대한임상병리사회지
:제 24 권 1 호
1992Dry Slide Technology 및 벌리루번 측정에서의 새로운 개념
학교건강관리소
이 명 자
Key words : Dry-slide, CM slide, PM slide, conjugated bilirubin. Unconjugated bilirubin.
1 • Kodak Ektachem
Analyzer의
Dry-slide Technology1.
건식 슬라이드 (dry-slide) 방법
건식 슬라이드 화학방식은 시약에 대신하는 슬 라이드를 사용하여 정량분석을 하는 것이며 슬라 이드는 우표만한 크기이지만 습식화학에서 수행하 는 모든 복잡한 기능을 한다.
건식 슬라이드를 두 가지 부분으로 나누어 설명 할 수 있는데 한 분야는 광학분야이고 하나는 임 상화학 분야로 나눌 수 있다.
건식 슬라이드 기법은 습식화학 방법을 그대로 옮겨놓은 독특한 방법으로서, 습식화학 (wet
chem-istry) 에서 시약을 회석하거나 혼합하는 불편을 멀 어 주고 반응 용기가 필요없고 특히 carryover가 없다.
시약 슬라이드는 투명한 포리에스터 필름 위에 여러 층으로 반응에 필요한 모든 시약이 도포, 건 조되어 있어 각 층에 각각의 특별한 화학적, 물리 적 기능을 갖고 분석을 행하는 독특한 방법이다.
슬라이 드의 종류는 colorimetric과
potentiometric두 가지 로 구별 되 며
, colorimetricslide로는 빛 의 반 사로 농도와 활성도를 측정하는데, 그 예로는
glu- cose, uric acid, albumin, calcium동을 측정 하고
potentiometricslide로는
electolyte농도를 측정 한 다. 즉
Na, K, CI,CO 2 이 다.
2. Slide
구조와 기능
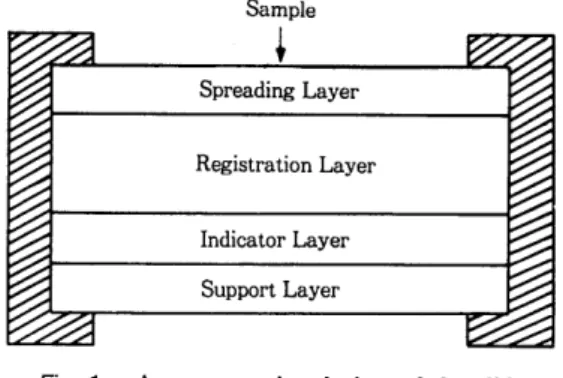
1) Colorimetric slide
Colorimetric
slide는 맨 위 층에 서 부터
spreadinglayer, reagent layer, indicater layer, support
layer로 이루어져 있다(그림
1 ).Sample
Spreading Layer
Registration Layer
Indicator Layer Support Layer
Fig. 1. A cross-sectional view of the slide
@
확산충 (spreading
layer)확산층은 슬라이드의 맨 위층에 자리하고 있으 며 스폰지와 같은 성질을 나타내는데 그 구조가 모세관 망상으로 되어 있어 처음 검체가 슬라이드 위에 고루 잘 퍼지게 하여 오차를 없애게 한다. 또 한 지질, 단백, 헤모글로빈 같은 고분자 물질이 내 려가지 않게 막아주는 역할을 하여 간섭물질을 제 거하고 선택적인 홉수 기능을 한다. 또한 반사효과 의 배경 역할을 하는데 그 작용을 하는 것은
BaS04또는 Ti0 2 로 구성 되 어 있 다.
@
시 약충 (reagent
layer)이 층은 확산충 아래에 있으며 생화학 반응이 일어나는데 필요한 시약이 도포되어 있다. 이들 시 약은 효소, 완충제, 촉매제 동을 포함한다.
때로는 몇몇 반응이 일어나야 할 때 하나씩 또 는 차례로 일어나도록 필요에 따라 만들어져 있으 며 이것은 여러 개의 시약충으로 이루어져 있다.
예
: Glucose검사용 슬라이드의 시약층(그림
2)- 42-
l e
빼 •
[b
Spreading Layer
Glucose Oxidase Peroxidase
Reagent Layer Chromogens Buffer at pH 5.0
Indicator and Support Layers
Fig.2. Ektachem clinical chemistry silde(GLU)
것을 측정할 수 있도록 빛을 통과 시켜 준다.
@ Reflectence spectrometry
(그림
3)색의 농도를 측정하는데 있어서 습식 생화학적 검사법에서는 시약과 반응이 일어나는 것을
cu-vette을 투사한 빛이 통과한 것을 읽지만 건식 생 화학적 검사법에서는 빛을 투사하면 확산층 (spre
ading
layer) 에서 반사한 것을 photodetector에서 읽는다. 그러므로 헤모글로빈이나 벌리루빈같은 방 해물질이 습식 생화학적 검사법에서는 혼합된 상 태로 윈어지지만 건식 생화학적 검사법에서는 확 산층 (spreading layer) 에서 걸러진 상태에서 원게 되므로 그들로 인한 오차가 없다(그림
4).또한 여기에는 경우에 따라
scavengerlayer라고 하는 특수층이 있어서 생화학 반응에서의 방해물 질을 제거한다. 즉 종래의
uric acid검사에서 방해 가 되 어 오던
ascorbicacid를 제 거 하여 검 사상의 오 차를 없애준다. 즉,
scavengerlayer에서 검체에 있 는
ascorbicacid와 결합히-여 ascorbateo-xidase로 되어 시약층에서
ascorbicacid를 제거히-여 준다.
@
발색 충 (indica
tor lay er)여기에는 발색 만응을 일으키는 발색제나 색소
가 들어 있는데 이런 발색제는 분석시약 농도에 /17/
Light Path비레해 있으며 이 층에서 시약층과 색소가 결합하
여 발색된다.
@ Support layer Fig. 3. Light is directed through support ]ayer
t。
이 층은 슬라이드의 맨 아래층에 있으며 투명한
measure the colored complex,
proportional플라스틱으로 되어 있다. 이 층의 효과는 발색된
to analyte concentration.Layer
Transmission .----. Reflectance
Analyte with interferents
Fig.4. Principle of the refectence spectrometry
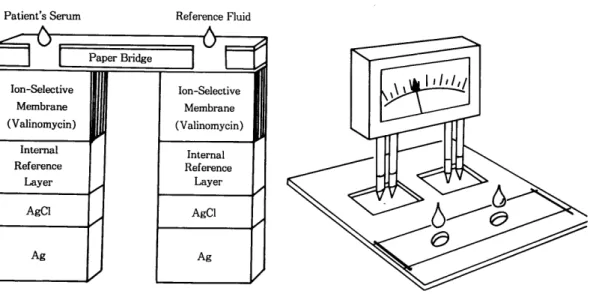
2) PM(potentiometric) slide
K를 검사하는데 쓰이는 슬라이드를 예를 들어 그
PM
슬라이드는 두 개의 흘이 있는
paper bridge구조를 본다(그림
5).로 되어 있으며, 한 흘에는 혈청(겸체)을 넣고 하 그림 5 에서
ion-selectivemembrane은
internal나는 electrolyte의 표준액을 넣게 되어 있다.
ref erancelayer로 침투하는 검 체와 referance로부 Ectachem 에서는
direct ISE(ion-selective elec-터 K 이온과 결합하는 valinomycin을 함유한다. 검
trode)
method를 쓰며 이 방법은
phygiological reg-제와 referance 에서 K 이온의 활성비를 3 개의 층을
ulation
상태에 있는 희석되지 않은 혈청으로 검사 통하여 측정한다. 두 쌍의 침투되는 지점에서 서로
하므로
displasewater로 인해 발생되는 영향을 받 다른 전극에 의해 전위차로 voltage를 측정한다.
지 않기 때문에 다른
ISE방법에서 발생되는
con-ERF 에는
known concentrationion 이 있다.
tamination
drift를 제거하도록 개발되었다. 다음은
Patient’s Serum Reference Fluid
Membrane Membrane
(Valinomycin) (Valinomycin)
Internal Internal
Reference Reference
Layer Layer
-
AgCl I
J
AgCI-
Ag I I Ag
Fig. 5. Principle of the PM slide technology
3.
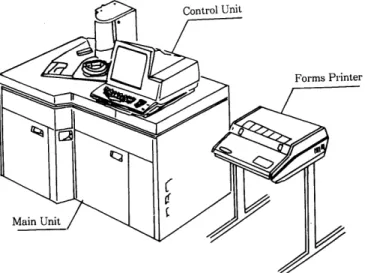
장비의 구조 및 원리
Main unit, control unit,
printer의 3부분으로 되 어
았다.
Mainunit는 컴퓨터 시스템과 슬라이드를 저
장, 공급하는 모률로 되어 있다.
Controlunit는 키
보드와
displayunit로 되어 있으며, 오퍼레이터와
장비의 교신 역할을 한다. 프린터는 2 대를 연결시 킬 수 있어서 검사실과 그 외 다른 곳에도 설치하 여 동시에 프린트 시킬 수 있다(그림
6).1) Modules
총 3,000 개의 슬라이드를 저장할 수 있으며, 슬 라이드는
supply1
, supplyn 로 두 곳에 각각 넣 게 되어 있고, 각각 30개의 캐드리지를 넣게 되어 있다.
Supply
1 : 습도가 25-45% 로 유지 되 도록 되 어
있으며,
TP. URIC. ALB.TRIG. CHOL. AMYL. Cl.K. Na. TBIL. LIPA.
Mg.의 슬라이드를 저장한다.
Supply
n : 습도가 20% 로 유지되도록 되어 있
다.
GLU. NH3. CREA. AST. ALKP. ALT. LDH.CK. GGT. THEO.
CKMB.의 슬라이드를 저장한다.
2) Rate incubator
24 개의 슬라이드를 37
0C 에서 5분 30초 동안
In-cubation
한다.
Supplyn 로부터 슬라이 드가 오면
sample metering
station으로부터 검 체 를 받고 incubaton한다. Incubation 이 끝날 때 까지 54회 읽 는다. 54회 읽는 것은 효소의 활성도를 측정하는 것이며 컴퓨터는 효소의 활성도를 측정하여
kine- ticcurve의 slope를 만들고 계산치가 프린터로 간 다. 즉 한 슬라이드에서 발색 변화속도에 따른 반 사도를 측정하여 효소 활성도를 측정하는 것이다.
- 44-
3) Colorimetric test
CM
incubator 에서 27 개의 슬라이드를 37
0C 로
ID-cubate
시킨다.
Supply 1
또는
R에서
CM slideblock 으로 슬라 이 드를 보내 면
sample meteringstation 에 서 10 마이
크론썩 검 제를 분주하며
preconditionstation 에서
4) PM slide techCM
incubater 로 가서 약 5 분간
incubation한 다읍
Supply1 에서 슬라이드가
sample metering sta- CM readstation 에 옮겨 져
lightreflectance로 측정 tion 으로 가면 검 체 가 10 마이 크론씩 분주되 고 동시
된다. 에 ERF 가 10 마이크론씩 분주된다.
*End pont : ALB. NH3 • CHOL. GLU. HDLC. Mg.
슬라-이드가 precondition 에 오면 즉시
PM incu- P. TP. TRIG. BUN.UA. 를 측정한다 bator 로 가서 25
0C 에서 3 분간 incubate하며, 총 슬
* Dual-wavelength :
각 두 종류의 다른 파장으 리-이드는 17 개가 들어간다.
로 한 개의 슬리-이드를 읽는다.
TBIL BuBc그 다음
readstation 에 가서 electrometer에 의해
* Blank corrected: Creatinine(two slide meth-
검체와 표준액 사이의 전위차가
reading된다.
* Two point colorimetric test : Incubator
cycle에 서 정해진 두 개의 시간 사이에서
reflectance익 변화에 의해서 효소를 측정하는 것이다.
, AMYL. LIPA. CREA(single slide). THEO.od),
ammonia는 두 개의 슬라이드를 읽는다.
Fig. 6. Kodak Ektachem analyzer unit.
4.
Calibration의 이론 n . 혈청 빌리루빈 측정에 있어서의 새로운 개념
Transmission
method 에 서 는 빛 을 투사하면 정 색
반응을 일으킨 물질의 일부는 통과한다. 이때
cu- 1.일반적 개념 vette을 통과한 빛을 원는다. 그러나
dryslide에서
는 빛을 입사하면 발색된 색조에 의해 일부는 흡 근간 70 여년 동안 검사실에서는, 직접 빌리루빈 수되고 나머지는 반사되는데 이 렇게 반사된 빛을 이 란 용어는 glucronic acid와 결합한 bilirubin을 의 측정지점에서 측정한다. Calibration은 농도가 각기 미하고 간접 빌리루빈은 unconjugated bilirubin을 다른 세 가지 표준액을 특정한 파장에서 측정하여 의미하는 것으로 불리어져 왔다.
이미 기계에 입력된 각 표준값과 표준액을 기계에 1913 년 Van den Bergh는 혈청에서 빌리루빈을 서 읽은 값을 구하여 자동으로 slope와 intercept를 측정하는 것을 착안해 냈으며 그후 직접 빌리루빈 계산하여 보정해준다. 과 간접 빌리루빈을 측정하는 것이 개발되었다.
※ Calibration diskette을 새로 넣을 때는 ERF의
Direct-reactingbilirubin은 1-2 개의
glucronicGemeration
No.를 확인해야 한다 acid 분자가 ester화 된 빌리루빈 분자로 이루어진
것으로 생각해 왔다. 이러한 형태는 수용성이며 신 장에서 여괴되고 즉시
diazotÏzed sulfanilicacid와
반응한다. Unconjugated로 분석되는 간접 빌리루 빈은 일차적으로 알부민과 결합되어 있고 디-만 methanol과 같은
mordant아 래 서
diazotized sulfa- nilicacid와 반응한다.
이 런 원 리 는
Malloy-Evelynmethod 에 서 또는
caffeine과
sodiumbenzoate를 이 용하는
Jendrassik-Groff( 이상 J.G로 표기) 원리에서 이용되었다.
간접
•직접 빌리루빈이란 용어는 검사실이나 임 상의학에서 오랫동안 통용되어 왔£며
hyperbiliru -binemia
진단에 흔히 이용되어 왔다.
그러나 이제는 직접 빌리루빈이란 용어가 잘못 정의된 것이라는게 알려졌다. 더구나 소변에서 빌 리루빈이 안나오거나 적게 검출되면서 혈청에
con- jugatebilirubin(Bc) 이 증가되는 것이 특정인 케이 스에서는 항상 Bc가 출현하리라는 일반적인 경향 과는 일치되지 않은 것이다.
그러므로
directbilirubin은 mono와
diglucuroni-dated form
외에 다른 종류가 있기 때문에 그 개
념은 바뀌어져야 한다.
2.
8i1irubin의 분류
Kuenzle과 Lauff는
LC (liquid choromatography)를 이 용하여 네 종류의
bilirubin(BIL)분류를 병 적
혈청에서 논증하였다.
그 하나는 a-form 으로 간접 또는 unconjugated
bilirubin(Bu) 이라 흔히 불려지는 것으로서 이는
비 수용성 이 며 알부민과 결 합되 어 lipophilicform을 구성하며 신장에서 여과되지 않는다.
두 번째 종류는 β 또는 monoconjugated bililubin
glucuronide 이고 셰 번째는
y또는 diglucuronide 이 며 나중 두 형태는 수용성£로서 직접 반응을 일 으키며 혈청에서 이들 직접 빌리루빈이 증가될 때,
소변에서도 증가된다.
마지막 한 종류는 델타 빌리루빈 (δ BIL) 으로서 가장 최근에 알려진 것으로서 알부민 분획에 붙어 있는 빌리루빈으로 구성된다. 텔타 빌리루빈은 전 반적으로 직접 반응을 일으키나 알부민과 배위 결 합 (covalently
bound)되 어 서 glomeruli 에 의 하여 여 과되지 않는다. 또한, 이는 알부민과 빌리루빈이 강하게 결합되었다고 biliprotein 이라고도 한다.
몇몇 빌리루빈 측정용 액체시약에는
indirect bili-rubin은 a-BIL과 거 의 같고 β,
ô, y 형 태 의 빌 리 루 빈의 합이 직접 빌리루빈 (DBIL) 과 거의 같다. 그 러나, 대부분의 액체시약 방법에서는 DBIL이
y,
ß그리고 δ BIL 보다 낮다.
3.
델타 빌리루빈 (ô 81니
델타 빌리루빈은 빌리루빈과 알부민의 복합체이 다. 이것은 정상인의 혈청에서는 검출되지 않으나 Bc 가 증가되면 어떤 경우에도 발견된다.
Mc
Donagh는 동물실험에서
bile-ductligation 이
Bu, Bc,
델타 빌리루빈의 빠른 축적을 이룬다는 것 을 증명하였다. 실제로 댈타 빌리루빈은 사람 혈청 이 나
Sprague-Dawley쥐 의 혈 청 과 함께
bilirubindiglucr‘onide를
370C에 서 incubate하므로써 형 성 될
수 있다.Mc
Donagh 팀 은 biliprotein의 형 성 이 알부 민 괴·
Bc의
nonenzymatic반응을 포함한다고 결론지 었
다.
Gautan동도
3TC, pH7 .4에서 쥐의 혈청에서 델타 빌리루빈을 형성할 수 있었다.
길버트 증후군을 가진 사람에 대한 그들의 연구
는 Bc 가 델타 빌리루빈의 precursor 이고 Bu는 아니라는 것이다.
즉 Bu는 델타 빌리루빈으로 바뀌기 전에
glucu-ronidated
되어야 한다는 것을 확인했다.
텔타 빌리루빈의 반감기는 12-14 일 또는 알부 민과 같은 것으로 알려져 있다. 텔타 빌리루빈은
glucuronidated bilirubin 보다 쥐 에 서 serum half-life가 더 길다.
Mc Donagh
연구에서 쥐에서의 담관 폐색은 신
체 밖으로 fistula를 통한 담즙 배설을 수반하며 담 관 폐 색 을 제 거 한 후 2시 간 안에
glucuronide bili-rubin의 빠른 감소를 보였으며 7시 간 안에 완전히 소실되었다.
담즙 배설 후 7-12 시간 후에 혈청의
LC분석
에서 9 마리 쥐 중에서 6 마리 에서 predominent bili- rubinfraction은 델타 빌리루빈이었다.
텔타 빌리루빈의 반감기는
Weiss둥에 의해서 12-14 일 또는 알부민과 같다고 추정되었다.
분명히 텔타 빌리루빈은 알부민으로부터 분리되 지 않고 또한 알부민과 독립적으로 소실되지 않는다.
4.
표준화의 경향
최근 거의 모든 임상검사실에서 실시하고 있는 임의의 수치는 표준액, 시약의 촉매 또는 다른 인 자에 달려 있다.
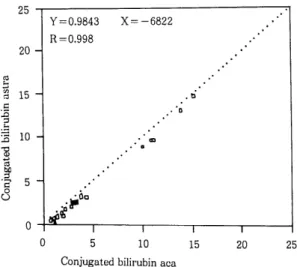
다음 그림은
John A.Lott팀 이 신선한 환자 혈청 으로 Bc를 aca와
Astra방법으로 측정하여 비교한 것이다(그림
7).- 46-
그림 9 는
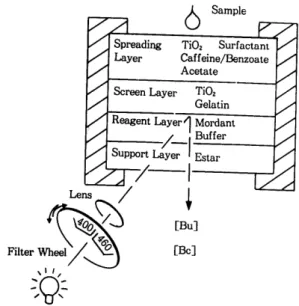
a,β ,
r bilirubin(Bu and glucuronida- tedform) 을 측정하는데 사용하는
BuBc슬라이드 를 나타낸 것이다.
발색 제 와 반응 한 후 mono-와
diglucuronidated bilirubin(Bc) 가
420--425nm 에서 반사를 보이는 반면 Bu는
460--465nm 에서 최고의 반사값을 보 인 다.
Mordant-enhanced bilirubinpigment 를 사용 하여 분광계를 직접 \}용하였을 때 발색제의 흔재 하에 Bu가
endogenousbilirubin의 약 두 배 의 반 사를 갖는다.
Dappen
동은 슬라이드 방법에서의 총 빌리루빈
값과
J. G.방법과의 값이 아주 정확하게 일치한다 고 했다(여기서 사용한 표준으로는
poolserum으로 된 Bu를 사용했으며
referancemethod는
J. G.방 법을 썼다).
ctry 에 의해 측정된다. Dye는
500--530nm 에서 plateau를 이 룬 다. 적 당한
computeralgorithms을 이용해서
460--540nm 에서 반사를 측정하여 빌리 루빈의 양을 알아낸다. 이 방법은 적어도
210 mg/dl 까지는 근사치를 측정할 수 있다. 혈청을 슬라이 드에 직접 떨구어서 각 층으로 이루어진 시약과 슬라이드에서 반응을 하게 한다(그립
8).Principle of dry film slide method for total bilirubin
6. Unconjugated and glucuronidated bilirubin Sample
[TBIL]
Fig.8.
Kodak은 모든 빌리루빈 분리를 위한 순차적인 과정 을
dry film기 술로 개 발했 다.
Filmslide법 에 서 빌리루빈을 알부민으로부터 분리하기 위하여
dy- phylline TritonX-I00 을 채 택 했 다.
모든 빌리루빈의 종류는
diazonium salt 4-(N-ca- rboxymethyl sulfamyl)-benzenediazonium hexafluo-rosphate와 반응하여
azodye를 생성하며 이것은 520nm에 서
absorbance피 크를 나타낸 다.
착색 료
copoly(styrene-/N-vinylbenzyl-N-N-dim- ethylbenzylammonium chloride / divinuylbenzene)에 의하여 반사 파장이 최고에 달하게 하고
diazobil-rubin의 발색 을 증대 시 킨 다.
발색된 색조는 투명한 필름을 통하여
ref1ectom- Regresionplot는 그림 7 에 서 와 같이 두 방법 에 서 우수한 관계를 보여 주는데 aca와 Astra의 값 의 차이는 Astra 의 결과에 대히-여 aca의 결과가 지속적으로 평균
0.7mg/dl 가 높게 니-왔다.
이와같이 Bc의 표준액이 없을 때는 그 검사결과 를 정확하디-고 말할 수 없다.
Bc의 결과가 정확하지 못하면 총 빌리루빈의 결 과가 믿을 만해도 간접 빌리루빈은 부정확할 것이 다. 그 이유는 간접 빌리루빈은 총 빌리루빈의 차 로 계산하기 때문이다.
Ou동은 DBIL 이 어떤 방 법에서는 임상적으로 중요할 수 있는 간접 빌리루 빈 분류를 과대 평가한 나머지 특히 neonates 에서 너무 낮게 나온다는 것을 증명하였다. 간접 빌리루 빈은 광선치료 또는 교환수혈시 비정상적으로 증 가한다.
25
Comparision of conjugated bilirubin
5. Dry film
방법에서의 빌리루빈 분류
20 15
b
∞
。·A
짜
--『
U·J b X
5 10
Conjugated bilirubin aca
x=
-6822 Y=0.9843R=0.998 20 -1
Fig.7.
O O
며
m
띠’i‘}”j 다i〔}그」:ij 언φid
벼되「다。”〕
5 - 25
6
SampleTi02 Gelatin Reagent Layer1 Mordant
/ Buffer t-S-u-pp-ort-Lay;;--1 Estar
/-1---.---J +
[Bu]
[Be]
Fig. 9. Principle of BuBc slide film
Conjugated form.£
~~ftll.9.1 ~A]lt>l-oJl-"-1 ~~ol
~~£1Ul q-aJtsl 460 nmoJlA-1 Bu Be .£!f.
~
1i2}o}E_oj}.A-1
~.78~:;::. ~c}-.
BuBc 1i2}o].=.i=-
t:~E} ~el.!f-~o] ~78£1Al ~
-Ec}-.
~ Y=i>l-~ t:~
EJ-~ el.!f-~ .g.
3.7]71- 3.7] n:JI~
oJ}
~{!-~oJ}-"-1 ~t!:l~-"-1 lfr%~77}-A} op:~}A}
*i>t 7]n:JI~o]
c}-.t:~
Et ~ el.!f-~.g. ~ ~
el.!f-~ l!}BuBc~ ~78 ~
n:JI :::::z.~1-oJl
.9.1 'Bl1-"1
~78 ~ c}-.~'
TBIL=a+.B+r+o BIL BuBc=a+,B+o BIL 8 BIL =TBIL- BuBcBuBc.9.] 1E~~78.g. ditaurobilirubin~ -"1-%~c}-.
Ditaurobilirubin %~.g. -T- 71]9.1 £1 t:Jl absorban-
ce-~ ~-E
til -&-}-ti--E 465 nm oJ] J.1,-T-
Jti~11-E ~ ~
{}~ lila.£. 425 nmoJ]~ ti-.
Ditaurobilirubin.g_ o}-T -AJ ~~ l:IJ-~E...£. biliru- bin-glucuronideill Eq
value~-
Al -AJ ?sll -T0-1 oJ:~c}-.
{f-:;;}~
E...£. ditaurobilirubin.g_ % 4i'-.9.1 diconjuga- ted forml!}-E q.S.Al~ ~ol]
ftllill~:;~:1]
-&-1-oJl J.1 dita- urobilirubin.g_ glucuronidated bilirubin.i!} %J.l-?>1- q.opJ
<(!if~
t:l]-.2} ~oj ~ ~ ~ el.!f-lfl.g_ l;jj 7]].9.1
fj=-~~
%fl-.£. T--"J£10-1~q. ~
unconjugat-ed, mono-, diglucuronidated,
::z.
el :J1.. 8-bilirubin o 1 q.t:~
EJ- ~ el _!f.lfl.g_~-¥- ~
l!} ~ ~ £1 0-1 ~ :JI.. DBILj~
ttl~%?>1-nl l!}~ el.!f-~ ~ .;g:-~~1-9.1 ~ ~
4i'-oJ1~4i'-~r:t.
%-
~ el.!f-~ .g_~~
§}-Q}l:IJ"~
oJl J.1~
1E~§}-
£j 0-1~Al~
Bc.9.]~78l!} lf:~§l-71- o}-~ .i!J-Q}~E...£.
~:Jl.~ ~el&t:l--E ~%~~ ~-2-oJl .9-]~~q.
:::::z.
2:l
t+ '-ll.£.-&:- dry-film 7]~.g. ::z.
-"3 {f-t:l]~
.¥~~
TBILill78 ~~ ~-AJ ~
7}-*t>l-711~q.
::z..c-1.!::..£. 0 BIL.9.]
'i:I -"J~ %%-"a~ ~
7}-i>l--E ~OJ o]ftl] 7}-*t>l-J!l £1 ~ q.
Cholestatic disoder
.£-¥-Ei
~~
£1-E~ ~1-
oJl 711 J.1%-
~ellf-~.g_
{J-±i>tAJ~ ~
E} ~ el_!f-~9-l ~rg:
l:l] (~ -ill§..)i=-
.;g:-7}-~q.
1}Zft>l-J!l o}~ ~~1-oJlA-1 TBIL.?:-
~±t>}i=-ti]
l:l]i>}O:]
t:~
EJ-~ ellf-~.9.) ~
-ill§..7} _;g:-7}i>}Aj ~.£.~o'J}~i=- ~Aj
*i>}c}-.t:~EJ- ~
ellf-lil.9.1 ~1(!-.af %%-"J~ ~~
-o-j~
0?>}71
.!fl&l-"-1~
c-] \t.g.~.AJ:&] ~-T-7} ~JLii}~Al
tfr
l!}~
el.!f-lil ~ "F~~1-oJl
711-Eo'J].;.~ ~
78 ?>}'=:-til*JL~
:S:.T-7}~ ~o]q.
Introduction to Dry-slide Technology
and New Concepts in Serum Bilirubin Measurment
ABSTRACT
Lee, M. J.
School Health Center
of Kodak's expertise : photographic layering tech- nology, and the science of laboratory chemicals. Dry ( 1) Introcuction to dry-slide technology -slide technology is a unique process which has re- Dry-slide technology is a combination of 2 areas placed traditional wet chemistry methods. It has e-
-48-
liminated the need to prepare and handle wet rea- gents. In
dry-~::·,
>cchnology, multilayered rea- gents are applieu cJ a clear polyester supportbase cut to the size of a postage stamp. When serum, urine, or CSF come into contact with these dry chemical layers, the reaction occurs. The chemical reactions thus incorporated into the slides are simi- lar to those used in traditional wet chemistries.There are two basic types of slides used by the Kodak Ektachem 700 analyzer.
Colorimetric ( CM) slides measure analyte concen- tration or activity by light reflectance. The intensity of light reflectance is preportional to the color densi- ty formed.
Potentiometric(PM) slides measure electrolyte concentration by the potential difference between the sample and referenced electrodes. The top layer of a colorimetric slide is the spreading layer.
A drop of undiluted sample is metered onto this layer of the slide. The term metered indicates that a precisely measured amount of sample is placed onto the slide by the analyzer. This method eliminates po-
in proportion to the analyte concentration.
The support layer is the bottom layer of the slide.
It is made of a clear plastic, onto which all other layers are applied. The purpose of the support layer is to allow light to pass through, so that the colored complex can be measured.
(2) New concepts in serum bilirubin mesurement.
For nearly 70 years, laboratorians have used the terms 'direct bilirubin' to mean bilirubin conjugated to glucuronic acid and 'indirect bilirubin' to mean unconjugated bilirubin. Van den Bergh described the measurement of bilirubin in serum in 1913 the 'di- rect' and 'indirect' tests were described shortly there after.
Direct-reacting bilirubin has always been thought to consist solely of bilirubin molecules esterfied to one or two molecules of glucuronic acid. These forms are water soluble, are cleared by the kidneys, and react at once with diazotized sulfanilic acid. In- direct bilirubin is the unconjugated analyte ; is bound primarily to albumin, and reacts with diazotized sulfanilic acid only in the presence of ac- tential errors caused by initial sample dilution. celerators such as methanol, which is used in the
The spreading layer is a porous capillary net- • Malloy-Evelyn method, or a mixture of caffeined work, which allows the liquid in the specimen to
penetrate through to the other layers. Its porous capillary network assures uniform distribution of the sample volume over the slide area. The struc- ture of the spreading layer traps large molecules such as lipids, proteins, and hemoglobins. This elimi- nates interference from these substances and cre- ates a type of protein-free filtrate.
The reagent layer contains the reagents neces- sary for the chemical reactions to occur. These rea- gents include enzymes, buffer, and catalysts. Often several different reactions must occur, making it necessary to separate and control each reaction se- quence. This is made possible by constructing the slide with serveral reagent layers. The indicator layer of the colorimetric slide contains a dye or simi- lar indicator to produce a colored complex formed is
and sodium benzoate, as employed in the Jendrassik -Grof procedure.
The terms direct and indirect bilirubin are now deeply embedded in the practice of laboratory and clinical medicine and have served reasonably well in the differential diagnosis of hyperbilirubinemias.
However, it is now known that 'direct' bilirubin is an ill-defined quantity. Furthermore, cases of an in- creased serum concentration of conjugated bilirubin with little or no bilirubin in the urine have been descrbed-a finding that contradicts the prevalent notion that conjugated bilirubin should always ap- pear in the urine when it is present in abnormal a- mounts in the serum. Accordingly, the concept of di- rect bilirubin must change, since there are species other than the mono and diglucuronidated forms.
REFERENCES
Klin. Med. llO : 540-561, 1913.
1. Van den Bergh. A. A. H. and Snapper, J.: Die
Fearbstoffe des Blusterums, Deutsch. Arch. 2. Van den Bergh. A. A. H. and Mueller P.:
Ueber eine direkte und eine indirekte Dia- zoreaktion auf Bilirubin. Biochem. Z. 77 : 90- 103, 1916.
3. Meites, S. : Bilirubin, direct-reacting and total, modified Malloy-Evelyn Method. In Selected Methods for the Small Clinical Chemistry Labo- ratory. Meites, S. and Faulkner, W. (eds) Washington, D. C.: American Association for Clinical Chemistry, pp.ll9-124, 1982.
4. Koch, T. R. and Doumas, B. T.: Bilirubin, total and conjugated, modified Jendrassik-Grof method. In selected methods for the Small Clini- cal Chemistry Laboratory. Meites, S. Faulkner, W.(eds.) Washington, D. C.: Amercin Associa- tion for Clinical chemistry, pp.ll3-118, 1982.
5. Kuenzld, C. C., et. al :Separation and quantita- tive estimation of four bilirubin fractions from serum and three bilirubin fractions from bile, J.
Lab. Clin. Med. 67 : 282-293, 1966.
6. Lauff, J. J., et al. : Isolation and preliminary characterization of a fraction of bilirubin in serum that is firmly bound to protein. Clin.
Chern. 28: 629-637, 1982.
7. Wu, T. W.: The Ektachem clinical chemistry slide for simultaneous determination of uncon- jugated and sugar-conjugated bilirubin. Clin Chern. 30: 1304-1309, 1984.
8. Du Pont TBIL and CBIL Methodology, Du Pont Clinical Systems, Wilmington, DE 1989. 8.
9. Me Donagh, A. F., Palma, L. A., Lauff, J. J.
and Wu, T. W.: Origin of mammalian biliprotein and rearrangement of bilirubin glucuronides in vivo in the rat. J. Clin. Invest.
74: 763-770, 1984.
10. Ou, C. N., et al. : Unconjugated hyperbilirubine- mia is overestimated in neonates with cholesta- sis. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 84 : 752-756, 1985.
11. Alpers. J., et al. : Interlaboratory comparison of direct bilirubin methods. Clin. Chern. 31 : 989 (Abstract), 1985.
12. Kodak TBIL and BuBc Methodology, Document MP2-39. Eastman Kodak Co., Rochester, NY 14650.
13. Dappen G. M., et al: A diazobased dry film for determination of total bilirubin in serum. Clin.
Chern. 29 : 37-41, 1983.
14. Chan K. W., et al.: Inacurate values for direct bilirubin with some commonly used direct biliru- bin procedures. Clin. Chern. 31 : 1560-1563, 1985.
15. Dry-slide technology. Eastman Kodak.
16. Kodak Ektachem 700 Analyzer Operater's Manuual for in vitro diagnostic use MP2-51 : Eastman Kodak Co. Rochester, NY 14650.
-50-