J. of Korean Orthopaedic Research Society Volume 15, Number 1, June, 2012
※ 통신저자: 김 영 진
전북 익산시 신용동 344-1
원광대학교 의과대학 정형외과학교실
TEL: 063) 472-5100, FAX: 063) 472-5105 E-mail: oschae68@hanmail.net 접수일: 2012년 3월 27일, 게재확정일: 2012년 6월 13일
요추부 퇴행성 척추 전방전위증과 척추 주위근의 연관성
원광대학교 의과대학 정형외과학교실
채수욱∙심대무∙김태균∙김영진∙김병수
= Abstract =
The Relation of Paraspinal Muscles and Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
Soo Uk Chae, M.D., Dae Moo Shim, M.D., Tae Kyun Kim, M.D., Yeung Jin Kim, M.D. Byung Soo Kim, M.D.
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea
Objectives: To evaluate the cross-sectional area (CSA) and the moment arm length (MAL) of the paraspinal muscles in the degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis patients compared to the matched control patients, which is through contribution to the stability of the back.
Material and Methods: We studied a comprised of 25 degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis on L4/5 patients and a controlled group with 42 chronic lower back pain patients. In both groups, we measured body mass index (BMI, kg/m2). On the standing lateral radiographs, we measured the total lumbar lordosis, and seg- mental lumbar lorodosis using Cobb’s methods. We measured the degree of slippage by Meyerding classifica- tion. The CSA of erector spinae (CSA) and CSA of psoas were measured at the L4/5 level by using the MRI.
The statistical analysis were performed to know the relationship between the CSA and the MAL of erector spinae, and the BMI. Multifidus and erector spinae atrophy were evaluated at the L4/5 level and the degree of fatty atrophy was estimated using three grades : mild, moderate, and severe.
Results: The patient group and the controlled group BMI (kg/m2) were 25.27±3.8 and 24.47±3.24. In patient group, Meyerding classification grade I was 92%. Total lumbar lordosis and each segmental lordosis were measured mean angle 44.54。(24.9。~70.4。) ,and each 9.23。(L3/4), 10.27。(L4/5), 18.81。(L5/S1). Pear- son’s rho indicated a positive association between the CSA and BMI (rho=0.603, p= 0.001), between the CSA of psoas and BMI (rho=0.445, p=0.026), and between the CSA and MAL (rho=0.627, p=0.001) in the degener- ative lumbar spondylolisthesis patients. In terms of the CSA versus MAL, there was a positive association in the both groups (rho=0.627, p=0.001, MAL=0.0008 CSA±5.293 in the degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis group; rho=0.812, p=0.000, MAL=0.001 CSA±5.245 in the control group with using linear regression analy- sis). Independent t-test revealed that both groups had statistically different mean values (p=0.038) in terms of the CSA. Proportion of fat deposits in the multifidus and erector spinae muscle at the L3/4 level were all mild
서 론
1963년 Newman과 Stone이 가성 척추 전방 전위증 대신 퇴행성이란 용어를 발표한 이래 요추 부 퇴행성 전방전위증에 대한 연구가 많이 이루어 져 왔다1,2). 퇴행성 전방전위증의 발생 원인으로 추간판의 퇴행성 변화가 일어나 척추 분절간 불안 정성과 후방 관절의 골성 관절염 변화와 황색인대 의 골화 및 비후가 이루어져 요추부 협착증과 함 께 척추 불안정성을 초래한다 하였으며, 이는 추 궁판과 후관절의 형태학적 이상으로부터 기인하는 것으로 알려져 있다2,3). 그러나 요추부 퇴행성 전 방전위증에서 척추 주위근의 크기와 역할에 대해 서는 많은 보고가 없는 실정이다.
이에 저자들은 요추부 퇴행성 척추 전방전위증 환자에서 척추 주위근의 위축으로 통증과 불안정 성에 척추 주위근의 단면적과 모멘트 팔길이 (moment arm length, MAL)를 측정하여, 척 추 주위근이 퇴행성 척추 전방전위증의 분절간 불 안정성에 기여하는지, 그 연관성에 대해 연구하고 자 하였다.
대상 및 방법
2006년 1월부터 2009년 12월까지 만성 요통 및 방사통을 주소로 내원한 환자들을 대상으로 하 였다. 단순 요추부 기립 전∙후면과 측면 방사선 사진, 요추부 자기공명영상(MRI)상 제 4-5요추 간 척추 분리증이나 외상 및 기타 선천성 질환을 제외한 퇴행성 척추 전방전위증으로 진단된 25명 의 여자환자(평균 63.4±8.3세)를 대상으로 하였 다. 성별 및 나이와 신체 질량지수의 오차를 줄이 고 증상이 있는 환자에 대해 비교키 위해, 척추 전방전위증이나 분리증에 의한 불안정성 없이 만
성 요통으로 내원한 42명의 여자환자(평균64.7±
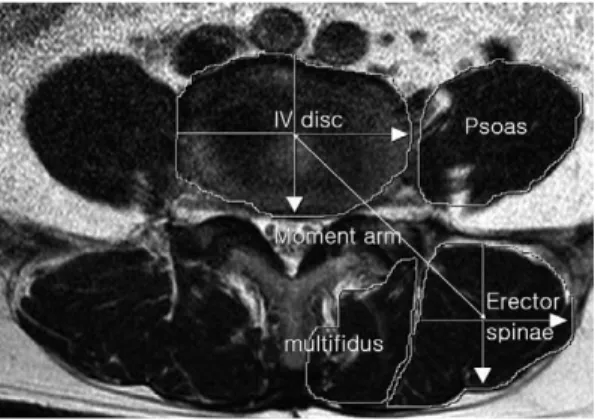
6.9세)를 대조군으로 하였다. 전 환자에서 신장, 체중을 측정하여 신체질량지수(BMI, kg/m2)를 측정하였다. 단순 요추부 기립 측면 방사선상 Meyerding 분류로 전방전위증의 전위 정도와 Cobb방법으로 요추 1번부터 천추 1번 상연까지 의 요추 전체의 전만각과 제 3-4요추간, 제4-5요 추간, 요추5번/천추1번간의 각각의 분절각을 측 정하였다. 제 4-5요추간 축상 MRI를 사용하여 후방 척추주위근과 요근의 단면적과 모멘트 팔길 이(moment arm length, MAL)를 측정하였다 (Fig. 1)4). 근육 단면적 측정은 영상저장장치 (PACS)에서 축상 MRI상 제 4-5요추간의 추간 판 위치의 척추 주위근과 요근의 경계를 표식한 후, pixel로 자동 산정을 하여 단면적 크기 (mm2)와 비율을 측정하였으며, 모멘트 팔길이 (moment arm length, MAL)는 척추 주위근 의 중심에서 척추체의 중심까지 거리(cm)로 측정 하였다. 척추 주위근의 지방 변성 정도를 경도, grades.
Conclusion: The patients with degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis had atrophied erector spinal muscles, which means harmful because of the poor compensation for the lower back load and poor assists to the lumbar stability. This suggests that the biomechanical factor of the muscles influence to the lumbar disability.
Key Words: Paraspinal muscles, Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis, Cross-sectional area, Moment arm length
Fig. 1. MR axial image shows cross section of the mus- cles at L4/5 disc level. IV Disc: L4/5 interverte- bral disc, moment arm length of the erector spinal muscle.
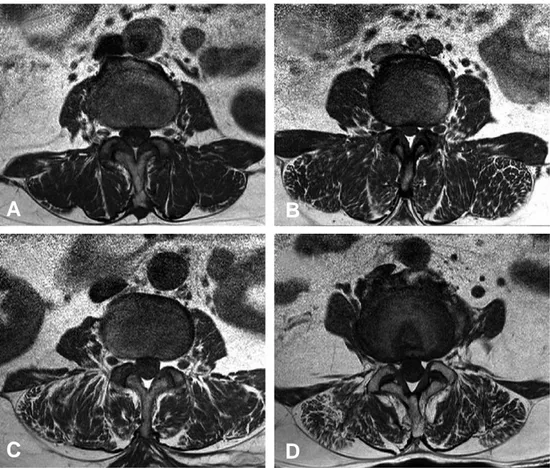
중등도, 중증의 3개의 단계로 분류하였다(Fig.
2A). 경도의 지방 변성 정도는 근육조직(muscle bulk)에 10%미만으로 지방이나 섬유조직으로 대 체되어 근위축이 있는 경우 분류 하였으며(Fig.
2B), 50%미만인 경우 중증도(Fig. 2C), 50%이 상인 경우 중증으로 정의 하였다(Fig. 2D). 통계 분석은 윈도우용 SPSS v18.0을 이용하였으며, 양 군간 연속변수 측정의 비교에는 independent T test를 사용하였으며, 각 변수간 상관 관계 분 석에는 Pearson correlation test를 사용하였다.
통계적 검정의 유의 수준은 0.05 이하로 하였다.
결 과
25명의 요추부 퇴행성 전방전위증 환자군(신
장:156±4.3 cm, 체중:60.68±9.6 kg)과 대조 군(신장: 157±4.3 cm, 체중: 60.38±9.6 kg) 의 신체질량지수(BMI, kg/m2)는 각각 25.27±
3.8, 24.47±3.24이었으며(Table 1), Meyerd- ing 분류상 요추부 퇴행성 전방전위증 환자군에 서 1등급이 92%, 2등급이 8%이었다. 환자군에 서 요추 분절간의 전만각의 평균은 각각 9.23。
(L3/4), 10.27。(L4/5), 18.81。(L5/S1)이었으며, 제 4-5요추간 축상 MRI상 척추주위근과 BMI, 요 근과 BMI는 각각 유의한 상관관계를 보였으며, 상관정도는 척추주위근 (rho=0.603), 요근 (rho=0.445)이였다(Table 2). 요추부 퇴행성 전 방전위증 환자군에서 후방 척추주위근의 단면적 크 기와 moment 팔길이는 통계적으로 유의한 차이 가 있었으며(p=0.001), 환자군과 대조군에서 단면
Fig. 2. MR axial images demonstrating fat distribution in the lumbar paraspinal muscles. (A) Normal (B) Mild fatty atrophy of paraspinal muscles (C) Moderate fatty atrophy of paraspinal muscles (D) Severe fatty atrophy of paraspinal muscles.
A
C D
B
적과 moment 팔길이간 상관계수는 환자군:
rho=0.627, p=0.001, MAL=0.0008 CSA+5.293, 대조군: rho=0.812, p=0.000, MAL=0.001 CSA+5.245으로 나타났다(Table 3). 두 군에서 후방 척추주위근의 단면적은 통계적으로 유의한 차이를 보였으나(p=0.038), moment 팔길이는 유의한 차이가 없었다(Table 4). 요추부 퇴행성 전방전위증 환자군에서 후방 척추 주위근의 근육
내 지방함량의 정도는 모두 경도(mild)이었다.
고 찰
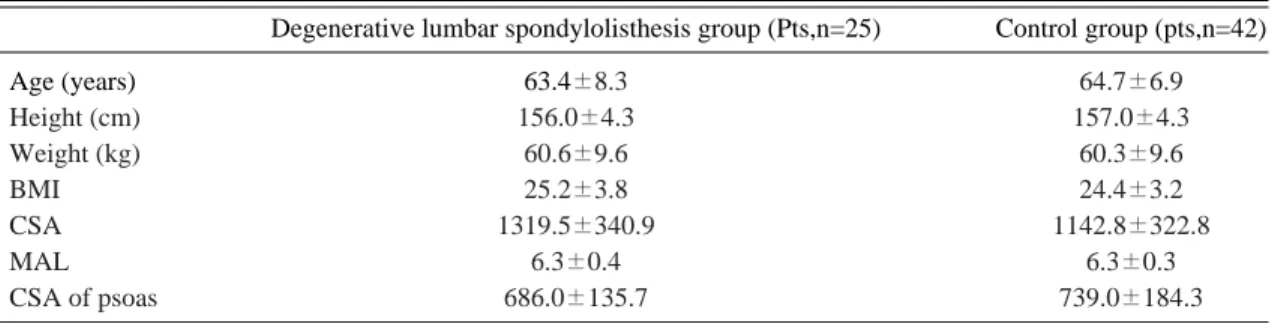
최근 노인 인구의 증가에 따른 고령화로 퇴행성 요추 질환이 증가하고 있으며, 특히 퇴행성 요추 전방전위증이 중년 이후에 척추관 협착증과 함께 하요추부 통증을 야기하는 중요한 원인으로 이는 Table 1. The characteristics of the degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis and control patients
Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis group (Pts,n=25) Control group (pts,n=42)
Age (years) 63.4±8.3 64.7±6.9
Height (cm) 156.0±4.3 157.0±4.3
Weight (kg) 60.6±9.6 60.3±9.6
BMI 25.2±3.8 24.4±3.2
CSA 1319.5±340.9 1142.8±322.8
MAL 6.3±0.4 6.3±0.3
CSA of psoas 686.0±135.7 739.0±184.3
The values are given as means±standard deviation.
BMI=body mass index (kg/m2), CSA=cross sectional area (cm2), MAL=moment arm length (cm).
Table 2. Pearson’s rho correlations between the body mass index and the cross sectional area of the erector spinae, the moment arm length of the erector spinae and the cross sectional area of psoas in both the degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis group and control group
Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis group Control group
rho p rho p
CSA 0.603 0.001** 0.280 0.072
MAL 0.278 0.179** 0.249 0.111
CSA of psoas 0.445 0.026** 0.205 0.193
p-values are for two sided test, * Significant at the 0.05 level, ** Significant at the level 0.001 CSA=cross sectional area (cm2), MAL=moment arm length (cm)
Table 3. Pearson’s rho correlations between the cross sectional area of the erector spinae and the moment arm length of the erector spinae and the cross sectional area of psoas and body mass index in both the degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis group and control group
Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis group Control group
MAL=0.0008 CSA+5.293 MAL=0.001 CSA+5.245
rho p rho p
MAL 0.627 0.001** 0.812 0.000**
CSA of psoas 0.362 0.075** 0.489 0.001**
p-values are for two sided test, * Significant at the 0.05 level, ** Significant at the level 0.001.
CSA=cross sectional area (cm2), MAL=moment arm length (cm).
장기간 지속되는 분절간 불안정성으로 추간판의 변성과 후관절의 변화의 삼중관절 연관성을 강조 하여 삼중관절의 퇴행성 변화로 후관절의 아탈구 와 변연부의 골극 형성이 일어난 후 추체의 전방 전위가 발생한다 하였다1,3). 불안정성은 굴곡-신전 의 불안정성이 아니라 축성-회전성과 전후방 평행 이동성 불안정성으로, 요통과 함께 하지 방사통, 신경성 파행을 유발한다. 퇴행성 요추 전방전위증 에서 요추의 전만이 감소되어 있음을 보고하고 전 만의 감소로 인하여 4, 5요추간 관절에 더 많은 스트레스가 집중되어 전위을 일으킨다 하였다3,4). 본 연구에서는 요추 전체 전만각과 분절간의 전만 각의 평균은 각각 44.54。, 9.23。(L3/4), 10.27。
(L4/5), 18.81。(L5/S1)도 이었다5).
요추부의 근육들은 전방과 후방의 2개의 군으로 나눌 수 있으며, 척추 주위 근육 중 다열근은 척 추 안정화 유지에 중요하며 단일 신경지배를 받고 있는 근육으로 기능장애와 추간판의 변성, 후관절 의 변화에 민감하게 변화한다. 이러한 척추 주위 근은 요추부가 운동할 때 척추를 안정시키는 데 매우 중요하며, 요통이 지속되면 척추 주위 근육 이 약화되어 정상인에 비해 요근과 척추 신전근 위축이 관찰되는데, 이는 요통으로 인해 근육의 활동이 줄어들었기 때문이다. 또 이로 인해 운동 량이 감소되므로 근육의 크기가 작아지게 된다.
또한 통증으로 인해 사용하지 않아 위축이 생기는 경우와 통증이 없는데도 반사적 근수축 억제에 의 해 손상 부위의 구심성 자극이 척수 반사를 통해 해당 근육을 지배하는 알파운동신경원(α motor neuron)의 활성화를 억제함으로써 근위축이 생
기는 경우가 있다1,7,8,). 요통 환자들에서 척추 주 위근의 크기를 측정하는 의의는 근육의 위축을 관 찰함으로써 증상의 만성 정도나 심한 정도를 알 수 있다는 것이다6). 이러한 척추 주위 근육의 변 화를 측정하는 생체 모델 지표로 근육의 단면적, 근육내 지방함량, 근력 및 능률, 근섬유 종류 등 이 있다. 만성 요통1), 요추부 수술 전후, 운동 치 료 후 근육 변화 및 퇴행성 요추 후만증에서 척추 주위근의 크기와 역할에 대해 연구가 보고 되고 있다7,8). 근육에 대한 측정은 초음파9), 전산화 단
층활영10-12), 자기 공명 영상13,14) 등을 이용하여 이
루어진다. 자기 공명 영상은 근육과 지방의 신호 강도의 차이로 근육 사이의 지방층 및 근육량과 근육군등에 대해서 구별하여 측정이 가능하다. 본 연구에서도 자기 공명 영상을 이용하여 측정시 T1강조 영상이 지방과 근육의 대조도가 10% 이 하인 것에 비해, T2강조영상이 50%인 것을 근거 하여 T2강조 영상을 채택하여 시행 하였다15,16). 요추 근육 측정시 요추 3/4번 사이보다 천극근과 다열근의 단면적 측정이 용이한 요추 4/5번 사이 에서 측정을 시행하는데, 이는 중립위에서 요추 3/4번, 요추 4/5번 사이에서 해부학적으로 최대 의 근육 단면적이며, 요근의 단면적 또한 요추 4/5번 사이에서 최대의 크기이다. 요추 4번 하종 판 부위에서 후방 척추 주위근에서 다열근이 1/3 을 차지한다 하였다17). 근육의 단면적의 감소는 근육양의 감소를 나타내는 것으로, 감소된 근육양 으로 같은 수축력을 위해서 근육이 많은 일을 하 게 된다. 생역학적 실험에서 요추 추간판의 압축 력과 체간 근육에 부하는 moment 팔길이와 체 Table 4. Independent T-test for the cross sectional area of the erector spinae and the moment arm length of the erec-
tor spinae between the degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis group and control group
Erector spinae (CSA) Moment arm (MAL)
Mean Std*. deviation Std. error mean Mean Std. deviation Std. error mean Degenerative lumbar
1319.5 340.96 68.19 6.3 0.43 0.08
spondylolisthesis group
Control group 1142.8 322.85 49.81 6.3 0.39 0.06
Independent t-test p=0.038** p=0.685
* standard, ** P value of <0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significant.
CSA=cross sectional area (cm2), MAL=moment arm length (cm).
간 근육의 단면적으로 결정이 된다 하였다4,8). 즉, moment 팔길이가 길수록 근육 수축력을 감소하 여 요추의 압박력을 감소할 수 있으며, 반대로 moment 팔길이가 짧거나 근육량이 작을수록 요 추부의 부하에 대해 견디기가 어려워 진다 하였 다. McLoughin 등18)은 후방 척추 주위근의 지 방 함량은 나이나 피하 지방의 양과 관계가 있으 며, 근육의 위축을 나타내는 증후가 아니라 하였 지만, 근육내 지방 함량 또한 근위축을 나타내는 것으로14), 본 연구에서는 후방 척추 주위근의 근 육내 지방 함량은 모두 경도소견이었다.
이에 본 연구에서 요추부 퇴행성 척추 전방전위 증 환자에서 척추 주위근의 근육의 크기와 역할에 대해서 고찰한 바, 요추부의 근력의 약화와 함께 요추의 불안정성에 영향을 줄 것으로 사료되며, 치료에 척추 분절의 안정성 제공하기 위해 동적 요부 안정화 운동이 필요하며 신전 근력 강화와 함께 운동의 효과를 위해 근력의 데이터화를 위한 추가 연구가 필요할 것으로 사료된다.
결 론
요추부 퇴행성 전방전위증 환자군에서 척추 주 위근의 단면적의 감소가 근력 약화와 응력의 증가 로 요추부 불안정성에 영향을 줄 것으로 사료되며, 이는 요추부 퇴행성 전방전위증의 불안정성에 척 추 주위근이 하나의 요소가 될 것으로 사료된다.
REFERENCES
1) Ahn MW: Spondylolisthesis. J Korean Soc Spine Surg, 6: 228-36, 1999.
2) You JW, Moon YL: Spondylolisthesis -Anato- my, classification, and natural history-. J Korean Soc Spine Surg, 8: 336-344, 2001.
3) Cho YS, Cho SD, Kim BS, Park TW, Kim YK, Kim YT: The pathologic anatomy of degenera- tive spondylolisthesis. J of Korean Orthop Assoc, 33: 1620-1626, 1998.
4) Reid JG, Costigan PA: Trunk muscle balance and muscular force. Spine, 12: 783-786, 1987.
5) Kim KT, Lee JH: Sagittal imbalance. J Korean Soc Spine Surg, 16: 142-151, 2009.
6) Suk Sl, Lee CS, Lo M, Kim WJ: Normal seg- mental sagittal angle of the lower dorsal and lum- bosacral spine in korean adult. J of Korean Orthop Assoc, 24: 237-244, 1989.
7) Park SI, Lee WY, Kim HS, Lee JH, Lee KT, Yun JS: Quantitative correlations of trunk mus- cles in young and middle-aged men with chronic low back pain by magnetic resonance imaging. J Korean Acad Rehab Med, 31: 1-6, 2007.
8) Lee H, Lee SJ, Lee SH: Correlation between the cross-sectional area and moment arm length of the erect spinae muscle and thickness of the psoas major muscle as measured by MRI and the body mass index in lumbar degenerative kyphosis patients. J Korean Radiol Soc, 54: 203-209, 2006.
9) Kang CH, Shin MJ, Kim SM, Lee SH, Lee CS:
MRI of the paraspinal muscles in lumbar degen- erative kyphosis patients and control patients with chronic low back pain. Clinical Radiology, 62:
479-486, 2007.
10) Han TR, Kim JH, Chung SG, Kwon BS, Lee KW: Correlation of ultrasonographic measure of lumbar multifidus muscles with isometric torque of low back. J of Korean Rehab Med, 23: 809- 814, 1999.
11) Kwon JY, Lee KW, Kim HS, Kim JM, Ahn JM: Correlation between cross-sectional areas of paraspinal muscles and isometric lumbar exten- sion strength. J of Korean Acad of Rehab Med, 24: 275-280, 2000.
12) Danneels LA, Vanderstraeten GG, Cambier DC, Witvrouw, EE, De Cuyper HJ: CT imag- ing of trunk muscles in chronic low back pain patients and healthy control subjects. Eur Spine J, 9: 266-272, 2000.
13) Kamaz m, Kiresi D, Oguz H, Emlik D, leven- doglu F: CT measurement of trunk muscle areas in patients with chronic low back pain. Diagn interv Radiol, 13: 144-148, 2007.
14) Parkkola R, Rytokoski U, Kormano M: Mag-
netic resonance imaging of the discs and trunk muscles in patients with chronic low back pain and healthy control subjects. Spine, 18: 830-836, 1993.
15) Bae JH, Na JK, Yu JY, park YO: Atrophy of multifidus on low back pain patients. J of Korean Rehab Med, 25: 684-691, 2001.
16) Kader DF, Wardlaw D, Smith FW: Correlation between the MRI changes in the lumbar multi- fidus muscles and leg pain. Clinical Radiology,
55: 145-149, 2000.
17) Jorgensen MJ, Marras WS, Gupta P: Cross- sectional area of the lumbar back muscles as a function of torso flextion. Clin Biomech, 18:
280-286, 2003.
18) McLoughlin RF, D’ Arcy EM, Brittain MM, et al.: The significance of fat and muscle areas in the lumbar paraspinal space: a CT study. J Com- put Assist Tomogr, 18: 275-258, 1994.