교신저자: 박진우, 경기도 고양시 일산동구 식사동 814
411-773, 동국대학교 일산병원 재활의학과 Tel: 031-961-7484, Fax: 031-961-7488 E-mail: jinwoo_park@duih.org
삼킴곤란평가
동국대학교 의과대학 재활의학교실 박 진 우
Evaluation of Dysphagia
Jin-Woo Park, M.D.Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Dongguk University College of Medicine
Dysphagia is common, especially in the elderly, and may cause dehydration, weight loss, aspiration pneumonia and airway obstruction. It may occur because of a wide variety of structural or functional conditions, including stroke, cancer, neurologic disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease. A thorough history and a careful physical examination are important in the diagnosis but investigations such as videofluoroscopic swallowing study (VFS), fiberoptic endoscopic examination of swallowing (FEES) and manometry are more useful for confirming diagnosis, identifying the pathophysiology of a swallowing disorder and testing the therapeutic and compensatory techniques. This article reviews various evaluating methods for dysphagia. (Brain & NeuroRehabilitation 2009; 2: 103-107)
Key Words: deglutition disorders, dysphagia, endoscopy, evaluation, manometry, scale
서 론
삼킴곤란은 근신경 계통의 이상이나 입에서 상부식도 에 구조적 이상으로 인해 발생하는 삼킴의 어려움으로 이 로 인해 흡인성 폐렴이나 기도 막힘이 일어날 수 있고 영 양장애나 탈수 등의 증상도 일으킬 수도 있다. 삼킴곤란에 접근하기 위해서는 근본적으로 이를 일으킨 원인 질환을 아는 것이 중요하며 원인 질환이 치료 가능한 경우 삼킴곤 란도 완치가 되는 경우도 종종 있다. 하지만 대개의 경우 원인 질환 치료가 어려우며 같은 원인 질환인 경우에도 다양한 형태의 삼킴 장애를 일으켜 삼킴 장애의 패턴을 분석하여 그 자체로 치료적 접근을 하는 것(재활의학적 접 근)이 더 도움이 된다.
따라서 삼킴 기능의 평가에 병력이나 이학적 검사도 매 우 중요한 수단이긴 하지만 이러한 삼킴 장애 패턴을 분석 하기 위해서는 검사실 검사가 훨씬 더 유용하다. 검사실 검사에는 비디오 투시 삼킴 검사, 광섬유 내시경적 삼킴 검사, 인두 및 식도 압력검사가 있다. 본 논문에서는 삼킴 곤란을 평가하는 다양한 검사들에 대한 기본적 개념, 장단 점 등에 대하여 알아보고자 한다.
본 론
1) 임상 검사(clinical tests for dysphagia) 침상에서의 임상 검사가 검사실 검사에 비하면 기도 흡 인을 밝혀내는데 한계가 있는 것은 사실이지만1 선별검사 로서의 충분한 의미를 줄 수 있기 때문에 다양한 연구가 진행되었다. Kidd 등2은 감소된 인두 감각과 뇌졸중의 중 등도가 기도 흡인과 매우 밀접한 관련이 있다고 보고하였 고, Mari 등3은 삼킴 시 사래가 든 경험과 3온스 물 마시기 검사4(3-oz water test)의 이상 소견이 기도 흡인의 예측에 좋은 결과를 보였다고 하였다. 3온스 물 마시기 검사 는 Depippo가 개발한 선별 검사로 높은 민감도와 특이도를 보이기는 하였지만 3온스의 물은 비교적 많은 양으로 삼 킴 곤란 환자가 이를 쉼 없이 마시기에는 어려운 점이 많 았다. 1994년 발표된 Burke 삼킴 곤란 선별검사5(Burke dysphagia screening test)는 3온스 물 마시기 검사를 포함 하면서 그밖에 뇌졸중의 병변, 식사의 양과 시간, 뇌졸중 급성기의 폐렴 등 7가지 항목으로 구성하여 이들 중 한가 지라도 이상이 있으면 불합격으로 간주하였고, 불합격인 경우 합병증 발생률이 합격인 경우에 비해 7.65배나 높다 고 보고하였다. Daniels 등6도 비슷한 방법으로 삼킴 시 기 침의 유무, 음색의 변화, 비정상적 자발적 기침 등 6가지 항목 중 2가지 이상에서 이상이 나타나면 중등도 이상의 삼킴 곤란과 관련이 있다고 하였다. 이들 두 방법은 비교
Fig. 1. Videofluoroscopic swallowing study (VFS). (A) Shows the preparation of VFS. (B) Shows VFS image illustrating the anatomy of the oropharynx.
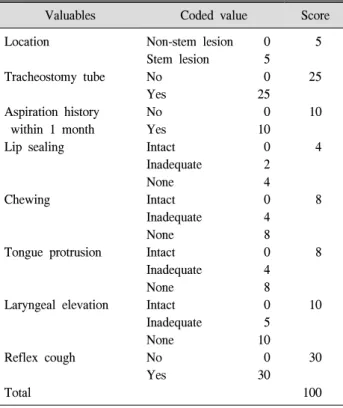
Table 1. Clinical Dysphagia Scale (CDS)
Valuables Coded value Score
Location
Tracheostomy tube
Aspiration history within 1 month Lip sealing
Chewing
Tongue protrusion
Laryngeal elevation
Reflex cough
Total
Non-stem lesion Stem lesion No Yes No Yes Intact Inadequate None Intact Inadequate None Intact Inadequate None Intact Inadequate None No Yes
0 5 0 25 0 10 0 2 4 0 4 8 0 4 8 0 5 10 0 30
5
25
10
4
8
8
10
30
100 적 여러 임상 소견을 포괄적으로 다루고는 있으나 어떤 항목이 더 중요한지에 대해서는 언급할 수 없고 또한 정량 적이지 못한 단점이 있었다. 한 등7은 이러한 단점을 보완 하여 임상적 삼킴 기능 척도(Table 1)를 개발하였고 40점 이상인 경우 기도흡인에 대한 민감도를 100%로 보고하였 다. 한편 최근 발표된 리뷰8에 의하면 맥박산소측정법 (pulse oximetry)을 조합한 물 마시기 검사(water test)가
73∼98%의 민감도를 보이며 가장 우수한 선별검사로 추 천되었다.
2) 비디오 투시 삼킴 검사(videofluoroscopic swallowing study; VFS)
삼킴 이상의 진단을 위해 가장 많이 사용하는 검사법이 며, 현재 표준 검사(gold standard)로 인정을 받고 있다.9,10 Logemann은 1980년대 초반 표준화된 방법(protocol)을 제시하였고 이후 약간씩의 변형은 있지만 기본 틀이 되고
있다.11,12 검사를 통해 삼킴 과정과 관련된 해부학적 구조
(구강, 인두, 후두, 식도)와 그들의 움직임, 조화 등을 관찰 할 수 있으며 기도 흡인(aspiration)의 원인을 확인하고 치 료적인 접근을 동시에 할 수 있는 장점이 있다.13 방사선 투시판과 x-선 튜브 사이에 환자를 앉히고 주로 옆면(lateral view)에서 검사식을 삼키는 과정을 투시해 보 면서 과정을 녹화한다(Fig. 1). 검사식은 점도를 달리한 음 식에 바륨을 섞어서 준비하며14 이를 통해 환자에게 안전 한 점도의 식이를 결정하는 것이 매우 중요하다.15-17 또한 다양한 마뉴버(maneuver)나 자세의 변화를 시도해 역시 치료적 효과 유무를 확인하는 과정이 필요하다.18-20 앞면 (anterior-posterior view) 촬영은 식도와 기도가 겹쳐지는 이유로 기도흡인의 확인은 어려우나 좌우 대칭성을 보는 데 유용하다. 삼킴의 과정이 불과 1초 미만이기 때문에 녹 화된 비디오를 저속으로 분석함으로써 보다 정확한 진단 을 할 수 있다.
방사선 노출의 위험이 있으나 그 정도가 크지 않으며 다른 방사선 검사와 비교해서도 받아드릴 수 있는 수준이
다.21,22 검사 시 기도흡인 되는 바륨도 비교적 안전한 것으
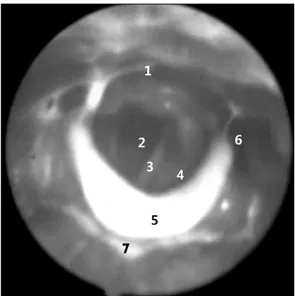
Fig. 2. View with fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES). (1) Route to esophagus, (2) trachea, (3) vocal cord, (4) aryepiglottic folds, (5) epiglottis, (6) pyriform sinus, (7) fluid with dye in vallecula.
Table 2. The Comparison Between VFS and FEES
Anatomic area/movement VFS FEES
Oral cavity/tongue Vocal cord mobility Hyo-laryngeal movement Pharyngeal wall motion UES opening
Laryngopharyngeal sensation
+++
+
+++
+++
+++
+
+
+++
+
++
+
+++
로 알려져 있다.23 하지만 결과 분석 및 치료 방향 결정을 위해서는 일정기간의 훈련이 필요하며 검사자간 해석이 다른 경우가 있어 단점으로 지적된다.24
3) 광섬유 내시경적 삼킴 검사(fiberoptic endo- scopic evaluation of swallowing; FEES) 1988년 Langmore에 의해 처음 소개되었으며,25 현재 비 디오 삼킴 검사와 함께 가장 많이 시행되고 있는 검사이다.
3∼4 mm 직경의 광섬유 내시경을 코로 삽입하여 코인 두(nasopharynx), 입인두(oropharynx) 그리고 후두 위까지 차례로 내리면서 해부학적 이상 유무 및 삼킴 생리를 관찰 한다(Fig. 2). 삼킴 기능 이상 및 기도 흡인을 관찰하면 그 원인에 따른 보상적 방법을 선택하여 치료적 접근을 할 수 있다.26 이동이 어렵고 자세를 취하기 어려운 환자도 가능하며 그림자가 아닌 칼라 영상으로 직접 관찰할 수 있어 도움이 된다. 검사에 방사선 조사의 위험이 없으며 음식물도 바륨을 섞어 변형된 음식이 아닌 일상적인 음식 으로 검사가 가능하다는 장점이 있다.
한편 검사를 시행하면서 감각 검사(fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing with sensory test; FEESST)를 동 시에 실시할 수 있는데 이는 모뿔-후두덮개 주름(aryepig- lottic fold)에 정량화된 공기 압력을 불어넣어 후두내전반 사(laryngeal adduction reflex; LAR)를 유발하는 것으로27 6 mmHg 이상에서도 반응이 없는 경우 이상으로 보며28 이런 경우 기도 흡인이나 흡인성 폐렴과 관련이 높다.29
하지만 삼킴이 일어나는 중요한 시기에 인두 수축근이 수축하고 후두 덮개가 뒤집히면서 렌즈를 가리는 ‘white out’ 현상이 일어나, 후두 통과나 기도 흡인 여부를 직접 볼 수 없으며, 구강기(oral phase)와 식도기(esophageal phase) 또한 관찰 할 수 없다는 단점이 지적된다. 그리고 검사를 하기 위해 숙련도 높은 기술이 필요하다.
검사로 인한 부작용으로 코피, 구역질, 실신, 후두경련 등이 있을 수 있으나 그 발생은 극히 드물며 매우 안전한 검사로 알려졌다.30,31 검사의 타당도는 대부분 VFS와 비 교한 것으로 기도 흡인의 민감도가 FEES가 매우 높은 것 으로 보고 됐다.32,33
그럼 과연 VFS와 FEES 중 어느 검사가 더 좋은 검사일 까? 앞서 언급했듯이 두 검사 모두 장단점을 가지고 있고 우수성에 있어서도 비슷하다는 평가를 받고 있다(Table 2).
따라서 어느 한 검사가 더 낫다기 보다 서로 보완적인 관 계를 가질 수 있고 검사하는 기관의 여건에 따라 혹은 환 자의 상태에 따라 선택을 달리 할 수 있겠다.34
4) 인두 및 식도 압력 검사(pharyngeal and upper esophageal manometry)
압력 검사는 직경 3 mm의 구부러지는 튜부 형태의 압력 센서를 코를 통해 삽입한 후 압력 측정부를 인두부 및 상 부 식도 조임근 위치에 거치시킴으로써 이 부위의 압력을 측정하는 것이다. 이는 기존의 식도 운동 장애의 진단을 위해 쓰인 식도 압력 검사와 차이가 있는데 이는 식도 압 력 검사가 8∼20초 정도의 진행을 측정하는 것과 달리 인 두부의 경우 1초 미만의 압력 변화를 측정해야 함으로 압 력에 민감한 센서를 사용해야 한다.12
모든 삼킴곤란 환자에 실시해야 하는 것은 아니며 주로 인두 수축근의 약화가 의심되거나 상부 식도 조임근이 잘 열리지 않는 경우, 혹은 이들 간의 협동 장애가 의심되는 경우에 매우 도움이 된다.35
하지만 기술적으로 정확한 데이터를 얻기가 매우 어려 운데 이는 삼킴 과정에서 움직임이 일어나 처음 센서를 둔 위치에서 벗어나기 때문이다.36 이러한 이유로 압력 검
Table 3. Penetration-Aspiration Scale 1. Material does not enter the airway
2. Material enters the airway, remains above the vocal folds, and is ejected from the airway 3. Material enters the airway, remains above the vocal folds, and is not ejected from the airway 4. Material enters the airway, contacts the vocal folds, and is ejected from the airway
5. Material enters the airway, contacts the vocal folds, and is not ejected from the airway
6. Material enters the airway, passes below the vocal folds and is ejected into the larynx or out of the airway 7. Material enters the airway, passes below the vocal folds, and is not ejected from the trachea despite effort 8. Material enters the airway, passes below the vocal folds, and no effort is made to eject
사는 단독으로 시행하기보다 VFS와 동시에 시행함으로써 압력 센서의 위치에 대한 확인 및 식괴의 움직임에 따른 부위별 압력에 대한 보다 정확한 정보를 얻을 수가 있으며 이를 manofluorography 혹은 videomanometry라고 한다.37
5) 종합 척도
삼킴 곤란은 삼킴 기능에 문제를 일으키는 일종의 장애 로 FIM (functional independence measure)나 바텔 지수 (Barthel index)와 같이 포괄적으로 그 기능을 평가할 수 있는 도구들이 필요하다. 이를 통해 환자의 상태를 전체적 으로 파악하여 치료진 간 의사소통을 원활하게 하고 시간 경과나 치료 후에 기능 변화 여부를 측정 할 수 있다.
미국언어청각협회(American Speech-Language-Hearing Association; ASHA)에서는 환자에게 요구되는 지도(super- vision)의 정도와 가능한 식사 수준에 따라 1에서 7까지 구분하는 포괄적 도구로서 삼킴 척도(National Outcome Measurement System swallowing level scale; NOMS)를 제 안 하였다.38 삼킴 곤란 결과 및 증증도 척도(The Dysphagia Outcome and Severity Scale; DOSS) 역시 7단계로 구성된 포괄적 척도로서 독립의 수준, 구강 섭취가 가능한 정도, 그리고 식사 수준 및 변형 정도에 따라 나누었으며 90%
이상의 검사자내, 검사자간 신뢰도를 보였다.39 한편 한 등40 은 뇌졸중 환자에서 6개월 이후에도 삼킴 곤란이 회복되 지 않는 것을 예측하고자 비디오 투시 삼킴 척도(Video- fluoroscopic Dysphagia Scale; VDS)를 개발하였는데, 이 또한 비디오 투시 삼킴 검사의 소견을 종합적으로 반영하 고 100점 만점의 점수로 표기되어 종합 척도로 사용할 수 있다고 제안하였다. 후두통과-기도흡인 척도(Penetration- Aspiration Scale; PA scale) (Table 3)는 Rosenbek 등41에 의해 제안되었고 이 역시 비디오 투시 삼킴 검사 소견상 후두통과와 기도흡인의 정도 및 음식물이 노력에 의해 기 도 밖으로 배출될 수 있는 지 여부에 따라 8단계로 나누어 져 있다. 검사자간 그리고 검사자내 신뢰도가 매우 높고 간단하고 쉬워서 널리 사용되고 있다.
결 론
이상에서 삼킴 기능 평가에 가장 널리 사용되고 있는 검사법 및 기능 척도에 대하여 알아보았다. 이들 평가 도 구들 중 어느 한 도구가 뛰어나다기 보다 장단점에 따라 혹은 검사 기관의 사정에 따라 적절히 선택해 사용하는 것이 중요하며, 평가는 평가로 끝나는 것이 아니라 반드시 치료적인 계획과 연결되야 한다는 점을 강조하고 싶다.
참 고 문 헌
1) Splaingard ML, Hutchins B, Sulton LD, Chandhury G.
Aspiration in rehabilitation patients: videofluoroscopy vs bedside clinical assessment. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1988;69:
637-640
2) Kidd D, Nesbitt LR, MacMahon J. Aspiration in acute stroke:
a clinical study with videofluoroscopy. QJM. 1993;86:825-829 3) Mari F, Matei M, Ceravolo MG, Pisani A, Montesi A,
Provinciali L. Predictive value of clinical indices in detecting aspiration in patients with neurological disorders. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1997;63:456-460
4) Depippo KL, Holas MA, Reding MJ. Validation of the 3-oz water test for aspiration following stroke. Arch Neurol. 1992;
49:1259-1261
5) Depippo KL, Holas MA, Reding MJ. The Burke dysphagia screening test: validation of its use in patients with stroke.
Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1994;75:1284-1286
6) Daniels SK, Ballo LA, Nahoney MC, Foundas AL. Clinical predictors of dysphagia and aspiration risk: outcome measures in acute stroke patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil.
2000;81:1030-1033
7) Han TR, Paik NJ, Park JW. The clincal functional scale for dysphagia in stroke patients. Korean J Stroke. 2001;3:
153-157
8) Bours GJ, Speyer R, Lemmens J, Limburg M, de Wit R.
Bedside screening tests vs. videofluoroscopy or fibreoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing to detect dysphagia in patients with neurological disorders: systematic review. J Adv Nurs. 2009;65:477-493
9) Palmer JB, Kuhlemeier KV, Tippett DC, Lynch C. A protocol
for the videofluorographic swallowing study. Dysphagia.
1993;8:209-214
10) Kuhlemeier KV, Yates P, Palmer JB. Intra- and interrater variation in the evaluation of videofluorographic swallowing studies. Dysphagia. 1998;13:142-147
11) Logemann JA. Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders. Austin, TX: Pro-Ed Publishers; 1983
12) Logemann JA. Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders. 2nd ed. Austin, TX: Pro-Ed Publishers; 1998 13) Leslie P, Carding PN, Wilson JA. Investigation and
management of chronic dysphagia. BMJ. 2003;326:433-436 14) Paik NJ, Han TR, Park JW, Lee EK, Park MS, Hwang IK.
Categorization of dysphagia diets with the line spread test.
Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85:857-861
15) Dooley CP, Di Lorenzo C, Valenzuela JE. Esophageal function in humans: effects of bolus consistency and temperature. Dig Dis Sci. 1990;35:167-172
16) Kim CH, Hsu JJ, O’'Connor MK, Weaver AL, Brown ML, Zinsmeister AR. Effect of viscosity on oropharyngeal and esophageal emptying in man. Dig Dis Sci. 1994;39:189-192 17) Raut VV, McKee GJ, Johnston BT. Effect of bolus
consistency on swallowing-does altering consistency help? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2001;258:49-53
18) Shanahan TK, Logemann JA, Rademaker AW, Pauloski BR, Kahrilas PJ. Chin-down posture effect on aspiration in dysphagic patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1993;74:736-739 19) Logemann JA, Kahrilas PJ, Kobara M, Vakil NB. The benefit of head rotation on pharyngoesophageal dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1989;70:767-771
20) Kahrilas PJ, Logemann JA, Krugler C, Flanagan E. Volitional augmentation of upper esophageal sphincter opening during swallowing. Am J Physiol. 1991;260:G450-456
21) Zammit-Maempel I, Chapple CL, Leslie P. Radiation dose in videofluoroscopic swallow studies. Dysphagia. 2007;22:13-15 22) Wright RE, Boyd CS, Workman A. Radiation doses to
patients during pharyngeal videofluoroscopy. Dysphagia. 1998;
13:113-115
23) Han TR, Paik NJ, Park JW. The safety of videofluoroscopic swallowing study (VFSS). J Korean Acad Rehabil Med.
2000;24:215-218
24) Stoeckli SJ, Huisman TA, Seifert B, Martin-Harris BJ.
Interrater reliability of videofluoroscopic swallow evaluation.
Dysphagia. 2003;18:53-57
25) Langmore SE, Schatz K, Olsen N. Fiberoptic endoscopic examination of swallowing safety: a new procedure. Dysphagia.
1988;2:216-219
26) Cichero J, Murdoch B. Dysphagia: foundation, theory and practice. West Sussex, UK: John Wiley & Sons Ltd; 2006 27) Aviv JE, Sacco RL, Diamond B, Kaplan S, Goodhart K,
Diamond B, Close LG. FEESST: a new bedside endoscopic
test of the motor and sensory components of swallowing. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1988;107:378-387
28) Setzen M, Cohen MA, Perlman PW, Belafsky PC, Guss J, Mattucci KF, Ditkoff M. The association between laryn- gopharyngeal sensory deficits, pharyngeal motor function and the prevalence of aspiration with thin liquids. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003;128:99-102
29) Aviv JE, Spitzer J, Cohen M, Ma G, Belafsky P, Close LG.
Laryngeal adductor reflex and pharyngeal squeeze as predictors of laryngeal penetration and aspiration. Laryng- oscope. 2002;112:338-341
30) Aviv JE, Murry T, Zschommler A, Cohen M, Gartner C.
Flexible endoscopic evaluation of swallowing with sensory testing: patient characteristics and analysis of safety in 1,340 consecutive examinations. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2005;
114:173-176
31) Cohen MA, Setzen M, Perlman PW, Ditkoff M, Mattucci KF, Guss J. The safety of flexible endoscopic evaluation of swallowing with sensory testing in an outpatient otolaryn- gology setting. Laryngoscope. 2003;113:21-24
32) Wu CH, Hsiao TY, Chen JC, Chang YC, Lee SY. Evaluation of swallowing safety with fiberoptic endoscope: comparison with videofluoroscopic technique. Laryngoscope. 1997;107:
396-401
33) Leder S, Sasaki CT, Burrell MI. Fiberoptic endoscopic evalu- ation of dysphagia to identify silent aspiration. Dysphagia.
1998;13:19-21
34) Langmore SE. Evaluation of oropharyngeal dysphagia: which diagnostic tool is superior? Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003;11:485-489
35) Hila A, Castell JA, Castell DO. Pharyngeal and upper esophageal sphincter manometry in the evaluation of dys- phagia. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001;33:355-361
36) Ergun GA, Kahrilas PJ, Logemann JA. Interpretation of pharyngeal manometric recordings: limitations and vari- ability. Dis Esophagus. 1993;6:11-16
37) McConnel FMS, Cerenko D, Hersh T, Weil LJ. Evaluation of pharyngeal dysphagia with manofluorography. Dysphagia.
1988;2:187-195
38) American Speech-Language Hearing Association National Outcomes Measurements System (NOMS): Adult Speech- Language Pathology Training Manual, Rockville MD: ASHA, 1998
39) O'Neil KH, Purdy M, Falk J, Gallo L. The Dysphagia Outcome and Severity Scale. Dysphagia. 1999;14:139-145 40) Han TR, Paik NJ, Park JW, Kwon BS. The prediction of
persistent dysphagia beyond six months after stroke. Dysphagia.
2008;23:59-64
41) Rosenbek JC, Robbins JA, Roecker EB, Coyle JL, Wood JL.
A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia. 1996;11:93-98