50(4) : 277 ∼ 284 (2019)
277
소리쟁이(Rumex crispus) 추출물의 제1형 알레르기 반응 억제 효과
고은교·김영미*
덕성여자대학교 약학대학
Rumex crispus Suppresses Type I Hypersensitive Immune Response
Eun Kyo Ko and Young Mi Kim*
College of Pharmacy, Duksung Women’s University, Seoul 01369, Korea
Abstract Rumex crispus is known to have anticancer, antioxidant, antibacterial, and bone loss inhibitory activities. Mast cells are critical immune cells that induce a type 1 IgE-mediated allergic reaction. However, there are no reports of inhibitory effects of Rumex crispus on mast cells and allergic reactions. In this study, we performed some experiments to investigate whether Rumex crispus ethanol extract(RCE) has any inhibitory effect on antigen-induced type I allergic response in vitro and in vivo.
RCE inhibited degranulation of IgE-mediated mast cells(IC50, ~57 μg/ml) and cytokine production such as TNF- and IL-4 in a dose-dependent manner. In vivo, RCE significantly inhibited passive cutaneous anaphylaxis(PCA)(ED50, ~198 mg/kg) in mice. Furthermore, RCE inhibited degranulation of MCs in ear tissue of mice with PCA. Mechanism studies showed that RCE inhibited the activation of Syk and Syk-dependent pathway such as LAT, PLC-, Akt, and MAP Kinase. Our results demon- strate for the first time that RCE inhibits type I hypersensitive response by suppressing the activity of Syk in mast cells, thereby reducing degranulation and cytokine production. Taken together, RCE could be used as a novel therapeutic material to suppress allergic diseases.
Keywords Rumex crispus extract(RCE), Mast cells, Allergy, Anti-allergic effect, Syk
음식 알레르기, 아토피성 피부염, 비염 및 천식 등 알레르 기 질환은 최근 세계적으로 증가하고 있는 추세이다.1) 비만 세포는 제1형 알레르기 질환을 유발하는 과정 중에 활성화 되는 중요한 원인 세포로 잘 알려져 있다.2,3) 비만세포 표면 의 Immunoglobulin(Ig) E 고친화성 수용체인 FcεRI에 부착 하는 IgE에 항원이 결합하여 세포가 활성화 되며 그 결과 히스타민, 헤파린, 류코트리엔, 프로스타글란딘 등을 분비하 는 탈과립과 다양한 염증성 사이토카인을 분비 하여 알레르 기성 면역 반응을 활성화시키고 이러한 결과로 알레르기 증 상이 유발된다.4) 따라서 비만세포를 억제하는 소재는 알레 르기 질환을 치료하는 소재로 중요하게 활용 되어 질 수 있다.
현재 시판중인 알레르기 치료제는 스테로이드제와 같은 면역억제제나 히스타민이나 류코트리엔 같은 분비된 알레 르기 반응 유발 인자들의 작용을 억제하는 길항제 등이 대 부분이다.5,6) 하지만 이 약물들은 단순히 증상 억제하는 약 제이며 장기간 사용 시 내성 때문에 환자들이 어려움을 겪 고 있다. 따라서 이러한 약제들은 근본적인 치료 방법으로
적절하지 않으므로 새로운 알레르기 치료제 개발을 위한 다 양한 연구들이 진행 중에 있다.
비만세포는 항원이 FcεRI에 결합되어 있는 IgE와 결합하 면 활성화 된다. 초기 신호 경로에는 Src family kinase인 Lyn, Fyn 및 Syk이 중요한 역할을 한다. Lyn에 의해 FcεRI 에 존재하는 immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activating motifs (ITAMs)가 인산화 되고 인산화 된 ITAM에 Syk이 결합하 게 된다.7) 결합된 Syk은 활성화 되어 하위 신호 분자인 linker for activated T cells(LAT), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), phospholipase C-(PLC-) 및 mitogen-activated protein(MAP) kinase 등을 활성화 시킨다.8) 활성화 된 하위 신호에 의해 탈과립 및 염증성 사이토카인 분비가 되어 알 레르기 반응이 유도된다. 따라서 최근에는 Lyn 및 Fyn Src family kinase나 Syk과 같은 초기 신호 분자가 알레르기 질 환 치료를 위한 표적으로 활용되고 있다.9)
소리쟁이(Rumex crispus)는 항암효과, 항산화 효과, 항균 효과 및 골손실 억제효과를 가지는 것으로 알려져 있다.10-13) 하지만, RCE(Rumex crispus ethanol extract)를 이용한 비만 세포에서의 생리적인 효과나 작용 기전에 대해 연구된 사
*교신저자(E-mail):kym123@ds.ac.kr (Tel): +82-2-901-8455
례는 없다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 RCE가 비만세포 활성화 에 대한 억제 효과와 그 작용기전을 알아보기 위해 in vitro 및 in vivo 실험을 수행하였고 그 결과 RCE는 Syk을 억제 하여 비만세포의 활성화와 제1형 알레르기 반응을 억제하 는 것을 확인하였다.
재료 및 실험
실험재료 소리쟁이(Rumex crispus) 추출물(RCE)는 한국 생명공학연구원의 한국식물추출물은행에서 구입하여 사용 하였다(분양번호: KPM023-062). 실험에 사용된 PP2는 Calbiochem(Lajolla, CA, USA)에서 구입하였고, Monoclonal dinitropheno(DNP)-specific IgE, DNP-bovine serum albumin (BSA), evans blue, cetirizine and toluidine blue는 Sigma (St.Louis, MO, USA)에서 구입하였다. Phospho-Syk, Phospho-LAT, Phospho-Akt, Phospho-Erk1/2, Phospho-p38, Phospho-JNK, Actin 항체는 Cell Signaling Technology Inc.(Danvers, MA, USA)에서 구입하였으며, Syk, LAT 항 체는 Santa Cruz Biotechnology(Santa Cruz, CA, USA)에 서 구입하여 사용하였다. 세포 배양에 사용된 배양액은 GIBCO/Life Technologies Inc.(Rockville, MD, USA)에서 구입하여 사용하였다.
실험동물 Balb/c 생쥐는 면역학 및 약효실험에서 가장 일반적으로 사용되는 종으로 우리는 이 실험에서 Orient bio Inc.(Gyeonggi, Korea)에서 5~6주령의 수컷 Balb/c 생쥐를 구입하여 사용하였고 골수유래 비만세포(bone marrow- derived mast cells, BMMC) 분화 및 passive cutaneous anaphylaxis(PCA) 실험에 이용하였다. 동물실험은 덕성여자 대학교 동물실험 관리위원회(IACUC)의 승인을 받은 후 규 정에 따라 진행하였다.
비만세포의 분리 및 배양 Rat basophilic leukemia (RBL)–2H3 cells은 American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA)에서 분양 받아 4 mM L- glutamine, 100 units/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin, 15% fetal bovin serum(FBS)이 포함된 minimal essential medium(MEM) 배양액에서 배양하였고, BMMCs는 5주령 의 수컷 Balb/c 생쥐로부터 골수 세포를 채취하여 4 mM L- glutamine, 100 units/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin, 0.1 mM nonessential amino acids, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 25 mM HEPES, 10% FBS, 10 ng/ml IL-3가 포함된 RPMI1640 배양액에 4~6주간 배양하여 BMMC로 분화시킨 후 실험에 이용하였다.
비만세포의 탈과립 측정 RBL-2H3 세포를 24 well-plate 에 분주하여(1.8×105cells/well) 20 ng/ml DNP(dinitrophenol)- specific IgE가 포함된 MEM에서 12시간 동안 감작시켰다.
1,4-Piperazinediethanesulfonic acid(PIPES) 완충액(25 mM
PIPES, pH 7.2, 119 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 0.4 mM MgCl2, 1 mM CaCl2, 5.6 mM glucose, and 0.1% fattyacid- free fraction V from a bovine serum)으로 세포를 2회 세척 후 RCE를 PIPES 완충액에 농도 별로 희석시키고 PP2도 희 석시켜 25 ng/ml의 항원(DNP-BSA)을 15분간 반응하기 전 에 각 well에 넣어 30분 전처리를 하였다. 항원 반응 후 상 층액과 세포용해액을 37oC에서 1시간 동안 1 mM p- nitrophenyl-N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminide와 반응시키고 micro- plate reader를 이용하여 405 nm에서 흡광도를 측정하였다.
비만세포의 탈과립은 배양액에 방출된 β-hexosaminidase와 배양액과 세포용해액 내에 존재하는 β-hexosaminidase 총량 의 비율로 나타내었다.
Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) RBL-2H3 cells에서 total RNA는 Easy-spinTM Total RNA Extraction Kit(iNtRON Biotechnology, Inc., Seongnam-si, Korea)를 이용하여 추출하였고 역전사는 Super- script first-strand synthesis system(Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA)을 사용하였다. PCR은 94oC에서 45초, 55oC에서 45초, 72oC에서 60초를 30회 반복하였다. Primer는 rat TNF-
forward 5'-CAC CACGCTCTTCTGTCTACTGAAC-3';
rat TNF- reverse: 5'-CCGGAC TCCGTGATGTCTAAGTAC T-3'; rat IL-4 forward 5'-ACCTTGCTGT CACCCTGTTC- 3'; rat IL-4 reverse 5'-TTGTGAGCGTGGACTCATT C-3';
rat GAPDH forward 5'-GTGGAGTCTACTGGCGTCTT C- 3'; rat GAPDH reverse 5'-CCAAGGCTGTGGGCAAGGTCA- 3'를 사용하였다.
Western Blotting 분석 RBL-2H3 cells(5×106cells/well) 을 20 ng/ml DNP-IgE로 12시간 감작 후 새로운 배양액으 로 2회 세척하였다. RCE를 농도 별로 30분간 전 처리 후 25 ng/ml DNP-BSA로 7분간 자극하고 얼음 위에서 반응을 정지 시켰다. Cold-PBS로 2회 세척 후 세포에 100 μl lysis buffer(20 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 1% Nonidet P - 40, 10% glycerol, 60 mM octyl β-glucoside, 10 mM NaF, 1 mM Na3VO4, 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 2.5 mM nitrophenylphosphate, 0.7 mg/ml pepstatin, and a protease-inhibitor cocktail tablet)로 세포를 파쇄하였다. 세포 용해액을 15,000×g에서 5분간 원심분리하고 상등액을 3×
Laemmli buffer와 혼합하여 95oC에서 5분간 단백질 변성을 진행하였다. 단백질은 sodium dodecyl sulfate- polyacryl- amide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)를 이용하여 분리하 고 nitrocellose membrane에 transfer 하였다. 5% BSA가 포 함된 TBS-T buffer에 각각의 특이적인 항체와 반응 후 HRP(horseradish peroxidase)가 표지된 2차 항체와 반응하였 다. TBS-T로 세척을 하고 ECL detection kit를 사용하여 blot을 검출 하였다.
Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis 동물모델 Balb/c
생쥐의 귀에 DNP-IgE를 0.5 μg를 주입하고 12시간 후 RCE (100, 300, 1000 mg/kg)와 cetirizine(50 mg/kg)을 5% 아라비 아검에 녹여 경구 투여하였다. 1시간 후 DNP-BSA를 5 mg/
ml Evans blue 용액에 1 mg/ml 농도로 희석하여 250 μl를 꼬리 정맥주사로 주입하였다. 1시간 뒤 생쥐를 안락사 하고 귀를 적출하여 700 μl 포름아마이드에 넣어 63oC에서 12시 간동안 귀에 염색된 Evans blue dye를 추출하였다. 추출한 dye는 620 nm 파장에서 흡광도를 측정하였다.
조직 내 비만세포 탈과립 측정 PCA를 유도한 생쥐의 귀를 적출하여 4% paraformaldehyde로 고정하였다. 고정된 귀 조직을 에탄올로 탈수하고 파라핀으로 고정하였다. 파라 핀 조직을 6 μm로 절단하고 toluidine blue 염색을 하여 비 만세포의 탈과립을 현미경으로 관찰하였다.
통계학적 분석 실험 결과는 독립적으로 3회 이상 진행 하고 평균 ± SEM으로 정리하였다. 통계적인 분석은 ANOVA 와 Dunnett’s test를 이용하여 진행하였다. 모든 통계적 계산 은(*p<0.05 and **p<0.01) Sigma Stat 4.0(Systat Software, Inc., Point Richmond, CA, USA)를 이용하여 계산하였다.
결 과
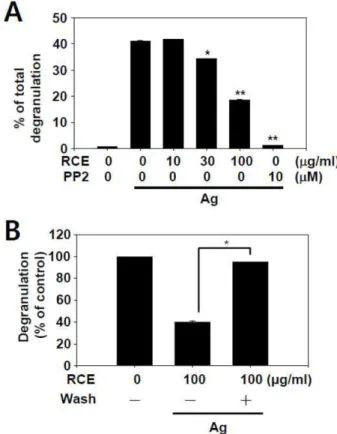
RCE의 비만세포에서 항원자극에 의한 탈과립 억제 효 과 비만세포에서 RCE의 항원 자극에 의한 탈과립 억제 효과가 있는지를 알아보기 위해 과립의 지표 단백질인 β- hexosaminidase의 세포 밖으로의 분비가 억제되는지를 조사 하였다. 그 결과 RBL-2H3 세포에서 항원에 의해 증가된 β- hexosaminidase의 분비가 RCE의 농도(10, 30, 100 μg/ml) 의존적으로 억제되는 것을 확인하였다(Fig. 1A). RCE에 의 한 탈과립 억제 효과는 Src-family kinase 억제제인 PP2의 효과와 유사하게 나타났다(IC50, ~57 μg/ml). 또한 RBL-2H3 세포에 100 μg/ml의 RCE를 30분간 전처리 한 후 S-buffer 로 세척한 뒤 탈과립 억제 효과를 확인한 결과 감소되었던 탈과립이 회복 되는 것을 통해 RCE의 억제 효과가 가역성 이 있음을 확인하였다(Fig. 1B).
RCE의 항원에 의한 비만세포에서 TN F- 및 IL-4의 발 현 억제 효과 비만세포에서 분비되는 TNF-와 IL-4는 알 레르기 질환을 유발에 중요한 염증성 사이토카인으로 널리 알려져 있다. 이러한 이유로 우리는 항원에 의해 활성화된 비만세포에서 생성되는 TNF-와 IL-4가 RCE에 의해 억제 되는지 확인하고자 RT-PCR을 수행하였다. 그 결과 비만세 포에서 RCE는 농도 의존적으로 TNF-와 IL-4의 mRNA 발현을 억제 하는 것을 확인하였다(Fig. 2A). RCE는 농도 의존적으로 그 사이토카인을 억제하였으며 최고농도인 100 μg/ml에서 TNF-와 IL-4의 발현을 거의 완전하게 억제 하였다. 이것은 대조물질로 사용된 PP2의 효과와 유사하였 다(Fig. 2B).
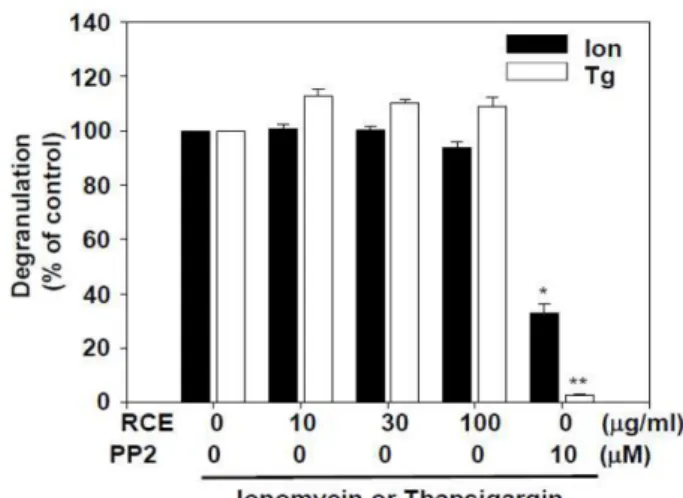
RCE의 비만세포에서 칼슘신호 자극에 의한 탈과립 억 제 효과 항원 자극에 의한 비만세포의 탈과립은 Lyn/Fyn- Syk-LAT 신호전달경로의 활성화에 의한 세포내 칼슘의 농 도증가가 매우 중요하다.14) 우리는 RCE의 기전연구를 위해 먼저 RCE가 칼슘 의존적 신호전달경로에 의한 탈과립을 억 제하는지를 실험하였다. 우리는 thapsigargin과 ionomycin을 사용하여 세포질 내 칼슘 이온의 농도를 증가시켰으며 이 에 의해 비만세포에서의 탈과립이 유도되었다. 실험결과 RCE는 thapsigargin과 ionomycin에 의한 비만세포의 탈과 립 반응을 억제하지 않았다(Fig. 3). 이러한 결과는 RCE는 항원자극에 의한 비만세포의 활성화 신호전달과정 중 칼슘 신호의 상위 신호전달과정을 억제하는 것을 추측할 수 있었다.
Fig. 1. Effect of RCE on antigen-induced degranulation in RBL-2H3 cells. (A) IgE-primed RBL-2H3 cells (2×105 cells/
well) were pre-treated with or without RCE for 30 min and subsequently stimulated with 25 ng/ml antigen for 15 min. (B) RBL-2H3 cells were washed 5 times after incubating with RCE for 30 min and stimulated with 25 ng/ml antigen for 15 min. Degranulation rate was measured as described in the section for “Materials and Methods”. Control refers to the mast cell degranulation rate by antigen stimulation without RCE. The values indicate the mean ± S.E.M. from three inde- pendent experiments (each in triplicate). The asterisks indicate significant differences from antigen-stimulated groups (A) or (B) as indicated, *p<0.05, **p<0.01. PP2 is a general Src- family kinase inhibitor.
RCE의 비만세포의 신호전달 단백질 활성화에 대한 억 제 효과 이전 실험에서 나타난 비만세포에서 RCE의 탈 과립 억제 효능이 어떤 신호 전달 단백질을 억제하여 나타 나는 것인지를 알아보기 위하여 항원 자극에 의해 매개되 는 비만세포의 신호 전달 과정을 확인하였다. 그 결과 RBL- 2H3 세포에서 초기 신호 전달에 관여하는 Syk kinase, LAT 및 PLC의 인산화가 RCE에 의해 농도 의존적으로 감소하 는 것을 확인하였다(Fig. 4). 또한 Akt와 MAP kinase인 Erk1/2, p38 및 JNK의 인산화도 RCE에 의해 감소됨을 확 인하였다(Fig. 4A, lower panel). 생쥐의 골수에서 분화시킨 비만세포인 BMMC에서 역시 RCE에 의해 Syk kinase, LAT 및 PLC의 인산화가 농도 의존적으로 감소하였다(Fig. 4B).
이러한 결과는 비만세포주인 RBL-2H3 세포 뿐 아니라 골 수에서 분화시킨 비만세포에서도 RCE는 억제효과를 가지 며 기전이 동일함을 알 수 있었다.
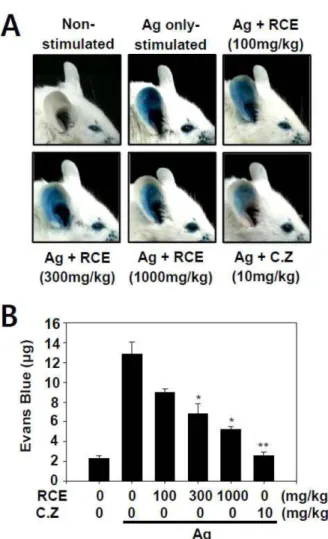
RCE의 국소피부자극 알레르기 반응의 억제 효과 비만 세포에서 RCE의 탈과립 억제효과가 마우스에서 제1형 알
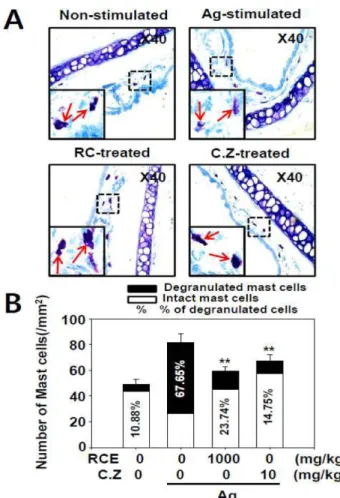
레르기 반응에서 효과가 있는지를 확인하기 위해서 국소적 알레르기 동물모델인 PCA 실험을 수행하였다. PCA는 생 쥐의 귀에 IgE를 주입 후 항원을 꼬리 정맥 주사로 주입하 여 국소적으로 알레르기를 유발하는 대표적인 알레르기 질 환 동물 모델이다. IgE 주입 후 알레르기 치료제로 알려져 있는 cetirizine 50 mg/kg와 RCE를 100, 300, 1000 mg/kg로 경구 투여 한 뒤 항원을 주입하여 PCA를 유발한 결과 대 조군은 생쥐의 귀 조직으로 Evans blue dye가 삼출된 반면 RCE를 투여한 생쥐의 귀에서는 그 삼출이 농도 의존적으 로 감소되어 있음을 확인하였다(Fig. 5A). PCA를 유도한 생 쥐의 귀에서 추출한 Evans blue dye 역시 대조군에 비해 RCE의 농도 의존적으로 감소하였다(Fig. 5B). RCE의 1000 mg/kg 농도에서는 알레르기 치료제로서 사용되고 있는 cetirizine의 효과와 유사한 정도로 나타났다. 추가적으로, 우 리는 PCA 유발 후 귀를 적출하여 조직 고정 후 toluidine blue 염색을 하여 조직 내 비만세포를 관찰한 결과 최고 농 도 투여군에서 항원에 의해 탈과립이 나타난 비만세포의 비 율이 RCE에 의해 감소되었음을 확인하였다(Fig. 6). 이 결 과를 통해 RCE의 항원 자극에 의한 알레르기 억제 효과는 조직 내 비만세포의 활성을 억제하여 나타남을 확인 할 수 있었다. 이러한 결과를 종합할 때 RCE는 in vitro 세포 수 준에서의 비만세포 억제 뿐 아니라 in vivo 알레르기 동물 모델에서도 그 억제 효과가 나타남을 확인할 수 있었다.
Fig. 2. Effect of RCE on the expression of TNF- and IL-4 mRNA. IgE-primed RBL-2H3 cells (1×106 cells/ well) were stimulated with 25 ng/ml antigen for 15 min after pre-treated with or without RCE or PP2 for 30 min. The expression of TNF- and IL-4 mRNA was measured by RT-PCR. Repre- sentative images (A) or the mean ± S.E.M. of band densities (B) for the upper panel from three independent experiments are shown. PP2, a Src-family kinase inhibitor. Significant dif- ferences with the values for the antigen-only groups are indi- cated, *p<0.05 and **p<0.01.
Fig. 3. Effect of RCE on degranulation by thapsigargin or ion- omycin in RBL-2H3 cells. The RBL-2H3 cells (3.0×105cells/
well) were pre-incubated with or without RCE or PP2 for 30 min and then stimulated with 1 μM ionomycin or 300 nM thapsigargin for 15 min as indicated. The values indicate the mean ± S.E.M. from three independent experiments (each in triplicate). Degranulation rate was measured as described in the section for “Materials and Methods”. Significant differ- ences with the values for the thapsigargin or ionomycin-only groups are indicated, *p<0.05 and **p<0.01. PP2, a Src-family kinase inhibitor.
고 찰
지난 수십 년 동안 전 세계적으로 알레르기 질환의 발병 율이 증가하고 있다.4) IgE 매개성 비만세포의 활성화는 알 레르기 질환을 유발하는 과정에서 아주 중요하게 관여하는 데 과립속의 히스타민이나 단백분해효소 등을 분비하거나 TNF-, TGF-β, IL-1β, IL-4 및 IL-6와 같은 많은 염증성 사 이토카인을 분비함으로써 알레르기 증상을 유발한다.15,16) 현 재 알레르기 치료에 주로 쓰이는 약제는 면역억제제나 항 히스타민제 등으로 알레르기의 원인에 대한 치료보다는 증 상 완화에 주안점을 두고 있는 한계를 가지고 있다.5,6) 따라 서 알레르기 질환에 대한 새로운 치료제 개발을 위해 비만
세포의 항원 자극에 의해 초기에 활성화되는 신호전달단백 질인 Lyn 그리고 Fyn 등의 Src family kinase와 Syk을 표적 으로 하는 연구가 많이 진행되고 있다. 본 연구에서 우리는 천연소재인 소리쟁이 추출물(RCE)이 비만세포 내 Syk의 활 성을 억제하여 비만세포에 의해 매개되는 알레르기 반응을 억제하는 것을 확인하였다.
Fig. 4. Effect of RCE on activations of Syk and its down- stream signaling proteins in RBL-2H3 cells and BMMCs. IgE- primed RBL-2H3 cells(1.0×106 cells/well in 6-well plate) and BMMCs(5.0×106cells/tube) were stimulated with 25 ng/ml DNP-BSA for 10 min after pre-incubation with RCE or PP2 for 30 min. The cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis as described in “Materials and Methods”. Represen- tative images are shown from three independent experiments.
PP2, a Src-family kinase inhibitor.
Fig. 5. Effect of RCE on IgE-mediated passive cutaneous ana- phylaxis The DNP-specific IgE (50 ng) was intradermally injected into mouse ear (n = 5). Next day, RCE in 5% Arabic gum was orally administrated as indicated. After 1 hour, 250 μl of Evans blue (5 mg/ml) with or without antigen (100 μg) was injected into mouse tail vein. The mice were euthanized 1 h after the injection of antigen and the ears where IgE was injected were isolated for the extraction of Evans blue dye. All data were obtained from three indepen- dent experiments (each experiment, n = 5 per group). (A) Rep- resentative images for the ear are shown. (B) The amount of Evans blue dye extracted from the ear skin are shown as the mean ± S.E.M. Significant differences with the values for the antigen group without RCE or PP2 are indicated, *p<0.05 and
**p<0.01. C.Z., a anti-histamine reference drug.
RCE는 항산화, 항균 및 골소실 억제효과 등이 보고되어 있다. RCE은 항산화 효과 및 Staphylococcus aureus 와 Bacillus subtilis에 항균 효과를 가지고 있다.12) RCE는 Runx2 신호 전달 및 RANKL 신호 전달 억제에 의해 파골 세포 분화를 억제하고 조골 세포 분화를 증가시켜 골다공 증을 억제할 수 있다고 보고되어 있다.10) 하지만 RCE의 염 증질환이나 알레르기 치료효과에 대한 연구는 아직 보고되 어 있지 않다. 우리는 이 연구를 통해 RCE가 비만세포 억 제를 통해 제1형 알레르기 반응을 억제한다는 것을 처음으 로 규명하였다(Figs. 1 and 5).
우리는 비만세포에서의 RCE 효과를 알아보고자 먼저 비 만세포의 탈과립 정도를 확인하기 위해 β-hexosaminidase를 측정하였다.17) 비만세포의 탈과립은 알레르기성 염증을 매 개함에 있어 중요한 역할을 하는데18) RCE는 항원에 의해 유도된 비만세포의 탈과립을 억제하였다(Fig. 1A). 또한 RCE 처리 후 세척을 통해 억제 효과가 감소하는 것을 확인함으 로써 가역성이 있음을 증명하였다(Fig. 1B). 우리는 이러한 RCE의 가역성은 이 소재를 사용한 알레르기 치료제를 개 발 시 부작용 측면에서 장점이 있을 가능성을 제시한다고 생각한다.
비만세포에서 항원 자극에 의해 생성되는 TNF-와 IL-4 등 많은 염증성 사이토카인들이 알레르기 반응 후기 단계 에서 염증성 증상을 유발하는데 중요한 역할을 한다고 알 려져 있다.19) 알레르기에서 TNF-는 염증을 유발하고 염증 부위에 면역세포들을 모이게 한다.20) IL-4는 형질세포의 증 식과 IgE의 생성을 촉진하고 염증과 평활근 수축을 통해 알 레르기에 기여한다고 보고되어 있다.21,22) 따라서 비만세포 에서 발현되는 사이토카인의 감소가 알레르기의 완화에 중 요한 지표임을 나타낸다. 우리는 비만세포에서 항원 자극에 의한 TNF-와 IL-4의 생산이 RCE의 농도 의존적으로 억 제 되는 것을 확인하였다(Fig. 3). 이는 RCE가 알레르기 증 상이 만성적으로 진행하는 과정을 억제 할 수 있음을 보여 주었다. 따라서 우리는 RCE가 급성 알레르기 질환 뿐 아니 라 아토피성 피부염과 같은 만성적인 알레르기 질환의 치 료소재로도 활용 가능성이 있다고 생각한다.
항원에 의해 매개된 비만세포의 활성화 신호 경로는 항원 자극을 통해 Lyn 및 Fyn Src family kinase가 활성화되고 FcεRI의 ITAM 부위가 인산화 되어 Syk이 결합하며 동시에 인산화 된다.23,24) Syk이 인산화 되면 활성화 되고 LAT, PI3K, PLC- 및 MAP Kinase 등 다양한 하위신호 활성으 로 이어진다.25) 본 연구에서 RCE가 Syk의 활성화를 농도 의존적으로 억제하고 다양한 하위신호 역시 억제하는 것을 확인하였다(Fig. 4). 이러한 결과는 RCE가 Syk의 활성을 억 제함으로써 비만세포의 탈과립과 사이토카인 생산을 억제 한다는 것을 보여준다. RCE가 비교적 초기 신호전달 단백 질인 Syk의 활성화를 억제하는 것은 항원 자극에 의한 비
만세포의 전체 신호전달과정의 활성화를 억제하는데 더욱 효과적이라는 것을 나타내었다.
비만세포에 의해 급성으로 국소부위에 알레르기 반응이 유도되는 제1형 알레르기 동물모델로는 PCA가 잘 알려져 있다.26) PCA 실험에서 RCE는 농도 의존적으로 실험동물 의 알레르기 반응을 억제하였다(Fig. 5B). 더 나아가 RCE 는 귀 조직 내 비만세포의 탈과립 역시 억제하였다(Fig. 6B).
우리는 실험을 통해 RCE의 비만세포 활성 억제는 알레르 기 동물모델에서도 조직 내 비만세포의 탈과립 억제 효과 가 있음을 증명하였다.
Fig. 6. Effect of RCE on the degranulation of mast cells in ear tissue. PCA experiments were performed as for Fig. 5.
The mice were euthanized 1 h after the injection of antigen and the ears where IgE was injected were isolated for histol- ogy. All data were obtained from three independent experi- ments(each experiment, n = 5 per group). (A) Representative images for the ear are shown. (B) The percent of degranulated mast cells(MCs) of total MCs were counted as described in
“Materials and Methods”. The number of degranulated MCs are shown as the mean ± S.E.M. Significance differences between the antigen-stimulated control group without RCE and CZ treatment groups are indicated, *p<0.05 and **p<0.01.
C.Z., a anti-histamine reference drug.
결 론
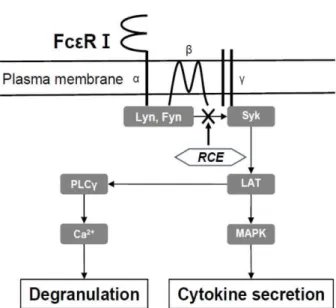
본 연구에서는 알레르기 반응을 유도하는 면역 세포인 비 만세포에서 소리쟁이 추출물(RCE)의 알레르기 억제 효과 및 기전을 알아보고자 in vivo와 in vitro에서 실험을 수행하 였다. 그 결과 RCE가 항원자극에 의한 비만세포 탈과립 및 사이토카인 생산 억제를 통해 동물에서 제1형 알레르기 반 응을 억제하는 것을 확인하였다. 또한 RCE는 비만세포에서 Syk의 활성 및 다양한 Syk 매개 하위 신호 전달을 억제하 여 항원 자극에 의한 알레르기 반응을 억제한다는 것을 발 견하였다(Fig. 7). 앞으로 우리는 RCE에 대한 독성 연구 및 약효 성분에 대한 추가 연구를 통해 알레르기 치료제로써 의 개발이 가능성을 높이고자 한다.
사 사
본 연구는 2017년도 덕성여자대학교 연구지원을 받아 수 행되었으며 이에 감사드립니다.
인용문헌
1. Asher, M. I., Montefort, S. and Bjorksten, B. (2006) World- wide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three repeat multicountry cross-sectional
surveys. Lancet 368: 733-43.
2. Metcalfe, D. D., Baram, D. and Mekori, Y. A. (1997) Mast cells 77: 1033-1079.
3. Gilfillan, A. M. and Beaven, M. A. (2011) Regulation of mast cell responses in health and disease. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 31:
475-530.
4. Gilfillan, A. M. and Rivera, J. (2009) The tyrosine kinase net- work regulating mast cell activation. Immunol. Rev. 228: 149- 169.
5. Gilfillan, A. M. and Tkaczyk, C. (2006) Integrated signaling pathways for mast-cell activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6: 218- 230.
6. Kobayashi, H., Ishizuka, T. and Okayana, Y. (2000) Human mast cells and basophils as sources of cytokines. Clin. Exp.
Allergy 30: 1205-1212.
7. Galli, S. J. and Tsai, M. (2012) IgE and mast cells in allergic disease. Nat. Med. 18: 693-704.
8. Bloemen, K., Verstraelen, S., Van Den Heuvel, R., Witters, H., Nelissen, I. and Schoeters, G. (2007) The allergic cascade:
review of the most important molecules in the asthmatic lung.
Immunol. Lett. 113: 6-18.
9. Galli, S. J., Tsai, M. and Piliponsky, A. M. (2008) The devel- opment of allergic inflammation. Nature 454: 445-454.
10. Shim, K. S., Lee, B. and Ma, J. Y. (2017) Water extract of Rumex crispus prevents bone loss by inhibiting osteo- clastogenesis and inducing osteoblast mineralization. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 17: 483.
11. Maksimović, Z., Kovacević, N., Lakusić, B. and Cebović, T.
(2011) Antioxidant activity of yellow dock (Rumex cris- pus L., Polygonaceae) fruit extract. Phyther. Res. 25: 101-05.
12. Yildirim, A., Mavi, A. and Kara, A. A. (2001) Determination of antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Rumex crispus L. extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 49: 4083-89.
13. Shiwani, S., Singh, N. K. and Wang, M. H. (2012) Car- bohydrase inhibition and anti-cancerous and free radical scavenging properties along with DNA and protein protection ability of methanolic root extracts of Rumex crispus. Nutr.
Res. Pract. 6: 389-95.
14. Beaven, M. A. and Metzger, H. (1993) Signal transduction by Fc receptors: the FcεRI case. Immunol. Today 14: 222-226.
15. Bischoff, S. C. (2007) Role of mast cells in allergic and non- allergic immune responses: comparison of human and murine data. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 7: 93-104.
16. Supajatura, V., Ushio, H., Nakao, A., Akira, S., Okumura, K., Ra, C. and Ogawa, H. (2002) Differential responses of mast cell toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in allergy and innate immunity.
J. Clin. Invest. 109: 1351-1359.
17. Rivera, J. and Gilfillan, A. M. (2006) Molecular regulation of mast cell activation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 117: 1214-25.
18. Siraganian, R.P., Zhang, J., Suzuki, K. and Sada, K. (2002) Protein tyrosine kinase Syk in mast cell signaling. Mol.
Immunol. 38: 1229-33.
Fig. 7. Schematic diagram of the effect of RCE on the inhib- itory effect of mast cell activation. RCE inhibits the activation of Syk and Syk-dependent signaling proteins in antigen-stim- ulated mast cells. Through this mechanism, RCE eventually inhibits degranulation and cytokine secretion, resulting in the suppression of IgE-mediated allergic responses.
19. Frossi, B., Rivera, J., Hirsch, E. and Pucillo, C. (2007) Selec- tive activation of Fyn/PI3K and p38 MAPK regulates IL-4 production in BMMC under nontoxic stress condition. J.
Immunol. 178: 2549-55.
20. Kabu, K., Yamasaki, S., Kamimura, D., Ito, Y., Hasegawa, A., Sato, E., Kitamura, H., Nishida, K. and Hirano, T. (2006) Zinc is required for FcεRI-mediated mast cell activation. J.
Immunol. 177: 1296-305.
21. Kyriakis, J. M. and Avruch, J. (1996) Sounding the alarm:
protein kinase cascades activated by stress and inflammation.
J. Biol. Chem. 271: 24313-16.
22. Lorentz, A., Klopp, I., Gebhardt, T., Manns, M. P. and Bis- choff, S. C. (2003) Role of activator protein 1, nuclear factor- kappaB, and nuclear factor of activated T cells in IgE recep- tor-mediated cytokine expression in mature human mast cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 111: 1062-68
23. Kim, J. W., Lee, J. H., Hwang, B. Y., Mun, S. H., Ko, N. Y.,
Kim, D. K., Kim, B., Kim, H. S., Kim, Y. M. and Choi, W.
S. (2009) Morin inhibits Fyn kinase in mast cells and IgE- mediated type I hyperpersensitivity response in vivo. Bio- chem. Pharmacol. 77: 1506-12.
24. El-Agamy, D. S. (2012) Anti-allergic effects of nilotinib on mast cell-mediated anaphylaxis like reactions. Eur. J. Phar- macol. 680: 115-21.
25. Alber, G., Miller, L., Jelsema, C., Varin-Blank, N. and Metzger, H. (1991) Structure: function relationships in the mast cell high-affinity receptor for IgE (FcεRI): role of cyto- plasmic domains. J. Biol. Chem. 266: 22613-20.
26. Oettgen, H. C., Martin, T. R., Wynshaw-Boris, A., Deng, C., Drazen, J. M. and Leder, P. (1994) Active anaphylaxis in IgE- deficient mice. Nature 370: 367-70.
(2019. 9. 21 접수; 2019. 10. 29 심사;
2019. 11. 15 게재확정)