개 parthenote in vitro culture시 EDTA 첨가에 의한 발달율 향상
정해윤1,2, Zhao Minghui3, 노진구1, Ullah Imran1, 이휘철1, 위하연1, 옥선아1, 우제석1, 허태영1, 임기순1, 김종국2, 이승훈1†
1농촌진흥청 국립축산과학원 동물바이오공학과
2전북대학교 농업생명과학대학 가축번식학 연구실
3Qingdao Agricultural University
Effect of EDTA on canine parthenote development during in vitro culture
Haeyun Jeong
1,2, Minghui Zhao
3, Jin-Gu No
1, Imran Ullah
1, Whi-Cheul Lee
1, Hayeon Wi
1, Sun A Ock
1, Tai-young Hur
1, Jae-Seok Woo
1, Gi-sun Im
1, Jong-Gug Kim
2and Seunghoon Lee
1†1
Animal Biotechnology Division, National Institute of Animal Science, Rural Development Administration, 1500, Kongjwipatjwi-ro, Iseo-myeon, Wanju-gun, Jeollabuk-do, (55365) Republic of Korea
2
Animal Reproduction Laboratory, College of Agriculture and Life Science, Chonbuk National University, 567 Baekje-daero, Deokjin-gu, Jeonju-si, Jellabuk-do (54896) Republic of Korea
3
Qingdao Agricultural University 700 Changcheng Rd, Chengyang Qu, Qingdao Shi, Shandong Sheng, China
Abstract
Somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) is a useful biotechnological tool for animal cloning.
Until now, SCNT has been inefficient, especially in dog. It is believed that an embryo developmental block in SCNT embryos is cause of low production efficiency. However, no studies have been performed on canines for embryo developmental block. In this study, we attempted to evaluate the beneficial role of EDTA in canine parthenogenic (PA) embryos development to overcome embryo developmental block. The PA embryos were divided into 0.01 mM EDTA treated and non-treated groups. Embryo developmental efficiency was measured by activating chemically parthenote. After EDTA induction, PA embryos were evaluated for embryonic development, Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) activity, mitochondrial integrity, ATP production and genomic activation. The EDTA treated PA embryos showed significantly higher survival rate and improved cavity formation compared to non-treated. Furthermore, cytoplasmic ROS level was mitigated and mitochondrial membrane potential was found significantly higher in EDTA treated group followed by higher ATP production. Moreover, major embryonic genomic activation specific markers/factors were also elevated in EDTA treated group. Conclusively, we elucidated that EDTA showed substantially positive effect to overcome embryo developmental block in canine.
Received
:
03 September 2018 Revised:
20 September 2018Accepted:21 September 2018
Key Words : canine, early development, EDTA, in vitro culture, parthenote
서 론
최초의 복제동물 ‘돌리’의 탄생 이후(Wilmut 등, 1997) 급격히 발달한 체세포 핵이식 기술의 발달로 소(Cibelli 등, 1998), 마우스 (Wakayma 등, 1998), 돼지(Polejaeva 등, 2000), 개(Lee 등, 2005) 등을 포함한 다수의 동물 종에서 복제동물의 생산이 보고되고 있다.
그러나 체세포 핵 이식 기술을 이용한 복제 산자의 생산효율은 낮은 실정이며, 특히 개에서는 5% 미만 정도로 낮은 결과를 보여준다 (Liu 등, 2015; Kim 등, 2015). 낮은 생산효율의 가장 큰 원인 중 하나는 체세포 복제란의 발달율 저하이다. 체세포 복제란 뿐만 아니라 체외에서 배양하는 모든 수정란의 발달에는 embryo developmental block 현상이 발생하는 경우가 빈번히 발생한다. 이런 embryo developmental block 현상으로 인한 배아의 발달 정지 시기는 포유동물에 따라 각각 다르다. 마우스에서는 초기 2-세포기에서 배아 발달이 정지되며(Goddard 등, 1983), 소, 돼지, 양에서는 8-16 세포기에(Gandolfi 등, 1987; Wright 등, 1981), 토끼에서는 morula 단계 에서(Kane 등, 1970) embryo developmental block이 일어난다.
이러한 block 현상을 극복하기 위하여 여러 종의 동물에서 다른 체세포와의 공배양 등 많은 시도가 이루어 졌다(Malekshah 등, 2006). 그 중 주목할만한 것이 배아의 초기 발달 시 Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA)를 첨가해 주는 시도였다. 마우스에서는 EDTA가 배양액에서 단백질을 대체하며 2-cell block을 극복하여 체외수정 배아의 발달을 촉진했으며(Gardner and Lane, 1996), 또한 소에서는 EDTA와 glucose를 첨가하여 소 배아의 발달능과 hatching ability를 향상시켰다는 보고가 있다 (Pirestani 등, 2011). EDTA 는 마그네슘, 칼슘과 같은 2가 양이온의 chelator로서의 역할로, 배아 발달 능력을 증가시키는 것으로 보고되었는데, EDTA가 3-phosphoglycerate kinase와 같은 당 분해 효소의 정상적인 활동에 필요한 세포 내 마그네슘을 chelation함으로써 포도당 대사가 예상 보다 이르게 전환되는 것을 막는 원리라고 주장한다(Gardner 등, 2000).
이렇게 마우스와 소에서는 EDTA를 사용하여 embryo developmental block을 극복한 사례가 있지만 아직까지 개에서는 EDTA를 사용하여 embryo developmental block을 극복한 사례는 보고되어 있지 않다. 개 난자의 경우 체외에서 성숙과 수정이 이루어질 경우, 8-세포기 이상으로 발달할 가능성은 낮다. 개에서는 체외수정 배아의 경우, 4-8세포기 단계까지 발달하였으며(Rodrigues, 2004;
Rodrigues 등, 2007), 개 배아 섬유아세포와의 공동배양에서 16-세포기 단계까지, 마우스 배아 섬유아세포와의 공동배양에서 morula 단계까지 발달하였다(Hatoya 등, 2006). buffalo rat liver cells와의 공동배양 결과, 8-16 세포기까지 발달하였다. (Saikhun 등, 2008).
따라서 본 연구는 개 배아에서 8-cell block 현상으로 인해 8-세포기 이상으로 발달하지 못하는 한계를 극복하기 위하여, 개 parthenote in vitro culture 시 EDTA의 첨가가 배아의 발달율에 미치는 영향을 조사해 보았다.
재료 및 방법
1. 시약 및 배양액
개 PA 배아를 배양하기 위해 사용된 배양액은 Gibco(Grand Island, NY, USA)제품을 사용하였고, 별도로 표시된 경우가 아니면 모든 시약은 Sigma-Aldrich(St. Louis, MO, USA)에서 구입하였다.
2. 체내성숙 된 개 난자의 채취와 Pathenogenesis(PA)
모든 동물실험은 국립축산과학원 동물실험윤리위원회 운영규정에 의해 엄격하게 심사하여 승인절차를 거쳐 수행되었으며 승인번호 는 2018-312이다.
성숙된 개 난자는 flushing 배양액(HEPES-buffered TCM-199; 10% FBS, 2mM NaHCO3, 0.5% bovine serum albumin [BSA], 1% penicillin and streptomycin [Gibco])을 사용하여 배란 후 72-76시간 안에 외과적인 방법을 통해 개 난관에서 채취하였다. Cumulus cells은 Holding 배양액(10% FBS를 첨가한 HEPES-buffered TCM-199)에서 부드럽게 피펫팅하여 제거하였다.
Cumulus cell을 제거한 개 난자는 10 µM Ca-ionophore(A23187)가 첨가된 modified synthetic oviduct fluid(mSOF)(106mM NaCl, 7.2mM KCl, 25mM NaHCO3, 1.2mM KH2PO4, 6.6 mM Na-lactate (60%), 1.7mM CaCl2, 0.5mM MgCl2, 0.3mM Na-pyruvate, 1.5mM Glucose, 1mM Glutamine, 2% Essential A.A, 1% Non-essential A.A, 0.8% FAF-BSA, Gentamycin)에 5분동안 인큐베이터
다. 실험군과 대조군은 활성화를 진행한 이후를 0일차로 보고, 0일차에서 2일차까지 5% CO2, 5% O2, 38.5°C의 조건으로 인큐베이터에 서 배양한다. 이 후, 3일차부터 8일차까지 각 실험군과 대조군은 EDTA가 첨가되지 않은 mSOF 배양액에서 5% CO2, 5% O2, 38.5°C 의 조건으로 인큐베이터에서 배양하였다.
3. 개 PA 배아의 세포 수 측정
8일차 배양된 배아를 Hoechst 염색하여 배아의 세포 수를 측정하였다. 배아를 5 µg/ml Hoechst 33342가 처리된 배양액에 5분간 인큐베이터에서 염색한 후, dPBS로 3회 세척하였다. 이후 형광현미경(Olympus, Tokyo, Japan)으로 청색 형광의 핵을 확인하여 총 세포 수를 측정하였다.
4. 개 PA 배아에서 Cytoplasmic Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) level 의 측정
EDTA를 처리하였을 시, 개 PA 배아에서 Cytoplasmic ROS level을 측정하기 위하여 녹색 형광 시약으로 2′, 7′
dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate를 사용하였다. 처리군과 대조군에서 8일차 배양된 개 배아 각 6개를 빛이 없는 환경에서 10 µg/ml 2′, 7′dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate를 처리한 배양액에서 50분간 배양한 후, dPBS로 3회 세척하였다. 형광현미경(Olympus, Tokyo, Japan)을 사용하여 녹색 형광을 측정하였으며 배아의 형광 강도는 image J software(National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA)를 사용하여 분석하였다.
5. JC-1 staining
Mitochondrial integrity와 membrane potential을 평가하기 위하여 JC-1 staning을 실시하였다. Stain에는 JC-1(Molecular Robes, USA)를 사용하였다. 8일차 배양된 개 배아를 10 µg/ml JC-1 포함된 배양액에 40분간 인큐베이터에서 처리한 후, dPBS에 3회 세척하 였다. J-aggregates는 적색 형광으로, monomer은 녹색 형광으로 나타나는 것을 형광현미경(Olympus, Tokyo, Japan)으로 확인 할 수 있었다.
6. ATP concentration detection
개 배아의 ATP를 분석하기 위하여 Molecular Probes◯RATP Determination kit(A22066, ThermoFisher)를 사용하였다. 분석하고자 하는 3개의 개 배아를 dPBS에 3회 세척한 뒤, 얼음에 둔 1mL tube에 각각 옮겨 담았다. 용액을 제거한 뒤, 개 배아를 동결과 해동을 반복하며 용해하였다. 약 100 µl의 ice-cold somatic cell reagent(FL-SAR)을 각 tube에 첨가하고 sample을 ice-water bath에 5분간 두었다. 이후 100 µl의 ice-cold assay buffer(희석 배수, 1:25 ; ATP assay buffer, FL-AAB)를 첨가하고, 빛이 없는 환경에서 5분동안 실온에서 처리하였다. ATP concentration은 0.01pm의 감도를 가진 luminometer를 사용하여 측정하였다. 대조군의 ATP concentration 은 임의로 1의 값으로 설정하였다.
7. 핵 관련 유전자 정량분석 (Real-time PCR)
배아의 total RNA 추출은 RNAqueous-Micro Kit (Ambion, Inc., Austin, TX)를 이용하여 제조사의 방법에 준하여 추출되었다.
cDNA는 random hexamer primers, T4 gene 32 protein (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA), Superscript III enzyme (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA)와 함께 total RNA와 같은 양으로 사용하여 55 ℃에서 120분 간 반응시켜 제조하였다. 준비된 cDNA를 정제하고 linear polyacrylamide (Ambion, Inc.), ammonium acetate, phenol/chloroform/isoamyl alcohol와 함께 침전시켰다.
8. 통계 처리
본 연구의 결과는 Statistical Package for the Social Sciences(SPSS,IBM)을 이용하여 통계처리 하였다. 두 그룹간의 비교는 Student’s t-test로 이루어졌다. 모든 통계 분석에서 P 값이 0.05 미만인 경우를 유의 한 것으로 판단하였다.
결과
1. 세포수, 생존율 및 cavity formation에 대한 EDTA의 효과
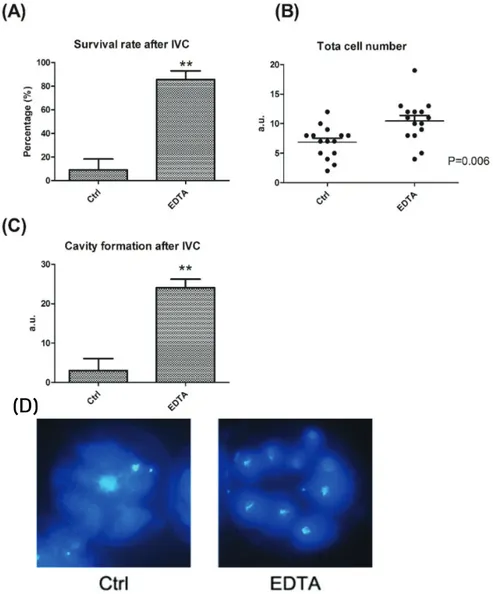
배아 발달에 대한 EDTA의 효과를 확인하기 위하여, 활성화 후 0.01mM의 EDTA가 첨가된 SOF 배양액에 배양하였다. 생존율은 8일차에서 확인하였다. EDTA를 처리한 배아의 경우 EDTA를 처리하지 않은 대조군에 비교하였을 때, 유의적으로 높은 생존율(figure 1A)과 세포 수(figure 1B)를 보여줬으며, cavity formation도 향상된 것을 확인하였다(figure 1C).
(D)
Figure 1. Effect of EDTA on cell number, survival and Cavity formation. (A) is Survival rate(%), (B) is total cell number as a graph
and (C) Cavity formation of canine PA embryo on day 8. Bar graph data represent as mean ± SD. Differences were considered significant at * P < 0.05; ** < 0.01 (D) total cell number after Hoechst staining. Blue fluorescence represents nuclei.2. EDTA 처리에 따른 cytoplasmic ROS level
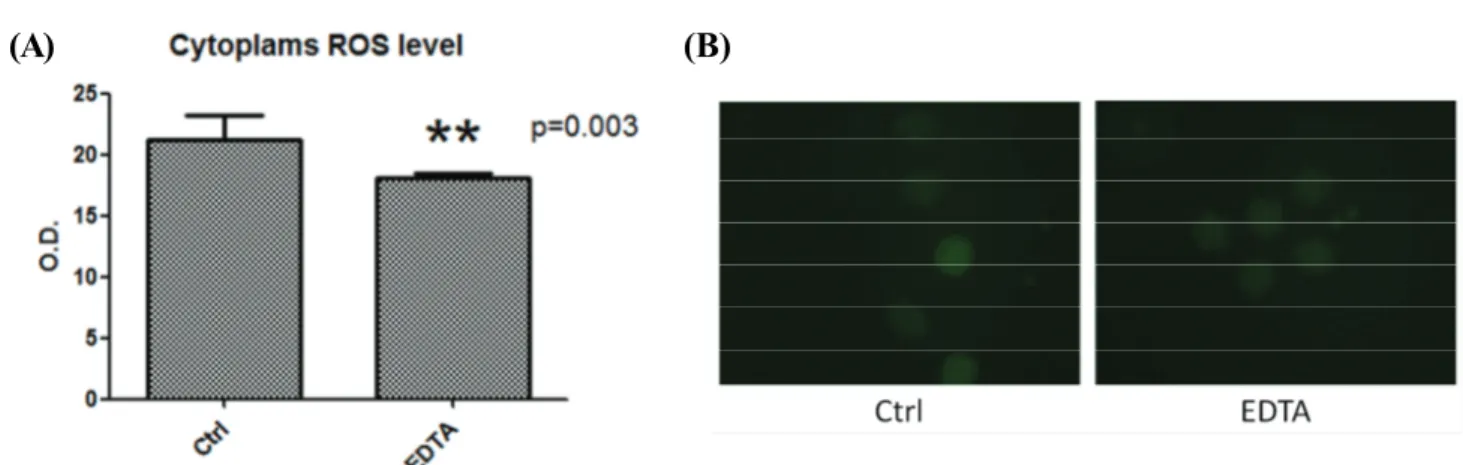
개의 배아에서 cytoplasmic ROS level을 확인하기 위하여 2′, 7′dichlorodi-hydrofluorescein diacetate를 사용해 측정하였다. ROS 의 발현은 대조군에 비교하였을 때 EDTA를 처리한 실험군이 유의적으로 낮게(p<0.003) 나타났다(figure 2)
(A) (B)
Figure 2. The effect of EDTA on ROS in canine parthenogenic (PA) embryos development. (A) Cytoplasmic ROS level of canine PA
embryos on day 8. Bar graph data represent as mean ± SD. (B) The ROS fluorescence (green) of canine PA embryos in control and EDTA treated group.3. mitochondrial integrity를 확인하기 위한 JC-1 staining
mitochondrial integrity와 membrane potential을 확인하기 위하여 JC-1 staining을 하였다. Apoptosis가 일어난 세포의 경우 녹색 형광으로 발현된 것을 확인하였으며, 살아있는 세포의 경우 적색 형광으로 발현된 것을 확인하였다(figure 3A). 실험군과 대조군을 비교 하였을 때, EDTA를 처리한 실험군의 JC-1 발현이 대조군보다 유의적으로 높게 나타난 것을 확인할 수 있다(figure 3B).
(A) (B)
Figure 3. Differential effect of EDTA on mitochondrial integrity Mitochondrial function measurements using JC-1 staining in EDTA and
control embryos. (A) Images of JC-1 staining in EDTA and control embryos. Red fluorescence indicates healthy state and green indicates state with mitochondrial dysfunction. (B) Quantitative analysis of JC-1 staining. Bar graph data represent as mean ± SD. Differences were considered significant at * P < 0.05.4. ATP production
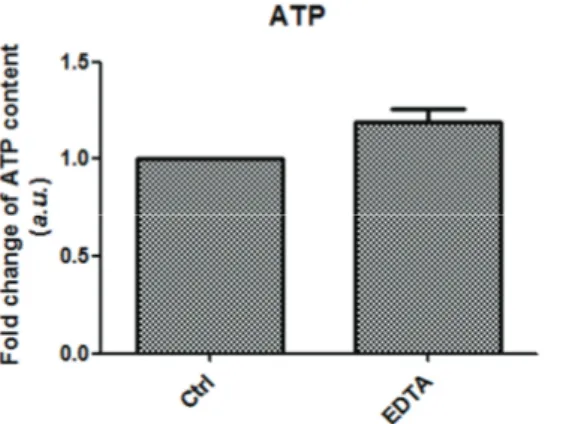
mitochondrial integrity 분석 후, ATP production을 확인하기 위하여 ATP analysis commercial kit를 사용하여 측정하였다. EDTA 를 처리한 실험군이 처리하지 않은 대조군에 비교하였을 때, 유의적인 차이는 보이지 않았으나 ATP production의 fold change가 높은 경향을 보이는 것으로 나타났다(figure 4). 이러한 결과는 mitochondrial integrity 분석과 일치된 결과라는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
5. Genomic activation
배아 관련 유전자의 주요한 전사 활성화에는 ribosomal RNA(rRNA)의 활성화가 포함되며, rRNA 유전자 전사에 관련된 중요한 단백질은 upstream binding factor(UBF)이다. EDTA를 처리한 실험군과 처리하지 않은 대조군에서 18s RNA와 UBF의 발현을 측정하 였다. 실험군과 대조군 사이에서 18s RNA와 UBF의 수준에 유의한 차이를 발견할 수 있었다(figure 5). 이를 통해 개의 배아 발달에서 EDTA가 긍정적인 역할을 한다는 사실을 확인할 수 있었다.
Figure 4. Intracellular ATP levels of canine PA embryo treated or not EDTA. The intensity of the signal of control was set at 1 and the
relative abundance of EDTA treated Group was expressed relative to that value. Bar graph data represent as mean ± SD.Figure 5. Nucleolar-related gene expression at 8-cell stage. 18s RNA and UBF expression were quantified. The intensity of the signal
of control was set at 1 and the relative abundance of EDTA treated Group was expressed relative to that value. Bar graph data represent as mean ± SD. Differences were considered significant at * P < 0.05.고찰
체세포 핵 이식 기술은 다양한 목적으로 복제동물을 생산하는데 이용되고 있다. 그러나 체세포 핵 이식 기술의 효율은 낮은 실정이 며, 특히 개에서는 더 낮은 결과를 보인다. 개 난자의 경우 체외에서 성숙과 수정이 이루어질 경우 대부분 8-세포기 단계에서 cell block 현상이 일어나며 발달이 정지된다. EDTA는 2가 양이온의 chelate로 배아 발달 능력을 증가시키는 것으로 보고되었으며, 앞선 연구에 따르면 마우스, 소에서 배아의 발달 능력에 효과가 있음을 입증하였다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 EDTA가 개 PA 배아에 미치는 영향을 평가하고자 개 PA 배아를 EDTA 실험군과 대조군으로 나누어 실험을 진행하였다. EDTA 처리 후 배아의 발달율, 분할율, ROS 활성, mitochondrial integrity, ATP production 및 genomic activation에 대해 PA 배아를 분석하였다.
주었다. 일반적인 체외수정 배지(5% fetal bovine serum [FBS]가 보충된 TCM)는 개 난자의 성숙을 유의적으로 향상시키지 못했다 (Lee 등, 2007). 그러나 FBS(Bolamba 등, 2002)나 fetal calf serum(FCS)(Saint-Dizier 등, 2004)를 보충한 배지에 개 cumulus oocytes complex(COCs)를 배양할 때 난자의 성숙이 향상되었다. 본 연구에서는 개 PA 배아의 발달을 향상시키기 위한 프로토콜을 디자인하기 위해 배양 배지에 EDTA를 첨가하였다.
EDTA는 2가 양이온의 chelator이며 이전 연구에서 마우스 및 소의 배아 발달에 사용되었다. 마우스 배반포가 발달하는 시기에 EDTA를 계속 첨가할 경우 배아 발달을 오히려 감소시킨다는 보고에 따르면(Gardner and Lane, 1996), EDTA의 배아 발달을 향상시키 는 역할은 배아가 분열되는 시기에 한정되어 있는 것으로 보인다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 개의 PA 배아에서 EDTA를 초기 2일간 처리하 였다. 48시간동안 개 PA 배아의 배양에 EDTA가 첨가하였을 때, 생존율과 총 세포 수가 향상되었으며 cavity formation을 증가시켰다.
이는 소에서 나타난 이전의 결과와 일치한다(Pirestani 등, 2011). EDTA의 정확한 역할은 아직 알려지지 않았지만, 아마도 중금속 오염 물질을 chelation하는 것이 긍정적인 영향을 주는 것이라는 보고가 있다(Pirestani 등, 2011). 또한 EDTA로 처리한 PA 배아는 대조 배지에서 배양한 것보다 현저하게 높은 발달 속도를 보였는데, 이는 이전에 보고된 마우스 및 소의 배아에서 보여준 양상과 일치한다 (Gardner 등, 2000).
높은 ROS 농도는 난자와 배아의 발달 능력을 손상시키는 것으로 보고되었다(Hashimoto 등, 2000). 이전 연구에 따르면 free cytoplasmic iron은 ROS를 억제하여 돼지의 배아 생산을 증가시켰다(Zhao 등, 2015). 그러므로 높은 ROS의 함량이 난자와 배아의 발달에 있어 해로운 영향을 주는 것을 확인할 수 있다. 본 실험에서 EDTA로 처리한 개 PA 배아의 ROS 함량은 처리하지 않은 대조군 에 비교하였을 때 유의미한 감소를 보였다.
세포의 에너지원이라 여겨지는 미토콘드리아는 oxidative phosphorylation을 통해ATP 생산에 적극적으로 관여한다. Mitochondrial membrane potential은 난자가 성숙되는 동안 유의적으로 증가하는 반면(Van and Davis, 2007), 배반포 형성이 제대로 이루어지지 않고 감소할 경우 항상 Mitochondrial membrane potential 감소를 동반한다(Lee 등, 2014; Lee 등, 2015). 따라서 우리는 개 PA 배아에 EDTA 처리를 하여 JC-1 발현 및 ATP 생산을 분석하여 Mitochondrial membrane potential을 조사하였다. 우리는 EDTA가 처리된 PA 배아에서 JC-1의 높은 발현과 증가된 ATP 함량을 발견하였다. 이러한 결과는 EDTA가 처리된 PA 배아에서 미토콘드리아가 정상 적인 활동을 통해 ATP 생산에 기여한다고 해석될 수 있으며, 이는 EDTA가 배아의 초기 발달에 있어 긍정적인 영향을 준다는 우리의 가설을 뒷받침한다.
배아 발달에 있어 또 다른 중요한 역할을 하는 것은 genomic activation이다. 착상 전 포유동물 배아의 초기 발달은 발달 과정에서 난자로부터 생성되고 저장되는 유전자에 의해 조절된다(Schultz 등, 1993). 그러나 배아의 분할 직 후, embryonic genome은 발달 조절 을 시작하며 점차적으로 모체로부터 유래된 전사물과 단백질을 degration한다(Telford 등, 1990). rDNA와 fibrillarin의 전사에서, major embryonic activation은 RNA polymerase
Ⅰ 뿐만 아니라 다른 단백질, topoisomerase Ⅰ, upstream binding factor(UBF)도 관여한다
(Svarcova 등, 2007). UBF는 major embryonic activation 시기에 배아에서 나타나며, rRNA의 초기 진행과정에 관련되어있다 (Maddox-Hyttel 등, 2007; Svarcova 등, 2007). 따라서 포유동물의 배아에서 rRNA 유전자 활성화, 그리고 그와 연관된 nucleous 형성 을 major embryonic activation을 위한 main maker로 보고 있다(Bjerregaard 등, 2007). 우리는 genomic activation의 두 가지 major maker인 18s RNA(rRNA)와 UBF의 발현을 분석하여 EDTA를 처리한 개 PA 배아가 처리하지 않은 대조군에 비해 발현정도가 유의하 게 증가하는 것을 확인하였다.결과에 따르면 EDTA를 처리한 개 PA 배아는 처리되지 않은 배아에 비해 높은 발달 속도와 함께 생존율과 총 세포 수가 향상되고 cavity formation을 증가됨이 밝혀졌다. 또한 EDTA는 높은 ATP 생산에 의해 Mitochondrial membrane potential을 높이고 ROS content가 감소함을 보여주었다. 결론적으로 개 PA 배아는 EDTA가 보충된 환경에서 생존율이 증가되며 발달율 역시 증가되는 것을 확인하였으나, EDTA가 개 PA 배아의 발달에 어떤 영향을 미치는지에 대한 정확한 기전을 밝히기 위해 추가적인 연구가 필요할 것으 로 보인다.
사사
본 연구는 농촌진흥청 연구사업(과제번호 PJ01398701) 사업에 의해 이루어진 것임. 본 연구는 2018년도 농촌진흥청 국립축산과학원 학·연협동연구과정 지원사업에 의해 이루어진 것임.
REFERENCES
Bjerregaard B, Pedersen HG, Jakobsen AS, Rickords LF, Lai L, Cheong HT, Samuel M, Prather RS, Strejcek F, Rasmussen ZR et al. 2007 Activation of ribosomal RNA genes in porcine embryos produced in vitro or by somatic cell nuclear transfer.
Molecular Reproduction and Development 74:35-41.
Bolamba D, Russ KD, Olson MA, Sandler JL and Durrant BS. 2002. In vitro maturation of bitch oocytes from advanced preantral follicles in synthetic oviduct fluid medium: Serum is not essential. Theriogenology 58:1689-1703.
Cibelli JB, Stice SL, Golueke PJ, Kane JJ, Jerry J, Blackwell C, Ponce de Leon F and Robl JM. 1998. Cloned transgenic calves produced from nonquiescent fetal fibroblasts. Science 280:1256-1258.
Cui XS, Jin YX, Shen XH, Lee JY, Lee HS, Yin XJ, Kong IK and Kim NH. 2006. Epidermal growth factor enhances meiotic resumption of canine oocytes in the presence of BSA. Theriogenology 66:267-274.
Gandolfi F and Moor RM. 1987. Stimulation of early embryonic development in the sheep by co‐culture with oviduct epithelial cells. J. Reprod. Fertil. 81:23-28.
Gardner DK and Lane M. 1996. Alleviation of the "2-cell block'' and development to the blastocyst of CF1 mouse embryos: role of amino acids, EDTA and physical parameters. Hum. Reprod. 11:2703-2712.
Gardner DK, Lane MW and Lane M. 2000. EDTA stimulates cleavage atage bovine embryo development in culture but inhibits blastocyst development and differentiation. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 53:256-261.
Goddard MJ and Pratt HP. 1983. Control of events during early cleavage of the mouse embryo: an analysis of the ‘2‐cell block’.
J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 73:111-133.
Hashimoto S, Minami N, Yamada M and Imai H. 2000. Excessive concentration of glucose during in vitro maturation impairs the developmental competence of bovine oocytes after in vitro fertilization: relevance to intracellular reactive oxygen species and glutathione contents. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 56:520-526.
Hatoya S, Sugiyama Y, Torii R, Wijewardana V, Kumagai D, Sugiura K, Kida K, Kawate N, Tamada H, Sawada T and Inaba T. 2006. Effect of co-culturing with embryonic fibroblasts on IVM, IVF and IVC of canine oocytes. Theriogenology 66:1083-1090.
Kane MT and Foote RH. 1970. Culture of 2‐ and 4‐cell rabbit embryos to the expanding blastocyst stage in synthetic media.
Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 133:921-925.
Kim MJ, Oh HJ, Kim GA, Suh, HN, Jo YK, Choi YB, Kim DH, Han HJ and Lee BC. 2015. Altering histone acetylation status in donor cells with suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid does not affect dog cloning efficiency. Theriogenology 84:1256-1261 Kim MK, Fibrianto YH, Oh HJ., Jang G, Kim HJ, Lee KS, Kang SK, Lee BC and Hwang WS. 2004. Effect of
beta-mercaptoethanol or epidermal growth factor supplementation on in vitro maturation of canine oocytes collected fromdogs with different stages of the estrus cycle. J. Vet. Sci. 5:253-258.
Lee BC, Kim MK, Jang G, Oh HJ, Yuda F, Kim HJ, Hossein MS, Kim JJ, Kang SK, Schatten G and Hwang WS. 2005. Dogs cloned from adult somatic cells. Nature 436:641.
Lee SK, Zhao MH, Kwon JW, Li YH, Lin ZL, Jin YX, et al. 2014. The association of mitochondrial potential and copy number with pig oocyte maturation and developmental potential. The Journal of reproduction and development 60:128-135.
Lee SK, Zhao MH, Zheng Z, Kwon JW, Liang S, Kim SH, et al. 2015. Polymerase subunit gamma 2 affects porcine oocyte maturation and subsequent embryonic development. Theriogenology. 83(1):121-130.
Lee SR, Kim BS, Kim JW, Kim MO, Kim SH, Yoo DH, Shin MJ, Park YS, Lee S, Park YB, Ha JH and Ryoo ZY. 2007. In vitro maturation, in vitro fertilization and embryonic development of canine oocytes. Zygote 15:347-353.
Liu Y, Li J, Løvendahl P, Schmidt M, Larsen K and Callesen H. 2015. In vitro manipulation techniques of porcine embryos:
a meta-analysis related to transfers, pregnancies and piglets. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 27:429-439.
Maddox-Hyttel P, Svarcova O and Laurincik J. 2007. Ribosomal RNA and nucleolar proteins from the oocyte are to some degree
granulosa cells on mouse embryo development. Indian. J. Exp. Biol. 44:189-192.
Pirestani A, Hossieni SM, Moulavi F, Hajian M, Fourozanfar M and Esfahani MHN. 2011. In Vitro Bovine Embryo Development with Glucose and EDTA in Different Modifications of SOF Medium. IPCBEE 24:283-287.
Polejaeva IA, Chen SH, Vaught TD, Page RL, Mullins J, Ball S, Dai Y, Boone J, Walker S, Ayares DL, Colman A and Campbell KH. 2000. Cloned pigs produced by nuclear transfer from adult somatic cells. Nature 407:86-90.
Rodrigues BA, dos Santos LC and Rodrigues JL. 2004. Embryonic development of in vitro matured and in vitro fertilized dog oocytes. Mol. Reprod. Dev, 67:215-223.
Rodrigues BA, dos Santos LC and Rodrigues JL. 2006. The effect of hyaluronan concentrations in hST-supplemented TCM199 on in vitro nuclear maturation of bitch cumulus–oocyte complexes. Theriogenology 66:1673-1676.
Rodrigues BA, dos Santos LC and Rodrigues JL. 2007. Effect of maturation medium on in vitro cleavage of canine oocytes fertilized with fresh and cooled homologous semen. Zygote 15:43-53.
Saikhun J, Sriussadaporn S, Thongtip N, Pinyopummin A and Kitiyanant Y. 2008. Nuclear maturation and development of IVM/IVF canine embryos in synthetic oviductal fluid or in co-culture with buffalo rat liver cells. Theriogenology 69:1104-10.
Saint-Dizier M, Reynaud K and Chastant-Maillard, S. 2004. Chromatin, microtubules and kinases activities during meiotic resumption in bitch oocytes. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 68:205-212.
Schultz RM. 1993. Regulation of zygotic gene activation in the mouse. Bioessays 15:531-538.
Svarcova O, Laurincik J, Avery B, Mlyncek M, Niemann H and Maddox-Hyttel P. 2007. Nucleolar development and allocation of key nucleolar proteins require de novo transcription in bovine embryos. Molecular Reproduction and Development 74:1428-1435.
Telford NA, Watson AJ and Schultz GA. 1990. Transition from maternal to embryonic control in early mammalian development:
a comparison of several species. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 26:90-100.
Van Blerkom J and Davis P. 2007. Mitochondrial signaling and fertilization. Molecular Human Reproduction 13(11):759-770.
Wakayama T, Perry AC, Zuccotti M, Johnson KR and Yanagimachi R. 1998. Full-term development of mice from enucleated oocytes injected with cumulus cell nuclei. Nature 394:369-374.
Wilmut I, Schnieke AE, McWhir J, Kind AJ and Campbell KHS. 1997. Viable offspring derived from fetal and adult mammalian cells. Nature 385:810-813.
Wright RW Jr and Bondioli KR. 1981. Aspects of in vitro fertilization and embryos culture in domestic animals. J. Anim. Sci.
53:702.
Zhao MH, Liang S, Kim SH, Cui XS and Kim NH. 2015. Fe(III) Is Essential for Porcine Embryonic Development via Mitochondrial Function Maintenance. PLoS ONE 10:e0130791. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0130791.