주요용어 치매 간호사 역할 업무: , , ,
서 론 I.
연구의 필요성 1.
,
(Kim et al., 2005).
3 (Korean Nurses
Association, [KNA], 2006)
, ,
,
. ,
.
치매 환자를 돌보는 간호사의 역할과 업무
하주영
1
BK21
1Roles and Tasks of Nurses Caring People with Dementia
Ha, Ju Young
11
College of Nursing Science, Ewha Womans University BK21 Post-doctoral Researcher
Purpose: The research aims to identify the roles of nurses at dementia clinics or geriatric hospitals to set their
tasks. Methods: This research has been conducted through literature review and focus group methodology. The field survey has been done for 195 nurses at 36 hospitals for the aged and dementia clinics from Oct. 9 to Oct.28, 2006. Results: The nurses were identified to play eight roles as clinical specialists, educators, researchers, counselors, consultants, collaborators, leaders, managers, and advocators. They were also known to implement 27 nursing tasks and 104 nursing activities. Conclusion: The findings of this research could provide a foundation for the nursing care work as well as become a practice guideline for the nurses, at these hospitals, to implement versatile roles and tasks.
Key Words : Dementia, Nurse, Roles, Tasks
Corresponding address: Ha, Ju Young, College of Nursing Science, Ewha Womans University, BK21 Post-doctoral Researcher, 11-1
Daehyun-dong, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 120-750, Korea. Tel: 82-2-3277-3293, Fax: 82-2-3277-2850, E-mail:jyh1028@ewha.ac.kr
투고일 2007 2 6 심사의뢰일 2007 2 14 심사완료일 2007 6 11
.
,
(Gauthier, 2002).
, , , ,
, ,
(Cohen- Mansfield & Bester, 2006). ․
2004 382 2005 583 52.6%
(Korea Ministry of Health & Welfare, 2006) .
. , (Lee et al., 2004),
(Kim & Yoo, 2003), (Song & Chi, 2003)
(Sung, Shin, Lee, & Kwon, 2005) . .
.
연구의 목적 2.
.
1) .
2) .
용어정의 3.
1) :
(Shin, 2004) ,
31 3
.
2) :
(KNA, 2003) ,
31 3
.
연구방법 II.
연구설계 1.
.
연구과정 2.1)
․
,
.
, ,
.
2)
, , , ,
, , , , 13
3
23 .
54 2 3
,
3 .
2006 9 1 9 20
.
3)
4 2
8 25 94
.
2 , 3
, ․ 8 27
104 .
4)
2006 10
9 10 28 36
195 .
.
‘ ’ ‘ ’
‘ ’ ‘ ’
‘ ’ ‘ ’ .
.
자료분석 3.
1)
․ ,
, , , ,
(KNA, 2006),
, ,
, , , ,
․ ․
, (KNA,
2004).
, . , , ,
,
(ANA, 2001)
, , , ( ),
(Ko- rean Accreditation Board of Nursing, [KABON], 2005).
(KNA, 2003),
(American Geriatrics Society, 2003), (University of North Carolina
Hospital, 2006) 38
70
, 54
124
42 82 . 38
25
, 82
4 16
94 .
2)
8
. 8 ‘ ’
4 , ‘ ’ 3 , ‘ ’ 2 , ‘
’ 1 3
4 CVI(Content Validity Index) 1.0
. 1 , ,
, , , , ,
CVI 0.7 2
CVI 1.0 .
25 94
1 ,
, , ,
CVI 0.7 ,
,
, , ,
, CVI 0.5
,
, ,
.
,
, ,
,
(
) .
,
, , ,
,
2 . 2
CVI 1.0
27 , , ,
, , , , ,
, , , ,
( ) , , , ,
, , , ,
, , , , ,
,
. CVI 0.7
3
, CVI 1.0 104
(Table 1).
연구결과 III.
36
195 .
대상자의 일반적 특성 1.
33.8±7.98 20
42.6 %(83 ) 30 30.8%(60 ), 40
22.6% (44 ), 50 4.1%(8 )
. 65.6% (128 )
15.4%(30 ), 16.9%(33 ),
2.1%(4 ) 77.4%
(151 ) 3 4 17.9%(35 ),
4.6%(9 ) .
대상자의 간호 관련 특성 2.
, .
8.07±6.09
10 29.7%(58 ) 3-5
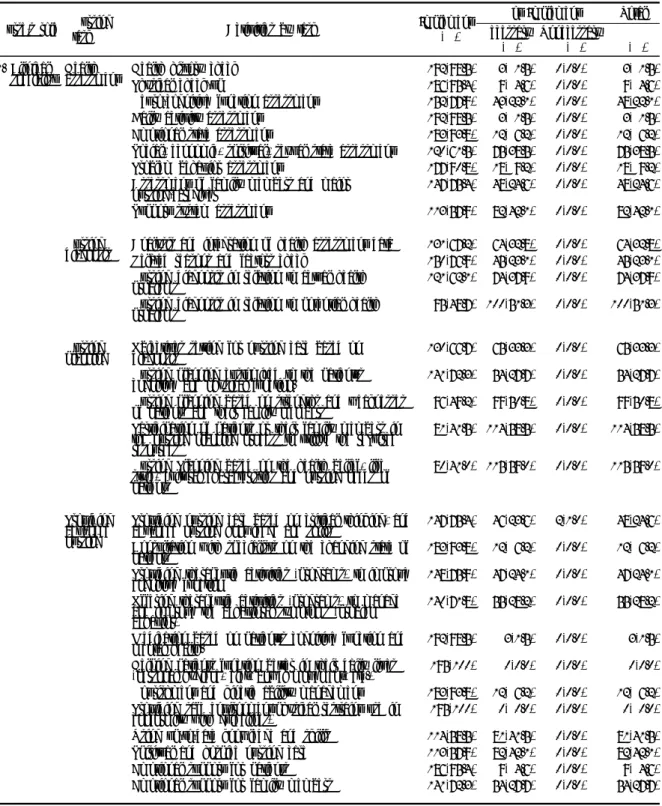
Table 1. Nurse's roles, tasks and activities for dementia patients (N=195)
Nurse's role Nursing
task Activities by task Implement
N(%)
Not Implement Total Necessary
N(%)
Unnecessary
N(%) N(%)
1. Clinical specialist Health
assessment Health history check Physical check-up
Neuro-cognitive function assessment Daily activity assessment
Emotional state assessment
Social, economic, spiritual, sexual state assessment Problem behavior assessment
Assessment of family members and major nursing-caregiver
Support system assessment
192(98.5) 186(95.4) 152(77.9) 192(98.5) 183(93.8) 120(61.5) 177(90.8) 147(75.4) 113(57.9)
3( 1.5) 9( 4.6) 43(22.1) 3( 1.5) 12( 6.2) 75(38.5) 18( 9.2) 48(24.6) 82(42.1)
0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0)
3( 1.5) 9( 4.6) 48(22.1) 3( 1.5) 12( 6.2) 75(38.5) 18( 9.2) 48(24.6) 82(42.1)
Nursing
diagnosis Analysis and integration of health assessment data Related reasons and factors check
Nursing diagnosis in relation to actual health problems
Nursing diagnosis in relation to potential health problems
131(67.2) 150(76.9) 121(62.1) 95(48.7)
64(32.8) 45(23.1) 74(37.9) 100(51.3)
0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0)
64(32.8) 45(23.1) 74(37.9) 100(51.3)
Nursing
planning Objectives setting for nursing care based on diagnosis
Nursing planning customized to the patient’s cognitive and physical function.
Nursing planning based on strengths and weaknesses of patients and their family members
Participation of patients or their family members in the nursing planning process to utilize the required resources
Nursing Planning based on the health belief, life style, cultural characteristics and nursing needs of patients
130(66.7) 141(72.3) 96(49.2) 81(41.5)
80(41.0)
65(33.3) 54(27.7) 99(50.8) 114(58.5)
115(59.0)
0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0)
0(0.0)
65(33.3) 54(27.7) 99(50.8) 114(58.5)
115(59.0)
Providing advanced nursing
Providing nursing care based on critical thinking, and advanced nursing knowledge and skills
Consultation with specialists on the changing state of patients
Providing therapeutic activities (programs) to improve cognitive function
Offering therapeutic activities (programs) to manage and improve the behavioral symptoms (problem behavior)
Medication based on patient’s cognitive function and mental health.
Helping patients function better in their daily lives (personal hygiene, diet, bowel movement, etc.) Nourishment and kinetic ability management Providing safe environment(physical restraint use in conformity with guidelines)
Using up-to-date knowledge and skills Spiritual and hospice nursing care Emotional support for patients Emotional support for family members
147(75.4) 183(93.8) 148(75.9) 140(71.8)
192(98.5) 195(100) 183(93.8) 195(100) 114(58.5) 113(57.9) 186(95.4) 141(72.3)
46(23.6) 12( 6.2) 47(24.1) 55(28.2)
3(1.5) 0(0.0) 12( 6.2) 0( 0.0) 81(41.5) 82(42.1) 9( 4.6) 54(27.7)
2(1.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0)
0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0)
48(24.6) 12( 6.2) 47(24.1) 55(28.2)
3(1.5) 0(0.0) 12( 6.2) 0( 0.0) 81(41.5) 82(42.1) 9( 4.6) 54(27.7)
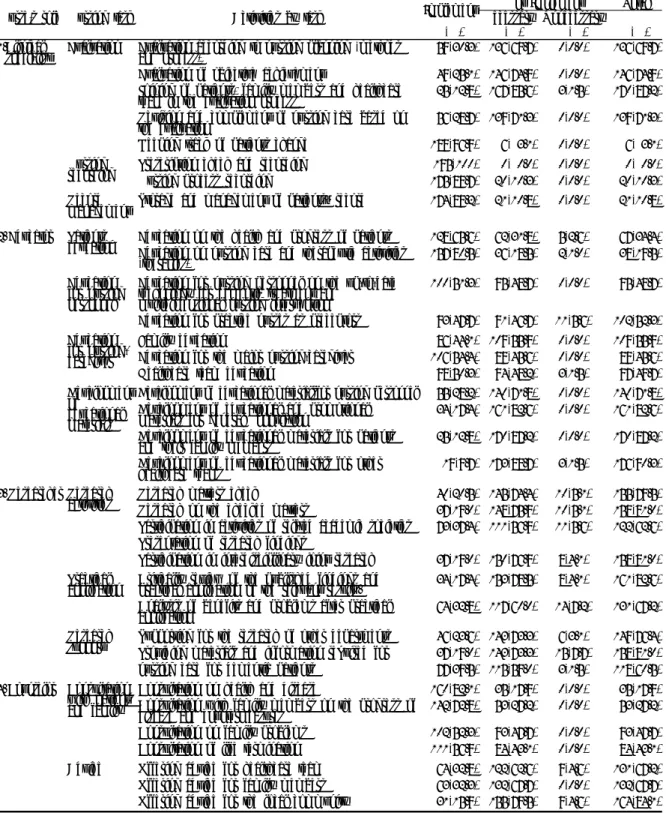
Table 1. Nurse's roles, tasks and activities for dementia patients(Cont.) (N=195)
Nurse's role Nursing task Activities by task Implement Not Implement Total
Necessary Unnecessary
N(%) N(%) N(%) N(%)
1.Clinical
specialist Evaluation Evaluation according to nursing planning (methods and process)
Evaluation of objective achievement
Joining of patients, family members and healthcare team in the evaluation process
Revision and complement of nursing care based on the evaluation
Keeping track of patients change
59(30.3) 49(25.1) 25(12.8) 56(28.7) 189(96.9)
136(69.7) 146(74.9) 167(85.6) 139(71.3) 6( 3.1)
0(0.0) 0(0.0) 3(1.5) 0(0.0) 0(0.0)
136(69.7) 146(74.9) 170(87.2) 139(71.3) 6( 3.1) Nursing
recording Prescription check and recording Nursing process recording
195(100) 175(89.7)
0( 0.0) 20(10.3)
0(0.0) 0(0.0)
0( 0.0) 20(10.3) Record
management Storage and management of patients’ record 174(89.2) 21(10.8) 0(0.0) 21(10.8) 2. Educator Patients
education Education on the health and progress of patients Education on nursing care and therapeutic activities (therapies)
128(65.6) 157(80.5)
62(31.8) 36(18.5)
5(2.6) 2(1.0)
67(34.4) 38(19.5) Education
for nursing personnel
Education for nursing personnel on the up-to-date technology for dementia treatment and
multidimensional nursing intervention Education for practice nurses as preceptors
100(51.3)
93(47.7)
95(48.7)
91(46.7)
0(0.0)
11(5.6)
95(48.7)
102(52.3) Education
for nursing- caregiver
Family education
Education for the major nursing-caregiver Healthcare team education
86(44.1) 106(54.4) 98(50.3)
109(55.9) 89(45.6) 94(48.2)
0(0.0) 0(0.0) 3(1.5)
109(55.9) 89(45.6) 97(49.7) Development
ofeducational materials
Development of educational materialsfor nursing personnel Development of educational and promotional materials for general population
Development of educational materials for patients and their family members
Development of educational materials for other healthcare teams
55(28.2) 34(17.4) 25(12.8) 19(9.7)
140(71.8) 161(82.6) 170(87.2) 173(88.7)
0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 3(1.5)
140(71.8) 161(82.6) 170(87.2) 176(90.3) 3. Researcher Research
activities Research matters check
Research on the checked matters
Participation in activities of related academic societies Presentation of research findings
Participation in interdisciplinary joint research
40(20.5) 37(19.0) 73(37.4)
37(19.0)
145(74.4) 148(75.9) 111(56.9)
150(76.9)
10(5.1) 10(5.1) 11(5.6)
8(4.1)
155(79.5) 158(81.0) 122(62.6)
158(81.0) Practical
application Critically review of the published findings and practical application of the relevant results.
Analysis of benefits and problems after practical application
34(17.4) 64(32.8)
153(78.5) 117(60.0)
8(4.1) 14(7.2)
161(82.6) 131(67.2) Research
support Supporting for the research of other departments Providing materials and information required for nursing care for dementia patients
46(23.6) 37(19.0) 77(39.5)
143(73.3) 143(73.3) 115(59.0)
6(3.1) 15(7.7) 3(1.5)
149(76.4) 158(81.0) 118(60.5) 4. Counselor Consultation
with patients and family
Consultation on health and disease
Consultation with family members on the progress of disease and countermeasures
Consultation on family problems Consultation of life termination
160(82.1) 142(72.8) 102(52.3) 111(56.9)
35(17.9) 53(27.2) 93(47.7) 84(43.1)
0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0)
35(17.9) 53(27.2) 93(47.7) 84(43.1) Advice Offering advice for healthcare team
Offering advice for family members Offering advice for the local community
64(32.8) 63(32.3) 31(15.9)
122(62.6) 132(67.7) 155(79.5)
9(4.6) 0(0.0) 9(4.6)
131(67.2) 132(67.7) 164(84.1)
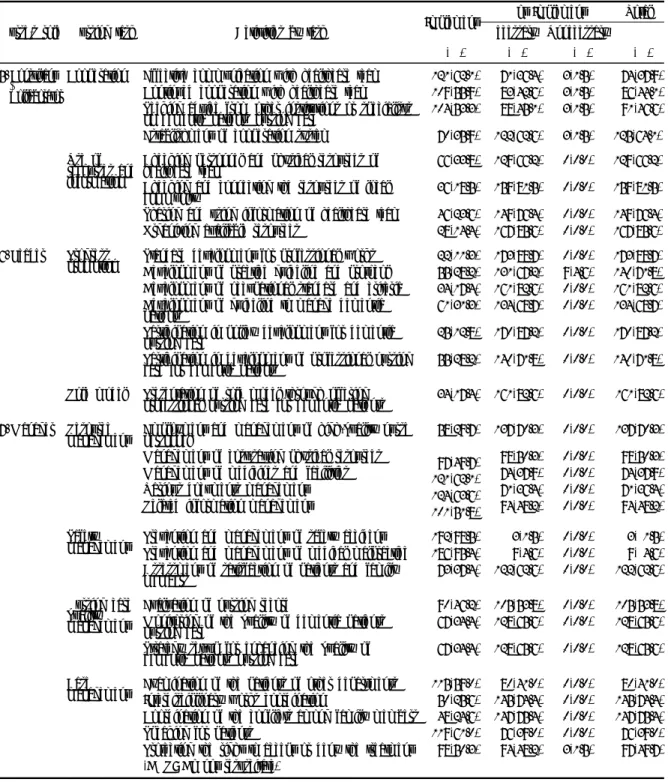
Table 1. Nurse's Roles, tasks and Activities for Dementia Patients(Cont.) (N=195)
Nurse's role Nursing task Activities by task Implement Not Implement Total
Necessary Unnecessary
N(%) N(%) N(%) N(%)
5. Consultant
&
Collaborator
Cooperation Effective communication with healthcare team Continued cooperation with healthcare team Seeking advice from other institutions or specialists on dementia patients nursing care
Establishment of cooperation system
121(62.1) 109(55.9) 104(53.3) 70(35.9)
71(36.4) 83(42.6) 88(45.1) 122(62.6)
3(1.5) 3(1.5) 3(1.5) 3(1.5)
74(37.9) 86(44.1) 91(46.6) 125(64.1) Use of
recourses and information
Checking personnel and physical resources of healthcare team
Checking and connecting the resources of local community
Sharing and using information of healthcare team Organizing available resources
66(33.8) 36(18.5) 46(23.6) 28(14.4)
129(66.2) 159(81.5) 149(76.4) 167(85.6)
0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0)
129(66.2) 159(81.5) 149(76.4) 167(85.6) 6. Leader Progress
promotion Standard development for professional works Development of practice guideline and protocol Development of occupational standard and criteria Development of guideline to manage dementia patients
Participation in policy development for dementia nursing care
Participation in development of professional nursing care for dementia patients
22(11.3) 55(28.2) 34(17.4) 61(31.3) 25(12.8) 55(28.2)
173(88.7) 131(67.2) 161(82.6) 134(68.7) 170(87.2) 140(71.8)
0(0.0) 9(4.6) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0)
173(88.7) 140(71.8) 161(82.6) 134(68.7) 170(87.2) 140(71.8)
Role model Presentation of role model through offering
professional nursing care for dementia patients 34(17.4) 161(82.6) 0(0.0) 161(82.6) 7. Manager Resource
management Employment and management of high-quality nurse personnel
Management of cost-saving physical resources Management of medicines and facilities Various documents management Related information management
58(29.7)
97(49.7) 121(62.1) 124(63.6) 101(51.8)
137(70.3) 98(50.3) 74(37.9) 71(36.4) 94(48.2)
0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0)
137(70.3) 98(50.3) 74(37.9) 71(36.4) 94(48.2)
Safety
management Prevention and management of safety accident Prevention and management of medical malpractice Assessment of satisfaction of patients and family members
192(98.5) 186(95.4) 73(37.4)
3(1.5) 9(4.6) 122(62.6)
0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0)
3( 1.5) 9( 4.6) 122(62.6)
Nursing care quality management
Evaluation of nursing record
Monitoring of the quality of dementia patients nursing care
Strategy set-up for enhancing the quality of dementia patients nursing care
90(46.2) 67(34.4) 67(34.4)
105(53.8) 128(65.6) 128(65.6)
0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0)
105(53.8) 128(65.6) 128(65.6)
Casemanagement Examination of the patients of other departments Interdisciplinary works coordination
Coordination of the conflicts among family members Speaking for patients
Protecting the right to accept or deny the treatment (DNR: Do not resuscitate)
115(59.0) 50(25.6) 48(24.6) 119(61.0) 98(50.3)
80(41.0) 145(74.4) 147(75.4) 76(39.0) 94(48.2)
0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 3(1.5)
80(41.0) 145(74.4) 147(75.4) 76(39.0) 97(49.7)
5-7 21.5%(42 ), 1-3 15.4%(30 ), 7-10 9.2%(18 )
1 2.6%(5 ) .
2.44±2.14 , 1-3
43.1%(84 ) 1 26.7%(52 ),
3-5 16.4%(32 ), 5-7 12.3%(24 )
7 1.5% (3 )
. 71.3%(139
) ․ 28.7%(56 )
.
역할 타당도와 수행여부 조사결과 3.
,
, , , ,
100% ,
, 90%
.
100%
, , 80%
Table 1. Nurse's roles, tasks and activities for dementia patients(Cont.) (N=195)
Nurse's role Nursing task Activities by task Implement Not Implement Total
Necessary Unnecessary
N(%) N(%) N(%) N(%)
8. Advocate Protection Protecting the right to choose the treatment method Protecting patients from physical harm (of family members, medical
personnel, or residents of the local community) Protecting patients from linguistic violence (of family members, medical personnel, or residents of the local community)
86(44.1) 116(59.5) 116(59.5)
106(54.4) 79(40.5) 79(40.5)
3(1.5) 0(0.0) 0(0.0)
109(55.9) 79(40.5) 79(40.5)
Compliance with ethical rule
Examination and revision of ethical rules Application of ethical rules
36(18.5) 51(26.2)
159(81.5) 144(73.8)
0(0.0) 0(0.0)
159(81.5) 144(73.8)
Support for ethical decision-making
Identification of ethical conflicts
Encouragement and respect of the decisions Selection and evaluation of available options
37(19.0) 104(53.3) 65(33.3)
158(81.0) 91(46.7) 130(66.7)
0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0)
158(81.0) 91(46.7) 130(66.7)
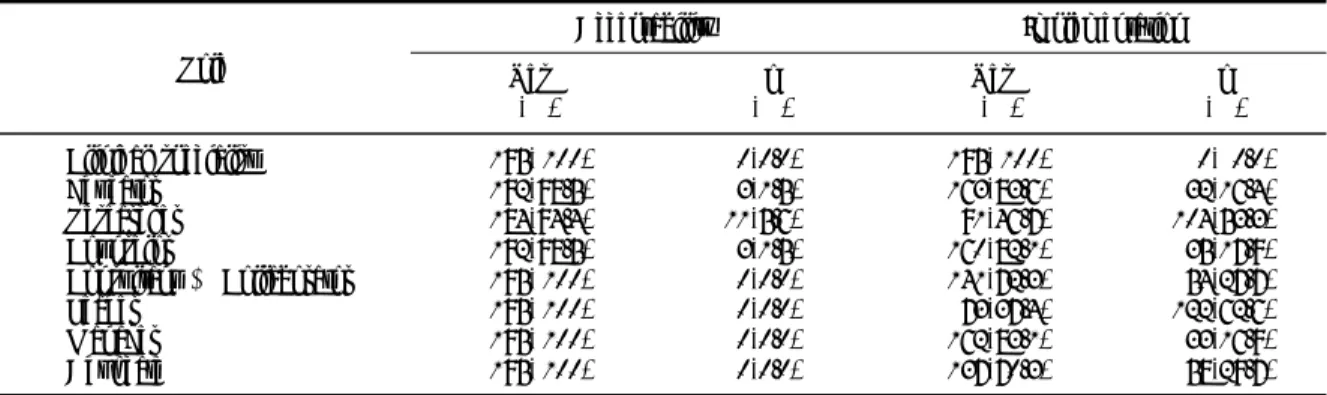
Table 2. Acceptability and implementation by role of nurse for dementia patients (N=195)
Role
Acceptability Implementation
Yes N(%)
No N(%)
Yes N(%)
No N(%) Clinical specialist
Educator Researcher Counselor
Consultant & Collaborator Leader
Manager Advocate
195( 100) 192(98.5) 184(94.4) 192(98.5) 195( 100) 195( 100) 195( 100) 195( 100)
0(0.0) 3(1.5) 11(5.6) 3(1.5) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0) 0(0.0)
195( 100) 163(83.6) 91(46.7) 160(82.1) 141(72.3) 73(37.4) 162(83.1) 137(70.3)
0( 0.0)
32(16.4)
104(53.3)
35(17.9)
54(27.7)
122(62.6)
33(16.9)
58(29.7)
37.4% 46.7%
(Table 2).
업무별 수행여부와 필요성 조사결과 4.
(Table 1) .
, , ,
,
, ,
, ․ ․ , , ․
. , ,
, , ,
, , , , ,
.
논 의IV.
.
,
, , , , , ,
.
,
, ,
,
,
.
Kim(2005) 134
.
83.6%, 82.1%
.
(Tolle, 2006)
. 46.7%
, Kim
(2005) 66.4%
Lincolon(2000) CNS 7%, NP 2%
. 4.6%
69.8% 3
.
, ,
, 37.4%
.
,
(Stanley, 2006).
.
,
,
, ,
(Sclan & Kanowski, 2001) , ,
,
.
Baldwin, Hughes, Hope, Jacoby Ziebland(2003)
1980 2000
, ,
, , DNR ,
, 4
. ․
, ,
.
.
,
, , , , ,
, , , ,
, , , ( ) ,
, , , ,
, , , , ,
, , , ,
27 104
.
Lee(2005)
, ,
, , ,
, , Sung
(2005)
, , , , ,
, , ,
, , ,
, , , ,
, , , , , ․
, .
,
, ,
( )
( , , )
, , ,
.
, , , ,
,
.
( ) (
)
,
, ,
. 104
( ,
, ) (
) ,
Kim(2003) ,
,
.
,
. 9.7%
, ,
.
. ,
, ,
, ,
( ) ,
, ,
.
,
( )
. , , ,
.
. , , .
.
13
3 23
.
.
.
결론 및 제언 V.