Pediococcus acidilactici is a probiotic bacterium that is industrially utilized in the food industry and antibiotics development. The whole genome sequencing using PacBio RS II platform was performed for a lactic acid bacteria P. acidilactici SRCM 103444 isolated from cheonggukjang. The genome of strain SRCM103444 is circular chromosome of 1,970,727 bp with a G + C contents of 42.1%, and included 1,833 protein coding genes and 71 RNA genes (15 rRNA genes, 56 tRNA genes).
Genes related to lactic acid production and alcohol tolerant enzymes were detected in the genome. The genome analysis showed that strain SRCM103444 might be associated with lactic acid fermentation and alcohol tolerant activity in the nutraceutical biotechnology field.
Keywords: Pediococcus acidilactici, cheonggukjang, complete genome, lactic acid bacteria
The genus Pediococcus includes Gram-positive, catalase- negative, and oxidase-negative lactic acid bacteria (Holzapfel et al., 2006). This group ubiquitously has been found in nature
and largely associated with fermented foods and feed products (Todorov and Dicks, 2004). Many studies recommend the use of these species, in single or mixed combinations, as starter cultures, in order to reduce the risk of unexpected growth of spoilage strains and to lead to a controlled and more predictable fermentation process (Hurtado et al., 2012). Moreover, P.
acidilactici has the high antimicrobial activity to clinically important pathogens, including Staphylococcus aureus, Strepto- coccus mutans, Enterococcus faecalis, Yersinia enterocolitica, and Escherichia coli O157:H7 (Huang et al., 2017; Moodley et al., 2018). Here, the complete genome sequence of SRCM103444 was characterized to identify potential genes, which are responsible for high lactic acid levels or could be associated with its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity.
Pediococcus acidilactici SRCM103444 was isolated from cheonggukjang, a traditional fermented soybean product, using the serial dilution method. When the 16S ribosomal RNA gene was compared to other members of the Pedicoccus group using the EzBioCloud database, the strain SRCM103444 was most closely related to P. acidilactici DSM 20284
T(99.93%). The genomic DNA of strain SRCM103444 was extracted using the
Korean Journal of Microbiology (2020) Vol. 56, No. 3, pp. 334-336 pISSN 0440-2413
DOI https://doi.org/10.7845/kjm.2020.0053 eISSN 2383-9902
Copyright ⓒ 2020, The Microbiological Society of Korea
Complete genome sequence of Pediococcus acidilactici strain SRCM103444 isolated from cheonggukjang
In-Seong Cha
1†, Seong-Yeop Jeong
2†, Woorim Kang
1, Je Hee Lee
1, Do-Youn Jeong
2, Byung-Yong Kim
1, and Min Seok Cho
1*
1
ChunLab, Inc., Seoul 06725, Republic of Korea
2
Microbial Institute for Fermentation Industry (MIFI), Sunchang 56048, Republic of Korea
청국장에서 분리한 Pediococcus acidilactici strain SRCM103444의 유전체 염기서열
차인성
1†・ 정성엽
2†・ 강우림
1・ 이제희
1・ 정도연
2・ 김병용
1・ 조민석
1*
1
천랩,
2발효미생물산업진흥원
(Received June 15, 2020; Revised September 1, 2020; Accepted September 1, 2020)
†
These authors contributed equally to this work.
*For correspondence. E-mail: minseok.cho@chunlab.com;
Tel.: +82-2-875-2501; Fax: +82-2-875-7250
Complete genome sequence of Pediococcus acidilactici strain SRCM103444 ∙ 335
Korean Journal of Microbiology, Vol. 56, No. 3 Fast DNA
TMSpin Kit For Soil (MP Biomedicals), according to
the manufacturer’s instructions. Total DNA was subjected to quality control by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis and quantified by a QuantiFluor
TM(Promega). The complete genome of strain SRCM103444 was sequenced using the PacBio RS II platform (Pacific Biosciences) with a 20 kb SMRTbell
TMtemplate at Macrogen Inc, and the reads were assembled using HGAP version 2.3 (Chin et al., 2013). The genome was annotated using the NCBI Prokaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline (Tatusova et al., 2016) with the best-placed reference protein set and GeneMarkS methods.
The complete genome of strain SRCM103444 contained one circular chromosome, with a total length of 1,970,727 bp and 346.26 × genome coverage. The DNA G + C content was 42.1%, and included 1,833 protein-coding genes and 71 RNA genes (15 rRNA genes, 56 tRNA genes) (Table 1). We also
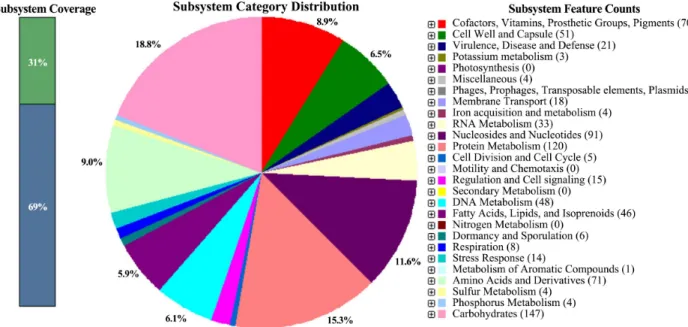
categorized 1,747 functional protein based on the cluster of orthologous genes (COG) designation. The protein-coding genes were assigned (31% of them) to functional categories of SEED subsystems at the RAST prokaryotic genome annotation server (http://rast.nmpdr.org/) (Aziz et al., 2008). Major sub- system categories were carbohydrates (18.8%), protein meta- bolism (15.3%), nucleosides and nucleotides (11.6%), amino acids and derivatives (9.0%), cofactors, vitamins, prosthetic groups, pigments (8.9%), cell wall and capsule (6.5%), DNA metabolism (6.1%), fatty acids, lipids, and isoprenoids (5.9%) (Fig. 1).
The orthologous average nucleotide identity (orthoANI) of strain SRCM103444 genome was 98.86% identical to Pedio- coccus acidilactici DSM 20284
T. Especially, the genome of SRCM103444 encodes enzymes for lactic acid production and antibiotic biosynthesis. The strain SRCM10344 contained genes encoding L-lactate dehydrogenase (locus tag EQZ51_
RS01590, accession number WP_002829746.1; locus tag EQZ51_RS08680, accession number WP_128737301.1) and acetolactate synthase (locus tag EQZ51_RS07645, accession number WP_002829993.1) which could synthesize lactic acid, alcohol tolerant enzymes such as alcohol dehydrogenase (locus tag EQZ51_RS01710, accession number WP_013728000.1) and aryl-alcohol dehydrogenase (locus tag EQZ51_RS06170, accession number WP_063504244.1). These genes include
Table 1. Genome features of P. acidilactici SRCM103444
Features Value
Genome size (bp) 1,970,727
G + C content (%) 42.1
CDS assigned by COG 1,833
rRNA genes 15
tRNA genes 56
Abbreviations: CDS, coding DNA sequence; COG, Cluster of Orthologous Groups of proteins.
Fig. 1. Subsystems distribution statistic of P. acidilactici strain SRCM103444 based on genome annotations performed according to RAST server.
336 ∙ Cha et al.
미생물학회지 제56권 제3호
those encoding for antibiotic resistance genes such as ABC-F type ribosomal protection protein (locus tag EQZ51_09490, accession number WP_128737369.1). Therefore, this strain will further help us in comprehension the genetic level potential of production of lactic acid and alcohol tolerance.
Pediococcus acidilactici SRCM103444 has been deposited in the Korean Culture Center of Microorganisms as KCCM 12743P.
Nucleotide sequence accession number
The complete genome sequence of Pediococcus acidilactici SRCM103444 was deposited at NCBI under the GenBank accession no. CP035266.
적 요
Pediococcus acidilactici는 식품 및 항생제 개발 부분에서 산업적으로 이용되는 프로바이오틱스 균주이다. Pediococcus acidilactici SRCM103444는 청국장에서 분리하였으며, 표준 발효균주 대상으로 선별되었다. Pediococcus acidilactici SRCM 103444 균주 유전체의 염기서열은 Pacific Biosciences (PacBio) single-molecule real-time (SMRT) RS II platform으로 분석하 였으며, 1,970,727 bp 크기로 GC 비율은 42.1%의 환형 구조를 가지고 있는 것으로 확인 되었고, 유전체 이외의 플라스미드 는 존재하지 않았으며, 유전체는 1,833개의 단백질 코딩 유전 자와 71개의 RNA (15 rRNA, 56 tRNA)로 구성되어 있음을 확 인하였다. 유전체에서 젖산 생성 및 알코올 내성 효소와 관련 된 유전자들이 발견이 되었다. 본 유전체 분석 결과는 건강기 능식품 생명공학 분야에서 균주 SRCM103444가 젖산 발효와 알코올 내성 활성과 관련이 있을 가능성을 보여준다.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE), Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT) and Establishment of Infrastructure for Industrialization of Korean Useful Microbes (R0004073).
References