간경변증의 원인과 병리
Histopathological diagnosis
< Pathology 특징 >
· Irreversible loss of functioning hepatocyte
· Extensive fibrosis
· Formation of regenerative nodule
In the past, cirrhosis : never 손상 원인 제거시 reversal of fibrosis 일부 가능.
Fibrosis 발달 + architectural distortion + formation of regenerative nodules .
Hepatocellular mass 와 function 저하, blood flow 변화 유도.
Hepatic stellate cells activation : Induction of fibrosis
collagen 과 다른 extracellular matrix 양 증가.
임상적 특성: pathologic changes 의 결과, 간질환 정도 반영
Pathologic grading and staging Advanced fibrosis :
bridging fibrosis with nodularity designated stage 3 cirrhosis stage 4.
Hepatocellular function 상실의 결과: jaundice, coagulation disorders, and hypoalbuminemia, portosystemic encephalopathy.
Portal hypertension 의 분류
PrehepaticPortal vein thrombosis
Splenic vein thrombosis
Massive splenomegaly (Banti's syndrome)
Hepatic
Presinusoidal
Schistosomiasis
Congenital hepatic fibrosis
Sinusoidal
Cirrhosis—many causes
Alcoholic hepatitis
Postsinusoidal
Hepatic sinusoidal obstruction (venoocclusive syndrome) Posthepatic
Budd-Chiari syndrome
Inferior vena caval webs
Cardiac causes
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
Constrictive pericarditis
Severe congestive heart failure
Portal HTN
만성간질환에서 흔한 합병증
형태학적 변화와 혈역학적 변화가 원인
고정원인- intrahepatic vascular resistance 증가 가변적 원인- hemodynamic change
Significant complicating features
Ascites , varices, encephalopathy,
hepatorenal syndrome, hepatopulmonary syndrome 정상 7-12mmHg
Wedged hepatic venous pressure 유사
임상에서는 HVPG (간정맥 압력차)=WHVP(간문맥압)-FHVP(간정맥압) 를 많이 사용 1-5mmm Hg 가 정상 : 6 이상시 문맥압 항진증으로 판단한다
HVPG> 10mmHg 정맥류 의미 있게 증가 >12mmHg : 출혈 증가
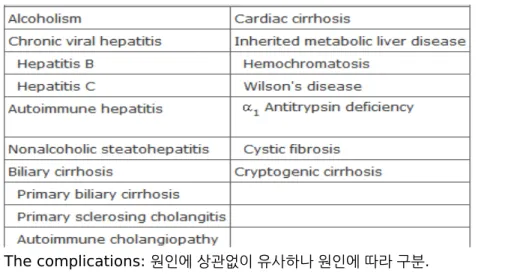
Table 302-1 Causes of Cirrhosis
The complications: 원인에 상관없이 유사하나 원인에 따라 구분.
alcoholic cirrhosis, cirrhosis due to chronic viral hepatitis, biliary cirrhosis,
less-common causes : cardiac cirrhosis, cryptogenic cirrhosis, and other miscellaneous
Table 308-2 Complications of Cirrhosis
Portal hypertension
Gastroesophageal varices
Portal hypertensive gastropathy
Splenomegaly, hypersplenism
Ascites
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
Hepatorenal syndrome
Type 1
Type 2
Hepatic encephalopathy
Hepatopulmonary syndrome
Portopulmonary hypertension
Coagulopathy
Factor deficiency
Fibrinolysis
Thrombocytopenia
Bone disease
Osteopenia
Osteoporosis
Osteomalacia
Hematologic abnormalities
Anemia
Hemolysis
Thrombocytopenia
Malnutrition Neutropenia
복수의 원인 감별
Alcoholic Cirrhosis
과도한 음주alcoholic fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and alcoholic cirrhosis.
동반시 간손상 악화되는 질환: hepatitis C, hemochromatosis, fatty liver disease (obesity) Chronic alcohol use can produce fibrosis.
Fibrosis : centrilobular, pericellular, periportal.
Micronodular, cessation mixed micronodular and macronodular cirrhosis.
Pathogenesis.
Ethanol : small intestine >> stomach Gastric alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH)
Three enzyme systems
cytosolic ADH, microsomal-oxidizing system (MEOS), peroxisomal catalase.
ADH 통해 acetaldehyde, aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) 의해서 acetate 로 대사.
Ethanol 섭취는 세포 내 triglycerides 증가시킴
(fatty acid uptake 증가, fatty acid oxidation 과 lipoprotein secretion 감소)
Oxidative damage to hepatocyte membranes: formation of reactive oxygen species;
acetaldehyde 는 highly reactive molecule 로 protein 과 결합: protein-acetaldehyde
adducts 형성, 특정 enzyme activities 방해Acetaldehyde-mediated hepatocyte damage+ certain reactive oxygen species
Kupffer cell activation stellate cell activation
Production of excess collagen and extracellular matrix.
- Regenerative nodules 생성.
- Hepatocyte loss + increased collagen production and deposition+ hepatocyte destruction liver size 감소
Clinical Features
- accurate history :both amount and duration of alcohol consumption.
- nonspecific symptoms
- specific complications : ascites, edema, or upper GI hemorrhage.
Physical examination
- liver and spleen enlarement, liver edge firm and nodular.
- Other frequent findings : scleral icterus, palmar erythema, spider angiomas, parotid gland enlargement, digital clubbing, muscle wasting, edema and ascites.
- Men : body hair loss, gynecomastia , testicular atrophy - Women : menstrual irregularities, amenorrheic.
Laboratory
- normal - early compensated alcoholic cirrhosis.
- anemia- chronic GI blood loss, nutritional deficiencies, hypersplenism related to portal hypertension, direct suppressive effect on the bone marrow.
- Hemolytic anemia (with spur cells and acanthocytes) called Zieve's syndrome : in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis.
- Platelet counts 감소 : portal hypertension with hypersplenism.
- Serum bilirubin 초기 정상일 수도.
- Prothrombin times 종종 연장되고 parenteral vitamin K 정주에도 호전 안 될 수.
- Hyponatemia: ascites 동반시 ingestion of excess free water 로 감소할 수도.
- Serum aminotransferases (ALT, AST) : usually by a 2:1 ratio.
Diagnosis
과거력: alcohol + other forms of chronic liver disease Liver biopsy : 잔존 기능, 가역성 판단
Complications of cirrhosis 가지고 음주 지속시 : <50% 5-year survival.
Treatment - Abstinence - good nutrition
- Glucocorticoids : severe alcoholic hepatitis in the absence of infection.
- pentoxifylline: TNF alpha 와 다른 proinflammatory cytokines 감소.
Glucocorticoid 보다 투여 쉽고 적은 side effects.
- nutritional therapies ?
- infliximab or etanercept : 다른 TNF alpha inhibitor - acamprosate calcium : craving 줄인다
- acetaminophen 하루 2g 까지는 큰 문제 없어
Cirrhosis Due to Chronic Viral Hepatitis B or C
- Exposed to the (HCV) 80% chronic hepatitis C,- 만성 환자 중 약 20–30% cirrhosis 진행: 20–30 years. (concomitant alcohol use?) - chronic hepatitis C 간질환 악화의 특징:
portal-based fibrosis with bridging fibrosis and nodularity cirrhosis.
mixed micro- and macronodular cirrhosis : liver biopsy.
- HCV genotype 3 : steatosis 자주 관찰
- Similar findings in patients with cirrhosis due to chronic hepatitis B.
- Exposed to hepatitis B: 5% chronic hepatitis B 약 20% cirrhosis 진행.
Clinical Features and Diagnosis
usual symptoms and signs of chronic liver disease.
Diagnosis
quantitative HCV RNA testing and analysis for HCV genotype,
hepatitis B serologies to include HBsAg, anti-HBs, HBeAg, anti-HBe, and quantitative HBV DNA levels.
Treatment 생략
Cirrhosis from Autoimmune Hepatitis and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) present with cirrhosisnot benefit from immunosuppressive therapy (glucocorticoids or azathioprine) liver biopsy : no significant inflammatory infiltration
- Diagnosis in this setting :
positive autoimmune markers : antinuclear antibody (ANA) or anti-smooth-muscle antibody (ASMA).
- active inflammation +elevated liver enzymes
considerable benefit from the use of immunosuppressive therapy.
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis 에서 cirrhosis 증가.
- obesity
- cryptogenic cirrhosis
Biliary Cirrhosis
- different from either alcoholic cirrhosis or posthepatitic cirrhosis - manifestations of end-stage liver disease.
- Cholestatic liver disease : necroinflammatory lesions, congenital or metabolic processes, or external bile duct compression.
anatomic sites of abnormal bile retention: intrahepatic and extrahepatic.
- Extrahepatic obstruction: surgical or endoscopic biliary tract decompression - Intrahepatic cholestatic processes : interventions 으로 해결 안 됨
The major causes of chronic cholestatic syndromes:
primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC), autoimmune cholangitis,
primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), and idiopathic adulthood ductopenia.
DDx by antibody testing, cholangiographic findings, clinical presentation.
-비슷한 Histopathologic features of chronic cholestasis :
cholate stasis, copper deposition, xanthomatous transformation of hepatocytes, and irregular so-called biliary fibrosis.
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
- 절대적으로 여성에서 호발, 진단시 평균 50 세.
- 원인 미상
- 병리 특징 portal inflammation and necrosis of cholangiocytes in small and medium- sized bile ducts.
- Antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA): present in about 90%.
intermitochondrial membrane proteins 을 인식
AMA : not pathogenic useful markers for diagnosisPathology
- 가장 초기소견: chronic nonsuppurative destructive cholangitis :necrotizing inflammatory process of the portal tracts
Medium and small bile ducts 가 lymphocytes 에 침윤되어 파괴 경도의fibrosis 와 간혹 bile stasis 관찰.
- 진행시 :
inflammatory infiltration 은 감소하면서 bile duct 수가 감소
더 작은 bile ductules proliferation.
- Increased fibrosis 최종적으로 cirrhosis (micronodular or macronodular) Liver biopsy 로 확인: Stage I : florid duct lesion
Stage II : ductular proliferation Stage III : periportal fibrosis Stage IV : cirrhosis
Clinical Features
- 대부분 end-stage manifestations 전에 진단되고 무증상 많다 - Pruritus : 진단시 약 50%
- Jaundice 발생 전 pruritus : severe disease and a poor prognosis.
- Physical examination : jaundice and other complications of chronic liver disease - Unique to PBC : hyperpigmentation, xanthelasma, and xanthomata,
- Hyperpigmentation : 몸통이나 각질부.
- Bone pain :osteopenia or osteoporosis 관련
Laboratory Findings
cholestatic liver enzyme 상승 : gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase, alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
IgM 상승 전형적.
Hyperbilirubinemia : cirrhosis 진행 후.
Liver biopsy
PBC 환자 10%에서 AIH 특성 가지는데 이를 "overlap" syndrome.
Diagnosis
10% of patients with PBC : AMA-negative.
Liver biopsy is most important in this setting of AMA-negative PBC.
In patients who are AMA-negative with cholestatic liver enzymes: PSC 를 cholangiography 로 감별해야.
Treatment
- UDCA : only approved treatment
biochemical and histologic features 모두를 개선 초기 치료시 예후 좋아
13–15 mg/kg per day
일부서 부작용- diarrhea or headache
progression 을 느리게 하지만 치유하거나 회복시키지는 못해.
- Liver transplantation : treatment of choice for patients with decompensated cirrhosis - Fatigue,pruritus 증상에 대한 치료
피로에 낮잠?
antihistamines, naltrexone, and rifampin.
Cholestyramine- osteopenia and osteoporosis bisphosphonate
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
- cause : unknown.- chronic cholestatic syndrome
특징: diffuse inflammation and fibrosis 가 전체 biliary tree 침범하여 chronic cholestasis 유발.
intra- and extrahepatic biliary tree obliteration
biliary cirrhosis, portal hypertension, liver failure.
- 원인은 모르지만 bacterial and viral infections, toxins, genetic predisposition, and immunologic mechanisms
- Pathologic changes : bile duct proliferation as well as ductopenia and fibrous cholangitis (pericholangitis).
- 종종 liver biopsy 로 진단 안 되기도 해서 biliary tree imaging 중요.
- Periductal fibrosis 는 조직검사로 진단에 도움되기도
Clinical Features
- 일반적인 cholestatic liver disease 특징들:
fatigue, pruritus, steatorrhea, deficiencies of fat-soluble vitamins 등 - Pruritus 가 cholestasis
- Metabolic bone disease 가 PBC 처럼 가능
Laboratory Findings
- ALP 두 배 이상 상승에 aminotransferases 도 상승.
- Albumin levels 저하, prothrombin times 증가 보이기도
- aminotransferase elevations 5 배 이상 증가는 조직검사시 AIH 소견 보이기도.
overlap syndrome between PSC and AIH.
overlap syndrome -autoantibodies (+) 많아- - PSC 단독시는 p-ANCA 외 음성.
perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (P-ANCA:약 65%) - Ulcerative colitis (UC) 동반 : 약 50% colonoscopy 해 봐야
Diagnosis
Definitive diagnosis of PSC : cholangiographic imaging 필요.
MRI, magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) 로 screen 뒤
ERCP 시행되어야.
전형적 image : intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary tree 모두를 침범하는 multifocal stricturing and beading
classic beaded appearance.
The gallbladder and cystic duct : 약 15% 에서 침범.
high-grade, diffuse stricturing of the intrahepatic bile ducts : poor prognosis.
결국 biliary cirrhosis
Treatment
no specific proven treatment UDCA?
Endoscopic dilatation of dominant strictures 도움이 될수는 있겠으나 결국 liver transplantation 가 치료
Cholangiocarcinoma- relative contraindication to liver transplantation.
pruritus : PBC 에서와 같은 치료
Cardiac Cirrhosis
- 지속적인 right-sided congestive heart failure 가 chronic liver injury 유발 - 매우 드물다
Etiology and Pathology
- 장기간 right-sided heart failure 로 증가된 venous pressure 가 inferior vena cava 와 hepatic veins 을 통해 liver sinusoids 로
- Long-term passive congestion and relative ischemia, centrilobular hepatocytes 가 necrotic pericentral fibrosis periphery 로 진행 전체가 fibrosis cirrhosis
Clinical Features
- signs of congestive heart failure
- enlarged firm liver on physical examination.
- ALP levels 특징적으로 증가 aminotransferases 정상이거나 다소 증가 AST > ALT 많아.
- variceal hemorrhage or encephalopathy.
Diagnosis
- Clear-cut cardiac disease + elevated ALP + enlarged liver.
- Liver biopsy : pattern of fibrosis 가 중요 감별진단
1. Budd-Chiari syndrome (BCS) : hepatic vein occlusion 으로
extravasation of red blood cells in BCS, but not in cardiac hepatopathy.
2. Venoocclusive disease : hepatic outflow 영향-liver 내 small vein occlusion bone marrow transplant with radiation and chemotherapy 같은 상황서 Treatment : management of the underlying cardiac disease.
Other Types of Cirrhosis
Wilson's disease, alpha1-antitrypsin (alpha1-AT) deficiency, and cystic fibrosis
manifestations of cirrhosis are similar