76
•교신저자:손환철, 서울대학교 보라매병원 비뇨기과 서울시 동작구 신대방동 425 우 156-752 Tel: 02-870-2391, Fax: 02-870-3863 E-mail: volley@snu.ac.kr
Received: March 2, 2010 Accepted: March 30, 2010
*이 연구는 서울대학교 보라매병원 2006년 임상공동연구 (연구번호: 03-2006-1)의 지원으로 이루어진 것임.
흰쥐 진피에 주입된 인간 무세포 진피 조직의 효과
1서울대학교 의과대학 비뇨기과, 2서울대학교 보라매병원 내과, 3서울대학교 보라매병원 비뇨기과
장진석
1∙고동우
1∙이한이
1∙오윤규
2∙손환철
1,2[Abstract]
The Effects of Human Acellular Dermal Matrix Injected into Mouse Dermis Jin Suk Chang 1 , Dong Woo Ko 1 , Hahn-Ey Lee 1 , Yun Kyu Oh 2 , Hwancheol Son 1,3
From
1the Department of Urology, Seoul National University College of Medicine and
2the Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Boramae Hospital and
3the Department of Urology, Seoul National University Boramae Hospital, Seoul, Korea
Purpose: Soft tissue augmentation using the injectable human acellular dermal matrix is widely used in Opthamology and Otorhinolaryngology. We performed this study to determine the efficacy and safety of injectable human acellular dermal matrix as a bulking agent, which may be applied to vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) or urinary incontinence later on.
Materials and Methods: 0.2ml of normal saline and 0.05, 0.1 and 0.2ml of human acellular dermal matrix were injected into the dermis of the back skin of mouse. At 1, 2, 4, 8 and 12weeks after injection, the volume changes, the histologic changes and the adverse effects were evaluated.
Results: In the mouse receiving injections, over 64% of the volume was maintained at 12weeks. The volume change was proportionate to the injected volume of injectable human acellular dermal matrix (p<0.05). After 8weeks, the volume change was stabilized. No inflammatory reaction was noticed in the mouse.
Conclusions: The injectable human acellular dermal matrix is effective and safe for augmentation of soft connective tissue. Long term follow-up experiment should be required to prove its usefulness in the treatment of urinary incontinence or VUR as a bulking agent. (Korean J UTII 2010;5:76-81)
Key Words: Injection, Bulking agent, Vesicoureteral reflux, Urinary incontinence
서 론
소아의 요로감염에 있어 방광요관역류는 주요한
원인의 하나이다.1 최근 소아의 방광요관역류에서 subureteral transurethral injection (STING)은 1차 치료 로 시행되고 있으며 다양한 주입물질이 사용되고 있다.2-3 또한 여성 복압성 요실금의 치료에도 슬링 수술과 함께 bulking agent 주입요법이 인정되고 있 으나4-5 새로운 물질 개발을 위한 연구는 부족한 실 정이다. 다른 의학 분야에서는 연조직 복원물질 주 사를 이용한 연부조직 증강을 안면미용성형 또는 다양한 재건 수술에 적용시켜 그 효과와 부작용이 보고되고 있고,6-9 비뇨기과 분야에서도 음경확대 등에서 연조직 증강을 이용한 조직 내 주사 치료의
Table 1. Weight change of mouse according to each week
Weights (mg) 1week 2weeks 4weeks 8weeks 12weeks
Base 34.3±0.9 34.7±1.0 34.1±0.9 34.7±1.0 35.6±0.8
Tissue extraction 36.1±1.3 37.9±1.8 39.2±1.9 42.1±1.7 42.9±2.5
Table 2. Volume change of injectable human acellular dermal matrix according to each week
Injection Volume 1week 2weeks 4weeks 8weeks 12weeks
N/S 0.2ml Base 105.3±38.6 107.1±28.1 74.5±31.3 88.0±24.9 184.0±26.0
I.H.A.D.M 0.5ml
Base 27.9±13.5 21.2±6.5 27.7±9.4 24.3±11.5 21.1±7.9
Extraction 11.4±10.8 9.3±3.3 12.1±3.0 10.5±6.3 7.9±6.8 Fixation 12.4±6.7 8.2±3.9 11.0±4.3 8.6±5.3 7.7±7.0
Base 51.5±11.9 44.2±9.2 48.5±11.9 49.9±14.8 46.1±14.5
I.H.A.D.M 1.0ml Extraction 32.9±13.5 17.9±3.4 24.8±10.7 22.1±5.2 25.2±7.1 Fixation 37.5±13.8 19.5±2.91 23.5±9.8 14.5±6.3 25.3±9.9
Base 163.3±49.6 196.6±49.4 199.7±48.5 180.2±55.6 154.2±36.5
I.H.A.D.M 2.0ml Extraction 72.3±35.6 33.4±11.1 100.9±43.4 58.4±36.5 62.3±23.7 Fixation 62.0±27.0 41.6±21.6 49.6±20.4 35.9±23.1 40.0±14.9 I.H.A.D.M: injectable human acellular dermal matrix
효과와 안전성에 대해 보고되고 있다.10-13
본 연구에서 이용한 분말화시킨 인간 무세포 진피 조직 (injectable human acellular dermal matrix)은 인체 조직을 동결 건조하여 분말 형태로 만든 주사용 연 조직 복원물질 (injectable soft tissue replacement materials)로 collagen, elastin, proteoglycans와 같은 조 직의 활성 요소를 모두 갖추고 있으면서, 조직 자체 를 이식하는 것에 비해 조직손상이 거의 없어 최근 여러 분야에 사용되고 있다.14-15 이번 연구에서 쥐의 진피에 분말화 무세포 진피 조직을 주입하여 이의 부피변화 관찰을 통해 주입물질의 안정성에 대해 조 사하고자 하였다.
대상 및 방법
흰쥐 50마리를 5군 (1주, 2주, 4주, 8주, 12주)으로 나누어 zoletil 0.1ml와 rumpun 0.1ml, 식염수 1ml를
섞은 마취제를 0.1ml씩 흰쥐 복강 내 주사하여 마취 하였다. 매주 무게를 잰 후 분말화 무세포 진피 조 직 450mg을 재수화하기 위하여 1% lidocaine 1ml와 생리식염수를 2ml를 섞어 총 3ml가 되게 혼합하였 다. 이후 마취된 흰쥐의 털을 깎고 척추를 중심으로 왼쪽 윗부분에는 생리식염수를 0.2ml 삽입하였고 오 른쪽 윗부분에는 분말화 무세포 진피 조직 0.05ml, 오른쪽 아랫부분에는 분말화 무세포 진피 조직 0.1ml, 왼쪽 아랫부분에는 분말화 무세포 진피 조직 0.2ml를 주입한 후 부풀어 오른 초기 주입부피를 측 정하였다 (Fig. 1).
해당 주 (1주, 2주, 4주, 8주, 12주)째 부풀어 오른 부분에 대한 겉보기 부피를 먼저 측정한 후 생리 식염수와 분말화 무세포 진피 조직을 주입한 부분 들이 모두 포함되도록 등 부위의 피부 층을 분리하 여 조직을 채취한 후 4% paraformaldehyde 용액에 담구어 고정시킨 다음 고정부피를 측정하였다. 병리
Fig. 1. Injectable human acellular dermal matrix was injected into the dermis of the back skin of mouse.
(%) 100
80
60
40
20
0
Base 1 2 4 8 12 (week)
0.05ml 0.1ml 0.2ml
Fig. 2. External volume change according to each week.
(%) 100
80
60
40
20
0
Base 1 2 4 8 12 (week)
0.05ml 0.1ml 0.2ml
Fig. 3. Fixation volume change according to each week.
조직검사는 통상적인 포르말린 고정 후 파라핀 포 매 후 4장의 연속 절편을 시행하였다. Hematoxylin 및 eosin (H&E) 염색을 시행하여 염증 반응, 이물 반응 및 섬유화 정도를 관찰하였다.
통계 프로그램은 SPSS 12.0을 사용하였고 각 군 및 각 주간의 부피 변화 차이를 검증하기 위해 student t-test를 사용하였고 p값이 0.05 미만을 통계 적으로 의미 있는 것으로 간주하였다.
결 과
주입 직후와 조직 채취 전 측정한 쥐의 무게 변 화는 표 1과 같다. 주입 직후 초기 용적은 주입한 생리 식염수 및 분말화 무세포 진피 조직 양에 비 례하였다 (Table 2). 겉보기 부피 분율 및 고정 부피 분율 모두 주입 직후부터 1주째까지만 통계적으로 유의하게 감소하였고 이후 용적 변화는 통계적으로 유의하지 않았다. 고정부피 분율은 8주째에 초기 용 적의 19∼35%로 감소하였고 12주째에 초기 용적의 25∼54%로 감소하였다. 겉보기 부피 분율은 8주째 에 초기 용적의 32∼44%로 감소하였고 12주째에 초기 용적의 40∼54%로 감소하였다. 8주 이후에는 오히려 용적이 증가하여 12주째 고정부피 용적 분 율은 8주에 비해 39% 증가, 겉보기 부피분율은 10% 증가하였다. 겉보기부피 분율 및 고정부피 분 율 모두 주입한 분말화 무세포 진피 조직 양에 비례 하는 경향이 관찰되었고 이는 0.1ml와 0.2ml 주입군
에서만 통계적으로 유의 하였다 (p<0.05)(Fig. 2,3).
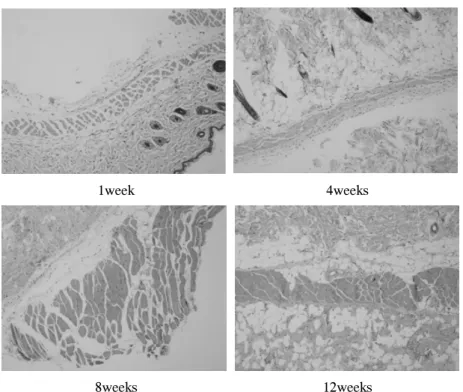
1, 2, 4, 및 8주째 조직학적 검사를 시행하였고 H&E 염색에서 모든 군에서 염증 반응과 이물반응 및 섬유화는 관찰되지 않았다 (Fig. 4).
고 찰
소아의 방광요관역류에서 요관 점막하 주사요법은 기존의 요관방광문합술 등의 수술적 치료에 비해 덜 침습적인 방법으로 고안되었으며 1984년 O'Donnell 과 Puri가 polytetrafluoroethylene (TeflonⓇ)을 사용한 것이 시초이다.16 이후 collagen, polydimethylsiloxane (MacroplastiqueⓇ), Dextranomer / hyaluronic acid
1week 4weeks
8weeks 12weeks
Fig. 4. No inflamatory reaction was noticed in the mouse until 12weeks after injection on the H&E stain (x40).
copolymer (DefluxⓇ) 등 다양한 물질을 이용한 주사 요법이 이루어지고 있지만 이상적인 bulking agent에 대한 논의는 계속되고 있는 실정이다.17-18
한편 여성의 복압성 요실금에서 중부요도 슬링수 술은 1차 치료로 시행되고 있으며 최근 들어 bulking agent 주사요법에 의한 치료도 시도되고 있다.17 이 는 요도 및 방광목에 bulking agent를 주사하여 출구 저항을 증가시켜 요실금을 감소시키는 방법으로 슬 링수술에 비해 교정의 성공률은 다소 떨어지나18 요 도 및 질의 미란, 감염, 지속적 배뇨곤란 등의 부작 용은 적은 것으로 보고되고 있다.19-22 현재 주사제제 로 사용되는 물질로는 polytetrafluoroethylene, silicon particle, carbon beads, collagen 등이 있고 최근 들어 재생의학을 근간으로 한 연골세포, 근육세포, 줄기 세포 등을 이용한 연구도 시행되고 있으나 아직 이 론은 확립되지 않은 상태이다.
연부조직 확대술을 위한 이상적인 주입물질의 조 건으로는 무독성, 생체적합성, 불이동성, 비항원성, 최소 국소 염증성 등을 생각할 수 있다.5 이번 연구
에서 사용한 분말화 무세포 진피 조직은 인체 조직 을 동결 건조하여 분말 형태로 만든 주사용 연조직 복원물질이다. 분말화 무세포 진피 조직은 이식 후 세포외 단백질 기질을 제공하므로 섬유아세포와 같 은 자가 세포 침투 및 이동이 가능하여 환자 본인 의 조직으로 생착되고 면역 반응의 원인이 되는 세 포를 모두 제거하였기 때문에 이식 후 면역거부 반 응이 발생하지 않는다고 알려져 있다.14-15 또한 이식 후 경화현상이 일어나지 않고 지속 효과가 우수하 며 주사용으로 제조하였으므로 비수술적인 방법으 로 조직 손상 없이 주입이 가능하다는 장점이 있다 고 보고되어 있다.14-15
Chen 등14은 분말화 무세포 진피 조직을 이용한 주사용 지지체로 이용한 지방조직의 재생에 대한 연구를 보고 하였다. 배양 후 1, 3주에 전자주사 현 미경으로 배양분말화 무세포 진피 조직 표면에 증 식된 지방전구세포를 확인할 수 있었고 Oil-red-O 염색으로 지방세포로의 분화를 확인할 수 있어 분 말화 무세포 진피 조직과 지방전구세포가 결합한다
면 연부 조직의 재생과 이식 후 부피유지에 적합한 주사용 연부조직 대체물질로 이용될 수 것으로 주 장하였다. 이번 연구에서는 분말화 무세포 진피 조 직을 흰쥐의 진피에 주입한 후 해당 주 (1주, 2주, 4 주, 8주, 12주)에 용적변화 및 조직변화를 관찰하였 다. 주입 초기용적이 8주까지 감소하지만, 8주 이후 12주까지 그 부피가 안정됨을 확인하였다. 부피증가 가 충분하지 않은 경우, 최소 8주 이상의 안정화 기 간 이후 추가적인 주입을 고려할 수 있을 것으로 생각한다. 또한 병리 조직 검사 결과 피부 내 조직 과 심한 염증반응 등을 일으키지 않는 장점이 있어 서, 비교적 안전하게 사용할 수 있을 것으로 생각한 다. 이번 연구에서 겉으로 보이는 부피는 변화가 심 하여 1주째 비해 2주째 평균 40% 감소하였고 2주째 비해 4주째 평균 130% 증가하였으며 이후 부피는 유지되었다. 겉보기 부피가 고정부피에 비해 변화 양상이 심한 것으로 보아 주입되는 위치나 모양에 따라 부피 변화가 달라질 수 있음을 의미한다.
하지만 이번 연구의 한계점은 흰쥐를 이용한 단 기 실험이었기 때문에 실제 인체에 주입 후 확대 효과와 조직 변화에 대해서는 직접적인 적용을 하 는 것이 어렵다는 점이다. 좀 더 많은 임상경험과 증례보고를 통하여 인체 안정성에 대한 평가가 필 요하다고 생각한다. 또한 주입위치도 진피이므로, 요로계통의 조직을 이용한 연구도 추후 필요할 것 이라 생각한다. 또한 장기간의 연구를 통하여 장기 안정성에 대한 고려도 필요하다고 생각한다.
결 론
본 연구 결과 분말화 무세포 진피 조직은 흰쥐의 진피에 주사 후 부피 감소가 8주에 안정화 되면서 12주까지 용적을 유지하였고 염증 반응과 부작용은 관찰되지 않았다. 이에 분말화 무세포 진피조직은 향후 장기간의 연구가 지속된다면 방광요관역류 또 는 요실금에 사용할 수 있는 효과적인 연부조직주 사제로 이용을 고려할 수 있을 것으로 생각한다.