곡시킨 상태에서 하고, 남아있는
원위부 횡수근 인대를 절개 시에는 손목을 수장부측으 로 굴곡시켜 정중신경 및 수지 굴곡근을 이완시켜 횡 수근 인대 사이에 공간을 만들어 다른 구조물에 손상 을 주지 않고 근위부와 원위부로 연장하여 유리술을 시행한다(Fig.3).
이때 정중신경을 직접 보면서 수술할 수 있는 장점 이 있고, 필요 시에는 정중신경을 이완시켜 신경 해리 술 등을 함께 시행할 수도 있다.
유리술을 시행한 후 배액관 삽입 및 피하층을 봉합 후 skin strip (3M Steri-Strip, St. Paul, U.S.A)로 피부 창상부위를 닫는다. 수술 후 수근부 신전상태에서 창상부 소독 후 수술 후 1일째 배액관을 제거하고 퇴원 후 2주 뒤에 외래 추시 하였다.
결 과
수술 전 감각변화를 보인 환자는 137명이며, 이 중
– 75 –
개방적 최소 절개를 이용한 수근관 감압술의 임상적 결과
Table 1. VAS score
VAS score
0 전혀 증상이 없다 2 아주 가벼운 증상이 있다 4 중강정도의 증상이 있다 6 꽤 심한 증상이 있다 8 아주 심한 증상이 있다
10 상상할 수 있는 것 중에 최악의 증상이 있다
Fig. 1. Make a ulnar side 1.5 cm curved incision in thenar crease.
Fig. 2. Identify transeverse carpal ligament.
Fig. 3. Extend the proximal and distal release in carpal tunnel.
Tinel 징후 양성이 104명이었고 무지구근 위축을 보 인 환자는 44명이었다. 수술 후 완전한 증상의 소실이 나 뚜렷한 증상소실로 수술을 받은 전체 환자 중에 92.4%에서 만족감을 표시하였다. Kelloid 형성은 없 었으며, 잔존 증상과 수술 후 반흔, 통증을 호소한 환 자는 18예 있었으나 시간이 경과함에 따라 증상의 호 전을 보였다. 1예에서 12개월 후에도 감각과다 증상을 호소하였다. VAS score를 이용한 수술 후 결과에서, 저린 감각이 수술 전 7.8에서 수술 후 1.0으로, 감각 둔화가 수술 전 7.0에서 수술 후 1.5로, 수부 운동 부 적절성이 수술 전 4.8에서 수술 후 1.1로, 근력약화가 수술 전 5.9에서 수술 후 0.8로, 부종이 수술 전 2.0 에서 수술 후 0.5로, 수장부 통증이 수술 전 2.1에서 수술 후 0.2로 감소하였다.
위의 6가지 증상에서 VAS의 현저한 감소소견을 보 였으며, 이는 SPSS의 independent-t test상 유의하 였다.
고 찰
수근관 증후군의 수술적 방법으로는 전통적인 개방 술, 내시경적 방법, 개방적 최소 절개를 이용한 감압 술로 나눌 수 있다. 전통적인 개방술은 수술 시야가 좋아 해부학적 구조물을 직접 보면서 수술을 시행할 수 있고, 골성 구조물의 이상이 있는 경우나 종양이 동반된 경우에도 이를 제거하면서 수술이 가능한 가장 확실한 방법이다3,4. 그러나 손목부위의 4~5 cm의 종 절개를 시행함으로 인하여, 수부의 힘이 감소하고, 상 처부위의 통증이 있으며, 무지구와 소무지구의 통증이 발생할 수 있다는 단점이 있다5-9.
내시경적 방법은 1989년 Okutsu 등10에 의해 처음 도입되어 만족스러운 결과들이 발표되었으며 그 후 많 은 저자들에 의하여 전통적인 개방성 감압술과 내시경 을 이용한 감압술에 대한 비교연구가 이루어지고 있 다. Berger11, Agee12, Bozentka 등13은 내시경적 감 압술의 장점으로는 집기력이나 파악력의 감소가 적고 회복이 빨라 젊은 층과 같이 많은 노동력이 필요하고 활동적인 사람에게 좋다고 하였다. 그러나 고가의 장 비가 필요하고 숙련된 기술을 요할 뿐 아니라, Chow14가 보고한 연구 결과에 따르면 내시경적 감압 술 시행 시 신경손상이 가장 흔히 발생하며 이를 비롯 하여 표재 수장동맥궁 손상을 포함한 혈관손상, 건 손 상, 횡수근 인대의 불완전 절개, 반사성 교감신경 이 영양증, 혈종, 창상감염 등의 합병증이 발생한다. 이 밖에 Shinya 등15은 표재 수장동맥궁이 횡수근 인대의 원위단에 가까이 있고 지방조직에 의해 둘러 쌓여 있 어서 내시경을 통해 잘 확인할 수 없기 때문에 이 동
맥의 손상 가능성이 높다고 보고 하였고, Tountas 등
16에 의하면 수근관 터널의 정중신경의 변이가 22% 정 도 되며, Ariyan 등17은 1/3에서 회선 운동분지가 횡 수근인대를 뚫고 나오므로 어쩔 수 없이 신경손상이 발생할 수 있다고 하였다. 또한 1999년 김 등18은 29 례 중 2례에서 표재 수장동맥궁 손상과 1례에서 척골 신경 일과성 마비, 1례에서 불완전절개를 보고하였다.
또한 전통적 개방술에 비하여 수술시간이 길어지고, 수술비용이 증가하며, 구조적으로 수근관이 내시경으 로 선명한 상을 얻을 수 없다는 단점이 있다6,11,19-21.
이와 아울러 최근의 연구에서 내시경을 이용한 방법 이나 전통적인 개방술을 이용하여 수술한 결과가 의미 있게 차이가 나지 않는다는 연구 논문이 다수 발표되 고 있으며18,,22-26 실제적으로 시행한 저자들의 연구 결 과에서도 내시경적 수술 방법과 전통적인 개방술은 장 기 추시 상 최종 결과에서 두 군간의 임상적 성적과 신경 전도 검사 소견의 차이가 거의 없었다. 그러나, Trumble 등7에 의하면 전향적 연구에서 내시경적 방 법이 더 신속히 환자에게 만족스러운 결과를 준다는 장점이 있다고 하였는데, 본 연구는 수술 후 6개월 추 시 결과만을 관찰한 것으로, 6개월 이전의 VAS 호전 정도는 알 수 없어 내시경적 감압술이 전통적 개방술 보다 더 신속하게 만족스러운 결과를 얻는지는 비교할 수 없었다.
제한된 절개를 이용한 감압술은 수장부 부위에 2 cm정도의 종절개를 가하여 횡수근 인대의 원위부를 확인하고 근위부로 수술 가위를 이용하여 절개하는 방 식으로 근위부를 확실히 볼 수 없어 불완전한 횡수근 인대의 절개가 가능하여 술자의 세심한 주의가 필요하 다는 단점이 있다. 하지만 제한된 절개를 이용한 감압 술은 내시경적 감압술에 비하여 어느 정도의 횡수근 인대와 정중 신경을 직접 시야로 확인한 상태에서 수 술을 할 수 있어 인접 조직의 손상을 줄일 수 있고 술 기의 습득이 어렵지 않고 수술 시간이 짧으며 고가의 장비도 필요 없다는 점에서 장점을 가지며, 전통적 개 방술에 비하여 피부 절개가 적고 수술 후 동통이 적은 장점이 있으며 또한 수술 후 결과가 다른 술식에 비교 해서 대등한 결과를 보이고 있어, 내시경적 감압술과 전통적 감압술의 장점을 살리며 단점을 최소화 하는 술식이라 사료된다.
결 론
개방적 최소 절개를 이용한 수근관 감압술은 합병증 이 적으며 기존의 내시경적 수술 및 개방적 고식적 수 술법과 대등한 효과를 보이는 안전하고 효과적인 수술 방법으로 사료된다.
– 76 –
신현대∙김경천∙양재훈∙김보건
– 77 –
개방적 최소 절개를 이용한 수근관 감압술의 임상적 결과
참고문헌
01) Biyani A, Downes EM. An open twin incision technique of carpal tunnel decompression with reduced incidence of scar tenderness. J Hand Surg Br. 1993;18: 331-4.
02) Bromley GS. Minimal-incision open carpal tunnel decom- pression. J Hand Surg Am. 1994;19:119-20
03) Einhorn N, Leddy JP. Pitfalls of endoscopic carpal tunnel release. Orthop Clin North Am. 1996;27: 373-80.
04) Phalen GS, Gardner WJ, Lalonde AA. Neuropathy of the median nerve due to compression beneath the transverse carpal ligament. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1950; 32:109-12.
05) Yoo JD, Yun YH, Jung JM, Kim JH, Ko YD, Jung WC.
Carpal tunnel release in the Bilateral carpal tunnel syn- drome. J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 2003;8: 56-9.
06) Phalen GS. The carpal tunnel syndrome. Seventeen years experience in diagnosis & treatment of 654 hands. J bone Joint Surg Am. 1966;48:211-28.
07) Kim SJ, Kang WS, Park JH. Endoscopic carpal tunnel release. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1993;28: 2429-34.
08) Mckinnon SE, McCabe SM, Murray JF, Szalai JP, Kelly L, Novak C, et al. Internal neurolysis fails to improve the results of primary carpal tunnel decompression. J Hand Surg Am. 1991;16: 211-8.
09) Trumble TE, Diao E, Abrams RA, Gilbert-Anderson MM.
Single-Portal Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Compared with Open Release: A prospective, Randomized Trial, J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84: 1107-15.
10) Okutsu I, Niomiya S, Hamanaka I, Kuroshima N, Inanami H. Measurement of pressure in the carpal canal before and after endoscopic management of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989;71:679-83.
11) Berger RA. Endoscopic carpal tunnel release. Hand Clin.
1994;10:625-36.
12) Agee JM, McCarrol HR, North ER. Endoscopic carpal tun- nel release using the single proximal incision technique.
Hand Clin. 1994;10: 647-59.
13) Bozentka DJ, Osterman AL. Complications of endoscopic carpal tunnel release. Hand Clin. 1995;11: 91-5.
14) Chow JC. Endoscopic carpal tunnel release. Clin Sports Med. 1996;15: 769-84.
15) Shinya K, Lanzetta M, Conolly WB. Risk and complica- tions in endoscopic carpal tunnel release. J Hand Surg Br.
1995;20: 222-7.
16) Tountas CP, MacDonald CJ, Meyerhoff, Bihrle DM.
Carpal tunnel syndrome: A review of 507 patients. Minn Med. 1983;66: 479-82.
17) Ariyan S, Watson HK. The palmar approach for the visual- ization and release of the carpal tunnel: An analysis of 429 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997;60: 539-47.
18) Kim JS, Shin KS, Lee DH, Jang IH, Kim YH. Endoscopic release of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Korean Orthop Assoc.
1999;34: 447-552.
19) Chow JC. Endoscopic carpal tunnel release: Two-portal technique. Hand Clin. 1994;10: 637-646.
20) Feinstein PA. Endoscopic carpal tunnel release in commu- nity-based series. J Hand Surg Am. 1993;18: 451-4.
21) Schuind F, Ventura M, Pasteels JL. Idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome: Histologic study of flexor tendon synovium. J Hand Surg Am. 1990;15: 497-503.
22) Bande S, De Smet L, Fabry G. The result of carpal tunnel release: Open versus endoscopic technique. J Hand Surg Br. 1994;19: 14-7.
23) Brown RA, Gelberman RH, Seiler JG 3rd, Abrahamsson SO, Weiland AJ, Urbaniak JR, et al. Carpal tunnel release.
A prospective, randomized assessment of open and endo- scopic methods. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75: 1265-75.
24) Ferdinand RD, MacLean JGB. Endoscopic versus open carpal tunnel release in bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome:
A prospective, randomized, blinded assessment. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84: 375-9.
25) Kerr CD, Gittins ME, Sybert DR. Endoscopic versus open carpal tunnel release: Clinical results. Arthroscopy.
1994;10: 266-9.
26) Pagnanelli DM, Barrer SJ. Carpal tunnel syndrome:
Surgical treatment using the Paine retinaculatome. J Neurosurg. 1991;75 :77-81.