딥러닝 기반의 자연어처리 최근 연구 동향
강원대학교 IT대학
이창기
차례
• 딥러닝 기반 자연어처리 최근 연구 동향
• 딥러닝 기반의 한국어 자연어처리
자연어처리 – 개요
3
NP S VP
N N V
나는 사과를 먹었다
• 형태소분석: 문장을 형태소 단위로 분리
어휘적 중의성 존재: ex. “감기는”의 결과
감기(명사:cold)+는(조사)
감(동사 어간)+기(명사화 어미)+는(조사)
감(동사 어간)+기는(어미)
나는 사과를 먹었다
sub
obj
• 구문분석: 문장을 구성하는 성분들간의 관계를 분석
어휘적 중의성과 구조적 중의성 존재
Time flies like light flies: 명사 or 동사 2 가지 이상 tree
A man see a woman with a telescope 전치 사구가 see or woman을 수식 2가지 이상 tree
Ex. “나는 사과를 먹었다"의 구문분석 결과
• 자연어처리 분석 단계
형태소 분석
(Morphological Analysis)
구문 분석 (Syntax Analysis)
의미 분석
(Semantic Analysis)
분석 결과 자연언어문장
담화 분석
(Discourse Analysis)
자연어처리 – 개요 (Cont‘d)
4
• 의미분석: 문장이 나타내는 의미를 분석하여 표현
단어 중의성 해소
단어가 현재 문장에서 어떤 의미로 사용되었는 지 분석
Ex) “말이 많다” 말: horse or speech ?
의미역 결정
서술어와 관계있는 논항의 역할을 결정
Ex) “먹다”의 행위주(agent)=“나“, 대상 (theme)=“사과”
• 자연어처리 분석 단계
형태소 분석
(Morphological Analysis)
구문 분석 (Syntax Analysis)
의미 분석
(Semantic Analysis)
분석 결과 자연언어문장
담화 분석
(Discourse Analysis)
• 담화분석: 문장간의 관계를 분석하여 표현
상초참조해결
같은 대상을 지칭하는 명사구들을 하나의 엔티 티(Entity)로 묶어주는 과정
“A씨는… B씨는 … 그는 …” 그: A or B ?
응집성(Coherence) 분석
담화는 내적 구조를 가짐: 조건, 결과, 요약, …
담화 구조 분석
화행(Speech act) 분석
화행: 발화에 나타난 화자에 의해 의도된 언어 적 행동 – 정보요구, 정보제공, 응답, 확인, 거절,
…
자연어처리 특징
• Natural languages are ambiguous
– Rule Classification (Maximum Entropy, SVM) Deep Learning
• NLP datasets are high dimensional
– One-hot representation Continuous representation (Word Embedding)
• Many NLP problems can be viewed as sequence labeling tasks
– Hidden Markov Model(HMM)
Conditional Random Fields (CRF) Deep Learning (RNN)
• Many NLP problems can be posed as sequence-to-sequence tasks
– Rule Statistical Machine Translation Neural MT
• “감기는” 감기(명사) or 감다(동사) + 기
• “말이 많다” 말 = horse or speech ?
• “A씨는… B씨는 … 그는 …” 그: A or B ?
• Ex. [0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
• Dimensionality
• 50K (PTB) – 500K (big vocab) – 3M …
Neural Networks
6
ni
w
ix
iw
o
0 1) exp(
1
1
o
Deep Neural Networks
• Deep Neural Network = Neural Network + multiple levels of nonlinear operations.
7
8
Perceptron learning rule
• On-line, mistake driven algorithm.
• Rosenblatt (1959)
suggested that when a target output value is
provided for a single neuron with fixed input, it can incrementally change weights and learn to produce the
output using the Perceptron learning rule Perceptron == Linear Threshold Unit
1 2
6 3 4 5
7
w 6
w 1
T y
x 1
x 6
x w T
i i
i x w
y ˆ
9
Perceptron learning rule
• We learn f:X{-1,+1} represented as f = sgn{wx)
Where X= or X= w {0,1} n R n R n
• Given Labeled examples: {(x 1 , y 1 ), (x 2 , y 2 ),..., (x m , y m )}
1. Initialize w=0
2. Cycle through all examples
a. Predict the label of instance x to be y’ = sgn{wx) b. If y’y, update the weight vector:
w = w + r y x (r - a constant, learning rate) Otherwise, if y’=y, leave weights unchanged.
R n
10
Linear Functions
w x = 0
- - - - - -
- - -
- - - -
- -
w x =
11
Footnote About the Threshold
• On previous slide, Perceptron has no threshold
• But we don’t lose generality:
, 1 , w w
x x
x
x
0x
1
x w
x
0x
1 w , x , 1 0
12
Geometric View
13
14
15
경사 하강법 (Gradient Descent)
출처: https://byungjun0689.github.io/1.-Basic_Deep_Learning/
출처: https://thebook.io/006958/part02/ch04/02-01/
출처: https://hamait.tistory.com/747
델타규칙 – 1
출처: © 2017, 장교수의 딥러닝, SNU CSE Biointelligence Lab., http://bi.snu.ac.kr
델타규칙 – 2
출처: © 2017, 장교수의 딥러닝, SNU CSE Biointelligence Lab., http://bi.snu.ac.kr
델타규칙 – 3
출처: © 2017, 장교수의 딥러닝, SNU CSE Biointelligence Lab., http://bi.snu.ac.kr
델타규칙 – 4
출처: © 2017, 장교수의 딥러닝, SNU CSE Biointelligence Lab., http://bi.snu.ac.kr
델타규칙 – 5
출처: © 2017, 장교수의 딥러닝, SNU CSE Biointelligence Lab., http://bi.snu.ac.kr
델타규칙 – 6
출처: © 2017, 장교수의 딥러닝, SNU CSE Biointelligence Lab., http://bi.snu.ac.kr
델타규칙 – 7
출처: © 2017, 장교수의 딥러닝, SNU CSE Biointelligence Lab., http://bi.snu.ac.kr
The Back-Propagation Algorithm
Word meaning as a neural word vector –
visualization
Recurrent Neural Network
• Many NLP problems can be viewed as sequence labeling or sequence-to-sequence tasks
• “Recurrent” property dynamical system over time
Bidirectional RNN
• Exploit future context as well as past
Long Short-Term Memory RNN
• Vanishing Gradient Problem for RNN
• LSTM can preserve gradient information
Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU)
• 𝑟 𝑡 = 𝜎 𝑊 𝑥𝑟 𝑥 𝑡 + 𝑊 ℎ𝑟 ℎ 𝑡−1 + 𝑏 𝑟
• 𝑧 𝑡 = 𝜎 𝑊 𝑥𝑥 𝑥 𝑡 + 𝑊 ℎ𝑧 ℎ 𝑡−1 + 𝑏 𝑧
• ℎ 𝑡 = 𝜙 𝑊 𝑥ℎ 𝑥 𝑡 + 𝑊 ℎℎ 𝑟 𝑡 ⊙ ℎ 𝑡−1 + 𝑏 ℎ
• ℎ 𝑡 = 𝑧 𝑡 ⊙ ℎ 𝑡 + 1 − 𝑧 𝑡 ⊙ ℎ 𝑡
• 𝑦 𝑡 = 𝑔(𝑊 ℎ𝑦 ℎ 𝑡 + 𝑏 𝑦 )
Encoder-Decoder Model
출처: https://haltaro.github.io/2018/03/03/kaggle-wikipedia-1st
Attention Mechanism
Transformer: Self Attention
(NIPS17, Google)
출처: https://nlp.stanford.edu/seminar/details/lkaiser.pdf
RNN
Multi-Head Self-Attention
출처: https://towardsdatascience.com/understanding-bidirectional-rnn-in-pytorch-5bd25a5dd66
Transformer Model
(NIPS17, Google)
Multi-Head Attention
BERT
• BERT (Bidirectional
Encoder Representation from Transformers)
– Transformer’s encoder – Self attention
– Multi-head attention – Residual network – Layer normalization – Positional encoding – BERT base
• L=12, H=768, A=12
– BERT large
• L=24, H=1024, A=16
Positional encoding
BERT – cont’d
BERT – cont’d
• Self attention
출처: https://ai.googleblog.com/2017/08/transformer-novel-neural-network.html
BERT – cont’d
• BERT pre-training
– Masked Language Model
• 15%의 token을 mask
• Mask token의 80%는 mask, 10%는 random word, 10%는
unchanged word
– Next Sentence Prediction
• 두 문장이 연속된 문장 인지 분류
BERT Pre-training 모델
Next Sentence
Prediction Masked LM
Tok1 TokN
BERT – cont’d
• Fine-tuning
– 11개의 NLP tasks 에 적용
– 11개 모두 최고
성능
Large Vocabularies
• Zipf’s Law: Many Rare Words
http://mt-class.org/jhu/slides/lecture-nmt2.pdf
Large Vocabularies
• Many Problems
– Sparse data
• words that occur once or twice have unreliable statistics
– Computation cost
• input word embedding matrix: |V| × 1000
• output word prediction matrix: 1000 × |V|
http://mt-class.org/jhu/slides/lecture-nmt2.pdf
Some Causes for Large Vocabularies
• Morphology
– tweet, tweets, tweeted, tweeting, retweet, ...
– 하다, 하였다, 했다, 했니, 할까, … – morphological analysis?
• Compounding
– homework, website, …
– 대학생선교회 (대학 생선 교회? 대학생 선교회?) – compound splitting?
• Names
– Netanyahu, Jones, Macron, Hoboken, … – transliteration?
• Breaking up words into subwords may be a good idea
http://mt-class.org/jhu/slides/lecture-nmt2.pdf
Byte Pair Encoding
• Neural Machine Translation of Rare Words with Subword Units
– ACL16, Rico Sennrich (University of Edinburgh)• Byte Pair Encoding (BPE) is a simple data compression technique
– Iteratively replaces the most frequent pair of bytes in a sequence with a single, unused byte
Byte Pair Encoding – cont’d
Byte Pair Encoding – cont’d
• 한국어 어절 + BPE
– 프랑스의_ 르 노_ 자동차_ 그룹 은_ 다음 주_
김 대중_ 대통령의_ 프랑스_ 방문_ 중_ 한국_
삼성 자동차_ 인수를_ 공식_ 제 의 할 지_ 모
른다고_ 르 노 사의_ 한_ 관계 자가_ 1일_ 밝혔
다 ._
Byte Pair Encoding – cont’d
• 한국어 형태소 + BPE
– 프랑스/NNP_ 의/JKG_ 르 노/NNP_ 자동 차 /NNG_ 그룹/NNG_ 은/JX_ 다음/NNG_ 주
/NNG_ 김대중/NNP_ 대통령/NNG_ 의/JKG_
프랑스/NNP_ 방문/NNG_ 중/NNB_ 한국 /NNP_ 삼성 자동차/NNP_ 인수/NNG_ 를
/JKO_ 공식/NNG_ 제의/NNG_ 하/XSV_ ㄹ지 /EC_ 모르/VV_ ㄴ다고/EC_ 르 노 사/NNP_ 의 /JKG_ 한/MM_ 관계 자/NNG_ 가/JKS_ 1/SN_
일/NNB_ 밝히/VV_ 었/EP_ 다/EF_ ./SF_
Why BPE?
• Open vocabulary
– operations learned on training set can be applied to unknown words
– compression of frequent character sequences improves efficiency
– trade-off between text length and
vocabulary size
차례
• 딥러닝 기반 자연어처리 최근 연구 동향
• 딥러닝 기반의 한국어 자연어처리
딥러닝 기반 한국어 의미역 결정
(한글 및 한국어 정보처리 15, 동계학술대회 15)
• 서술어 인식(PIC)
– 그는 르노가 3월말까지 인수제의 시한을 [갖고]
갖.1있다고 [덧붙였다]
덧붙.1• 논항 인식(AIC)
– 그는 [르노가]
ARG0[3월말까지]
ARGM-TMP인수제의 [시한을]
ARG1[갖고]
갖.1[있 다고]
AUX덧붙였다
– [그는]
ARG0르노가 3월말까지 인수제의 시한을 갖고 [있다고]
ARG1[덧붙였 다]
덧붙.1• Bi-LSTM+CRF 성능 (AIC) – F1: 78.2% (+1.2)
– Backward LSTM+CRF: F1 77.6%
– S-SVM 성능 (KCC14)
• 기본자질: F1 74.3%
• 기본자질+word cluster: 77.0%
– 정보과학회 논문지 2015.02
x(t-1) x(t ) x(t+1)
y(t+1) y(t-1) y(t )
bh(t-1) bh(t ) bh(t+1)
h(t )
h(t-1) h(t+1)
Stacked BI-LSTM CRF 기반 한국어의미역결정
(정보과학회지 17)
Syntactic information w/ w/o
Structural SVM FFNN
Backward LSTM CRFs Bidirectional LSTM CRFs
Stacked Bidirectional LSTM CRFs (2 layers) Stacked Bidirectional LSTM CRFs (3 layers)
76.96 76.01 76.79 78.16 78.12 78.14
74.15 73.22 76.37 78.17 78.57 78.36
Sequence-to-sequence 기반 한국어 구구조 구문 분석 (한글 및 한국어 16)
43/SN + 국/NNG 참가/NNG
NP NP
NP
(NP (NP 43/SN + 국/NNG) (NP 참가/NNG))
GRUGRU GRUGRU GRUGRU
x1 h1t-1 h2t-1 yt-1
h1t h2t yt
x2 xT ct
Attention + Input-feeding
입력 선 생 <NNG> 님 <XSN> 의 <JKG> <sp> 이 야 기 <NNG> <sp>
끝 나 <VV> 자 <EC> <sp> 마 치 <VV> 는 <ETM> <sp> 종
<NNG> 이 <JKS> <sp> 울 리 <VV> 었 <EP> 다 <EF> . <SF>
정답 (S (S (NP_SBJ (NP_MOD XX ) (NP_SBJ XX ) ) (VP XX ) ) (S (NP_SBJ (VP_MOD XX ) (NP_SBJ XX ) ) (VP XX ) ) )
RNN-search[7] (S (VP (NP_OBJ (NP_MOD XX ) (NP_OBJ XX ) ) (VP XX ) ) (S (NP_SBJ (VP_MOD XX ) (NP_SBJ XX ) ) (VP XX ) ) )
RNN-search + Input-feeding +
Dropout
(S (S (NP_SBJ (NP_MOD XX ) (NP_SBJ XX ) ) (VP XX ) ) (S (NP_SBJ (VP_MOD XX ) (NP_SBJ XX ) ) (VP XX ) ) )
모델 F1
스탠포드 구문분석기[13] 74.65
버클리 구문분석기[13] 78.74
형태소의 음절 + 품사 태그 + <sp>
RNN-search[7] (Beam size 10) 88.00 RNN-search + Input-feeding 88.68 RNN-search + Input-feeding + Dropout 89.03
End-to-End 한국어 형태소 분석
(동계학술대회 16)
Attention + Input-feeding + Copying mechanism
Abstractive Text Summarization
(한글 및 한국어 16)
로드킬로 숨진 친구의 곁을 지키는 길고양이의 모습이 포착 되었다.
RNN_search+input_feeding+CopyNet
Pointer Network (Google NIPS 15)
• Travelling Salesman Problem: NP-hard
• Pointer Network can learn approximate solutions: O(n^2)
포인터 네트워크를 이용한 한국어 의존구문분석
(동계학술대회 16)
CJ그룹이 대한통운 인수계약을 체결했다
SBJ MOD OBJ
포인터 네트워크 기반 상호참조해결
(KCC 16, Pattern Recognition Letters 17)
• 상호참조해결: “A씨는… B씨는 … 그는 …” 그: A or B ?
• 입력: 단어(형태소) 열, 출발점(대명사, 한정사구(이 별자리 등)) – X = {A:0, B:1, C:2, D:3, <EOS>:4}, Start_Point=A:0
• 출력: 입력 단어 열의 위치(Pointer) 열 Entity – Y = {A:0, C:2, D:3, <EOS>:4}
• 특징: End-to-end 방식의 대명사 상호참조 해결 (mention detection 과정 X)
A B C D <EOS> A C D <EOS>
Encoding Decoding
Hidden Layer Projection
Layer Attention
Layer
포인터 네트워크 기반 멘션 탐지
(한글 및 한국어16, ETRI Journal 17)
• 멘션 탐지
– 멘션의 중복: … [[[조선 중기+의] 무신] 이순신+이] … – BIO representation 가장 긴 멘션만 탐지 가능
• 기존: 구문 분석 정보 + 규칙
• 포인터 네크워크 기반 멘션 탐지 중복된 모든 멘션 탐지 가능
– … [[[조선 중기+의] 무신] 이순신+이] …
Model Long boundary All boundary
Rule-based MD[5]
44.08 72.42Bi-LSTM CRF based MD
76.24Pointer Networks based MD
73.23 80.07S 3 -Net for MRC
(ETRI Journal 19)
Korean BERT Pre-training (ETRI)
• 학습 데이터
– 뉴스 및 위키피디아
• 23.5 GB
– 형태소 분석 후,
BPE(Byte Pair Encoding) 적용
• Vocab size: 30,349
• BERT-base
– L=12, H=768, A=12 – 최대 문장 길이: 512
• ETRI에서 학습 및 배포
– 엑소브레인 과제
Next Sentence
Prediction Masked LM
Tok1 TokN
BERT 기반 개체명 인식
• BERT + Bi-LSTM + CRF
• 학습/평가셋: ETRI TV domain NE set (15 tags)
• 사전 자질 추가
• 성능
– GRU+CRF: F1 85.27%
– BERT+LSTM+CRF: F1
87.59% (+2.3)
BERT 기반 한국어 개방형 정보추출
(KCC 19)
• BERT + Bi-LSTM + CRF – 동사와의 위치 자질 추가
• 학습셋
– Parsing+SRL+Rule 자동 추출 결과
– News 10,000 문장 – Wiki 10,000 문장
• 평가셋
– News 50 문장 + Wiki 50 문장 – 202 + 172 트리플
News Wiki Parsing+SRL+Rule
Prec 72.59 70.87F1 58.16 60.20
BLSTM+CRF
Prec 70.29 63.64 F1 57.06 52.56BERT+LSTM+CRF
Prec 72.30 72.66 F1 61.14 62.00BERT 기반 한국어 의존구문분석
(KCC 19)
• BERT + Bi-LSTM + Deep Biaffine attention
• 학습셋
– 세종구문분석 코퍼스
• 의존구조로 변환
– 학습: 53,842 문장 – 평가: 5,817 문장
세종코퍼스 UAS LAS
이창기[16] with MI 90.37 88.17
나승훈[6]: deep biaffine attention 91.78 89.76
박천음[5]: 포인터 네트워크 92.16 89.88
안휘진[10]: deep biaffine + 스택 포인터 네트워크 92.17 90.08
박성식[11]: ELMo + 멀티헤드 어텐션 92.85 90.65
BERT + LSTM deep biaffine (ours) 94.02 91.97
𝑠𝑗,𝑖𝑎𝑟𝑐 = 𝐡T𝑖𝑑𝑒𝑝 𝑈𝐡𝑗ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑 , 𝑏𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑒𝑎𝑟 𝐡T𝑖𝑑𝑒𝑝 𝑈𝐡𝑗ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑 + 𝐰T𝐡𝑗ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑 , 𝑏𝑖𝑎𝑓𝑓𝑖𝑛𝑒 𝐡𝑖𝑑𝑒𝑝 = elu FFNN 𝑑𝑒𝑝 𝐫𝑖
𝐡𝑖ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑 = elu FFNN ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑 𝐫𝑖
BERT 기반 한국어 의미역 결정
(KCC 19)
• BERT + Bi-LSTM + CRF
– 동사와의 위치 자질 추가
• 학습셋
– Korean PropBank
• 의존구조 기반으로 변환
– 학습: 19,307 문장 – 평가: 3,778 문장
[CLS] tok1 tok2 … tokn [SEP] verb
Korean PropBank F1 (AIC) Highway BiLSTM-CRF
BERT+LSTM+CRF (ours)
78.84
85.74 (+6.9)
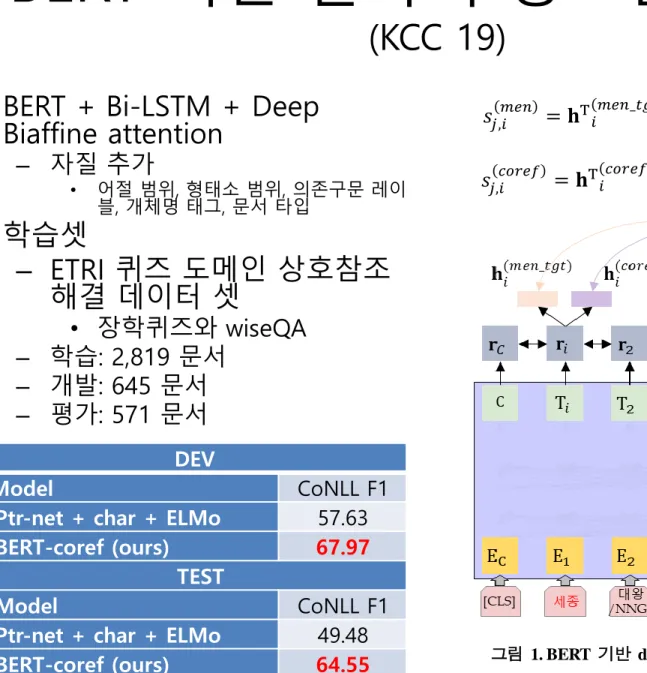
BERT 기반 한국어 상호참조해결
(KCC 19)
• BERT + Bi-LSTM + Deep Biaffine attention
– 자질 추가
• 어절 범위, 형태소 범위, 의존구문 레이
블, 개체명 태그, 문서 타입
• 학습셋
– ETRI 퀴즈 도메인 상호참조 해결 데이터 셋
• 장학퀴즈와 wiseQA – 학습: 2,819 문서
– 개발: 645 문서 – 평가: 571 문서
그림 1. BERT 기반 deep biaffine을 이용한 상호참조해결 모델
𝑠𝑗,𝑖𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒𝑓 = 𝐡T𝑖𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒𝑓_𝑡𝑔𝑡 𝐔𝐡𝑗𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒𝑓_𝑠𝑟𝑐 + 𝐰T𝐡𝑗𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒𝑓_𝑠𝑟𝑐 𝑠𝑗,𝑖𝑚𝑒𝑛 = 𝐡T𝑖𝑚𝑒𝑛_𝑡𝑔𝑡 𝐔𝐡𝑗𝑚𝑒𝑛_𝑠𝑟𝑐 + 𝐰T𝐡𝑗𝑚𝑒𝑛_𝑠𝑟𝑐