J Health Tech Assess 2016;4(2):58-66 ISSN 2288-5811 Copyright © 2016 The Korean Association for Health Technology Assessment
서 론
우리나라의 국민의료비 중 약제비의 연평균 증가율(2000~
2012년)은 9.7%로 경제협력개발기구(Organization for Eco- nomic Co-operation and Development, 이하 OECD) 회원 국가의 연평균 증가율인 5.8%에 비해 성장률이 매우 빠르 며, 2012년 OECD 평균 국민의료비 중 약제비 비중인 15.7%
보다 높은 수준인 19.8%를 차지하고 있다.1) 우리나라의 건 강보험 약품비 지표로 살펴보았을 때, 2001년 4조 1804억 원 에서 2011년 13조 4230억 원으로 10년 만에 221% 증가하였 으며, 이는 동 기간 건강보험 진료비가 159% 증가한 속도에
비해 훨씬 빠르게 증가함을 보여준다.2)
이러한 건강보험 약품비의 증가 속도를 감소시키기 위해 보건복지부는 2006년 12월부터 ‘약제비 적정화 방안’을 시행 하여 왔으며, 약제비 적정화 방안은 선별등재목록 제도 도입 을 통해 신약의 임상적 유용성 및 경제성 평가, 그리고 가격 협상 방식을 도입하였다.3) 또한 경제성 평가를 활용한 기등 재약 목록정비 등 획기적인 약가 관리 방식을 포함하고 있 을 뿐 아니라, 의약품 사용량의 적정관리를 위해 약제적정성 평가 확대 및 도입을 포함하였다.
그럼에도 불구하고, 정부의 약제비 절감을 위한 적정화 방 안은 약제비 지출의 규모는 지속적으로 증가하고 건강보험 Review Article
JoHTA
A Roadmap to Contain Pharmaceutical Expenditures under the National Health Insurance System
Seong-Ok Kim
College of Pharmacy, Inje University, Gimhae, Korea
건강보험 약품비의 체계적 관리를 위한 로드맵 구축
인제대학교 약학대학
김 성 옥
Received November 20, 2016 Revised November 29, 2016 Accepted December 6, 2016 Address for Correspondence:
Seong-Ok Kim
College of Pharmacy, Inje University, 197 Inje-ro, Gimhae 50834, Korea Tel: +82-55-320-3457
Fax: +82-55-320-3940 E-mail: kimseongok@inje.ac.kr
The growth rate of pharmaceutical expenditures covered by the National Health Insurance had been rapidly growing and also its proportion among the health expenditures had been compara- tively high (29.15% in 2011). This study presented a roadmap to contain pharmaceutical expendi- tures under the National Health Insurance System composed of five agenda, which were initiated by the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) in the perspective of insurer in 2012. Five agenda com- posed of strengthening of the negotiation power of the insurer and diversification of risk sharing arrangement, global pharmaceutical budget system, reference pricing system, pharmaceutical ten- dering system, and public fund for orphan drugs, which were selected from the discussion among the staff in the NHIS. Then expert opinion survey were conducted to investigate stakeholers’ antici- pated impact of each 5 agenda with the criteria of pharmaceutical expenditure control, sustainablity and equity, efficiency, availability, accessibility, quality and health outcomes, satisfaction of consum- er and patient, and objective of pharmaceutical company (R&D and innovation). And anticipated in- troduction time of these agenda, policy compliance of stakeholders. 19 experts from academic, gov- ernment, pharmaceutical company, doctors, pharmacist and consumer and patient group. The roadmap to control pharmaceutical expenditures composed of 5 agenda initiated by the NHIS were presented in detail as result of experts’ opinion.
Key Words Pharmaceutical exmpenditure · Pharmaceutical tendering system · Orphan drug fund · Reference pricing system · Pharmaceutical budget · Risk sharing arrangement.
지출 중 약품비 비중도 30% 선에서 감소하지 않았다. 다만, 건강보험 약품비 증가율은 하락하는 추세를 보이다, 2009년 에 다시 상승세를 보이는 등의 안정적인 감소추세를 보여주 지는 못해 왔다.4) 이에 보건복지부는 2012년 4월 일괄약가 인하 조치를 단행하였으며, 그 결과로 건강보험약제비 비중 은 감소하였고 증가율도 마이너스 성장률을 보였다.5)
그러나 약가일괄인하 이후 정부는 개량신약 약가우대, 제 약산업 육성지원 특별법, 4대 중증질환 보장성 강화, 제약산 업 육성지원 5개년 종합계획, 복합제 개량신약 우대, 위험분 담제, 중증질환 보장성 강화 관련 약제 급여적용 확대, 신속 등재, 희귀질환 경제성평가면제, 허가특허연계 제네릭 우선 판매권 등의 제약산업 육성 정책을 약제비 적정화보다는 우 선순위에 두고 있는 행보를 보이고 있어, 건강보험약품비의 증가가 지속될 것으로 예상된다. 건강보험 약품비의 급속한 증가를 효과적으로 관리할 수 있는 체계적 관리 방안을 마 련하지 않을 경우, 건강보험 제도의 미래 지속가능성은 담보 하기 어려운 상황이다.
본 연구는 지난 2012년에 국민건강보험공단에서 보험자 의 관점에서 건강보험 보장성 80% 달성을 목표로 설정하고, 소요재원 추계 및 재원확보 방안까지 함께 제시한 종합플랜 을 계획하기 위해 설치된 국민건강보험쇄신위원회 활동의 일환으로 작성되었다.2,5) 국민건강보험쇄신위원회는 국민건 강보험공단의 각 분야별로 행동계획(action plan)을 수립하 는 것을 목적으로 보장성 강화를 위한 재원확보를 위해 필 요한 주요 내용으로 1) 지속가능한 건강보험 보장성 강화, 2) 소득 중심의 보험료 부과체계 단일화, 3) 평생 맞춤형 통 합 건강서비스 제공, 4) 급여결정 구조 및 진료비 청구・심 사・지급체계 합리화, 5) 노인장기요양보험 제도의 보완・
개선 방안, 6) 보건의료 공급체계 개선방안 등을 포함한 세 부실천계획을 수립하였다.6) 국민건강보험쇄신위원회의 세 부실천계획은 국민건강보험공단의 각 부서별로 주관하고 있는 업무별로 책임을 분장하여 부서 내에서 주기적인 내부 회와와 논의를 통해 마련되었으며, 외부 전문가의 자문을 통 해 수립되었다.
국민건강보험쇄신위원회의 전사적인 노력으로 마련된 세 부실천계획의 세부 내용 중에서 4년이 지난 현 시점에서 아직 도 보장성 강화와 이를 위한 재원확보, 즉 재정안정화 대책 은 일부 실현되고 있지 않다. 특히 약제비와 관련하여 마련된 약제비 적정화 방안을 더욱 그러하다.
본 연구는 국민건강보험쇄신위원회의 세부실천계획으로 마련된 약제비 적정화를 실현하기 위한 핵심 아젠다(agenda) 5가지를 소개하고, 이에 대한 전문가 의견조사를 통해 각 아 젠다별 정책 영향 평가 및 적정도입시기에 대한 구체적인
계획안을 마련하여 약제비 적정화를 위한 체계적인 로드맵 을 구축하고자 하였다.
체계적 약품비 관리 로드맵 구축을 위한 아젠다(agenda) 설정
본 연구는 의약품정책 관련 이해당사자를 대상으로 하여 건강보험제도의 미래 지속가능성을 달성하기 위한 건강보 험 약품비의 목표 증가율의 범위를 설정하고, 향후 약품비의 체계적 관리를 위해 필요한 중요 정책 agenda의 영향에 대 한 예측 및 도입을 위한 선결과제에 대한 전문가의 견해를 청취하는 것이 조사의 주요 목적이다.
이를 위해 국내의 건강보험약품비 적정화 방안에 대한 기 존 문헌고찰과 OECD 주요국의 정책 사례를 고찰한 후에, 현재 우리나라에 우리나라 보험약품비 관리 제도에서 아직 도입되지 않았으나, 건강보험제도의 미래발전 지속가능성 을 달성하기 위하여 향후 필요한 건강보험 약품비 절감 정 책으로 고려해 볼 만한 가치가 있다고 판단되는 핵심 정책 을 선정하였다(표 1).7-23) 우리나라 건강보험 약제비를 주도 하고 있는 요인들이 노인인구 및 만성질환자 증가에 따른 의 약품 사용증가, 고가 의약품 선호, 의약품 유통거래가 복잡하 고 불투명한 점을 염두에 두었다.4)
건강보험재정의 안정화 및 지속가능성을 달성하기 위한 것일 뿐 아니라, 제네릭 활성화와 의약품 수량 및 총액 관리, 그리고 유통투명화를 추구하기 위해서 건강보험에서 향후 추진해야 할 건강보험 약품비 절감 정책으로 1) 보험자의 협 상력 강화 및 risk-sharing 다양화, 2) 총액예산제 도입, 3) 참 조가격제 도입, 4) 의약품 입찰제 도입, 5) 희귀난치성 의약 품의 (정부)기금 조성의 5가지 agenda를 설정하였다(표 2).
건강보험 약품비를 절감할 수 있는 5가지 중점 agenda의 내용은 다음과 같다. 우선, 보험자의 협상력 강화 및 risk- sharing 다양화 방안은 신약(신규의약품, 혁신적 신약, 희귀 난치성 의약품 포함)의 보험등재 및 가격결정에 있어서 의 사결정을 촉진시키기 위하여 근거생산, 유효약가인하(결과 기반, 재정 기반) 등의 다양한 요소를 도입하여 협상에 활용 하는 것이다. 두 번째, 총액예산제 도입 방안은 신약 및 기등 재약 대상 의약품을 대상으로 약품비 목표지출 총액・목표 증가율을 설정하여 의약품 사용수량, 저가약 사용 등을 촉진 하는 것이다. 이를 통해 목표 미달성 시 수가 인하 또는 목표 달성 시 수가 인상 등의 인센티브를 설계하는 것이라 할 수 있다. 셋째, 참조가격제 도입 방안은 저가약 활용 촉진 목적 으로 동일 효능군(therapeutic group)의 범위까지 확대하여 참조가격제를 실시하는 것이다. 이는 기등재약을 우선 대상
으로 하되, 참조가격군 설정위원회를 설치하여 신약(오리지 널의약품) 포함 여부를 논의하는 것이다. 넷째, 의약품 입찰 제 도입 방안은 의약품을 최저가격으로 공급할 뿐 아니라
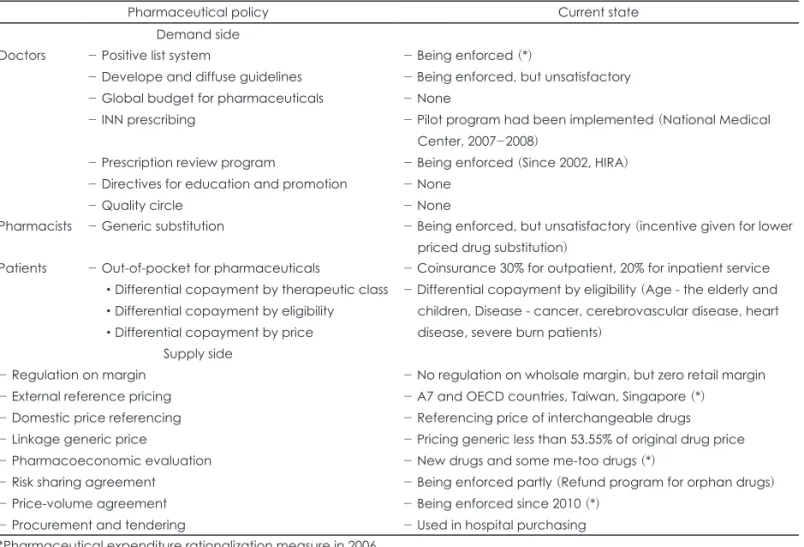
거래의 투명성을 향상시킬 수 있다고 기대된다. 우선 입찰제 를 대체가능한 의약품의 품목수가 많은 동일 효능군(thera- peutic group)을 중심으로 비용효과적인 의약품의 선택을 전 Table 1. Current state of pharmaceutical policies in South Korea
Pharmaceutical policy Current state
Demand side Doctors - Positive list system
- Develope and diffuse guidelines - Global budget for pharmaceuticals - INN prescribing
- Prescription review program
- Directives for education and promotion - Quality circle
- Being enforced (*)
- Being enforced, but unsatisfactory - None
- Pilot program had been implemented (National Medical Center, 2007-2008)
- Being enforced (Since 2002, HIRA) - None
- None
Pharmacists - Generic substitution - Being enforced, but unsatisfactory (incentive given for lower priced drug substitution)
Patients - Out-of-pocket for pharmaceuticals
•Differential copayment by therapeutic class
•Differential copayment by eligibility
•Differential copayment by price
- Coinsurance 30% for outpatient, 20% for inpatient service - Differential copayment by eligibility (Age - the elderly and children, Disease - cancer, cerebrovascular disease, heart disease, severe burn patients)
Supply side - Regulation on margin
- External reference pricing - Domestic price referencing - Linkage generic price
- Pharmacoeconomic evaluation - Risk sharing agreement - Price-volume agreement - Procurement and tendering
- No regulation on wholsale margin, but zero retail margin - A7 and OECD countries, Taiwan, Singapore (*)
- Referencing price of interchangeable drugs - Pricing generic less than 53.55% of original drug price - New drugs and some me-too drugs (*)
- Being enforced partly (Refund program for orphan drugs) - Being enforced since 2010 (*)
- Used in hospital purchasing
*Pharmaceutical expenditure rationalization measure in 2006
Table 2. Agenda to contain pharmaceutical expenditure
Agenda Target
Agenda 1:
Strengthening insurer’s bargaining power and diversification of risk-sharing
•New drugs (Incl. new drugs, innovative new drugs, orphan drugs)
• To expedite listing and pricing of new drugs, Insurer introduce and utilize a diverse components of negotiation, such as evidence-producing and effective price discount (outcome based, finance based) and etc.
Agenda 2:
Introduction of global budget
•For new drugs and listed drugs
• To design incentives for target pharmaceutical expenditures or growth rate using programs such as volume control, lower cost generic substitution, drug price cut, or raising fee schedule under condition pharmaceutical expenditures decrease etc.
Agenda 3:
Introduction of reference price system
• To implement reference price system to the extent of same therapeutic groups to promote less expensive drug use
• Firstly, listed drugs are included in reference price system, then setting a reference price committee and discussing inclusion of new drugs (original drugs)
Agenda 4:
Introduction of pharmaceutical tendering system
• Tendering system for same therapeutic groups with a large number of interchangealbe drugs in nationwide or regional basis
•To establish drug selecting committee for tendering system nationwide or regional basis Agenda 5:
Introduction of orphan drug fund
• Financing orphan drugs which are not covered by national health insurance through special fund
국・광역 단위에서 시행하는 것이다. 즉, 입찰제 대상의약품 선정위원회를 전국・광역 단위에 설치하여 해당 효능군을 선정하는 것을 의미한다. 마지막으로 희귀난치성 의약품의 (정부) 기금 조성 방안은 희귀난치성 의약품에 대한 기금 조 성을 통한 재원조달을 주요 내용으로 하고 있다.
전문가 의견 조사
설문조사 문항 설계
사전준비 단계에서 마련된 아젠다별 정책영향 예측 및 도 입가능 시기 등에 대한 전문가 의견을 조사하기 위하여 설 문조사 항목을 구성하였다. 조사항목은 다음 내용을 포함하 고 있다. 첫째, 건강보험 약품비 지출 증가 목표치 수립, 둘 째, 건강보험 약품비 적정화 방안 아젠다(agenda) 5가지인 1) 보험자의 협상력 강화 및 risk-sharing 다양화 방안, 2) 총 액예산제 방안, 3) 참조가격제 방안, 4) 의약품 입찰제 방안, 5) 희귀난치성 의약품의 (정부) 기금 조성 방안을 도입할 경 우 정책 영향을 예측하기 위해 다음의 항목에 대한 질문을 하였다. (1) 보건의료체계 성과목표 항목별 영향 평가 점수, (2) 정책실현가능성을 높이기 위한 선결과제, (3) 적정 도입 시기에 대한 질문을 포함하였으며, 이 중 보건의료체계 성과 목표는 OECD에서 활용하고 있는 8가지 평가 항목을 활용 하였다(표 3).
조사 방법
조사대상 전문가 선정은 학계/연구기관, 실무기관(보건복 지부/건강보험심사평가원/국민건강보험공단), 의료공급자/
제약사 등 총 21인으로 다양하게 구성하였다.
조사지는 이메일로 발송되었으며, 조사기간은 2012년 9월 18일부터 10월 4일까지였으며, 응답률은 90.5%였다(21인 중 19인 응답). 응답자 구성은 학계/연구기관 9인, 실무기관(보 건복지부/건강보험심사평가원/국민건강보험공단) 6인, 의 료공급자/제약사 4인이었다.
전문가의견 조사를 수행하기 위해 보험약품비 관리 중점 agenda 5가지 항목에 대한 외국 제도 운영현황을 포함한 개 요와 약품비 목표치를 설정할 수 있도록 다음 두 가지 관련 기초 자료로 1) 2000~2010년 기간의 건강보험 약품비 규모 및 전년대비 증가율과 진료비 대비 비중 자료와 2) 2000~2008년 기간의 국민의료비 대비 비중 자료를 제시하였다.
전문가 의견조사 결과
건강보험 약품비의 증가율 목표치 설정
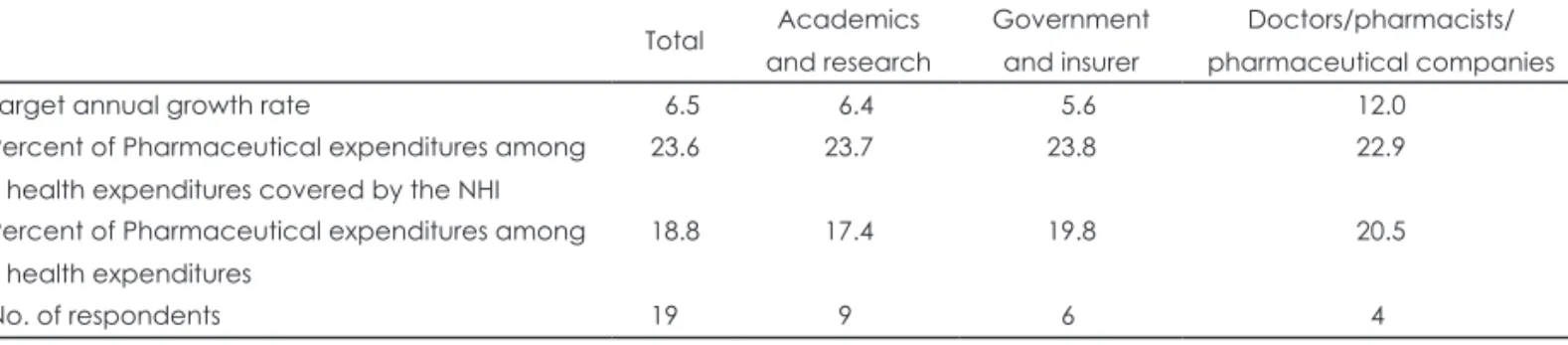
건강보험제도의 미래 지속가능성을 달성하기 위한 목적 으로 건강보험 약품비의 증가율 목표치 등에 대한 전문가조 사 결과, 증가율 목표 평균은 전체 6.5%로 응답이 모아졌으 며, 이해당사자 특성별로 학계/연구기관 6.4%, 실무기관(보
Table 3. Evaluation criteria for health care system outcomes
Evaluation criteria Consideration
1 Containment of pharmaceutical expenditure
- What impact will it have on drug price and price cut?
2 Sustainability and equity of financing for pharmaceuticals
- What impact will it have on out-of-pocket and insurer’s coverage rate?
3 Efficiency of expenditures - What impact will it have on pharmaceutical expenditure control including diminishing number of prescription, generic substitution and so on?
4 Availability of pharmaceuticals - What impact will it have on accelerating market access?
5 Accessibility of pharmaceuticals - What impact will it have on listed durg and diffusion of new drugs?
6 Quality of care and health outcomes - What impact will it have on quality of care and outcomes?
7 Satisfaction of patients and consumers - What impact will it have on satisfaction of patients and consumers?
8 Industrial policy goal: R&D and Innovation - What impact will it have on R&D and innovation new drugs?
Table 4. Target growth rate of pharmaceutical expenditures covered by NHI (unit: %, person) Total Academics
and research
Government and insurer
Doctors/pharmacists/
pharmaceutical companies
Target annual growth rate 06.5 06.4 05.6 12.0
Percent of Pharmaceutical expenditures among health expenditures covered by the NHI
23.6 23.7 23.8 22.9
Percent of Pharmaceutical expenditures among health expenditures
18.8 17.4 19.8 20.5
No. of respondents 19 09 06 04
건복지부/건강보험심사평가원/국민건강보험공단) 5.6%, 의 약공급자/제약사 12.0%으로 의약공급자와 제약사가 상대적 으로 높은 증가율을 목표하고 있음을 나타냈다(표 4).
건강보험 약품비의 진료비 중 비중은 23.6%로 응답하였 다. 이해당사자 특성 별로 학계/연구기관 23.7%, 실무기관 (보건복지부/건강보험심사평가원/국민건강보험공단) 23.8%, 의약공급자/제약사 22.9%였다. 약제비의 국민의료 비 중 비중은 18.8%가 되어야 한다고 응답하였다. 이해당사 자 특성별로 학계/연구기관 17.4%, 실무기관(보건복지부/건 강보험심사평가원/국민건강보험공단)/정부(보건복지부) 19.8%, 의약공급자/제약사 20.5%였다.
건강보험 약품비 적정화 방안의 5가지 agenda별 성과목표 영향 평가
각 agenda를 대상으로 성과목표 항목별 영향 평가 점수를 0점(영향 없음)부터 3점(큰 영향 있음)의 범위로 평가하도록
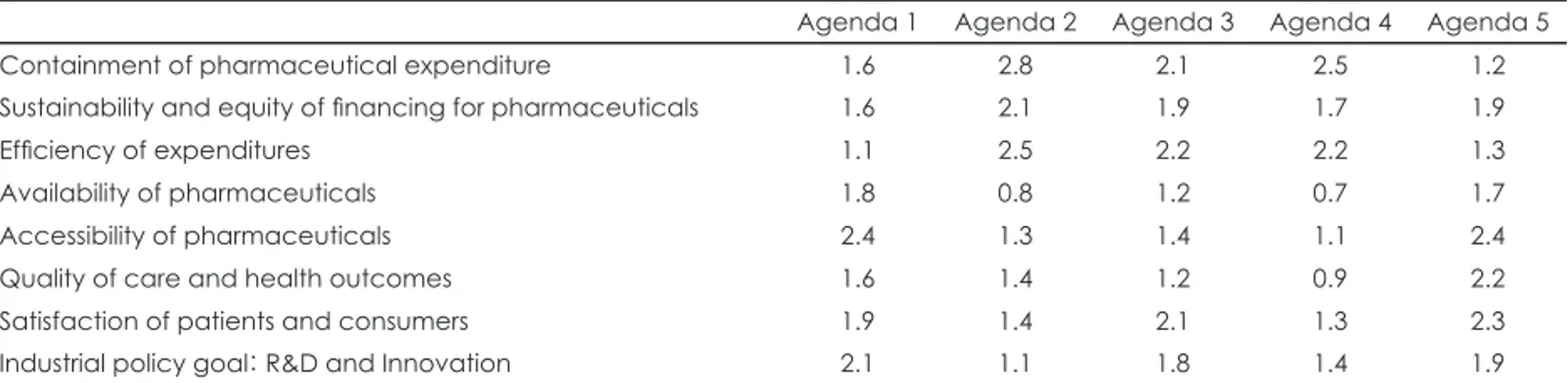
하였다. 조사 결과, 약제비 통제 측면에서 가장 영향을 미치는 정책은 총액예산제 도입 방안(2.8점), 의약품 입찰제 방안(2.5 점), 참조가격제 도입 방안(2.1점)이 영향이 클 것으로 예측 하였다(표 5, 그림 1).
의약품 재원조달의 지속가능성 및 형평성 측면에서는 5개 의 정책이 모두 약간의 영향이 있을 것이라고 예측하였다.
총액예산제 도입(2.1점), 참조가격제 도입(1.9점), 희귀난치 성 의약품의 (정부)기금 조성(1.9점), 의약품 입찰제 도입(1.7 점), 그리고 보험자의 협상력 강화 및 risk-sharing 다양화 방 안(1.6점) 순으로, 점수 차이는 크지 않았다.
의약품 부문의 지출 효율성 측면에서는 총액예산제 도입 (2.5점)이 영향력이 클 것으로 예측하였고, 다음으로 참조가 격제 도입(2.2점), 의약품 입찰제 도입(2.2점)이 약간의 영향 력이 있을 것이라고 나타났다.
의약품 이용가능성 측면에서 약간의 영향이 있을 것이라 예 측되는 정책은 보험자의 협상력 강화 및 risk-sharing 다양 화 방안(1.8점)과 희귀난치성 의약품의 (정부)기금 조성(1.7점) 으로 응답되었다.
의약품 접근성 측면에서는 보험자의 협상력 강화 및 risk- sharing 다양화 방안(2.4점)과 희귀난치성 의약품의 (정부) 기금 조성(2.4점)이 약간의 영향이 있을 것으로 나타났다.
보건의료의 질과 건강결과 측면에서 희귀난치성 의약품 의 (정부)기금 조성(2.2점)이 비교적 큰 영향을 미치며, 보험 자의 협상력 강화 및 risk-sharing 다양화 방안(1.6점)과 총 액예산제 도입(1.4점)은 약간의 영향을 미칠 것으로 예상하 였다.
환자와 소비자 만족도 측면에서, 희귀난치성 의약품의 (정 부)기금 조성(2.3점), 참조가격제 도입(2.1점), 보험자의 협상 력 강화 및 risk-sharing 다양화 방안(1.9점)이 약간의 영향을 미칠 것이라 예측하였다.
기업 정책 목표(의약품 연구개발・혁신정책) 측면에서, 보 험자의 협상력 강화 및 risk-sharing 다양화 방안(2.1점), 희 Fig. 1. Impact score by policy goals by agenda. Score (0): No im-
pact, Score (1): Minor Impact, Score (2): Some Impact, Score (3):
Big Impact. Agenda 1: Strengthening insurer’s bargaining power and diversification of risk-sharing, Agenda 2: Introduction of glob- al budget, Agenda 3: Introduction of reference price system, Agen- da 4: Introduction of pharmaceutical tendering system, Agenda 5:
Introduction of orphan drug fund.
Agenda 1 Agenda 2 Agenda 3 Agenda 4 Agenda 5
Containment of pharmaceutical expenditure Industrial policy goal:
R&D and Innovation
Sustainability and equity of financing for pharmaceuticals
Efficiency of expenditures
Availability of pharmaceuticals 3
2 1 0
Accessibility of pharmaceuticals Quality of care and
health outcomes Satisfaction of
patients and consumers
Table 5. Impact score by policy goals by agenda
Agenda 1 Agenda 2 Agenda 3 Agenda 4 Agenda 5
Containment of pharmaceutical expenditure 1.6 2.8 2.1 2.5 1.2
Sustainability and equity of financing for pharmaceuticals 1.6 2.1 1.9 1.7 1.9
Efficiency of expenditures 1.1 2.5 2.2 2.2 1.3
Availability of pharmaceuticals 1.8 0.8 1.2 0.7 1.7
Accessibility of pharmaceuticals 2.4 1.3 1.4 1.1 2.4
Quality of care and health outcomes 1.6 1.4 1.2 0.9 2.2
Satisfaction of patients and consumers 1.9 1.4 2.1 1.3 2.3
Industrial policy goal: R&D and Innovation 2.1 1.1 1.8 1.4 1.9
Score (0): No impact, Score (1): Minor Impact, Score (2): Some Impact, Score (3): Big Impact. Agenda 1: Strengthening insurer’s bargaining power and diversification of risk-sharing, Agenda 2: Introduction of global budget, Agenda 3: Introduction of refer- ence price system, Agenda 4: Introduction of pharmaceutical tendering system, Agenda 5: Introduction of orphan drug fund
귀난치성 의약품의 (정부)기금 조성(1.9점), 참조가격제 도입 (1.8점)이 약간의 영향을 미칠 것으로 예측하였다.
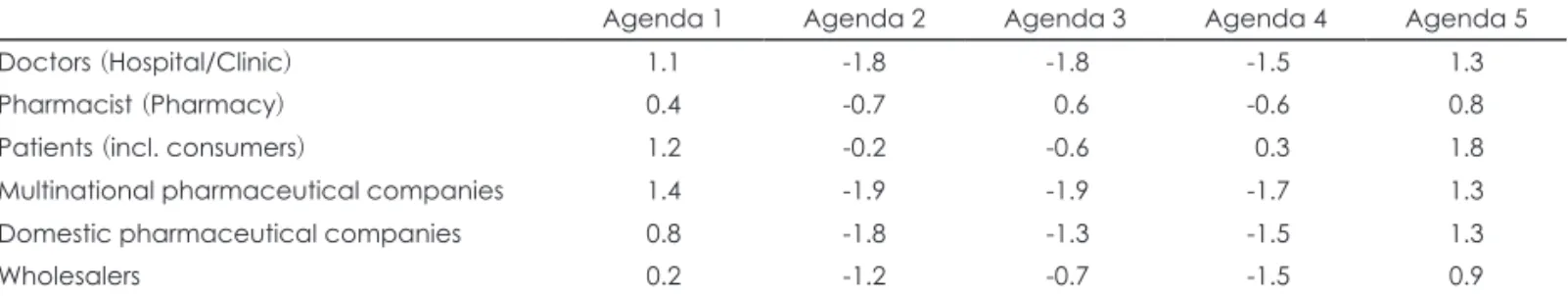
이해당사자별 정책순응도 예측
각 Agenda를 대상으로 이해당사자별 정책순응도를 -2점 (강한 반대)부터 2점(강한 찬성)까지의 점수범위로 평가하게 한 결과, 보험자의 협상력 강화 및 risk-sharing 다양화 방안 에 대해 다국적 제약업체(1.4), 환자(1.2), 의사(1.1) 그룹에서 찬성을 하였다(표 6, 그림 2). 총액예산제 도입 방안에 대해서 는 모든 이해당사자에서 도입반대 의견을 냈으며, 특히 다국 적 제약업체(-1.9), 국내 제약업체(-1.8), 의사(-1.8)에서 강한 반대의견을 보였다. 참조가격제 방안에 대해 약사를 제외한 모든 이해당사자의 도입반대 의견이 나타났으며, 특히 다국 적 제약업체(-1.9), 의사(-1.8)에서 강한 반대의견을 보였다.
의약품입찰제 방안의 경우 환자단체를 제외한 모든 이해
당사자가 반대의견을 보였으며, 특히 다국적 제약업체 (-1.7), 국내 제약업체(-1.5), 의사(-1.5), 도매업체(-1.5)에서 강한 반대의견을 보였다. 희귀난치성 의약품의 (정부)기금 조성 방안에 대해서는 이해당사자 모두에서 찬성의견이 나 타났으며, 특히 환자(1.8)에서 강한 찬성의견을 보였다.
Agenda별 적정 도입 시기에 대한 의견
전문가들이 예측한 보험자의 협상력 강화 및 risk-sharing 다양화 방안의 적정 도입시기로는 3~5년 내에 도입해야 한 다는 의견이 47.1%, 다음으로 1~2년 내 도입해야한다는 의 견이 41.2%로 나타났다(표 7). 그리고 총액예산제 방안의 적 정 도입시기로는 3~5년 내에 도입해야 한다는 의견이 41.2%
를 차지하였다. 참조가격제 방안의 적정 도입시기로는 3~5 년 내에 도입해야 한다는 의견이 50.0%를 차지하였다. 또한, 의약품 입찰제 방안의 적정 도입시기로는 3~5년 내에 도입 해야 한다는 의견과 9~10년 내에 도입해야 한다는 의견이 29.4%로 같은 비율을 차지하였다. 희귀난치성 의약품의 (정부) 기금 조성의 적정 도입 시기로는 1~2년 내에 도입해야 한다 는 의견이 63.2%를 차지하였다.
종합하면, 희귀난치성 의약품 (정부)기금 조성의 적정 방 안이 단기적으로 1~2년 내에 도입해야 하며, 단기와 중기적으 로 추구되어야 할 아젠다는 보험자의 협상력 강화 risk- sharing 다양화 방안이다. 중장기적으로는 참조가격제 방안, 총액예산제 방안의 도입을 고려해야 할 것이다. 또한 도입 시 기에 있어서 추가적인 논의가 더 필요하지만, 장기적인 관점 에서 의약품 입찰제 방안 도입을 고려해볼 수 있다.
건강보험 약품비의 체계적 관리를 위한 로드맵 구축
건강보험 약품비 체계적 관리를 위한 로드맵은 전문가의견 조사 결과를 바탕으로, 향후 약품비 증가율 목표치를 6.5%, 건강보험 진료비 중 약품비 비중을 23.6%로 국민의료비 중 Fig. 2. Policy compliance by stake-holders and agenda. Score
(-2): Disagree strongly, Score (-1): Disagree, Score (0): No opinion, Score (1): Agree, Score (2): Agree strongly. Agenda 1: Strengthen- ing insurer’s bargaining power and diversification of risk-sharing, Agenda 2: Introduction of global budget, Agenda 3: Introduction of reference price system, Agenda 4: Introduction of pharmaceutical tendering system, Agenda 5: Introduction of orphan drug fund.
Agenda 1 Agenda 2 Agenda 3 Agenda 4 Agenda 5
Doctors (Hospital/Clinic) 2.00
1.00 0.00 -1.00 -2.00 Wholesalers
Domestic pharmaceutical companies
Patients (incl.
consumers) Pharmacist (Pharmacy)
Multinational pharmaceutical companies
Table 6. Policy compliance by stake-holders and agenda
Agenda 1 Agenda 2 Agenda 3 Agenda 4 Agenda 5
Doctors (Hospital/Clinic) 1.1 -1.8 -1.8 -1.5 1.3
Pharmacist (Pharmacy) 0.4 -0.7 0.6 -0.6 0.8
Patients (incl. consumers) 1.2 -0.2 -0.6 0.3 1.8
Multinational pharmaceutical companies 1.4 -1.9 -1.9 -1.7 1.3
Domestic pharmaceutical companies 0.8 -1.8 -1.3 -1.5 1.3
Wholesalers 0.2 -1.2 -0.7 -1.5 0.9
Score (-2): Disagree strongly, Score (-1): Disagree, Score (0): No opinion, Score (1): Agree, Score (2): Agree strongly. Agenda 1:
Strengthening insurer’s bargaining power and diversification of risk-sharing, Agenda 2: Introduction of global budget, Agenda 3:
Introduction of reference price system, Agenda 4: Introduction of pharmaceutical tendering system, Agenda 5: Introduction of orphan drug fund
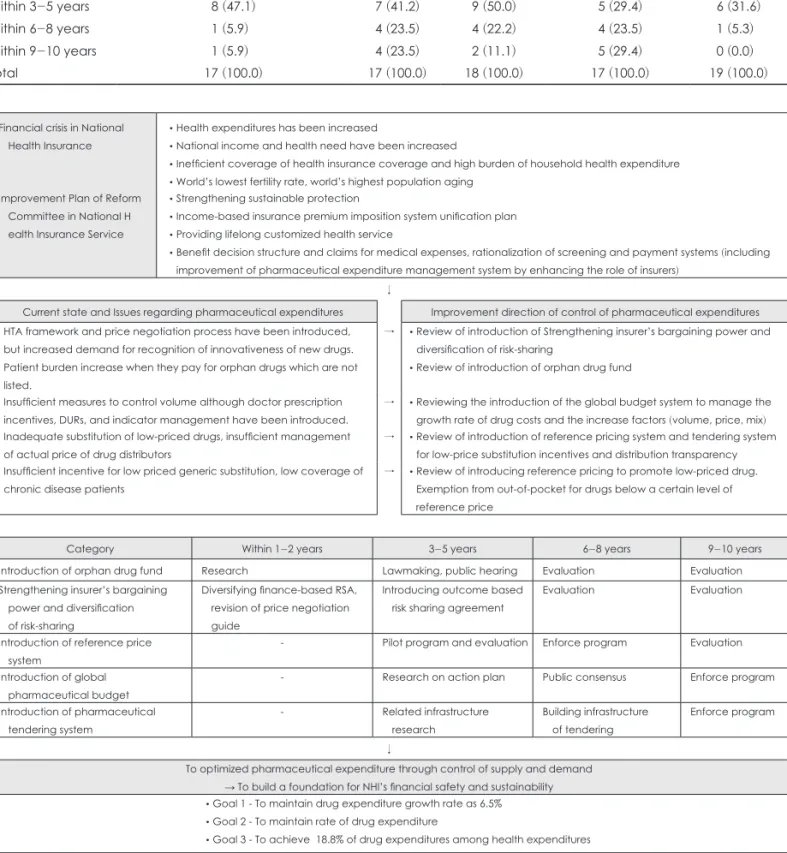
약제비 비중을 18.8%를 달성하겠다는 목표를 두고, 국민건 강보험공단 내부에서 설정한 5가지 아젠다를 단기, 중기, 장 기 계획으로 설정하였다(그림 3).
희귀난치성 의약품 기금조성 방안에 대비한 각 이해당사 자의 정책 순응도는 비교적 높은 편으로 단기적으로 달성가
능한 아젠다로 설정하였다. 희귀난치성 의약품 기금조성 방 안은 의약품의 접근성을 향상시키고, 환자와 소비자의 만족 도를 향상시킬 뿐 아니라 보건의료의 질과 건강성과 측면에 서도 가장 긍정적인 정책 아젠다로 평가된다.
중기적으로 추진해야 할 아젠다로 보험자의 협상력 강화
Table 7. Introduction time by agenda [unit: person (%)]
Strengthen insurer’s bargaining power and diversify risk-sharing
Global budget
Reference price system
Pharmaceutical tendering system
Orphan drug fund
Within 1-2 years 07 (41.2) 02 (11.8) 03 (16.7) 03 (17.6) 12 (63.2)
Within 3-5 years 08 (47.1) 07 (41.2) 09 (50.0) 05 (29.4) 06 (31.6)
Within 6-8 years 01 (5.9) 04 (23.5) 04 (22.2) 04 (23.5) 01 (5.3)
Within 9-10 years 01 (5.9) 04 (23.5) 02 (11.1) 05 (29.4) 00 (0.0)
Total 17 (100.0) 17 (100.0) 18 (100.0) 17 (100.0) 19 (100.0)
Financial crisis in National Health Insurance
• Health expenditures has been increased
• National income and health need have been increased
• Inefficient coverage of health insurance coverage and high burden of household health expenditure
• World’s lowest fertility rate, world’s highest population aging Improvement Plan of Reform
Committee in National H ealth Insurance Service
• Strengthening sustainable protection
• Income-based insurance premium imposition system unification plan
• Providing lifelong customized health service
• Benefit decision structure and claims for medical expenses, rationalization of screening and payment systems (including improvement of pharmaceutical expenditure management system by enhancing the role of insurers)
↓
Current state and Issues regarding pharmaceutical expenditures Improvement direction of control of pharmaceutical expenditures
• HTA framework and price negotiation process have been introduced, but increased demand for recognition of innovativeness of new drugs.
• Patient burden increase when they pay for orphan drugs which are not listed.
→ • Review of introduction of Strengthening insurer’s bargaining power and diversification of risk-sharing
• Review of introduction of orphan drug fund
• Insufficient measures to control volume although doctor prescription incentives, DURs, and indicator management have been introduced.
→ • Reviewing the introduction of the global budget system to manage the growth rate of drug costs and the increase factors (volume, price, mix)
• Inadequate substitution of low-priced drugs, insufficient management of actual price of drug distributors
→ • Review of introduction of reference pricing system and tendering system for low-price substitution incentives and distribution transparency
• Insufficient incentive for low priced generic substitution, low coverage of chronic disease patients
→ • Review of introducing reference pricing to promote low-priced drug.
Exemption from out-of-pocket for drugs below a certain level of reference price
Category Within 1-2 years 3-5 years 6-8 years 9-10 years
Introduction of orphan drug fund Research Lawmaking, public hearing Evaluation Evaluation
Strengthening insurer’s bargaining power and diversification of risk-sharing
Diversifying finance-based RSA, revision of price negotiation guide
Introducing outcome based risk sharing agreement
Evaluation Evaluation
Introduction of reference price system
- Pilot program and evaluation Enforce program Evaluation
Introduction of global pharmaceutical budget
- Research on action plan Public consensus Enforce program
Introduction of pharmaceutical tendering system
- Related infrastructure
research
Building infrastructure of tendering
Enforce program
↓
To optimized pharmaceutical expenditure through control of supply and demand
→ To build a foundation for NHI’s financial safety and sustainability
• Goal 1 - To maintain drug expenditure growth rate as 6.5%
• Goal 2 - To maintain rate of drug expenditure
• Goal 3 - To achieve 18.8% of drug expenditures among health expenditures
Fig. 3. Roadmap to Contain Pharmaceutical Expenditures.
risk-sharing 다양화 방안을 설정하였는데, 다국적 제약업계 와 환자, 의사의 긍정적인 정책순응도가 예상되며 이를 통해 의약품 접근성 향상과 기업정책 목표인 의약품 연구개발에 큰 영향이 있을 것으로 평가된다.
중장기적으로 추구되어야 할 아젠다는 참조가격제 방안, 총액예산제 방안, 입찰제 방안으로 제시되었다. 참조가격제 의 경우 도입될 경우 약제비 통제와 지출의 효율성 향상, 환 자와 소비자 만족도가 향상될 것으로 예상되는 약제비 관리 정책이다. 그러나 다국적 제약업계와 의사, 그리고 국내 제 약업계의 반대가 만만치 않아 상대적으로 도입하기 어려운 정책이며, 이미 우리나라에서도 한 차례 정책 도입에 대한 의 료계와 제약업계, 소비자 단체의 반대를 거쳤던 정책이다.
그럼에도 불구하고 유럽의 많은 국가에서 성분명 처방 정책 과 제네릭 대체조제 정책과 더불어 약제비를 관리하기 위한 주된 제도로 활용되고 있다.23)
약제비에 대한 총액예산제 방안은 약제비 통제와 재원조 달의 지속가능성과 형평성, 그리고 지출의 효율성을 달성하 는 정책 목표를 충실히 달성할 수 있는 제도로 나타났다. 총 액예산제에 대해서는 유럽 국가에서 주로 수행되고 있는 제 도로, 찬성의 의견을 내는 이해당사자가 거의 없는 도입의 가능성에 있어서 매우 회의적인 약제비 관리 제도이다. 그럼 에도 불구하고, 우리나라와 이웃한 대만의 경우 2013년부터 약제비에 대한 총액예산제를 시범사업으로 도입하여 실행 한 경험이 있다. 건강보험 재정 안정화와 제도의 지속가능성 을 염두에 둔다면, 도입되어야 할 제도이나 이에 대한 제도 실행방안 연구와 사회적 협약이 가능한 사회적인 변화가 필 요하다.
마지막으로 의약품 입찰제 또한 약제비 통제와 지출의 효 율성을 달성하는 정책 목표를 달성할 수 있는 제도로 조사 되었다. 의약품 입찰제는 외래처방 의약품을 대상으로 보험 자가 입찰을 통해 전국 혹은 특정 지역 범위 내에서 동일 효 능군 내에서 최저가 의약품에 대한 급여대상을 일정기간 동 안 한정하는 제도이다. 입찰을 통해 최저가 의약품의 사용을 촉진하여 약제비를 절감하려는 취지인데, 뉴질랜드, 네덜란 드, 독일, 벨기에에서 일부 효능군을 중심으로 시행되고 있 는 약제비 관리 제도이다. 입찰제에 대해서도 환자를 제외한 모든 이해당사자의 반대 의견이 개진되어 도입에 있어서 어 려움이 예상되는 제도 중의 하나이다. 따라서 국민건강보험 공단에서 제안된 약제비 관리제도를 위한 정책 아젠다 5가 지에 대해 이해당사자의 정책순응도와 정책 영향에 대한 예 측 결과를 근거로 로드맵이 구축되었다.
결 론
이 글은 보험자의 관점에서 보험자의 약제비 관리 제도를 실천적으로 마련하기 위해서 핵심 아젠다 5가지를 제안하 고, 이에 대한 이해당사자(정부, 제약업계, 의료계, 약계, 환 자 및 소비자단체 등)가 바람직하다고 예상하는 약제비 지 출 증가율 목표와 약제비 비중, 그리고 각 아젠다별로 정책 영향에 대한 예상결과, 정책 순응도와 도입 예상시기를 설정 하여 전문가 의견조사를 실시한 결과를 제시한 것이다.
의약품 정책에서 이해당사자별로 입장에 따른 시각 차이 가 존재한다는 점을 확인할 수 있었으며, 보험자의 시각으로 설정된 약제비 관리 정책 아젠다 5가지에 대한 각 이해당사 자의 순응도 및 정책영향 평가 점수, 그리고 도입 시기에 대 한 의견을 통해 국민건강보험공단이 보험자의 단기, 중기, 장기적인 체계적 건강보험약품비 관리 방안을 수립하였다 는 것에 의의를 모색하고자 한다.
Acknowledgments
본 논문은 2012년 국민건강보험공단 건강보험정책연구원 연구
보고서의 내용 일부를 수정하여 작성된 원고입니다.24)
REFERENCES
1) OECD. OECD Health Data 2014. Available from: http://stats.oecd.org/
index.aspx?DataSetCode=HEALTH_STAT. Accessed April 30, 2015.
2) National Health Insurance Reform Committee. 「Practical health wel- fare plan II」 National Health Insurance Service Reform Committee Activity Report. 2013.03. Seoul: National Health Insurance Service;
2013.
3) National Health Insurance Service. Drug price negotiation status and system improvement briefing session. 2008.11.25. Seoul: National Health Insurance Service;2008.
4) Board of Audit and Inspection. Audit Result Report - Health Insurance Drug Administration. 2012.10-. Seoul: Board of Audit and Inspection;
2012.
5) Byeon JO, Kim YR, Lee JH. Population based analysis of trend and component of pharmaceutical expenditure. Seoul: National Health Insurance Service;2015.
6) National Health Insurance Reform Committee. 「Practical health wel- fare plan」 National Health Insurance Service Reform Committee Ac- tivity Report. 2012.07. Seoul: National Health Insurance Service;2012.
7) Park S, Park EJ. Future directions for pharmaceutical policy in the new era of high cost medicines. Seoul: Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs;2011.
8) Kim KH. Analysis of drug prescription behavior according to the policy to strengthen the protection of cancer patients. Seoul: Health In- surance Review & Assessment Service;2010.
9) Park CM, Jang SM, Kang HA, Bae EY, Jang SH. Study on differen- tial out-of-pocket payment for pharmaceuticals. Seoul: Health Insur- ance Review & Assessment Service;2012.
10) Bae EY, Jeong Y, Lee BR. Study on drug pricing process and improve- ment plan. Seoul: Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service;
2007.
11) Bae EY. Contribution analysis by drug cost component. Seoul: Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service;2007.
12) Ryu KC. A new approach to drug pricing: pricing based on risk shar-
ing agreement. 2009 Open forum of Policy Korean Association of Health Economics and Policy. 2009.4.29. Seoul: Policy Korean Asso- ciation of Health Economics and Policy;2009.
13) Lee SM, Jang SH, Jang SM. Policy research on volume control to ra- tionalize pharmaceutical expenditures. Seoul: Health Insurance Re- view & Assessment Service;2010.
14) Lee YK. Development of re-evaluation of drug price considering vol- ume. Seoul: Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service;2005.
15) Lee TJ, Bae EY, Kim S, Jeong CR, Sohn KB. Introduction of risk shar- ing agreement. Seoul: National Health Insurance Service・Seoul Na- tional University;2012.
16) Jang SM, Park CM, Bae G, Lee HJ, Kim HS. Analysis of attributing factors of national health insurance pharmaceutical expenditures.
Seoul: Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service;2010.
17) Jeong HJ, Lee JM, Moon SY, Baek SC, Yoon YD. Review and impli- cation of global budget system in major countries. Seoul: National Health Insurance Service;2011.
18) Cho KJ. Impact of drug price reduction policy on domestic pharma- ceutical industry. Available from: https://rd.kdb.co.kr/er/cmscontents/
common/cmsERFileDown.jsp?cid=8171&fid=12&fname=binary1&
index=1. Accessed October 15, 2016.
19) Cho DH, Park MH, Park KY, Choi SR. Trends and prospects of US generic drug market. Cheongju: Korea Health Industry Development Institute;2011.
20) Choi SE, Shin JY, Leem MK. Positive list system design plan. Seoul:
Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service;2007.
21) Vogler S. The impact of pharmaceutical pricing and reimbursement policies on generics uptake: implementation of policy options on ge- nerics in 29 European countries–an overview. GaBI J 2012;1:44-51.
22) Schäfer W, Kroneman M, Boerma W, van den Berg M, Westert G, Devillé W, et al. The Netherlands: health system review. Health Syst Transit 2010;12:v-xxvii, 1-228.
23) Dylst P, Vulto A, Simoens S. Tendering for outpatient prescription pharmaceuticals: what can be learned from current practices in Eu- rope? Health Policy 2011;101:146-152.
24) Kim SO, Lee JH. Shin KY. Roadmap for comprehensive management of health insurance pharmaceutical expenditures. Seoul: National Health Insurance Service;2011.