서 론
대사 증후군에 대한 기술은 1923 년 kylin 이 언급한 이래, 1980 년 대 이후 개념이 정립되었다. 아직까지 정확한 원인은 확인되지 않았 으나, 인슐린 저항성이 대사 장애를 이루는 질병의 주요 원인임을 제 시하면서 1998 년 이후 지속적인 진단 기준의 변화가 있었다. 현재 는 미국 콜레스테롤 교육 프로그램( National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III , NCEP - ATP III )와 세계당뇨 병학회( International Diabetes Federation )에서 제시한 기준을 사
용하고 있다. 2007 년 윤 등은 대사 증후군의 유병률을 남성의 경우 25 . 7 %, 여성의 경우 31 . 9 %로 보고하였으며,
1)2008 년 국민영양조사 를 이용한 리 등은 18 . 5 %라고 보고하였다.
2)대사 증후군에 대한 관 심이 높아지면서 이에 대한 연구가 많이 이루어졌으며, 특히 만성 염
증,
3, 4)인슐린 저항성
5, 6)이 관여된다고 알려져 있다.
최근 아시아 지역을 중심으로 빌리루빈( bilirubin )과 대사 증후 군에 대한 연구가 진행되었으며,
7-12)대다수의 연구에서 총 빌리루 빈( total bilirubin )과 대사 증후군 사이의 역의 상관관계가 있다는 것을 보고하였다. 또한 일부 연구에서는 직접 빌리루빈도 역시 같
건강 검진에서 관찰되는 한국 성인의 대사 증후군과 빌리루빈 수치와의 관련성
최봉석, 장미, 김선희, 김영진, 신경숙, 유병욱, 조용진
*, 오정은, 조주연, 홍성호
순천향대학교 의과대학 가정의학교실
Relationships between serum bilirubin levels and metabolic syndrome at the health care check-up in Korea adults
Bong-Suk Choi, Mi Jang, Sun-Hee Kim, Young-Jin Kim, Kyung-Suk Shin, Byung-Wook Yoo, Yong-Jin Cho
*, Jung-Eun Oh, Choo-Yon Cho, Sung-Ho Hong
Department of Family Medicine, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine
Background: Serum bilirubin has a potential antioxidant effect and is also associated with metabolic syndrome in Asian people. The aim of this study was to evaluate the characteristics of and the relationship between total bilirubin level and metabolic syndrome in Korean subjects.
Methods: Following a retrospective review, 10,458 patients aged 20 years and over who visited the Health Promotion Center for check-up were enrolled in this study. We excluded subjects with chronic viral liver diseases, liver cirrhosis confirmed by ultrasonography, a fasting total bilirubin level>3mg/dL, or immune compromised status.
Results: The prevalence of metabolic syndrome was 17.3%(1130/6508) in men and 5.2%(208/3910) in women. There was no age difference between the group with and without metabolic syndrome. However, women in the group with metabolic syndrome were significantly older (50 versus 37.5 years). Total bilirubin level decreased in men with an increase in the number of metabolic syndrome components with higher fasting glucose level, hypertriglycemia and lower high density lipoprotein. In men, total bilirubin level was related with metabolic syndrome after adjusting for age, body mass index, smoking and alcohol drinking. The odds ratio(95% confidence interval) for metabolic syndrome for each total bilirubin quartile was 0.83 (0.70~0.98), 0.63 (0.53~0.75) and 0.52 (0.43~0.63) in men. However, total bilirubin level was not associated with metabolic syndrome in women.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that prevalence of metabolic syndrome has decreased recently, and total bilirubin level is inversely associated with metabolic syndrome, especially in men.
Keywords: serum bilirubin, metabolic syndrome, men.
Received February 27, 2015 Revised July 27, 2015 Accepted September 23, 2015 Corresponding Author Yong-Jin Cho
Tel: +82-41-570-2238 E-mail: lipr@lycos.co.kr
Copyright © 2015 The Korean Academy of Family Medicine
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Bong-Suk Choi, et al. Relationships between serum bilirubin levels and metabolic syndrome at the health care check-up in Korea adults
Korean Journal of Family Practice
KJFP
은 결과를 보인다고 보고하였다.
11)빌리루빈은 헴 이화작용( heme catabolism )의 최종 산물
13)로 항염증 효과( anti - inflammatory effect )가 있는 항산화( antioxidant ) 효과가 있다고 알려져 있으며,
14,15)
높은 빌리루빈은 신경독성이 있지만 낮은 빌리루빈 역시 심혈관 질환
16)및 말초동맥 질환
17)과 뇌졸중
18)의 위험을 높이는 것으로 이 미 보고되었다. 하지만 일본의 Oda 등에 의하면, 빌리루빈과 대사 증후군이 역의 상관관계는 있으나 위험 인자는 아니라고 보고하였 고,
7)2014 년 아산 병원에서 4 년 동안 6 천여명을 대상으로 조사한 결과를 보면 총 빌리루빈이 낮은 군에서 대사 증후군의 발생빈도가 높았다는 보고가 있어,
12)더 많은 연구가 필요할 것으로 보인다. 따 라서 본 연구는 국내 일개 지역의 대사 증후군의 유병률과 그 특징 을 확인하고, 빌리루빈과 관계를 확인하고자 한다.
대상 및 방법
본 연구는 2013 년 1 월부터 2014 년 6 월까지 한 대학병원 종합 검 진센터를 방문한 20 세 이상의 수검자를 대상으로 조사하였다. 건 강 검진 시 작성된 설문지를 바탕으로 흡연력, 음주력을 확인하였 다. 흡연 여부와 흡연량을 확인하였으며, 최근 6 개월까지 흡연한 경 우는 현재 흡연자( current smoker ), 6 개월 이상 금연한 경우는 과 거 흡연자( ex - smoker )에 포함되었다. 알코올 소비는 1 주일 동안 섭 취한 횟수를 조사하였다. 신장과 체중은 자동 신체 계측기를 이용 하여 측정하였고, 체질량지수( body mass index , BMI )는 체중( kg )/
[신장( m )]
2의 공식을 통하여 산출하였다. 허리 둘레는 늑골 최하단 부와 장골능 최상단부의 중간지점에서 가볍게 숨을 내쉰 상태에서 측정하였다. 혈압은 자동혈압 측정계로 우측 상완에서 측정하였으 며, 혈압이 140 / 90mmHg 이상 측정되었을 시에는 10 분 이상 안정 한 이후 수은주 혈압계를 이용하여 재측정하였다. 야간 공복을 포 함한 12 시간 이상 금식 후 정맥혈에서 혈액을 채취하여 빌리루빈 ( bilirubin ), AST , ALT , GGT , 공복혈당, 요산, 혈색소, 백혈구 수, 혈소판 수, 총 콜레스테롤, 중성지방, 고밀도 지단백 콜레스테롤 ( HDL - C )를 측정하였다.
모든 수검자는 혈액 검사와 함께 복부 초음파가 시행되었고, 복 부 초음파 결과 간경화가 있거나 B 형 혹은 C 형 간염 보균자인 경우, 공복 혈중 총 빌리루빈 수치가 3 . 0mg / dL 이상인 경우는 제외하였 다. 또한 HIV 감염이나 악성종양과 같이 면역저하 상태로 의심된 경우에도 본 연구에서 제외하였다.
대사 증후군은 2001 년 개정된 제 3 차 콜레스테롤 관리 지침( The third national cholesterol education program expert panel on detection , evaluation , and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults , NCEP - ATP III )
6)에 따라 5 가지 대사 이상 항목 중 3 가지 이상을 만족시키는 경우에 진단하였으며, 허리 둘레는 2006 년 대한
비만학회에서 정한 복부 비만의 진단 기준으로 남성의 경우 90cm 이상, 여성의 경우 85cm 이상을 기준으로 하였다.
19)본 연구에서 사용한 대사 증후군의 진단 기준은 다음과 같다.
1 ) 허리 둘레 남자 90cm 이상, 여자 85cm 이상 2 ) 중성 지방 150mg / dL 이상
3 ) 고밀도 지단백 콜레스테롤( HDL - C ) 남자 40mg / dL 미만, 여 자 50mg / dL 미만
4 ) 혈압 130 / 85mmHg 이상 5 ) 공복 혈당 100mg / dL 이상 통 계
모집단에 대해서는 성별을 구분하여 대사 증후군의 동반 여부 를 기준으로 연속 변수와 범주형 변수에 대해 각각 t 검정 및 Chi - square test 를 이용하여 특성을 확인하였다. 총 빌리루빈, 직접/
간접 빌리루빈의 사분위( quartile range )를 나누었다. 총 빌리루 빈은 Q1 (
<0 . 7mg / dL ), Q2 ( 0 . 7 ~ 0 . 9mg / dL ), Q3 ( 0 . 9 ~ 1 . 2mg / dL ), Q4 (
>1 . 2mg / dL )로, 직접 빌리루빈은 Q1 , Q2 (
<0 . 3mg / dL ), Q3 ( 0 . 3 ~ 0 . 4mg / dL ), Q4 (
>0 . 4mg / dL )로, 간접 빌리루빈 은 Q1 (
<0 . 5mg / dL ), Q2 ( 0 . 5 ~ 0 . 6mg / dL ), Q3 ( 0 . 6 ~ 0 . 8mg / dL ), Q4 (
>0 . 8mg / dL )로 나눈 후 대사 증후군을 구성하는 인자와 대사 증후군의 연관 관계를 확인하였다. 로지스틱 회귀 분석( Logistic regression analysis )을 통해 총 빌리루빈 사분위( Total bilirubin quartile range )에 따라 차이가 있는 지 성별에 따라 알아보았으 며 나이, 체질량지수, 흡연력, 음주 상태를 보정 후 확인하였다. P value
<0 . 05 인 경우 통계적으로 의미가 있다고 판단하고, 모든 통 계 분석은 Statistical Package for the Social Science ( SPSS ) version 17 . 0 ( SPSS , Chicago , IL )으로 시행하였다.
결 과
연구 기준을 만족한 10 , 458 명의 수검자 중에서 남성의 경우
17 . 3 % ( 1130 / 6508 )가 대사 증후군의 조건을 만족하였고 여성의 경
우 5 . 2 % ( 208 / 3950 )만 해당되었다. 대사 증후군이 있는 군과 없는
군에서 평균 나이는 남성은 차이를 보이지 않았으나( 44 . 1 versus
41 . 6 , P = 0 . 115 ), 여성에서는 대사 증후군이 있는 군에서 월등히 평
균 나이가 높았으며( 50 . 0 versus 37 . 5 years , P
<0 . 001 ), 비만도 역
시 높았다. 남성의 경우 흡연력에서 비흡연자의 비율이 30 % 내외였
으나, 여성의 경우 90 % 이상으로 차이를 보였고, 음주 정도 역시 성
별에 따른 차이를 큰 차이를 보였다. 대사 증후군에 따라 총 빌리루
빈과 직접 빌리루빈의 평균 값의 차이는 남성에서는 그 정도가 통
계학적으로 의미가 있었으나, 여성의 경우 차이를 보이지 않았다.
( Table 1 )
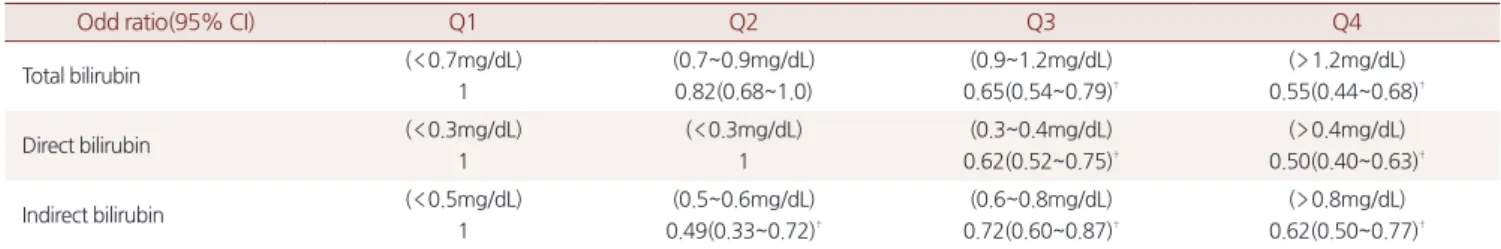
총 빌리루빈을 사분위로 구분하여 가장 낮은 사분위인 0 . 7mg / dL 미만을 기준으로 대사 증후군의 유병률을 비교하였으며 남성의 경 우, 단별량 분석에서 대사 증후군의 유병률은 사분위가 높아질수록 위험도( odd ratio )가 낮아지는 것을 확인하였다( Table 2 ). 또한 나
이, 체질량지수, 음주 정도, 흡연 상태에 따른 다변량 분석을 시행 한 결과에서도 같은 결과를 보였다( 0 . 83 versus 0 . 63 versus 0 . 52 ).
대사 증후군에 해당하는 지표인 복부 비만과 고혈압에서는 총 빌리 루빈의 사분위에서 위험도의 차이를 보이지 않았으나, 높은 공복혈 당, 고중성지방혈증, 낮은 고밀도 지단백 콜레스테롤혈증에서는 대 사 증후군과 같이 사분위가 높아질수록 위험도가 감소하는 것으로
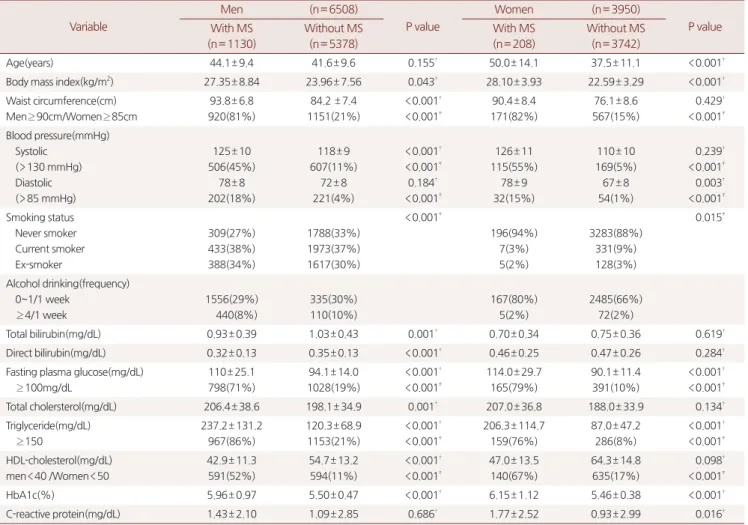
Table 1. Clinical characteristics of all subjects
Variable
Men (n= 6508)
P value
Women (n= 3950)
P value With MS
(n= 1130)
Without MS (n= 5378)
With MS (n= 208)
Without MS (n= 3742)
Age(years) 44.1± 9.4 41.6± 9.6 0.155† 50.0± 14.1 37.5± 11.1 <0.001†
Body mass index(kg/m2) 27.35± 8.84 23.96± 7.56 0.043† 28.10± 3.93 22.59± 3.29 <0.001†
Waist circumference(cm) Men≥ 90cm/Women≥ 85cm
93.8± 6.8 920(81%)
84.2 ± 7.4 1151(21%)
<0.001†
<0.001‡
90.4± 8.4 171(82%)
76.1± 8.6 567(15%)
0.429†
<0.001‡ Blood pressure(mmHg)
Systolic (>130 mmHg) Diastolic (>85 mmHg)
125± 10 506(45%)
78± 8 202(18%)
118± 9 607(11%)
72± 8 221(4%)
<0.001†
<0.001‡ 0.184†
<0.001‡
126± 11 115(55%)
78± 9 32(15%)
110± 10 169(5%) 67± 8 54(1%)
0.239†
<0.001‡ 0.003†
<0.001‡ Smoking status
Never smoker Current smoker Ex-smoker
309(27%) 433(38%) 388(34%)
1788(33%) 1973(37%) 1617(30%)
<0.001‡
196(94%) 7(3%) 5(2%)
3283(88%) 331(9%) 128(3%)
0.015‡
Alcohol drinking(frequency) 0~1/1 week
≥ 4/1 week
1556(29%) 440(8%)
335(30%) 110(10%)
167(80%) 5(2%)
2485(66%) 72(2%)
Total bilirubin(mg/dL) 0.93± 0.39 1.03± 0.43 0.001† 0.70± 0.34 0.75± 0.36 0.619†
Direct bilirubin(mg/dL) 0.32± 0.13 0.35± 0.13 <0.001† 0.46± 0.25 0.47± 0.26 0.284†
Fasting plasma glucose(mg/dL)
≥ 100mg/dL
110± 25.1 798(71%)
94.1± 14.0 1028(19%)
<0.001†
<0.001‡
114.0± 29.7 165(79%)
90.1± 11.4 391(10%)
<0.001†
<0.001‡
Total cholersterol(mg/dL) 206.4± 38.6 198.1± 34.9 0.001† 207.0± 36.8 188.0± 33.9 0.134†
Triglyceride(mg/dL)
≥ 150
237.2± 131.2 967(86%)
120.3± 68.9 1153(21%)
<0.001†
<0.001‡
206.3± 114.7 159(76%)
87.0± 47.2 286(8%)
<0.001†
<0.001‡ HDL-cholesterol(mg/dL)
men<40 /Women<50
42.9± 11.3 591(52%)
54.7± 13.2 594(11%)
<0.001†
<0.001‡
47.0± 13.5 140(67%)
64.3± 14.8 635(17%)
0.098†
<0.001‡
HbA1c(%) 5.96± 0.97 5.50± 0.47 <0.001† 6.15± 1.12 5.46± 0.38 <0.001†
C-reactive protein(mg/dL) 1.43± 2.10 1.09± 2.85 0.686† 1.77± 2.52 0.93± 2.99 0.016†
*Data are showed as mean±SD(standard deviation) or number(%).
† P value by t-test
‡ P value by chi-square test
Table 2. Odds ratio for metabolic syndrome and components according to serum total bilirubin quartile in Men
Q1(<0.7mg/dL) Q2(0.7~0.9mg/dL) Q3(0.9~1.2mg/dL) Q4(1.2~3.0mg/dL)
Metabolic syndrome 1 0.82(0.68~1.0) 0.65(0.54~0.79)† 0.55(0.44~0.68)†
Central obesity 1 0.996(0.817~1.214) 1.031(0.853~1.245) 1.155(0.936~1.427)
SBP≥ 130 mmHg 1 1.000(0.833~1.200) 1.109(0.928~1.325) 1.102(0.905~1.340)
DBP≥ 85 mmHg 1 1.047(0.787~1.393) 0.963(0.735~1.263) 0.817(0.613~1.088)
FPG≥ 100mg/dL 1 0.90(0.77~1.05) 0.83(0.71~0.96)† 0.76(0.65~0.91)†
TG≥ 150mg/dL 1 0.69(0.59~0.80)† 0.55(0.47~0.63)† 0.43(0.37~0.51)†
HDL-C<40mg/dL 1 0.72(0.61~0.86)† 0.58(0.49~0.69)† 0.50(0.41~0.61)†
SBP: systolic blood pressure; DBP: diastolic blood pressure; FPG: fasting plasma glucose; TG: Triglyceride; HDL-C: High-density lipoprotein-cholesterol.
*: Adjusted for age, body mass index, alcohol habit, and smoking status(never, current, ex-smoker).
† P-value by logistic regression(P<0.05)
‡ Odd ratio(95% confidence interval)
Bong-Suk Choi, et al. Relationships between serum bilirubin levels and metabolic syndrome at the health care check-up in Korea adults
Korean Journal of Family Practice
KJFP
나타났다. 하지만 여성의 경우 대사 증후군을 포함한 다른 지표에 서도 의미 있는 값을 보이지 않았다. 또한 남성에서 총 빌리루빈 외 직접 빌리루빈과 간접 빌리루빈의 사분위로 대사 증후군의 위험도 를 확인한 결과, 모두 가장 낮은 사분위와 비교하여 위험도는 감소 하였으나 간접 빌리루빈에서는 3 분위에서 2 분위보다 위험도가 높 은 경향을 보였다( Table 3 ). 총 빌리루빈 사분위에 따라 대사 증후군 과 해당 지표 간의 관계를 보면 고혈당, 고중성지방혈증 그리고 낮 은 고밀도 지단백 콜레스테롤혈증에서 사분위가 높아질수록 점차 그 빈도가 점차 감소하는 것으로 나타났으나, 복부 비만과 혈압에 서는 의미가 없는 것으로 나타났다( Figure 1 ).
고 찰
본 연구는 최근에 보고된 연구들과 같이
10, 12)대사 증후군의 발생 정도가 감소되었다는 것을 보여주고 있으며, 남성의 경우 빌리루빈
수치가 낮을수록 대사 증후군의 유병률이 증가하는 것으로 나타났 다. 특히 빌리루빈과 고혈당, 고중성지방혈증, 낮은 고밀도 지단백 콜레스테롤혈증과 연관이 높았으며, 혈압과 복부 비만은 총 빌리루 빈과 큰 연관이 없었다.
이 연구는 10 여년 전의 결과와 비교하여 남성과 여성 모두 대사 증후군의 발생 빈도가 월등히 저하되었으며, 여성의 경우 그 빈도 가 낮음을 알 수 있다. 2013 년 최 등이 보고한 바에 의하면, 남성에 서는 10 %, 여성에서는 4 . 9 %로 발생 빈도를 보고하였으며,
10)2014 년 이 등은 4 년간 남성 환자를 추적 관찰한 결과 15 . 1 %의 유병률을 보고한 바 있다.
12)이러한 변화는 식습관과 생활 습관의 서구화로 인하여 복부 비만과 고혈압, 당뇨에 대한 위험이 증가되었으나, 그 만큼 건강에 대한 관심 증대와 음주, 흡연에 대한 인식의 변화, 주 기적인 건강 검진 등을 통해 점차 그 빈도가 감소되었을 것으로 판 단된다. 기존의 연구는 모집단의 크기가 비슷하였으나,
7, 10, 11, 20)대 사 증후군의 발생 빈도는 차이가 있었고 또한 성별에 따라 총 빌리
Table 3. Odds ratio for metabolic syndrome according to serum bilirubin quartile in MenOdd ratio(95% CI) Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4
Total bilirubin (<0.7mg/dL)
1
(0.7~0.9mg/dL) 0.82(0.68~1.0)
(0.9~1.2mg/dL) 0.65(0.54~0.79)†
(>1.2mg/dL) 0.55(0.44~0.68)†
Direct bilirubin (<0.3mg/dL)
1
(<0.3mg/dL) 1
(0.3~0.4mg/dL) 0.62(0.52~0.75)†
(>0.4mg/dL) 0.50(0.40~0.63)†
Indirect bilirubin (<0.5mg/dL) 1
(0.5~0.6mg/dL) 0.49(0.33~0.72)†
(0.6~0.8mg/dL) 0.72(0.60~0.87)†
(>0.8mg/dL) 0.62(0.50~0.77)†
*: Adjusted for age, body mass index, alcohol habit, and smoking status(never, current, ex-smoker).
† P-value by logistic regression(P<0.05)
‡ Odd ratio(95% confidence interval)
Figure 1. The relation of metabolic syndrome and metabolic components with each serum total bilirubinquartile in men
MS: metabolic syndrome; SBP: systolic blood pressure; DBP: diastolic blood pressure; FPG: fasting plasma glucose; TG:Triglyceride; HDL-C: High-density lipoprotein- cholesterol.
*: P value by chi-square test(P<0.05)
루빈과 연관성도 다르게 보고되었다. 여성의 경우, 폐경기 후 대사 증후군이 증가되는 것은 이미 알려진 사실로, 2011 년 권 등이 40 세 이상의 여성을 대상으로 조사한 결과를 보면 대사 증후군의 발생 빈 도는 39 %로 높았으며,
20)총 빌리루빈과 대사 증후군의 역의 상관 관계를 보였으나, 40 세 이상의 남성에서는 차이를 보이지 않았다고 하였다. 2010 년 황 등이 보고한 바에 의하면 남성과 여성 모두 역의 상관관계가 있다고 보고하였으나, 여성의 경우 더 연관이 높았다.
11)본 결과와 다른 연구간의 이러한 차이는 모집단의 연령 분포에 따 른 것으로 판단된다. 본 연구의 모집단의 평균 연령은 다른 연구와 비교하여 낮은 편이며, 특히 여성에서 대사 증후군이 없는 군은 월 등히 차이를 보였다. 따라서 본 연구에서도, 여성의 경우 40 세를 기 준으로 구분하여 층화분석을 하였으나 통계학적인 의미를 보이지 않았다. 이러한 성별의 차이는 생활 습관의 차이, 즉 흡연력과 음주 습관의 차이, 성 호르몬 그리고 빌리루빈 수치의 차이에 의해 나타 난다고 생각된다. 흡연은 내당능 장애,
21)그리고 지질 이상을 유발
22)하는 독립된 인자로 알려져 있으며, 본 연구에서도 성별에 따른 흡 연력 차이를 보이고 있다. 또한 일반적으로 빌리루빈은 남성이 여 성보다 높은 것으로 알려져 있으며, 여성의 경우 폐경시 콜레스테 롤 대사와 당 조절에 변화가 나타난다.
23, 24)따라서 이러한 근본적인 차이가 있어, 추후 대규모 연구가 더 필요할 것으로 생각된다.
기존의 연구에서는 총 빌리루빈과 대사 증후군에 대하여 역의 상 관관계가 있음을 보고하였다. 황 등은 여성에서 총 빌리루빈과 직 접/간접 빌리루빈 모두 관련되어 있으나 남성에서는 직접 빌리루빈 과 연관이 있음을 보고하였고, 이에 대해 알부민과 결합하지 않은 빌리루빈인 직접 빌리루빈이 표적 장기에 작용하기 용이할 수 있기 때문이라고 언급하였다.
11)하지만 본 연구에서는 여성에서는 모든 빌리루빈과 대사 증후군에서 연관성을 확인하지 못하였으며, 남성 의 경우 총 빌리루빈 뿐만 아니라 직접/간접 빌리루빈에서도 역의 관련성이 있음을 확인하였으나, 간접 빌리루빈에서는 2 사분위보다 3 사분위에서 위험비가 좀 더 높게 나타났다. 이러한 이유는 혈청으 로 측정 가능한 총 빌리루빈과 직접 빌리루빈의 차를 이용하여 간접 빌리루빈이 계산되었기 때문에 수치상 0 인 경우가 포함되었기 때문 일 수 있으며, 황 등과 차이가 있는 이유는 모집단의 크기 및 성별 구성과 집단 특징이 다르기 때문이라고 판단된다.
본 연구에서는 대사 증후군뿐만 아니라 대사 증후군의 구성 요 소와 빌리루빈과의 관계에서 고혈압을 제외하고 빌리루빈의 수치 가 더 낮은 것으로 나타났고, 다변량 분석에서는 총 빌리루빈과 고 혈당, 고중성지방혈증, 낮은 고밀도 지단백 콜레스테롤혈증이 대 사 증후군처럼 역의 상관관계가 있음을 확인하였다. 이미 많은 연 구에서 인슐린 저항성과 총 빌리루빈과 역의 상관관계가 있음이 보 고되었고,
25)또한 저밀도 지단백을 포함한 다른 지질의 산화를 억 제한다는 보고와 일치한다.
26)대사 증후군에 대한 상승된 빌리루빈
의 효과는 빌리루빈 대사와 연관되었을 것으로 생각된다. 헴( heme ) 은 hemeoxygenase 을 통해 빌리루비딘( bilirubidin ) 과 일산화탄소 ( carbon monoxide )로 분리된다. 이것은 항동맥경화성 역할( anti - atherosclerotic properties )이 있다고 알려져 있다.
26, 27)분해된 빌리 버딘( biliverdin )은 빠르게 biliverdin reductase 에 의해 분해되어 빌 리루빈으로 분해된다. Biliverdin reductase 가 분해과정의 산물과 함 께 항산화 효과가 있음이 밝혀졌으며, 또한 인슐린 분해 과정을 조 절하는 유전자 발현을 조절하는 것으로 나타났다.
28, 29)Li 등은 동물 실험을 통하여 상승된 빌리루빈이 아디포넥틴( adiponectin )을 증가 시켜 인슐린 저항성을 호전시킨다고 보고하였다.
30)따라서 이러한 빌리루빈의 생성 과정에서 발생하는 항산화 효과와 인슐린 저항성 을 호전시키는 효과로 인하여, 대사 증후군과 역의 관련성이 있는 것으로 생각된다.
본 연구는 모집단의 크기가 크다는 장점이 있으나, 1 개 지역의 건 강 검진을 목적으로 방문한 수검자를 대상으로 조사되었기 때문에 전체를 대표하는데 제한이 있다. 또한 본 연구는 단면 조사( cross - sectional study )를 통하여 빌리루빈과 대사 증후군의 관계에 대한 보편성을 확인하지 못했다. 그리고 남성과 여성 모두 혈압약, 당뇨 약, 콜레스테롤 강하제등과 같은 약물 복용력에 대한 기록과 운동 과 같은 생활 습관에 대한 조사가 부족하고, 여성의 경우 폐경 여부 를 확인하지 않았기 때문에 빌리루빈 수치 변화에 대한 영향을 확 인하지 못했다는 제한점이 있다. 아직까지 간담도계 질환을 포함한 조사는 이루어지지 않았으며, 대부분의 연구가 통상적으로 알려진 정상 범위보다는 더 높은 빌리루빈 수치에서 대사 증후군의 발생이 적었다고만 보고하였기 때문에, 추후 허용되는 범위에 대한 조사와 함께 약물학적으로 빌리루빈을 일정 수준 유지할 수 있는 약제 혹은 방법에 대한 연구도 필요할 것으로 보인다.
결론적으로, 시대의 변화에 따라 건강에 대한 관심의 증가로 대 사 증후군과 관련된 연구가 이루어지고 있으며, 이전과 비교하여 대사 증후군의 유병률은 감소되었다. 본 연구는 총 빌리루빈 뿐만 아니라 직접/간접 빌리루빈에서도 대사 증후군과 역의 관련성이 있 음을 밝혀냈으나 남성에서만 확인되었다. 추후 대사 증후군을 유발 하는 인슐린 저항성, 만성 염증, 산화 스트레스와 빌리루빈과의 관 계에 대한 장기적인 조사를 통하여 이와 관련된 치료가 빌리루빈에 미치는 영향에 대한 조사가 더 필요할 것으로 생각된다.
요 약
연구배경: 혈청 빌리루빈은 잠재적인 항산화작용과 더불어 아시아
인에서 대사 증후군과 연관이 있다고 알려져 있다. 본 연구의 목표
는 한국인에 있어 총 빌리루빈과 대사증후군과의 관계 및 특성에 대
해 알아보고자 하였다.
Bong-Suk Choi, et al. Relationships between serum bilirubin levels and metabolic syndrome at the health care check-up in Korea adults
Korean Journal of Family Practice
KJFP
방법: 2013 년 1 월부터 2014 년 6 월까지 일개 대학병원 종합 검진센 터를 방문한 20 세 이상의 수검자 중 남자 6 , 508 명, 여자 3 , 950 명으 로 총 10 , 458 명을 대상으로 하였다. 영상의학과 전문의 1 인이 시행 한 복부 초음파상 만성간질환자 또는 간경변으로 확인된 수검자, 공복 총 빌리루빈이 3mg / dL 초과한 수검자, 면역 저하상태로 의심 되는 수검자는 제외하였다.
결과: 대사 증후군의 유병률은 남성의 경우 17 . 3 %( 1130 / 6508 ), 여 성의 경우 5 . 2 %( 208 / 3910 )로 나타났다. 남성의 경우 대사 증후군 이 있는 군과 없는 군에서 연령 차이가 없는 반면, 여성의 경우 대 사 증후군이 있는 군이 없는 군에 비해 연령이 더 높은 것으로 나타 났다. ( 50 versus 37 . 5 years ).남성의 경우에 있어서만 총 빌리루빈 수치는 대사 증후군의 구성 요소인 공복 혈당, 중성 지방이 높을수 록 감소였으며, 고밀도 지단백 콜레스테롤이 낮을수록 감소하였다.
총 빌리루빈 수치는 나이, BMI , 흡연력, 음주력등을 보정한 후에 도 대사 증후군과 관련이 있는 것으로 나타났다. 남성의 경우 대사 증후군과 각 총 빌리루빈 사분위의 상대 위험도는( 95 % confidence interval ) 0 . 83 ( 0 . 70 ~ 0 . 98 ), 0 . 63 ( 0 . 53 ~ 0 . 75 ), 0 . 52 ( 0 . 43 ~ 0 . 63 )을 보였다. 그러나, 여성의 경우 총 빌리루빈과 대사 증후군과의 연관 성은 보이지 않았다.
결론: 본 연구에서 대사 증후군의 유병률은 감소하는 추세이며, 남 성의 경우 총 빌리루빈과 대사 증후군은 역의 관련성이 있는 것으로 나타났다
중심단어: 빌리루빈, 대사증후군, 남성.
REFERENCES
1. Yoon YS, Lee ES, Park C, Lee S, Oh SW. The new definition of metabolic syndrome by the international diabetes federation is less likely to identify metabolically abnormal but non-obese individuals than the definition by the revised national cholesterol education program: the Korea NHANES study. International journal of obesity (2005) 2007;31:528-34.
2. Rhee SY, Park SY, Hwang JK, Son JI, Chin SO, Kim YS et al.
Metabolic syndrome as an indicator of high cardiovascular risk in patients with diabetes: Analyses based on Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2008. Diabetology
& metabolic syndrome 2014;6:98.
3. Ridker PM, Wilson PW, Grundy SM. Should C-reactive protein be added to metabolic syndrome and to assessment of global cardiovascular risk? Circulation 2004;109:2818-25.
4. Rohde LE, Hennekens CH, Ridker PM. Survey of C-reactive protein and cardiovascular risk factors in apparently healthy men.
The American journal of cardiology 1999;84:1018-22.
5. Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J. Metabolic syndrome--a new world- wide definition. A Consensus Statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabetic medicine: a journal of the British Diabetic Association 2006;23:469-80.
6. Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute scientific statement: Executive Summary.
Critical pathways in cardiology 2005;4:198-203.
7. Oda E, Aizawa Y. Total bilirubin is inversely associated with metabolic syndrome but not a risk factor for metabolic syndrome in Japanese men and women. Acta diabetologica 2013;50:417-22.
8. Lin LY, Kuo HK, Hwang JJ, Lai LP, Chiang FT, Tseng CD, et al.
Serum bilirubin is inversely associated with insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome among children and adolescents.
Atherosclerosis 2009;203:563-8.
9. Wu Y, Li M, Xu M, Bi Y, Li X, Chen Y, et al. Low serum total bilirubin concentrations are associated with increased prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Chinese. Journal of diabetes 2011;3:217-24.
10. Choi SH, Yun KE, Choi HJ. Relationships between serum total bilirubin levels and metabolic syndrome in Korean adults. Nutrition, metabolism, and cardiovascular diseases: NMCD 2013;23:31-7.
11. Hwang HJ, Kim SH. Inverse relationship between fasting direct bilirubin and metabolic syndrome in Korean adults. Clinica chimica acta; international journal of clinical chemistry 2010;411:1496- 501.
12. Lee MJ, Jung CH, Kang YM, Hwang JY, Jang JE, Leem J, et al.
Serum bilirubin as a predictor of incident metabolic syndrome:
a 4-year retrospective longitudinal study of 6205 initially healthy Korean men. Diabetes & metabolism 2014;40:305-9.
13. Stocker R, Yamamoto Y, McDonagh AF, Glazer AN, Ames BN.
Bilirubin is an antioxidant of possible physiological importance.
Science (New York, NY) 1987;235:1043-6.
14. Baranano DE, Rao M, Ferris CD, Snyder SH. Biliverdin reductase: a major physiologic cytoprotectant. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2002;99:16093-8.
15. Sedlak TW, Saleh M, Higginson DS, Paul BD, Juluri KR, Snyder SH. Bilirubin and glutathione have complementary antioxidant and cytoprotective roles. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2009;106:5171-6.
16. Troughton JA, Woodside JV, Young IS, Arveiler D, Amouyel P, Ferrieres J, et al. Bilirubin and coronary heart disease risk in the Prospective Epidemiological Study of Myocardial Infarction (PRIME).
European journal of cardiovascular prevention and rehabilitation:
official journal of the European Society of Cardiology, Working Groups on Epidemiology & Prevention and Cardiac Rehabilitation and Exercise Physiology 2007;14:79-84.
17. Perlstein TS, Pande RL, Beckman JA, Creager MA. Serum total bilirubin level and prevalent lower-extremity peripheral arterial disease: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999 to 2004. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology 2008;28:166-72.
18. Perlstein TS, Pande RL, Creager MA, Weuve J, Beckman JA.
Serum total bilirubin level, prevalent stroke, and stroke outcomes:
NHANES 1999-2004. The American journal of medicine
2008;121:781-8.e781.
19. Lee SY, Park HS, Kim DJ, Han JH, Kim SM, Cho GJ, et al.
Appropriate waist circumference cutoff points for central obesity in Korean adults. Diabetes research and clinical practice 2007;75:72- 80.
20. Kwon KM, Kam JH, Kim MY, Kim MY, Chung CH, Kim JK, et al. Inverse association between total bilirubin and metabolic syndrome in rural korean women. Journal of women's health (2002) 2011;20:963-9.
21. Houston TK, Person SD, Pletcher MJ, Liu K, Iribarren C, Kiefe CI.
Active and passive smoking and development of glucose intolerance among young adults in a prospective cohort: CARDIA study. BMJ (Clinical research ed) 2006;332:1064-9.
22. Tan XJ, Jiao GP, Ren YJ, Gao XR, Ding Y, Wang XR, et al.
Relationship between smoking and dyslipidemia in western Chinese elderly males. Journal of clinical laboratory analysis 2008;22:159- 63.
23. Nakhjavani M, Imani M, Larry M, Aghajani-Nargesi A, Morteza A, Esteghamati A. Metabolic syndrome in premenopausal and postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes: loss of protective effects of premenopausal status. Journal of diabetes and metabolic disorders 2014;13:102.
24. Yun BH, Chon SJ, Lee YJ, Han EJ, Cho S, Choi YS, et al. Association of metabolic syndrome with coronary atherosclerosis in non-
diabetic postmenopausal women. Climacteric: the journal of the International Menopause Society 2014:1-6.
25. Guzek M, Jakubowski Z, Bandosz P, et al. Inverse association of serum bilirubin with metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in Polish population. Przeglad epidemiologiczny 2012;66:495-501.
26. Wu TW, Fung KP, Wu J, Yang CC, Weisel RD. Antioxidation of human low density lipoprotein by unconjugated and conjugated bilirubins. Biochemical pharmacology 1996;51:859-62.
27. Morita T. Heme oxygenase and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology 2005;25:1786-95.
28. Schwertner HA, Vitek L. Gilbert syndrome, UGT1A1*28 allele, and cardiovascular disease risk: possible protective effects and therapeutic applications of bilirubin. Atherosclerosis 2008;198:1- 11.
29. Lerner-Marmarosh N, Shen J, Torno MD, Kravets A, Hu Z, Maines MD. Human biliverdin reductase: a member of the insulin receptor substrate family with serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2005;102:7109-14.
30. Li M, Kim DH, Tsenovoy PL, Peterson SJ, Rezzani R, Rodella LF, et al. Treatment of obese diabetic mice with a heme oxygenase inducer reduces visceral and subcutaneous adiposity, increases adiponectin levels, and improves insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance.
Diabetes 2008;57:1526-35.