IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
기후변화와 환경
- 수십 년 동안 대기 및 해양 등에서 일어나는 여러 현상을 평균화한 것, 주로 30년 동안의 평균값으로 나타내며 날씨와는 다른 개념 - 날씨(기상)는 우리가 매일 경험하는 기온, 바람, 비 등의 대기상태를 일컫는 말
-
자연적·인위적 원인에 의해 기후가 변화하는 것 - 대기 중의 이산화탄소, 메탄 등 지구를 따뜻하게 감싸 적당한 온도를 유지시켜 주는 기체 - 우리에게 꼭 필요하지만, 과도할 경우 지구온난화를 유발기후
기후
변화
온실
가스
기후변화
원인
다량의
온실가스
대기 배출
증가하는
쓰레기
무분별한
벌목
- 대기 중 온실가스 농도가 증가하여 지구의 지표온도가 과도하게 상승, 지구 온난화 현상 초래 - 산업화 이전 280ppm → 산업혁명 이후 2011년 391ppm (약 40% 증가) * 1960~2005년 평균 이산화탄소 농도 증가율은 1.4ppm/년 - 쓰레기를 분해하는 과정에서 메탄 등의 온실가스 배출 - 온실가스를 흡수하는 자연의 능력 감소IPCC 4차 보고서,Tyndall Centre
+ 4℃
- 아시아와 아프리카 인구 밀집 저지대 홍수 겪는 인구 수백만명 증가- 저위도 지역 곡물 생산량 심각한 감소 - 영양실조·이질·호흡기·심장질환 및 전염성 증가+ 3℃
- 해안습지대 30% 침수- 45억 인구 기아의 위험에 처함 - 12 ~ 30억 인구 물스트레스에 처함+ 2℃
- 2억 인구 기아의 위험에 처함 - 10억 ~ 28억 인구 물스트레스에 처함 0 1 2 3 4 (oC )최악의 기후 재앙 방지를 위해 넘어서는 안 되는 온도 상승폭
2020년까지 국가별로 1990년 대비 20~40% 감축 2050년까지 1990년 대비 50%수준으로 감축 CO2 농도 450ppm 이하 유지 필요 (cf. 2007년 현재 385ppm)+ 1℃
- 1,800 ~6,000만 인구 기아의 위험에처함 - 3억 ~ 16억 인구 물스트레스에 처함지구 평균기온 상승에 따른 영향(지구규모)
• 미 국립해양기상청(NOAA) : ‘2012년 기후보고서’를 통해 해수면이 기록적으로 상승하고 있고 북극 빙하 또한 급격히 줄고 있어 지난해의 이상고온이 일시적 현상이 아님을 강조
필리핀 태풍 하이엔 (13.11.8
)
필리핀 중남부지역 타클로반지역은 태풍으로 1만 여명 사망, 재산피해 7억 1160만 달러 추정 “기후변화 부정하려면 필리핀 가 보라” 유엔기후협약총회서 필리핀 대표 눈물의 호소
(제19차 유엔기후변화협약(UNFCCC) 당사국 총회)
IPCC Fifth Assessment Report
Synthesis Report
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
Key Messages
➜
Human influence on the climate system is clear
➜
The more we disrupt our climate, the more we
risk severe, pervasive and irreversible impacts
➜
We have the means to limit climate change and
build a more prosperous, sustainable future
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
Humans are changing the climate
Year
Globally averaged combined land and ocean surface temperatures
It is extremely likely that we are the dominant cause of warming
since the mid-20th century
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
Temperatures continue to rise
Year
Globally averaged combined land and ocean surface temperatures
Each of the past 3 decades has been successively warmer than
the preceding decades since 1850
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
Oceans absorb most of the heat
➜
More than 90% of the
energy accumulating
in the climate system
between 1971 and
2010 has
accumulated in the
ocean
➜
Land temperatures
remain at historic
highs while ocean
temperatures
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
GHG emissions growth between 2000 and 2010 has been
larger than in the previous three decades
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
Sources of emissions
Energy production remains the primary driver of GHG emissions
35%
24%
21%
14%
6.4%
2010 GHG emissions
Energy Sector Agriculture, forests and other land usesIndustry Transport
Building Sector
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
Some of the changes in extreme weather and climate events
observed since about 1950 have been linked to human influence
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
Impacts are already underway
• Tropics to the poles
• On all continents and in the ocean
• Affecting rich and poor countries
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
Projected climate changes
Continued emissions of greenhouse gases will cause further
warming and changes in the climate system
Global glacier volume will
further decrease
Global mean sea level will
continue to rise during the
21st century
It is very likely that the Arctic sea
ice cover will continue to shrink
and thin as global mean surface
temperature rises
Oceans will continue to warm
during the 21st century
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
Potential Impacts of Climate Change
Food and water shortages
Increased poverty
Increased displacement of
people
Coastal flooding
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
The window for action is rapidly closing
65% of our carbon budget compatible with a 2°C goal already used
Amount Used
1870-2011:
515
GtC
Amount
Remaining:
275
GtC
Total Carbon
Budget:
790
GtC
AR5 WGI SPMIPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
Climate Change Poses Risk for Food Production
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
Stabilization of atmospheric concentrations requires moving away from the
baseline – regardless of the mitigation goal.
Based on Figure 6.7
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
Stabilization of atmospheric concentrations requires moving away from the
baseline – regardless of the mitigation goal.
~
3°C
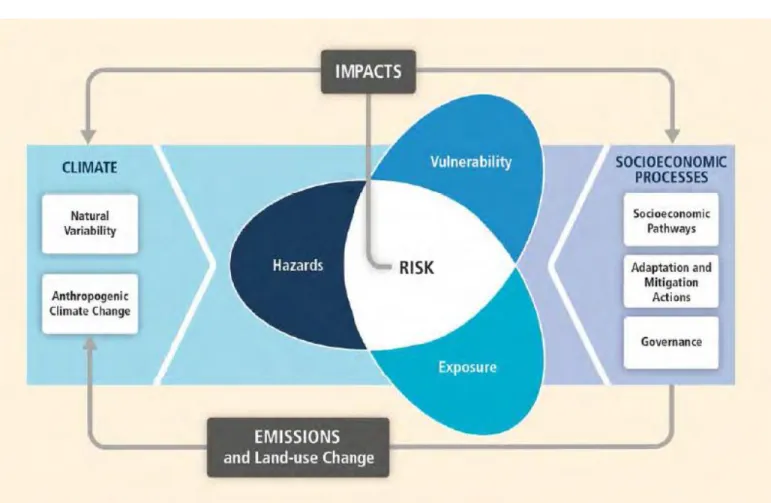
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report Figure SPM.10, A reader’s guide From climate change risks to GHG emissionse
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
Limiting Temperature Increase to 2˚C
Measures exist to achieve the substantial emissions
reductions required to limit likely warming to 2°C
A combination of adaptation and substantial, sustained reductions in
greenhouse gas emissions can limit climate change risks
Implementing reductions in greenhouse gas emissions poses
substantial technological, economic, social, and institutional
challenges
But delaying mitigation will substantially increase the
challenges associated with limiting warming to 2°C
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
Mitigation Measures
More efficient use of energy
Greater use of low-carbon and no-carbon energy
• Many of these technologies exist today
Improved carbon sinks
• Reduced deforestation and improved forest management
and planting of new forests
• Bio-energy with carbon capture and storage
Lifestyle and behavioural changes
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report
Ambitious Mitigation Is Affordable
➜
Economic growth reduced by ~ 0.06%
(BAU growth 1.6 - 3%)
➜
This translates into delayed and not forgone
growth
➜
Estimated cost does not account for the
benefits of reduced climate change
➜
Unmitigated climate change would create
increasing risks to economic growth
IPCC AR5 Synthesis Report