ISSN: 2233-601X (Print) ISSN: 2093-6516 (Online)
− 223 −
Received: September 13, 2017, Revised: September 29, 2017, Accepted: October 7, 2017, Published online: June 5, 2018
Corresponding author: Hyeong Ryul Kim, Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, 88 Olympic-ro 43-gil, Songpa-gu, Seoul 05505, Korea
(Tel) 82-2-3010-3580 (Fax) 82-2-3010-6966 (E-mail) scena@dreamwiz.com
© The Korean Society for Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. 2018. All right reserved.
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/
licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
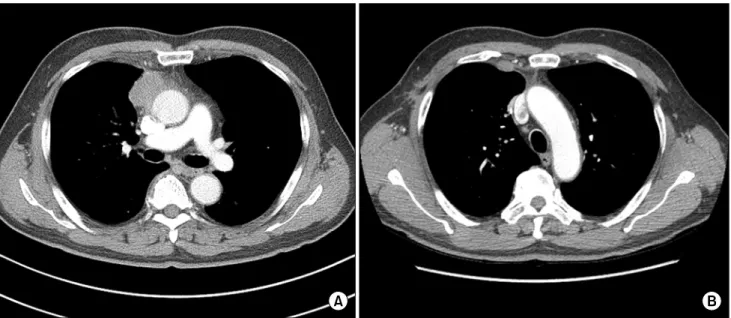
Erdheim-Chester Disease Presenting as an Anterior Mediastinal Tumor without Skeletal Involvement
Kanghoon Lee, M.D. 1 , Hyeong Ryul Kim, M.D., Ph.D. 2 , Jin Roh, M.D. 3 , You Jung Ok, M.D. 2 , Bo Bae Jeon, M.D. 2 , Young Woong Kim, M.D. 2
1