교신저자: 이동국, 대구시 남구 대명 4동 3056-6,
705-718, 대구가톨릭대학교 의과대학 신경과학교실 Tel: 053-650-4756, Fax: 053-654-9786, E-mail: dklee@cu.ac.krDiabetic peripheral polyneuropathy (DPN) is one of the most common long-term complications of dia- betes, characterized by progressive sensory loss predisposing to neuropathic foot ulceration and asso- ciated with premature mortality. DPN is associated in some patients with neuropathic pain that responds poorly to conventional analgesics. Despite its clear typical clinical expression, neuropathic pain still goes underdiagnosed. A DPN prevalence rate as high as 50% has been reported in the literature, but there are considerable differences across studies, which may be due to methodological differences and the lack of consensus on its diagnostic criteria. Although most patients with DPN do not have pain, approximately 11% of patients with DPN have chronic, painful symptoms that diminish quality of life, disrupt sleep, and can lead to depression. Despite the number of patients affected by DPN pain, little consensus exists about the pathophysiology, best diagnostic tools, and primary treatment choices.
Key Words: Diabetic peripheral neuropathy, Clinical, Quality-of-life
당뇨병성 말초신경병환자의 임상과 삶의 질
이 동 국
대구가톨릭대학교 의과대학 신경과학교실
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain: Clinical and Quality-of-Life
Dong Kuck Lee, M.D.
Department of Neurology, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
서 론 1-11)
당뇨병은 임상에서 가장 흔하게 볼 수 있는 만성 질환 중의 하나이다. 당뇨병에서 가장 흔한 합병증 중의 하나가 신경병(neuropathy)으로 당뇨병을 앓고 25년이 지나면 50% 이상에서 신경병이 생긴다. 다양한 형태의 신경병이 생기지만 그중 가장 흔한 것이 원위 대칭성 감각신경병 또는 다발신경병(polyneuropathy)이다. 인슐 린 의존형 당뇨병환자의 11.6%에서 하지와 발에 통증이 생기고 인슐린 비의존형 당뇨병환자에서는 32.1%
에서 통증이 생긴다. 최근 연구에서는 전체 당뇨병성 말초신경병 환자의 11%에서 신경병 통증이 생긴다고
한다. 하지만 아직까지 당뇨병성 말초신경병의 발병기전는 모르며 완치법도 없는 실정이다. 당뇨병성 신경
병 통증은 임상 징후나 치료반응으로 미루어 보아 다른 원인에 의한 신경병 통증과 유사점도 많이 있으나
당대사와 연관되어 있다는 점에서 독특한 측면도 있다. 그러나 당뇨병성 말초신경병 환자 중 많은 경우에
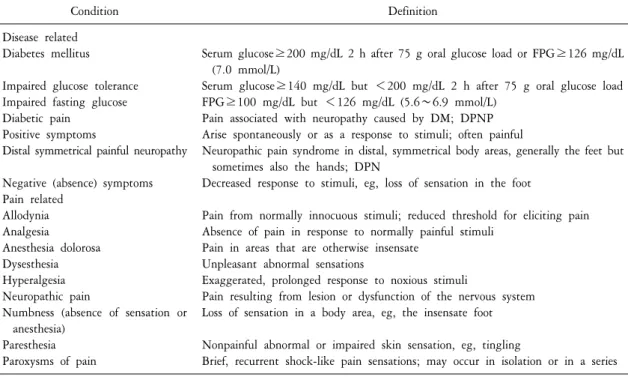
Table 1. Definitions related to diabetes mellitus and pain
Condition Definition
Disease related Diabetes mellitus Impaired glucose tolerance Impaired fasting glucose Diabetic pain
Positive symptoms
Distal symmetrical painful neuropathy Negative (absence) symptoms Pain related
Allodynia Analgesia
Anesthesia dolorosa Dysesthesia Hyperalgesia Neuropathic pain
Numbness (absence of sensation or anesthesia)
Paresthesia Paroxysms of pain
Serum glucose≥200 mg/dL 2 h after 75 g oral glucose load or FPG≥126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L)
Serum glucose≥140 mg/dL but <200 mg/dL 2 h after 75 g oral glucose load FPG≥100 mg/dL but <126 mg/dL (5.6∼6.9 mmol/L)
Pain associated with neuropathy caused by DM; DPNP Arise spontaneously or as a response to stimuli; often painful
Neuropathic pain syndrome in distal, symmetrical body areas, generally the feet but sometimes also the hands; DPN
Decreased response to stimuli, eg, loss of sensation in the foot
Pain from normally innocuous stimuli; reduced threshold for eliciting pain Absence of pain in response to normally painful stimuli
Pain in areas that are otherwise insensate Unpleasant abnormal sensations
Exaggerated, prolonged response to noxious stimuli
Pain resulting from lesion or dysfunction of the nervous system Loss of sensation in a body area, eg, the insensate foot Nonpainful abnormal or impaired skin sensation, eg, tingling
Brief, recurrent shock-like pain sensations; may occur in isolation or in a series DM: diabetes mellitus, DPN: diabetic peripheral neuropathy, DPNP: diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain, FPG: fasting plasma glucose.
통증을 느끼지 않지만 왜 일부 환자에서만 통증으로 고생하게 되는지는 아직도 모른다. 더구나 신경병 통증 이 생기면 숙면이 되지 않아 삶의 질이 떨어지고 심지어는 우울증에 빠지기도 한다. 최근 수명이 증가하고 따라서 당뇨병도 증가함에 따라 당뇨병성 말초신경병 환자의 유병률도 증가한다. 따라서 이런 환자의 임상 과 삶의 질을 잘 관리해야 할 것으로 생각한다.
본 론 1-11)
1. 정의
당뇨병 및 통증과 연관된 여러 가지 용어의 정의는 Table 1과 같다.
2. 유병률
당뇨병성 말초신경병의 유병률을 알기 위해서는 우선 신경병에는 다양한 형태가 있이 있다는 것을 먼저
생각해야 한다. 당뇨병과 연관된 신경병에는 크게 보아 전신에 대칭적으로 생기는 다발신경병과 국소 또는
다발성 국소 신경병이 있다. 대칭성 신경병에는 급성 감각신경병, 보통 당뇨병성 말초신경병이라고 하는
만성 감각운동 원위 대칭 다발신경병 및 자율신경병이 있다. 당뇨병에서 생기는 신경병중 가장 흔한 형태는
당뇨병성 말초신경병이며 환자중 50% 이상에서는 어느 정도의 통증을 느끼고 10∼20%에서는 치료를 해야
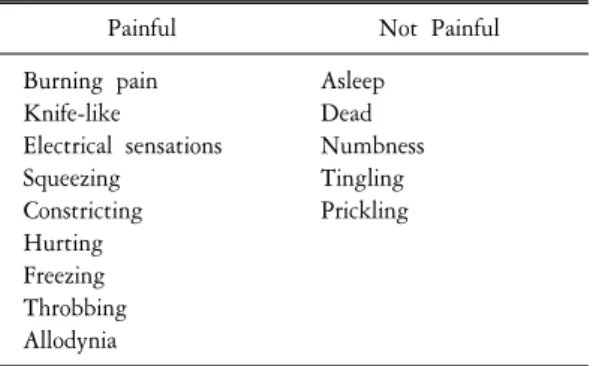
Table 2. Typical descriptors for neuropathic pain
Painful Not Painful
Burning pain Knife-like
Electrical sensations Squeezing
Constricting Hurting Freezing Throbbing Allodynia
Asleep Dead Numbness Tingling Prickling
할 정도의 심한 통증을 느낀다. 제1형 당뇨병에서는 54%, 제2형 당뇨병에서는 45%에서 말초신경병이 생기 며 각각 15%와 13%에서 증상을 느낀다고 한다. 특히 제2형 당뇨병에서 더 흔히 이상감각(paresthesia)과 불타 는 듯한 통증이 생기며 당뇨병의 이환기간이 길어질수록 신경병 증상의 유병률이 증가한다. 그러나 당뇨병 성 말초신경병 통증이란 그 정의가 다양하고 또한 통증이란 주관적인 증상이 많이 포함되어 있으므로 정확 한 유병률을 알기가 힘들다. 한편 일부에서는 통증성 말초신경병을 조사하다가 당뇨병이나 당내성장애 (impaired glucose tolerance)를 진단하기도 하므로 원인을 잘 모르는 말초신경병에서는 당뇨병에 대한 검사가 필요하다. 당뇨병에서는 큰 신경섬유를 잘 침범하지만 당내성장애에서는 작은 신경섬유를 잘 침범한다.
3. 자연 경과
당뇨병성 말초신경병이나 신경병 통증의 자연 경과는 아직도 잘 모른다. 그러나 신경병 진단 후 1년 정도 지나서 검사해 보면 거의 대부분의 감각 및 운동신경전도속도가 감소한다. 당뇨병성 말초신경병의 발병 위험인자는 자세히 모르지만 당뇨병의 유병기간이 가장 중요하다고 생각된다. 또한 고혈당과 신경병과의 관계도 중요하므로 더 이상의 합병증을 막기 위해 발병 초기부터 적극적인 혈당조절이 필요하다.
4. 평가
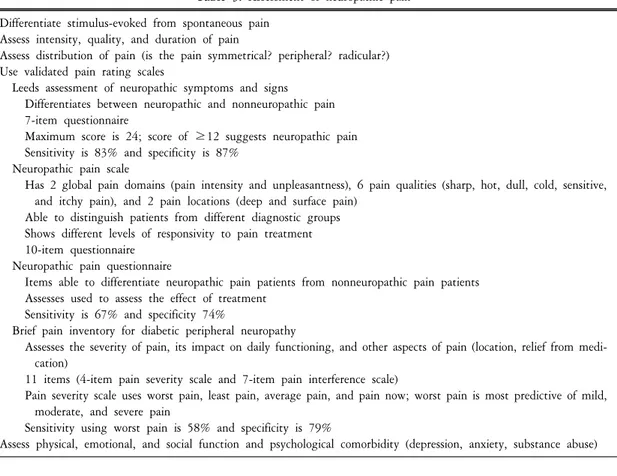
신경병 통증은 신경계 병변이나 손상으로 인해 자발통이 생기며 또한 통증에 대해 과민해진 (hypersensitivity) 상태이다. 유해자극에 대해 반응하는 일반적인 통증과는 달리 신경병 통증은 적응하기가 힘들며 아예 경고체계보다는 질병으로 여겨지고 있다. 신경병 통증은 무해자극통증(allodynia)같이 자극 후에 생기는 것과 자극과는 무관하게 생기는 것으로 나눈다. 자발통은 가끔 돌발적으로 생기며 욱신거리고 칼로 베는 듯이 또는 전기자극같이 나타난다. 일반적으로 당뇨병성 말초신경병 통증을 포함하는 신경병 통증은 염증성 또는 통각 치료에 잘 반응하지 않는다. 신경병 통증은 환자에 따라 다양하게 표현되는데 크게 통증 성과 비통증성 표현으로 나눌 수 있다(Table 2). 신경병 통증을 분석하기 위해선 Leeds 신경병 증상 및 징후평 가, 신경병 통증척도 및 설문지 및 당뇨병성 말초신경병에 대한 간단 통증 목록 등을 이용한다(Table 3).
5. 증상
같은 당뇨병성 말초신경병이라도 다른 신경장애 없이 심한 통증을 주로 보이는 환자가 있는 반면에 어떤 경우에는 통증은 없이 족부궤양을 주로 보이는 경우도 있다. 특히 당뇨병성 말초신경병은 특수한 검사보다 는 병력과 진찰로 진단되므로 환자가 다양한 증상과 징후를 보일 수 있다는 것을 염두에 두고 진단해야 한다. 급성 감각신경병과 다르게 당뇨병성 말초신
경병은 하지나 발에 대칭적으로 서서히 불타는 듯 한 통증, 이상감각 및 무감각 등이 생겨 결국 상지도 침범하여 양말신고 장갑끼는 부위에 증상을 일으킨 다. 사지에 진동감, 고유감각(proprioceptive) 및 온도 감 등을 잃어가다가 결국 통각을 모르게 된다. 특히 고유감각을 잃게 되면 보행장애가 오고 잘 넘어진 다. 그러나 심한 운동징후가 오거나 비대칭적으로 생기면 당뇨병 외에 다른 원인을 알아보아야 한다.
당뇨병성 말초신경병의 드문 형태인 급성 감각 신
경병은 특히 밤에 불타는 듯한 통증이 빠르게 진행
Table 3. Assessment of neuropathic pain Differentiate stimulus-evoked from spontaneous pain
Assess intensity, quality, and duration of pain
Assess distribution of pain (is the pain symmetrical? peripheral? radicular?) Use validated pain rating scales
Leeds assessment of neuropathic symptoms and signs Differentiates between neuropathic and nonneuropathic pain 7-item questionnaire
Maximum score is 24; score of ≥12 suggests neuropathic pain Sensitivity is 83% and specificity is 87%
Neuropathic pain scale
Has 2 global pain domains (pain intensity and unpleasantness), 6 pain qualities (sharp, hot, dull, cold, sensitive, and itchy pain), and 2 pain locations (deep and surface pain)
Able to distinguish patients from different diagnostic groups Shows different levels of responsivity to pain treatment 10-item questionnaire
Neuropathic pain questionnaire
Items able to differentiate neuropathic pain patients from nonneuropathic pain patients Assesses used to assess the effect of treatment
Sensitivity is 67% and specificity 74%
Brief pain inventory for diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Assesses the severity of pain, its impact on daily functioning, and other aspects of pain (location, relief from medi- cation)
11 items (4-item pain severity scale and 7-item pain interference scale)
Pain severity scale uses worst pain, least pain, average pain, and pain now; worst pain is most predictive of mild, moderate, and severe pain
Sensitivity using worst pain is 58% and specificity is 79%
Assess physical, emotional, and social function and psychological comorbidity (depression, anxiety, substance abuse)
되며 체중이 줄기도 한다. 이런 증상은 대사조절이나 혈당이 잘 조절되지 않을 때 더 잘 생긴다. 그러나 이런 감각 신경병은 혈당을 잘 조절하면 발병후 1년 정도 지나 호전된다.
6. 진단
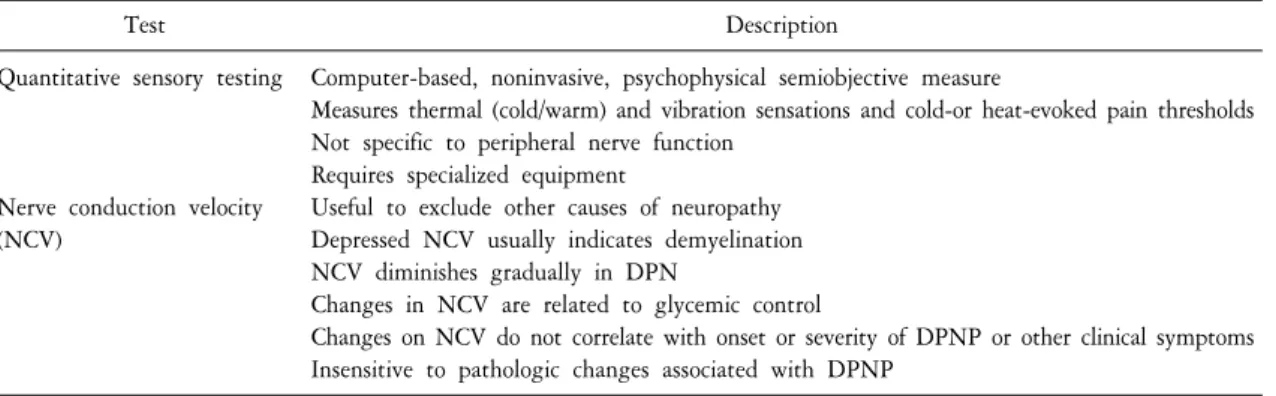
당뇨병성 말초신경병은 병력과 진찰로 진단되며 대부분의 경우 다른 검사는 필요하지 않다. 비록 다른 검사상 신경병이 있다고 판정해도 발병원인을 알기는 힘들다. 더구나 당뇨병성 말초신경병 통증의 정도는 신경전도속도와 일치하지는 않으며 또한 이런 신경병을 진단하는데 반드시 큰 신경섬유의 이상유무를 확 인할 필요는 없다. 만약 진찰상 쇠약같은 운동징후가 보이면 신경과의사의 자문 후 전기진단검사가 도움이 된다(Table 4). 만약 증상이 없다고 해서 신경병이 없는 것은 아니다. 당뇨병성 말초신경병환자의 50% 이상 에서는 증상은 없지만 족부궤양의 위험이 있다. 그러므로 당뇨병환자에서는 증상의 유무를 떠나 항상 신경 병이 있는지 주의깊게 관찰해야 한다. 당뇨병성 말초신경병 통증의 진단기준은 Table 5와 같다.
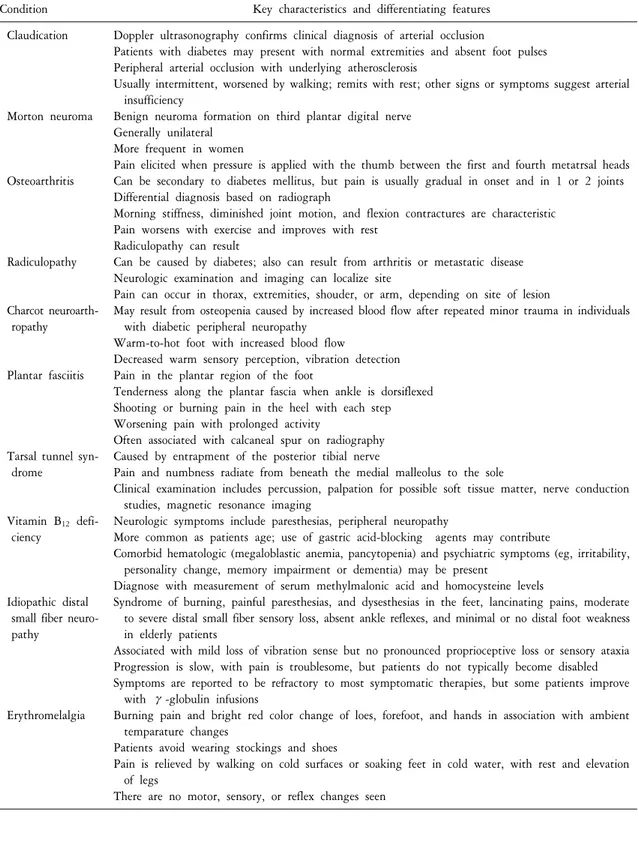
7. 감별진단
당뇨병환자를 진찰할 때 만약 환자가 발이 저리거나 불에 타는 것 같다고 하면 대부분 당뇨병성 말초신경
병이라고 진단하면 된다. 그러나 말초신경병과 감별진단해야 할 병으로는 파행(claudication), Morton 신경종,
골관절염, 신경근병증(radiculopathy), Charcot 신경관절병증, 족저근막염, 발목굴 증후군, 비타민 B
12부족, 원
Table 4. Neurologic testing for assessment of DPN
Test Description
Quantitative sensory testing
Nerve conduction velocity (NCV)
Computer-based, noninvasive, psychophysical semiobjective measure
Measures thermal (cold/warm) and vibration sensations and cold-or heat-evoked pain thresholds Not specific to peripheral nerve function
Requires specialized equipment
Useful to exclude other causes of neuropathy Depressed NCV usually indicates demyelination NCV diminishes gradually in DPN
Changes in NCV are related to glycemic control
Changes on NCV do not correlate with onset or severity of DPNP or other clinical symptoms Insensitive to pathologic changes associated with DPNP
DPN: diabetic peripheral neuropathy, DPNP: diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain.
Table 5. Key elements in diagnosis of DPNP Estabish diagnosis of DM or IGT
2-hour OGTT>200 mg/dL for diabetes and 140∼199 mg/dL for IGT Estabish presence of neuropathy
Use validated questionnaires (NPQ, BPI-DPN, MNSI)
Use simple, handheld screening devices (10-g monofilament, 128-Hz tuning fork) Assess pain characteristics
Distal, symmetrical
Numbness, tingling vs burning, aching, throbbing pain
Spontaneous pain (continuous or intermittent) vs stimulus-evoked pain Rule out nondiabetic causes for neuropathy and/or pain
Metastatic disease Infection Toxic substances
BPI-DPN: brief pain inventory for diabetic peripheral neuropathy, DM: diabetes mellitus, DPN: diabetic peripheral neuropathy, DPNP: diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain, IGT: impaired glucose tolerance, MNSI: Michigan neuropathy screening instru- ment, NPQ: neuropathic pain questionnaire, OGTT: oral glucose tolerance test.
인불명의 원위 소섬유 신경병 및 홍색사지통증(erythromeralgia) 등이 있다(Table 6).
8. 동반질병
당뇨병성 말초신경병은 당뇨병성 망막병(retinopathy), 우울증, 수면장애, 진행성 근쇠약, 및 족부궤양 등과 잘 동반된다. 특히 당뇨병성 말초신경병은 망막병 및 신장병과 동반이 많다. 신경병 통증이 있으면 수면장 애, 우울증 및 일상생활에 여러 가지 장애가 생긴다. 따라서 신경병 외에 동반되는 많은 질환도 다 같이 관리할 필요가 있다.
9. 삶의 질
다른 만성 통증과 마찬가지로 당뇨병성 말초신경병에서 통증이 생기면 감정반응, 활력, 운동력 및 수면
등에 다양한 장애가 생겨 삶의 질이 떨어진다. 또한 당뇨병성 말초신경병에서는 발병 초기부터 감각장애가
생겨 족부궤양이 잘 생긴다. 특히 40세 이상되는 당뇨병 환자의 7.7%에서 궤양이 생긴다. 따라서 발을 잘
Table 6. Differential diagnosis: common pain syndromes similar to diabetic peripheral neuropathy pain
Condition Key characteristics and differentiating features
Claudication
Morton neuroma
Osteoarthritis
Radiculopathy
Charcot neuroarth- ropathy
Plantar fasciitis
Tarsal tunnel syn- drome
Vitamin B
12defi- ciency
Idiopathic distal small fiber neuro- pathy
Erythromelalgia
Doppler ultrasonography confirms clinical diagnosis of arterial occlusion
Patients with diabetes may present with normal extremities and absent foot pulses Peripheral arterial occlusion with underlying atherosclerosis
Usually intermittent, worsened by walking; remits with rest; other signs or symptoms suggest arterial insufficiency
Benign neuroma formation on third plantar digital nerve Generally unilateral
More frequent in women
Pain elicited when pressure is applied with the thumb between the first and fourth metatrsal heads Can be secondary to diabetes mellitus, but pain is usually gradual in onset and in 1 or 2 joints Differential diagnosis based on radiograph
Morning stiffness, diminished joint motion, and flexion contractures are characteristic Pain worsens with exercise and improves with rest
Radiculopathy can result
Can be caused by diabetes; also can result from arthritis or metastatic disease Neurologic examination and imaging can localize site
Pain can occur in thorax, extremities, shouder, or arm, depending on site of lesion
May result from osteopenia caused by increased blood flow after repeated minor trauma in individuals with diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Warm-to-hot foot with increased blood flow
Decreased warm sensory perception, vibration detection Pain in the plantar region of the foot
Tenderness along the plantar fascia when ankle is dorsiflexed Shooting or burning pain in the heel with each step Worsening pain with prolonged activity
Often associated with calcaneal spur on radiography Caused by entrapment of the posterior tibial nerve
Pain and numbness radiate from beneath the medial malleolus to the sole
Clinical examination includes percussion, palpation for possible soft tissue matter, nerve conduction studies, magnetic resonance imaging
Neurologic symptoms include paresthesias, peripheral neuropathy
More common as patients age; use of gastric acid-blocking agents may contribute
Comorbid hematologic (megaloblastic anemia, pancytopenia) and psychiatric symptoms (eg, irritability, personality change, memory impairment or dementia) may be present
Diagnose with measurement of serum methylmalonic acid and homocysteine levels
Syndrome of burning, painful paresthesias, and dysesthesias in the feet, lancinating pains, moderate to severe distal small fiber sensory loss, absent ankle reflexes, and minimal or no distal foot weakness in elderly patients
Associated with mild loss of vibration sense but no pronounced proprioceptive loss or sensory ataxia Progression is slow, with pain is troublesome, but patients do not typically become disabled Symptoms are reported to be refractory to most symptomatic therapies, but some patients improve
with γ-globulin infusions
Burning pain and bright red color change of loes, forefoot, and hands in association with ambient temparature changes
Patients avoid wearing stockings and shoes
Pain is relieved by walking on cold surfaces or soaking feet in cold water, with rest and elevation of legs
There are no motor, sensory, or reflex changes seen
관리하는 것도 삶의 질을 유지하는데 아주 중요하다. 결국 신경병 통증과 동반된 다양한 증상을 의사와 환자가 서로 도와가며 적극적으로 해결하도록 노력해야 신경병 통증환자의 삶의 질이 개선될 것이다.
결 론
당뇨병성 말초신경병 환자를 잘 치료하기 위해서는 이 병의 임상을 잘 알고 적극적으로 치료하면서 동반 된 다양한 불편함도 같이 관리해서 삶의 질을 높이도록 노력해야 한다. 임상에서 잘 알아야 할 중요 사항으 로는 첫째 당뇨병환자에서 생기는 신경병은 모두 당뇨병만의 의한 것이 아니라 다른 원인에 의한 신경병도 있다, 둘째 당뇨병성 말초신경병 환자의 50% 이상에서는 증상이 없을 수 있다, 셋째 신경병 증상 없어도 족부궤양의 위험은 아직도 높다, 넷째 당뇨병성 말초신경병에서는 의학적 및 심리적 동반질병이 많다, 다섯 째 당뇨병성 말초신경병의 증상에 대해선 다양한 치료법이 있다, 여섯째 신경병뿐만 아니라 동반질병을 잘 관리하기 위해선 당뇨병과 동반된 합병증에 대한 꾸준한 교육이 필요하다 등이 있다.
참고문헌
1. Benbow SJ, Wallymahmed ME, Macfarlane IA. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy and quality of life. Q J Med 1998;91:733-37.
2. Galer BS, Gianas A, Jensen MP. Painful diabetic polyneuropathy: epidemiology, pain description, and quality of life. Diabetes Research Clinical Practice 2000;47:123-28.
3. Castillo JLDIR, Sosa JJS, Santiago PB, Rojas TLA. Quality of life patients with diabetic neuropathy. Invest Educ Enferm 2005;
23:30-43.
4. Argoff CE, Cole BE, Fishbain DA, Irving GA. Diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain: clinical and quality-of-life issues. Mayo Clin Proc 2006;81:S3-11.
5. Currie CJ, Poole CD, Woehl A, Morgan CL, Cawley S, Rousculp MD, et al. The health-related utility and health-related quality of life of hospital-treated subjects with type 1 or type 2 diabetes with particular reference to differing severity of peripheral neuropathy. Diabetologia 2006;49:2272-80.
6. Jensen MP, Chodroff MJ, Dworkin RH. The impact of neuropathic pain on health-related quality of life. Neurology 2007;68:1178-82.
7. Happich M, John J, Stamenitis S, Clouth J, Polnau D. The quality of life and economic burden of neuropathy in diabetic patients in Germany in 2002-results from the diabetic microvascular complications (DIMICO) study. Diabetes Research Clinical Practice 2008;81:223-30.
8. Van Schie CHM. Neuropathy: mobility and quality of life. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2008;24:S45-51.
9. Wrobel MP, Szymborska-Kajanek A, Wystrychowski G, Biniszkiewicz T, Sieron-Stoltny K, Sieron A, et al. Impact of low frequency pulsed magnetic fields on pain intensity quality of life and sleep disturbances in patients with painful diabetic polyneuropathy. Diabetes & Metabolism 2008;34:349-54.
10. Wu SC, Wrobel JS, Armstrong DG. Assessing the impact of pharmacologic intervention on the quality of life in diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia. American Academy Pain Med 2007;8:S33-42.
11. Van Acker K, Bouhassira D, De Bacquer D, Weiss S, Matthys K, Raemen H, et al. Prevalence and impact on quality of life of peripheral neuropathy with or without neuropathic pain in type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients attending hospital outpatients clinics. Diabetes & Metabolism 2009;35:206-13.