대한외과학회지:제 67 권 제 2 호
□ 증 례 □ Vol. 67, No. 2, August, 2004
171
서 론
호중구감소성 소장결장염(neutropenic enterocolitis)은 백 혈병이나 림프종에 대한 항암화학요법 후에 주로 발생하며 그 외 재생 불량성 빈혈, 골수 이형성 증후군, 장기이식 후 면역억제제를 사용하는 경우 등에도 발생하는 장 점막의 염증성 질환이다. 호발부위는 회장말단, 맹장, 우측 결장이 며, 조기에 진단하여 치료하지 않으면 장관 벽의 전 층에 비화농성, 무과립성 괴사가 생겨 장출혈, 장천공, 복막염, 패혈증 등으로 사망까지 이르는 질환이다.(1) 특히 항암제
Neutropenic Enterocolitis with Liver Abscess in a Young Patient with Leukemia after Chemo- therapy
Hyung Seok Park, M.D., Seung Hyun Lee, M.D., Byung Kwon Ahn, M.D., Sung Uhn Baek, M.D., and Jae Sun Park, M.D.1
Neutropenic enterocolitis is a serious complication of che- motherapy for malignancies such as acute leukemia or lymphoma. The acute inflammatory disease may involve the terminal ileum, cecum and ascending colon. Although conservative care is recommended as the primary treatment modality, surgical intervention is essential for intestinal perforations, abscesses, or bleeding. We experienced a case of neutropenic enterocolitis with a liver abscess in a young leukemia patient. A 13-year-old boy with acute myelogenous leukemia had completed two cycles of chemotherapy (Ara- binoside 300 mg, Dactinomycin 40 mg, VP-16 150 mg, 6- mercaptopurin 60 mg, dexametasone 3 mg). Ten days after completing the second cycle he had abdominal pain, low abdominal tenderness and a high fever. The WBC count in the peripheral blood was 210 cell/mm3. A CT scan demon- strated wall thickening of the terminal ileum and ascending colon, as well as 5 cm, and 6 cm sized homogeneous low-density areas in both hepatic lobes. A presumptive diagnosis was neutropenic enterocolitis with a liver abscess.
The patient was managed conservatively with fluid resuscitation, a bowel rest, and broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Twenty-five days later his abdominal pain was abruptly aggravated. The CT scan and Chest X-ray demonstrated free air in the peritoneal cavity. An emergency laparotomy was performed under a diagnosis of peritonitis with an
책임저자:이승현, 부산광역시 서구 암남동 34번지 ꂕ 602-702, 고신대학교 의과대학 외과학교실 Tel: 051-990-6462, Fax: 051-246-6093 E-mail: gscrslsh@hanmail.net
접수일:2004년 1월 17일, 게재승인일:2004년 4월 9일
본 논문의 요지는 2003년 대한외과학회 추계학술대회에서 구연 발표되었음.
소아 백혈병 환자에서 화학요법 후 간농양을 동반한 호중구감소성 소장결장염
고신대학교 의과대학 외과학교실, 1소아과학교실
박형석․이승현․안병권․백승언․박재선1
intestinal perforation. The laparotomy show that, there were perforations at the pylorus of the stomach, and full thickness necrosis at multiple segments of the small bowel. Primary closure of the stomach, a segmental resection and an end-to-end anastomosis of the small bowel, and ileostomy were performed. However, postoperative leakage developed at the stomach. The patient recovered with supportive management. The patient had a third chemotherapy series 3 months after surgery. Three days after completing the third cycle, the patient developed peritonitis. A pyloric re-perforation of the stomach was observed on the laparotomy. Post- operative leakage developed after the primary closure of the stomach. The patient died of sepsis 54 days later. Therefore, intensive monitoring and close collaboration between the hematologist and the surgeon is essential for patients with neutropenic enterocolitis. Postoperative complications are quite common and can be fatal in patients with neutropenic enterocolitis that develops after chemotherapy. (J Korean Surg Soc 2004;67:171-174)
Key Words: Neutropenic enterocolitis, AML, Intestinal perfo- ration
중심 단어: 호중구감소성 소장결장염, 급성 골수성 백혈병, 위장관천공
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ Departments of Surgery, and 1Pediatrics, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
172 대한외과학회지:제 67 권 제 2 호 2004
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ 를 투여 받은 백혈병 환자에서 급성 복통이 발생되었을 때
에 급성 충수염, 우측 대장 게실염, 위막성 대장염, 간농양, 췌장염 등과 정확한 감별이 필요하다.(2,3) 진단을 위한 방 사선학적 검사로는 복부 초음파검사 또는 복부 컴퓨터단층 촬영이 안전하고 정확한 방법으로 알려져 있으며 대부분 우측결장 및 맹장 장벽의 전반적인 비후, 결장주위의 액체 저류, 복강 내 기종, 인접 근막의 비후와 같은 소견을 관찰 할 수 있다.(4-6) 합병증이 없는 호중구감소성 소장결장염 에 대해서는 대개의 경우 보존적 요법이 우선 적용되나 여 전히 사망률이 높은 실정이며, 장이 괴사되어 천공되는 경 우, 지속적인 장출혈이 있는 경우, 범발성 복막염 증세가 있 는 경우에는 수술적 치료가 필요하다.(7)
저자들은 최근 급성 골수성 백혈병으로 항암화학요법을 받은 소아 환자에서 간농양과 동반되어 호중구감소성 소장 결장염에 의한 위, 소장의 다발성 괴사 및 천공, 범발성 복 막염 소견을 보인 1예를 경험하였기에 보고하고자 한다.
증 례
급성 골수성 백혈병으로 진단받은 13세 남아가 관해 유 도 요법으로 DCTER (arabinoside 300 mg, dactinomycin 40 mg, VP-16 150 mg, 6-mercaptopurin 60 mg, dexametasone 3 mg) 항암화학요법을 2차례 투여받은 후 10일째부터 복통, 하복부 압통, 복부팽만 및 발열 소견을 보였다. 당시 혈압은 120/80 mmHg, 맥박은 120회/분, 호흡수는 24회/분, 체온은 38.5oC였으며, 말초혈액검사에서 혈색소 9.8 g/dl, 헤마토크 리트 25.1%, 백혈구 210/mm3 (호중구 88/mm3), 혈소판 32,000/mm3의 소견을 보였다. 혈액화학검사는 단백질 4.4 g/dl, 알부민 2.6 g/dl, 총 빌리루빈 1.5 mg/dl, 직접 빌리루빈 1.0 mg/dl, 알칼리성 포스파타제 330 U/L, AST 22 U/L, ALT
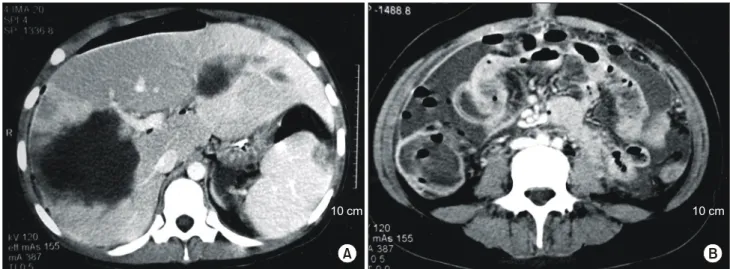
33 U/L, 혈중뇨질소 11 mg/dl, 크레아티닌 0.6 mg/dl의 소견 을 보였다. 복부 초음파검사와 복부 컴퓨터단층촬영에서는 우하복부의 회장말단, 맹장의 장벽이 비후되어 있었으며, 양측 간엽에 각각의 직경이 5 cm, 6 cm로 측정되는 균질성 의 저음영 병소가 관찰되었다. 혈액배양검사에서는 klebsiella pneumonae가 검출되었으나 양측 간엽에 있었던 병소의 세 침흡입을 통한 균 배양 검사에서는 균이 검출되지는 않았 다. 이에 진단은 간농양을 동반한 호중구감소성 소장결장 염으로 추정하여 수액 및 전해질 공급, 장 휴식, 항생제 및 항진균제의 사용으로 보존적 치료를 하였다. 보존적 치료 를 하던 중 항암화학요법 후 25일째 복통이 갑자기 악화되 었으며 당시의 말초혈액검사에서는 혈색소 12.5 g/dl, 헤마토 크리트 31.5%, 백혈구 1,490/mm3, 혈소판 39,000/mm3의 소 견을 보였고, 복부 컴퓨터단층촬영에서는 이전 검사에서 관찰되었던 양측 간엽의 병소 직경이 각각 7 cm, 11 cm로 커져 있었고 우하복부의 회장말단, 맹장, 상행결장의 장벽 이 심하게 비후되어 있으며 주위에는 다량의 액체가 저류 되어 있는 소견과 복강 내 유리가스가 관찰되었다(Fig. 1).
이에 호중구감소성 소장결장염의 합병증으로 장천공에 의 한 범발성 복막염을 진단하여 진단적 개복술을 시행하였 다. 수술 소견에서 위장 유문부의 전벽에 직경 1 cm 정도의 천공 소견이 보였으며, 소장에 다발성으로 장벽의 전 층이 괴사, 파열된 분절을 관찰할 수 있었다. 수술은 위장의 유문 부는 1차 봉합술, 소장 부위는 분절절제술 및 단단문합술을 시행하였으며 회장루 조성술을 추가 시행하였다. 수술 전 관찰되었던 간농양에 대해서는 수술 중 다시 세침흡입 및 간 표면에 부분 절개를 가하여 배농을 시도하였다(Fig. 2).
수술 1 주일 후 1차 봉합술을 시행한 위장의 유문부에 누출 이 발생되어 경구 식이 섭취를 중단하고 중심정맥을 이용 한 경정맥 고영양법 및 보존적 요법으로 치료하였으며 수
Fig. 1. Abdominal CT scan shows homogenous hypodense mass lesions (diameter 7 cm, and 11 cm) in both hepatic lobe (A), wall thickening of terminal ileum, cecum and ascending colon, fluid collection at pericolic space, and free air in intraperitoneal cavity (B).
10 cm 10 cm
A B
박형석 외:소아 백혈병 환자에서 화학요법 후 간농양을 동반한 호중구감소성 소장결장염 173 ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ
술 후 46일째 회복하여 퇴원하였다.
수술한 지 3개월 후 3차 항암화학요법을 시행하였으며 항암화학요법 후 3일째부터 구토, 심한 복통 및 발열 소견 을 보였다. 당시의 말초혈액검사에서는 혈색소 10.5 g/dl, 헤 마토크리트 31.5%, 백혈구 5,070/mm3, 혈소판 196,000/mm3의 소견을 보였으며, 흉부 X-선 및 복부 초음파검사에서는 복 강 내 유리 가스가 보여 장천공에 의한 복막염의 재발로 진단하여 2차 진단적 개복술을 시행하였다. 수술 소견에서 는 위장의 유문부에 천공이 있고 주위로 위 내용물이 누출 되어 있어 변연절제술 및 1차 봉합술을 시행하였다. 수술 후 3일째 말초혈액의 혈색소 7.4 g/dl, 헤마토크리트 21.5%, 백혈구 220/mm3, 혈소판 45,000/mm3으로 면역기능이 더 저 하되는 소견을 보였으며, 봉합 부위의 누출이 다시 발생하여 보존적 치료하던 중 수술 후 54일째 패혈증으로 사망하였다.
고 찰
호중구감소성 소장결장염(neutropenic enterocolitis)은 괴 사성 소장결장염(necrotizing enterocolitis), 회맹장 증후군 (ileocecal syndrome), 맹장염(typhilitis) 등으로 명명되며 백 혈병, 임파종으로 항암화학요법 치료를 받고 있는 경우에 상대적으로 호발하지만, 진행암의 항암화학요법 후에, 재생 불량성 빈혈, 골수 이형성 증후군, 장기이식 후 면역억제제 치료 중에도 나타난다. 관련 있는 항암제에는 cytosine arabinoside, etoposide, methotraxate 등이 있으며, 특히 cyto- sine arabinoside가 가장 많이 관여하는 것으로 보고되고 있 다.(8,9) 발생기전은 항암제의 사용이 빠른 속도로 재생되는 장관의 점막 세포를 파괴시키고 호중구가 감소된 상태에서 장벽을 통한 세균의 침습을 유발시켜 장 점막에 염증이 발 생하는 것으로 추정되며 경우에 따라서는 세균의 침습이
장벽 전 층의 괴사를 가져오기도 한다. 본원의 경우에서도 급성 골수성 백혈병으로 진단받은 13세의 소아 환자에서 항암화학요법으로 cytosine arabinoside를 투여받은 후에 호 중구감소성 소장결장염이 발생하였으며 증상 발현까지의 기간은 10일 정도였다. 초기에는 보존적 치료를 적용하였 으나 장관의 염증이 진행되어 위장 유문부가 천공되고 소 장에 다발성으로 장벽 전 층의 괴사, 파열 소견을 보였던 경우였으며 양측의 간엽에도 간농양으로 추정되는 비화농 성 간괴사가 동반되기도 하였다. 호발부위는 회장말단과 맹장으로 이는 일차적으로 혈액 공급량이 적고, 장의 팽창 으로 인하여 혈류량이 더욱 감소되어서 허혈증이 유발되기 쉬우며, 임파절 분포가 다른 장기에 비해 적어서 감염에 노 출되기 쉽기 때문이다.(10,11) 발생빈도는 비교적 드물게 나 타나는 것으로 알려져 있다. Exelby 등(12)은 백혈병 286명 중 6명(2.1%)에서 호중구감소성 소장결장염이 발생하였다 고 보고하였으나 Katz 등(1)의 보고에서는 급성 백혈병으로 사망한 137명을 부검한 결과 37명(24%)에서 호중구감소성 소장결장염의 소견을 관찰하였다고 보고하여 실제 발생빈 도에 비해 진단율이 비교적 낮음을 보여 주고 있다.
임상증상으로는 고열, 복통, 복부팽만, 하복부 종괴, 구 토, 설사, 위장관 출혈 등의 특이적이지 않은 증상을 나타내 며, 특히 우하복부 동통을 호소하는 경우가 많아 급성충수 염, 장중첩증, 장폐쇄증, 간농양, 췌장염 등의 급성 복증과 감별 진단이 중요하다.(2,3) 말초혈액검사에서 대부분 백혈 구 감소증, 혈소판 감소증이 동반되며 백혈구 감소증은 말 초혈액 내의 백혈구 수가 500/mm3 이하인 경우가 많다고 보고하고 있다.(1,9), 혈액배양검사에서는 녹농균, 대장균, 포도상 구균, 캔디다, aspergillus가 흔히 발견된다. 본 예에 서는 호중구감소성 소장결장염을 진단할 당시 고열, 하복 부 동통, 복부팽만, 우하복부 압통 등의 증상을 보여 이학적 검사 소견만으로는 급성충수염과 감별이 어려웠으며, 말초 혈액의 백혈구 수는 210/mm3으로 심한 백혈구감소증의 소 견을 보였다. 혈액배양검사에서는 klebsiella pneumonae가 검출되었으나 양측 간엽의 병소에 대한 세침흡입을 통한 균 배양검사에서는 균이 검출되지 않았다. 이는 백혈구감 소증으로 인해 간조직의 염증 및 괴사가 비화농성으로 이 루어졌기 때문이라 생각한다. 수술로 절제된 소장의 분절 의 점막하 혈관에서는 진균의 색전(fungal emboli)이 관찰되 기도 하였다. 진단을 위한 방사선학적 검사로는 복부 초음 파 또는 복부 컴퓨터단층촬영이 효과적이며 회장말단, 맹 장, 상행결장의 장벽비후, 결장주위의 액체 저류, 복강 내 기종, 인접 근막의 비후와 같은 소견을 관찰할 수 있다.(4-6) 치료는 환자의 전신상태가 불량하고 장천공, 패혈증으로 진행하는 경우가 많아 수술적 치료가 선호되기도 하였으나 (12,13) 수술 자체에 관련된 위험성 및 수술 후 합병증이 동 반될 가능성이 많아 최근에는 주로 보존적 치료가 선호된 다.(14,15) 보존적 치료로는 수액교정 및 경정맥 고영양법과 Fig. 2. On laparotomy, multiple segments of small bowel were
transected because of full thickness necrosis.
174 대한외과학회지:제 67 권 제 2 호 2004
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ 더불어 광범위 항생제, 항진균제의 사용, 성분수혈, 백혈구
감소증을 호전시키는 약제 투여, 정맥 내 글로불린 투여 등 이 적용되며 보존적 치료의 사망률은 10∼50% 정도로 보고 되고 있다.(9,16) 장관이 천공되거나, 장출혈이 지속될 때, 범발성 복막염 증세가 있을 때, 보존적 치료에도 불구하고 환자의 상태가 악화되는 경우에는 외과적 치료가 적용되어 야 한다.(7,9) 국내에서 박 등(17)은 비록 장천공이 되어 복 강 내 농양이 생기더라도 병소가 국한되어 있거나 환자의 상태가 양호할 경우에는 보존적인 치료로도 좋은 결과를 얻을 수 있다고 하였다. 치료의 예후는 예측하기 힘드나 Wade 등(9)은 수술적 치료가 적용된 경우 말초혈액의 백혈 구 수가 1,000/mm3 이상 회복되면 수술 후 생존할 가능성이 높다고 언급하였으며, Cartoni 등(18)은 복부 초음파검사에 서 장벽의 두께가 10 mm 이상인 경우 사망률이 높다고 하 였다. 본원의 경우에는 1차로 발생했던 범발성 복막염의 경 우 수술 후에 누출과 같은 합병증은 생겼으나 보존적 치료 로 호전되었다. 반면 2차로 발생했던 범발성 복막염의 경우 에는 수술 후에 동일한 합병증이 발생하였으나 회복하지 못하고 패혈증으로 사망한 예였다. 비록 수술 후 합병증 및 사망률은 수술자의 수술방법의 선택, 수술의 숙련도, 수술 후 환자관리의 정도에 따라 다양한 양상을 나타내지만 여 러 치료방법의 개선에도 불구하고 여전히 수술 후 합병증 발생이나 환자가 사망할 가능성이 높은 질환이므로 향후 합병증이나 치명적 상태를 호전시키기 위한 보다 나은 집 중치료에 대해서 지속적인 연구가 필요할 것으로 생각한 다.
REFERENCES
1) Katz JA, Wagner ML, Gresik MV, Mahoney DH Jr, Fernbach DJ. Typhilitis-an 18-year experience and postmortem review.
Cancer 1990;65:1041-7.
2) Sherman JN, Williams K, Woolley MM. Surgical complica- tions in the patient with leukemia. J Ped Surg 1973;8:235-44.
3) Skibber JM, Matter GJ, Pizzo PA, Lotze MT. Right lower quadrant pain in young patients with leukemia: a surgical perspective. Ann Surg 1987;206:711-6.
4) Frick MP, Maile CW, Crass JR, Goldberg ME, Delaney JP.
Computed tomography of neutropenic colitis. AJR 1984;143:
763-5.
5) Sloas MM, Flynn PM, Kaste SC, Patrick CC. Typhilitis in children with cancer: a 30-year experience. Clin Infest Dis 1993;17:484-90.
6) Gomez L, Martino P, Rolston KV. Neutropenic enterocolitis:
Spectrum of the disease and comparison of definite and pos- sible cases. Clin Infest Dis 1998;27:695-9.
7) Keidan RD, Fanning J, Gatenby RA, Weese JL. Recurrent typhilitis-a disease resulting from aggressive chemotherapy.
Dis Colon Rectum 1989;32:206-9.
8) Slavin RE, Dias MA, Saral R. Cytosine arabinoside-induced gastrointestinal toxic alteration in sequential chemotherapeutic protocols. Cancer 1978;42:1747-59.
9) Wade DS, Nava HR, Douglass HO Jr. Neutropenic enterocoli- tis: Clinical diagnosis and treatment. Cancer 1992;69:17-23.
10) Dosik GM, Luna M, Valdivieso M, McCredie KB, Geban EA.
Necrotizing colitis in patients with cancer. Am J Med 1979;
67:646-56.
11) Mower WJ, Hawkins JA, Nelson EW. Neutropenic enterocoli- tis in adults with acute leukemia. Arch Surg 1986;121:571-4.
12) Exelby PR, Ghandchi A, Lansigan N, Schwarz I. Management of the acute abdomen in children with leukemia. Cancer 1975;
35:826-9.
13) Ikard RW. Neutropenic typhilitis in adults. Arch Surg 1981;
116:943-5.
14) Song HK, Kreisel D, Canter R, Krupnick AS, Stadtmauer EA, Buzby G. Changing presentation and management of neut- ropenic enterocolitis. Arch Surg 1998;133:979-82.
15) Baerg J, Murphy JJ, Anderson R, Magee JF. Neutropenic enterpathy: a 10-year review. J Pediatr Surg 1999;34:1068-71.
16) Shamberger RC, Weinstein HJ, Delorey MJ, Levey RH. The medical and surgical management of typhilitis in children with acute nonlymphocytic(myelogenous) leukemia. Cancer 1986;
57:603-9.
17) Park WH, Ahn KS, Choi SO. Two cases of perforated typhilitis in acute lymphocytic leukemia. Journal of the Korean Associ- ation of Pediatric Surgeons 2001;7:59-63.
18) Cartoni C, Dragoni F, Micozzi A, Prescarmona E, Mecarocci S, Chirletti P, et al. Neutropenic enterocolitis in patients with acute leukemia: prognostic significance of bowel wall thicken- ing detected by ultrasonography. J Clin Oncol 2001;19:756-61.