Vol. 15, No. 2, November, 2007
□ 원 저 □1)
서 론
말초성 안면신경 마비를 일으키는 원인에는 다른 기질적인 원인들이 들어나지 않는 편측성 말초성 안면 신경 마비인 벨마비(Bell's facial palsy), 이
책임저자 : 권순학, 경북대학교 의과대학 소아과학교실 Tel : 053)420-5704, Fax:053)425-6683 E-mail : shkwon@knu.ac.kr
성대상포진, 외상성 마비, 청신경 종양, 이하선 종 양, 당뇨병성 신경증 등이 있다1).
발생 기전에 대한 가설로는 바이러스에 의한 감 염, 허혈성 혈관질환이나 당뇨에 의한 혈관 장애, 유전적 요인, 자가면역반응 등이 생각되고 있으나 아직은 논란의 여지가 많다1, 2). 이런 여러 원인에 의해 안면신경의 수초에 대한 자가면역 반응과 염 증세포의 침윤 및 그에 따른 부종으로 탈수초 현상
말초성 안면신경마비에서 신경생리검사와 예후에 관한 상관성 연구
경북대학교 의과대학 소아과학교실
홍은희·김정미·권순학
= Abstr act =
Prognostic Value of Electrophysiologic Tests in Children with Facial Nerve Palsy
Eun Hui Hong, M.D., Jung Mi Kim, M.D. and Soon Hak Kwon, M.D.
Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
Purpose : This study was aimed to evaluate the value of electrophysiologic tests for determining prognosis in children with facial nerve palsy.Methods : We retrospectively analyzed 37 children diagnosed as the facial nerve palsy at the pediatric neurology clinic, Kyungpook National University Hospital from January 1, 2000 to March 31, 2007.
Results : A total of thirty seven children were involved in the study(male to female 21:16, and the mean age 87.5 months). Among those twenty one had electrophysiologic tests. As compared with the normal values, the amplitude decreased by 54.5%(0.6±0.5 mV) and the latency was prolonged by 11.0%(3.6±0.5 msec) in electroneurography(ENoG).
Early response(R1) was absent in 15 out of 21(71.4%) and ipsilateral response(R2) was absent in 19 children(90.5%). As compared with the children who had the decrease of amplitude 90% or less in ENoG, the children with the decrease of amplitude greater than 90% showed poor recovery(100% vs 60%, P<0.05) and longer duration of follow-up(43.7
±30.0 days vs 184.00±196.8 days, P<0.05). All children who had R1 and R2 responses in the Blink test were completely recovered from the illness, but they were not statisti- cally different from the other groups.
Conclusion : Decrease of amplitude in ENoG and responsiveness in the Blink test can be important prognostic determinants in children with facial nerve palsy, but further studies are needed.
Key Words : Facial nerve palsy, Electroneurography, Blink test
이 일어나서 신경 전도에 이상이 오는 것이 병인으 로 추정된다1). Austin 등3)에 의하면 스테로이드 치 료가 이러한 염증 및 부종을 줄임으로서 신경변성 억제와 증상 호전에 효과적이며 최근에는 여러 원 인 중에서 단순포진바이러스에 의한 감염이 주목을 받으면서 항바이러스 제제로 치료하여 좋은 결과를 보이고 있다4, 5).
벨마비의 경우 치료를 하지 않아도 자연경과에서 약 70%가 완전히 회복되는 것으로 알려져 있으며 스테로이드 등의 치료로 회복율이 더욱 증가되었으 나 안면신경의 마비라는 특성으로 인해 병의 예후 는 환자의 사회적인 대인관계에 크게 영향을 미치 게 되는데 소아과를 찾는 벨마비의 환자들의 경우 그 연령이 대부분 사춘기 이전이기 때문에 환자의 삶 전체에 큰 영향을 준다. 따라서 병의 진단 못지 않게 병의 예후를 예측하고 적절한 치료방법을 선 택하는 것이 중요하다.
예후예측 인자들 중 신경생리검사는 신경 및 근 육의 변화를 객관적으로 기록할 수 있어 신경손상 에서 예후를 결정하거나 치료를 선택하는데 도움을 주는 것으로 알려져 있으나 국내 특히 소아에서의 연구는 미미한 상태이다.
이에 저자들은 2000년 1월부터 7년간 경북대학 교병원 소아과에서 말초성 안면신경마비로 진단받 은 37명의 환아를 대상으로 하여 신경생리검사를 중심으로 임상경과 및 예후와의 관계를 후향적으로 분석하여 보았다.
대상 및 방법
2000년 1월부터 2007년 3월까지 7년간 경북대학 교병원 소아과에서 임상적 특성 및 신경생리검사 (ENoG: electroneurography 및 Blink test)를 근 거로 말초성 안면신경마비로 진단받은 37명을 대상 으로 의무기록 및 전화확인을 통해 후향적 조사를 시행하였다.
치료 제제로는 경구 스테로이드 prednisolone 1 mg/kg씩 기본적으로 5일간 사용하였으며 5일째 치 료가 되지 않는 경우에는 추가적으로 기간을 늘려
사용하였다. Ramsay-Hunt syndrome로 진단된 3 명은 추가적으로 항바이러스 제제 acyclovir(Zoy- rexⓇ)을 5 mg/kg씩 8시간 단위로 1주일간 정맥투 여 받았다.
치료 판정은 치료 후 경과 관찰기간이 최소한 3 개월 이상 지난 환자들로 제한하였으며 이후 다른 질병으로 진단된 환아들은 분석에서 제외시켰다. 치 료 성공여부는 이학적 검사상 전혀 문제점을 발견 하지 못하고 환자가 주관적으로 전혀 불편함을 못 느낄 정도로 호전된 경우를 완전 회복군, 이학적 검 사상 문제점이 발견되지 않으나 환자가 주관적으로 불편함을 호소하는 경우를 불완전 호전군, 이학적 검사에서도 뚜렷하게 문제점이 발견되는 경우를 비 호전군이라고 정의하고, 완전 회복된 경우만을 치료 가 성공한 군으로 정의하고 완전 회복 이외의 군은 치료가 실패한 군으로 정의하였다.
치료가 성공한 군과 실패한 군에서의 각 항목에 대한 비교를 통해 각 항목이 치료의 성공에 미치는 통계학적 의미를 조사하였으며 ENoG에서 정상측 에 비해 amplitude 감소정도[100%-(환측 amplitu- de/정상측 amplitude)×100%]를 90%기준으로 나 누어 비교하였고 latency 지연정도[100%-(환측 la- tency/정상측 latency)×100%]를 10%기준으로 비 교하였으며 Blink test에서 early response(R1) 및 ipsilateral late response(R2)의 유무에 따라 나누 어 치료성공과의 연관성을 조사하였다.
모든 수치는 평균±표준편차 형식으로 표시하였 고 모든 통계는 SPSS for windows(version 12.0, SPSS inc., Chicago, IL)을 이용하였으며 통계학적 유의성에 대한 기준은 P-value<0.05로 정하였으며 빈도수에 대한 비교는 교차비교분석을 이용하였다.
결 과
대상환자는 남자 21명(56.8%), 여자 16명(43.2%), 평균나이 87.5±58.6개월이었고 최저연령 7개월, 최 고연령이 175개월이었으며 환측은 우측이 26명(70.2
%), 좌측이 11명(19.8%)로 우측이 많았다. 이들 중 33명은 스테로이드 경구 투여하였고 Ramsay-Hunt
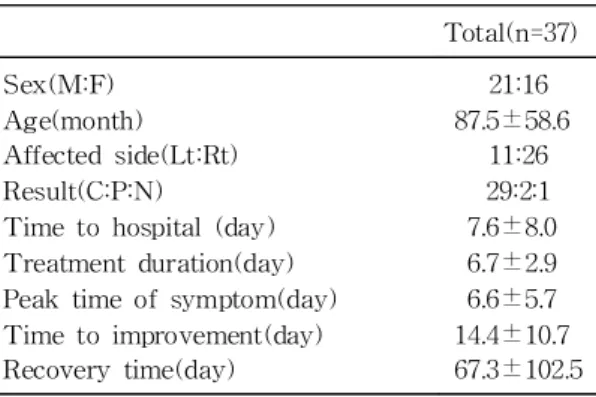
syndrome으로 진단된 3명은 acyclovir을 투여하였 으며 1명은 임의로 투약하지 않았으며 평균 치료기 간은 6.7±2.9일 이었다. 내원하기까지 걸린 평균 기간은 7.6±8.0일이었고 증상의 최고 악화까지 걸 린 기간은 평균 6.6±5.7일이었으며 호전되기 시작 하는데 걸린 기간은 14.4±10.7일이었다. 회복 또는 추적관찰기간은 평균 67.3±102.5일 이었으며 32명 에서 최종경과 확인이 가능하였는데 완전회복이 29 명(90.6%)이었으며 부분회복은 2명(6.2%)이었고 1 명(3.1%)은 호전이 되지 않았다. 전체 환아중 19명 (51%)에서 상기도감염이 선행하였고 3명(7.1%)은 재발성이었다(Table 1).
신경생리검사는 21명에서 시행되었는데 ENoG에 서는 환측의 amplitude가 정상측에 비해 평균 54.5
% 감소되어 0.6±0.5 mV였으며, latency는 정상측 에 비해 평균 11.0% 지연되어 3.6±0.5 msec 이었 다.
Blink test에서는 R1이 response가 없던 경우가 15명(71.4%)이었고 response가 있었던 6명은 정상 측에 비해 2.4±1.2 msec 지연되어 12.6±0.6 msec 이었으며 R2는 response가 없던 경우가 19명(90.5
%)이었고 response가 있었던 2명은 정상측에 비해 5.5±0.2 msec 지연되어 36.4±0.3 msec 이었다 (Table 2).
1) 완전 회복군과 불완전 회복군으로 나누어 비 교하였을 때, 불완전 회복군의 회복에 걸리는 시간
또는 추적관찰 종료 시점이 유의하게 길었다(58.8±
70.7일 vs 203.3±274.7일, P<0.05). Blink test에 서는 불완전회복군의 R1 및 R2가 모두 response가 없어, 완전 회복군에 비해 response가 없는 경우가 R1에서 68.4% vs 100%(P>0.05), R2에서 89.4%
vs 100%(P>0.05)로 높았으나 통계적 의의는 없었 다(Table 3).
2) ENoG에서 amplitude 가 90% 미만 감소된 군과 90% 이상 감소된 군의 임상양상 및 경과를 비교한 결과, 90% 이상 감소한 군에서 완전 회복율 이 유의하게 낮았으며(100% vs 60%, P<0.05), 내 원까지의 시간이 유의하게 길었고(5.0±3.6일 vs 14.6±10.5일, P<0.05), 회복 또는 추적 관찰기간이 유의하게 길었다(43.7±30.0일 vs 184.0±196.8일, P<0.05)(Table 4). 또한 amplitude가 90% 이상 감 소된 군에서 완전회복이 되는 경우는 통계적 유의 성은 없었으나 회복까지의 시간이 길었다(43.7±
30.0일 vs 123.3±60.3일, P>0.05)(Table 5).
Table 1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Patients
Total(n=37) Sex(M:F)
Age(month) Affected side(Lt:Rt) Result(C:P:N)
Time to hospital (day) Treatment duration(day) Peak time of symptom(day) Time to improvement(day) Recovery time(day)
21:16 87.5±58.6
11:26 29:2:1 7.6±8.0 6.7±2.9 6.6±5.7 14.4±10.7 67.3±102.5 Abbreviations : C, complete recovery; P, partial recovery; N, no recovery
Table 2. Electrophysiologic Tests(ENoG: electro- neurography, Blink test)
ENoG(n=22) Amp(mV) Diff-Amp*(mV) Diff-Amp†(%) Latency(msec) Diff-Latency‡(%) Blink test(n=21)
R1(msec) Diff-R1∫(msec) Abscent R1(n) R2(msec) Diff-R2∥(msec) Abscent R2(n)
0.6±0.5 0.7±0.5 54.5±28.1
3.6±0.5 11.0±9.0
12.6±0.6 2.4±1.2 15(71.4%) 36.4±0.3
5.5±0.2 19(90.5%)
*Diff-Amp(difference of amplitude, mV): amplitude of unaffected side amplitude of affected side.
†Diff-Amp(%): 100(amplitude of affected side/am- plitude of unaffected side)×100(%). ‡Diff-Latency (difference of latency, %) : 100(latency of affected side/latency of unaffected side)×100(%). ∫Diff-R1 (difference of R1): R1 of affected sideR1 of unaf- fected side. ∥Diff-R2(difference of R2): R2 of af- fected sideR2 of unaffected side. Abbreviations : Amp, amplitude; R1, early response; R2, ipsilateral late response
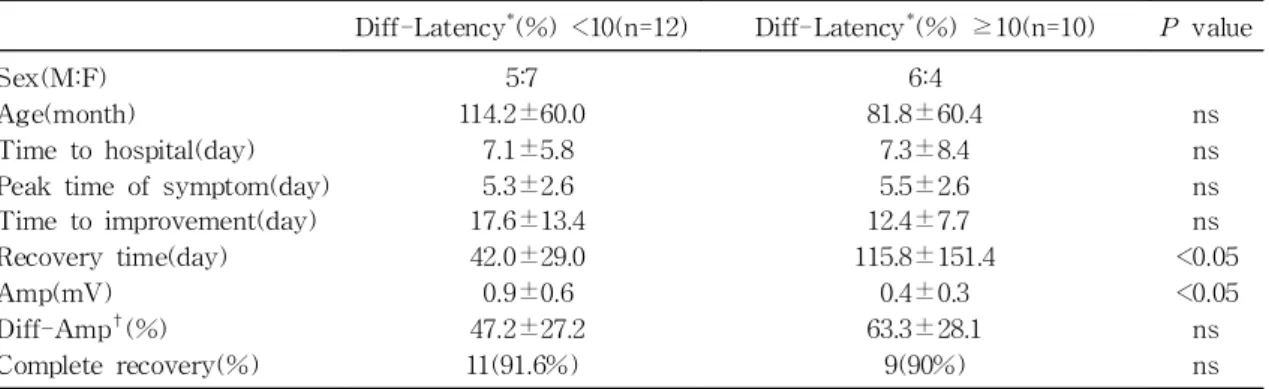
3) 신경전도검사에서 latency가 10% 미만 지연 된 군과 10%이상 지연된 군의 임상양상 및 경과를 비교한 결과 10% 이상 지연된 군에서 회복 또는 추적관찰 종료시점이 유의하게 길었고(42.0±29.0일 vs 115.8±151.4, P<0.05), amplitude가 유의하게 낮았으나(0.9±0.6 mV vs 0.4±0.3, P<0.05), am- plitude 감소정도와는 상관관계가 없었으며(P>0.05) 완전회복율도 차이가 없었다(P>0.05)(Table 6).
4) Blink test에서는 R1 또는 R2에서 response
가 있었던 환아들은 모두 완전 회복이 되었다. Re- sponse가 있었던 군은 response가 없었던 군에 비 해 완전회복율이 R1에서 100% vs 86.6%(P>0.05), R2에서 100% vs 89.5%(P>0.05)로 높았으나 통계 적 유의성은 없었다(Table 7).
고 찰
말초성 안면신경마비 특히 벨마비의 예후 인자로 Table 4. Comparison between Group with Difference of Amplitude <90% and Group with Difference of Amplitude ≥90%
Diff-AMP* <90% (n=17) Diff-AMP* ≥90% (n=5)
P value
Sex(M:F)Age(month)
Time to hospital (day) Peak time of symptom(day) Time to improvement(day) Recovery time(day) Latency(msec) Diff-Latency†(%) Complete recovery(n)
8:9 103.9±58.6
5.0±3.6 4.9±2.6 15.1±11.8 43.7±30.0 3.5±0.5 10.4±8.8 17(100%)
3:2 84.2±73.8 14.6±10.5 7.3±0.6 16.0±9.9 184.0±196.8
3.7±0.3 13.5±11.1
3(60%)
ns
<0.05 ns ns
<0.05 ns ns
<0.05
*Diff-Amp(difference of amplitude, %) : 100(amplitude of affected side/amplitude of unaffected side)×100 (%). †Diff-Latency(difference of latency, %) : 100(latency of affected side/latency of unaffected side)×
100(%). Abbreviation : ns, not significant
Table 3. Comparison between Group with Complete Recovery and Group with Incomplete Recovery Complete recovery(n=29) Incomplete recovery(n=3)
P value
Sex(M:F)Age(month)
Time to hospital(day) Peak time of symptom(day) Time to improvement(day) Recovery time(day)
16:13 92.2±57.9
7.8±8.5 6.4±6.1 14.8±11.3 58.8±70.7
2:1 84.3±83.4 13.0±7.0
9.0±1.4 13.0±2.8 203.3±274.7
ns ns ns ns
<0.05 Complete recovery(n=20) Incomplete recovery(n=2)
P value
Amp(mV)Diff-Amp*(mV) Diff-Amp†(%) Absent R1(n) Absent R2(n)
0.7±0.5 0.6±0.5 50.5±26.1 13(68.4%) 17(89.4%)
0.1±0.1 0.9±1.1 95.0±7.1 2(100%) 2(100%)
ns ns ns ns ns
*Diff-Amp(difference of amplitude, mV): amplitude of unaffected sideamplitude of affected side. †Diff- Amp(difference of amplitude, %): 100(amplitude of affected side/ amplitude of unaffected side)×100(%) Abbreviations : Amp, amplitude; R1, early response; R2, ipsilateral late response; ns, not significant
는 완전마비의 유무, 회복되는 시기, 환자의 연령, 등골반사 및 눈물분비의 이상 유무, 후이개 통증의
유무, 당뇨병의 유무 및 신경생리검사의 결과 등이 고려되고 있다2, 6). 질병의 특성상 예후를 판단하는 Table 7A. Complete Recovery Rate According to R1 on Blink Test
Presence of R1(n=6) Absence of R1(n=15)
P value
Complete recovery(n) 6(100%) 13(86.6%) ns
Abbreviations : R1, early response; ns, not significant
Table 7B. Complete Recovery Rate According to R2 on Blink Test
Presence of R2(n=2) Absence of R2(n=19)
P value
Complete recovery(n) 2(100%) 17(89.5%) ns
Abbreviations : R2, ipsilateral late response; ns, not significant
Table 6. Comparison between Group with Difference of Latency <10% and Group with Difference of Latency ≥10%
Diff-Latency*(%) <10(n=12) Diff-Latency*(%) ≥10(n=10)
P value
Sex(M:F)Age(month)
Time to hospital(day) Peak time of symptom(day) Time to improvement(day) Recovery time(day) Amp(mV)
Diff-Amp†(%) Complete recovery(%)
5:7 114.2±60.0
7.1±5.8 5.3±2.6 17.6±13.4 42.0±29.0 0.9±0.6 47.2±27.2 11(91.6%)
6:4 81.8±60.4
7.3±8.4 5.5±2.6 12.4±7.7 115.8±151.4
0.4±0.3 63.3±28.1
9(90%)
ns ns ns ns
<0.05
<0.05 ns ns
*Diff-Latency(difference of latency, %) : 100(latency of affected side/latency of unaffected side)×100(%)
†Diff-Amp(difference of amplitude, %) : 100(amplitude of affected side/amplitude of unaffected side)×
100 (%). Abbreviations : Amp, amplitude; ns, not significant
Table 5. Comparison between Completely Recovered Group with Difference of Amplitude <90% and Completely Recovered Group with Difference of Amplitude ≥90%
Diff-AMP* <90%(n=17) Diff-AMP* ≥90%(n=3)
P value
Sex(M:F)Age(month)
Time to hospital(day) Peak time of symptom(day) Time to improvement(day) Recovery time(day) Latency(msec) Diff-Latency†(%)
8:9 103.9±58.6
5.0±3.6 4.9±2.6 15.1±11.8 43.7±30.0 3.5±0.5 10.4±8.8
2:1 78.3±63.5 14.6±13.3 7.3±0.0 16.3±12.1 123.3±60.3 3.7±0.3 18.0±8.0
ns
<0.05 ns ns ns ns ns
*Diff-Amp(difference of amplitude, %) : 100(amplitude of affected side/amplitude of unaffected side)×100 (%). †Diff-Latency(difference of latency, %) : 100(latency of affected side/latency of unaffected side)×
100(%). Abbreviation : ns, not significant
것은 치료에서 가장 중요한 부분이나 아직까지 정 확히 예후를 예측할 수 있는 단일 인자 혹은 단일 검사방법은 없는 상태이다.
여러 신경생리검사 중 ENoG는 신경의 변성정도 를 정량적으로 표시할 수 있는 검사법으로 신경 및 근육의 변화를 객관적으로 기록할 수 있으며 말초 성 안면신경손상에서 예후판정 및 치료를 선택하는 데 도움을 주는 것으로 알려져 있다7-9).
ENoG는 첫 3일에는 신경부종이 충분히 진행되 지 않아 위양성으로 보일 수 있으며, 신경변성이 2 주에서 3주까지 진행할 수 있어 단일검사로 생리적 신경차단(neurapraxia), 축삭절단(axonotmesis), 신 경절단(neurotmesis)은 구분할 수 없기 때문에 반 복 혹은 연속 검사가 추천된다. Amplitude의 감소 정도가 신경변성의 정도에 직접적인 상관관계를 가 지며, 여러 신경생리 검사들 중에서 말초성 안면신 경마비의 예후를 가장 정확히 예측하는 검사로 알 려져 있다8-10).
Esslen 등11)은 amplitude 감소정도에서 90%를 임계점이라 하였는데, 90% 이상 감소된 군 중 약 반수만이 회복되는 반면 90% 미만으로 감소된 경 우에는 모두 완전 회복되어 정상적인 안면신경기능 을 보여 준다고 하였으며, Fisch9)에 의하면 ampli- tude가 90% 이상 감소된 군을 1년간 추적 관찰한 결과 86%에서 불완전 회복하였다고 하였다. 또한 amplitude 감소정도가 심할수록 완전 회복율이 감 소하며 회복되기까지의 시간이 길어진다고 하였는 데, 특히 amplitude 감소정도가 98% 이상인 경우 에는 거의 회복 가능성이 없으며 회복이 되더라도 300일 이상의 많은 시간이 소요된다고 하였다13). 본 연구에서도 amplitude 감소정도를 90% 기준으로 하여 나누어 보았을 때 90% 미만 감소군이 100%
전원 완전회복이 된데 반하여 90%이상 감소된 군 의 60%만이 완전회복이 되어 유의한 차이를 보여 주었고 회복되는데 더 많은 시간이 소요되었으며, 90%이상 감소군의 내원까지의 시간이 유의하게 길 었는데 이는 amplitude가 감소된 만큼 신경의 변성 이 진행된 것에 의한 것으로 보인다. 특히 amplitude 가 100% 감소되어 0 mV였던 환아 1명은 진단 후
2년이 경과한 지금까지 호전이 없는 상태로, 진단당 시 ENoG 결과가 신경의 불가역적 완전 손상을 반 영했으리라 생각된다. 따라서 ENoG에서 amplitude 감소정도는 향후 회복 가능성을 예측하는 데 도움 을 주는 인자로 생각되며, 특히 90% 이상 감소하는 것은 향후 회복이 불완전 할 수 있음을 시사하는 소견이라 하겠다.
Qiu 등10)에 의하면 ENoG의 latency는 개인차가 크고 자극의 정도에 따라 차이가 크며 말초성 안면 신경마비의 예후와 관계가 적어 예후예측인자로서 부적합하다고 하였는데, 본 연구에서도 latency의 차를 10% 기준으로 나누어 비교하였을 때, 10%이 상 지연된 경우가 치료 및 회복기간이 길고 ampli- tude가 유의하게 낮았으나, 완전회복율 즉, 치료성 공율과는 유의한 상관관계가 없었다.
Lu 등14)에 의하면 Blink test는 성별, 환측, 나이 와 무관하게 R1이 평균 10 msec, R2가 평균 29 msec이나 개인적인 편차가 커서 절대치를 기준으 로 한 해석보다는, 동일 환자에서 정상측과의 차이 를 이용한 개체단위의 해석이 필요하다고 하였다.
또한 정상에서는 R1의 차는 1.2 msec, R2의 차는 5 msec를 넘지 않는데15) 본 연구에서 반응이 있었 던 경우는 R1이 평균 2.4 msec, R2가 평균 5.5 msec 지연되어 정상 기준치보다 지연되어 안면신 경마비에 부합하는 소견을 보였다.
Blink test와 말초성 안면신경마비의 예후와의 관계는 논란이 많으나, R1이 많이 지연되더라도 (delayed R1) R1이 존재하면(present R1) 예후가 양호한데 반해, R1이 없는 것(absent R1)은 나쁜 예후를 시사하며, 환측과 정상측의 차이가 예후와 유의한 관계를 갖는다고 하였다16-18). 본 연구에서는 R1 및 R2의 반응이 있었던 군에서는 완전회복율이 100%였으며, R1 및 R2의 반응이 없었던 군에서는 완전회복율이 각각 86.6%, 89.5% 였다. 그러나, 개 체수가 적어 통계적 유의성을 갖기에는 무리가 있 었다.
결론적으로 ENoG에서 amplitude가 90% 이상 감소한 군에서 완전 회복율이 유의하게 낮은 것으 로 보아 amplitude 감소정도는 말초성 안면신경마
비 환아에서 예후를 예측하는데 유용한 검사라 할 수 있으며 시간간격을 두고 연속적으로 시행한다면 경과를 예측하는데 더욱더 정확성을 가질 수 있을 것으로 사료된다. 또한 Blink test에서 반응이 있는 경우는 100% 완치율을 보여주어 완전회복을 예측 함에 유용할 것으로 생각되며 좀더 큰 규모의 연구 를 통해 Blink test의 예후 인자로서의 가치에 대한 재평가가 필요할 것으로 사료된다.
요 약
목 적 : 말초성 안면신경마비 환자에서 신경생리 검사의 예후 예측인자로서의 유용성을 알아보고자 시행하였다.
방 법 : 2000년 1월부터 2007년 3월까지 경북대 학교병원 소아과에서 말초성 안면신경마비로 진단 받은 37명을 대상으로 하여 의무기록 및 전화통화 를 통한 후향적 조사를 시행하였다.
결 과 : 대상환자의 남녀비는 21:16, 평균나이 87.5개월(7-175개월), 좌우비는 11:26이었고 내원까 지 기간, 최고악화시점, 스테로이드 및 acyclovir 투여기간, 호전시작시점은 각각 7.6±8.0, 6.6±5.7, 6.7±2.9, 14.4±10.7일이었다. 경과가 확인된 32명 의 환아들 중 완전회복은 29명(90.6%), 부분회복 2 명(6.2%) 및 1명(3.1%)은 호전이 없었다. 신경생리 검사는 21명에서 시행되었으며 ENoG에서 환측의 amplitude는 정상측에 비해 평균 54.5% 감소되어 0.6±0.5 mV, latency는 평균 11.0% 지연되어 3.6
±0.5 msec 이었다. Blink test에서 R1이 반응이 없었던 경우가 15명(71.4%), 반응이 있었던 6명은 2.4±1.2 msec 지연되었으며 R2가 반응이 없었던 경우는 19명(90.5%), 반응이 있었던 2명은 5.5±0.2 msec 지연되었다. ENoG에서 amplitude가 90% 미 만 감소된 군에 비해 90% 이상 감소한 군에서 완 전회복율이 유의하게 낮았으며(100% vs 60%, P<
0.05), 내원까지의 시간이 유의하게 길었고(5.0±3.6 vs 14.6±10.5, P<0.05) 회복 또는 추적 관찰기간 이 유의하게 길었다(43.7±30.0 vs 184.00±196.8, P<0.05). Blink test에서 R1 또는 R2의 반응이 있
었던 환아들은 모두 완전회복이 되었으나 반응이 없었던 군과의 통계적 유의성은 없었다.
결 론 : ENoG에서 amplitude 감소정도는 말초성 안면신경마비 환아에서 예후를 예측함에 있어 매우 유용한 것으로 생각되며 또한, Blink test에서 반응 이 있음은 완전회복을 예측하는 검사법이 될 수 있 을 것으로 생각된다. 그러나 보다 체계적이고 큰 규 모의 연구가 필요할 것으로 사료된다.
References
1) Roob G, Fazekas F, Hartung HP. Peripheral facial palsy: etiology, diagnosis and treatment.
Eur Neurol 1999;41:3-9.
2) Hydn D, Sandstedt P, dkvist LM. Prognosis in Bell's palsy based on symptoms, signs and laboratory data. Acta Otolaryngol 1982;93:407- 14.
3) Austin JR, Peskind SP, Austin SG, Rice DH.
Idiopathic facial nerve paralysis: a randomized double blind controlled study of placebo versus prednisolone. Laryngoscope 1993;103:1326-33.
4) Adour KK, Ruboyianes JM, VonDoersten PG, Byl FM, Trent CS, Quesenberry CP, et al.
Bell's palsy treatment with acyclovir and prednisolone compared with prednisolone alone:
a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial.
Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1996;105:371-8.
5) Diego JI, Prim MP, Sarriá MJ, Madero R, Gavilan K. Idiopathic facial paralysis:A rando- mized, prospective, and controlled study using single-dosed prednisolone versus acyclovir three times daily. Laryngoscope 1998;108:573-5.
6) Peitersen E. Bell's palsy:The spontaneous course of 2,500 peripheral facial nerve palsies of different etiologies. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 2002;549:4-30.
7) Smith IM, Maynard C, Mountain RE, Hamilton RB, Armstrong M, Murray JA. The prognostic value of facial electroneurography in Bell's pasly. Clin. Otolaryngol 1994;19:201-3.
8) Kanzaki J. Electrodiagnostic findings in the early stages of Bell's palsy and Ramsay- Hunt's syndrome. Acta Otolaryngol(Suppl) 1988;446:42-6.
9) Fisch U. Prognostic value of electrical tests in
acute facial paralysis. Am J Otol 1984;5:494-8.
10) Qiu WW, Yin SS, Stucker FJ, Hoasjoe DK.
Neurophysiological evaluation of acute facial paralysis in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhino- laryngol 1997;39:223-36.
11) Esslen E. Electromyography and electroneuro- graphy in facial nerve palsy. Birmingham : Aesculapious Publishing 1977:93-100.
12) Fisch U. Surgery for Bell's palsy. Arch Oto- laryngol Head Neck Surg 1981;107:1-11.
13) Dumitru D, Amato AA, Zwarts W. Electrodi- agnostic medicine. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Hanley
& Belfus,inc., 2002:677-80.
14) Lu Z, Tang X. Blink reflex: normal values and its findings on peripheral facial paralysis. Chin
Med J(Engl) 1996;109:308-12.
15) Oh SJ. Clinical electromyography: nerve con- duction studies. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: LWW.
com, 2003:400-4.
16) Ghonim MR, Gavilan C. Blink reflex: progno- stic value in acute peripheral facial palsy. ORL 1990;52:75-9.
17) Zhang S, Wang Y, Xu H. Prognostic value of blink reflex in patients with Bell's palsy.
Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi 1994;29:
155-7.
18) Mizukoshi K, Watanabe Y, Aso S, Asai M.
Prognostic value of blink test in patients with facial paralysis. Acta Otolaryngol(Suppl) 1988;
446:70-5.