대한소화기학회지 2003;42:72-76
서 론
1)회장낭염(pouchitis)은 회장낭내 비특이적인 급성 염증으 로 궤양성 대장염, 가족성 선종성 용종증 환자에게 전대장 절제술과 회장낭-항문문합술(ileal pouch-anal anastomosis, IPAA) 후 발생하는 가장 흔한 합병증으로 발생률은 20- 50%로 보고되고 있다.1 국내 연구에서는 궤양성 대장염 환 자 50명에게 치료로 IPAA 후 9명에서 회장낭염이 발생하 였다고 보고하였다.2 발생 원인은 불명확하나 궤양성 대장 염의 재발, 점막의 허혈 상태3 및 회장낭내 세균의 과성장 등이 관여한다고 추정된다.4 대부분 회장낭염 환자에 있어
접수: 2002년 11월 6일, 승인: 2003년 3월 21일
연락처: 김효종, 130-720, 서울특별시 동대문구 회기동 1번지 경희의료원 내과
Tel: (02) 958-8147, Fax: (02) 958-8151 E-mail: hjkim@khmc.or.kr
항생제 치료는 효과적이지만, 5-15%에선 재발률이 높고 치 료에 듣지 않는다.5 원인으로는 회장낭염 자체가 치료에 저 항적인 일차적인 경우와 골반내 2)패혈증, 대변량이 많은 경 우, 크론병을 궤양성 대장염으로 잘못 진단하고 수술한 경 우, 조절되지 않는 변실금으로 인한 이차적인 원인이 있다.6 이차적인 경우를 제외한 원발성 저항성 회장낭염은 만성 회장낭염의 1-2%를 차지하고7 이에 대한 치료로 여러 약물 들이 시도되고 있지만 대부분의 환자들은 회장낭을 제거하 고 영구적인 회장루조성술을 받게 된다. 저자들은 약물치 료에 반응이 없었던 궤양성 대장염 환자에게 전대장절제술 과 회장낭-항문문합술 시행 후 발생한 내과적 치료에 반응
Correspondence to: Hyo Jong Kim, M.D.,
Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine
1 Hoigi-dong, Dongdaemoon-gu, Seoul 130-702, Korea Tel: +82-2-958-8147 Fax: +82-2-958-8151
E-mail: hjkim@khmc.or.kr
내과적 치료에 반응하지 않는 만성 회장낭염 1예
경희대학교 의과대학 내과학교실
장재영·김효종·김완중·정용희·이병욱·한요셉·동석호·김병호·장영운·이정일·장 린
A Case of Chronic Pouchitis Resistant to Medical Treatment
Jae Young Chang, M.D., Hyo Jong Kim, M.D., Wan Jung Kim, M.D., Yong Hee Jung, M.D., Byoung Wook Lee, M.D., Yo Seb Han, M.D., Seok Ho Dong, M.D., Byung-Ho Kim, M.D.,
Young Woon Chang, M.D., Joung Il Lee, M.D., and Rin Chang, M.D.
Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
Pouchitis, a non-specific acute inflammation occurring in the ileal pouch, is one of the most common complications developed after the restorative proctocolectomy and ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (IPAA) performed for the treatment for the patients with ulcerative colitis and familial adenomatous polyposis. The prevalence of pouchitis is known to range from 20% to 50%. One to two percent of the cases are chronic and resistant to the drug therapy. The effective treatment for this chronic resistant pouchitis is to remove the ileal pouch and perform the permanent ileostomy. Hereby, we report one case of chronic pouchitis resistant to multiple drug therapy developed after IPAA performed for the treatment of ulcerative colitis in a patient. (Korean J Gastroenterol 2003;42:72-76)
Key Words: Colitis, ulcerative; Pouchitis; Ileal pouch-anal anastomosis
장재영 외 10인. 내과적 치료에 반응하지 않는 만성 회장낭염 1예
하지 않는 만성회장낭염 1예를 경험하여 이에 보고한다.
증 례
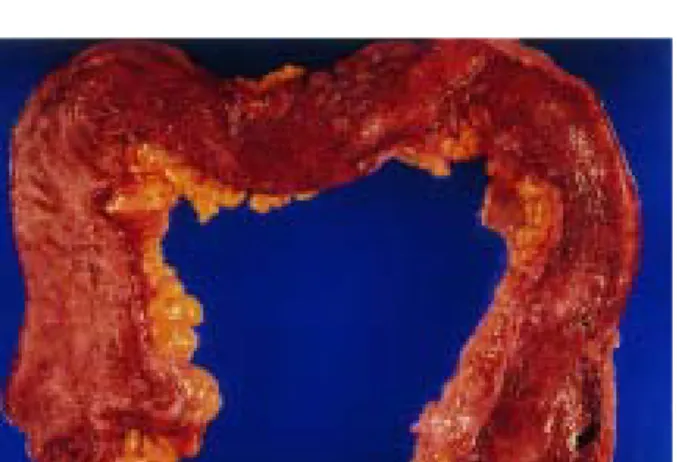
46세의 여자 환자로 1985년도에 모대학병원에서 궤양성 대장염을 진단받고 이후 여러 병원에서 스테로이드 치료를 받았으나 증세 호전이 없고 악화되어, 1998년 6월 본 병원 에 입원하여 전대장절제술과 회장낭-항문문합술을 시행받 고 회장루조성술을 하였으며 이후 증상의 현저한 호전이 있었고 3개월 뒤 회장루재건술을 시행하였다. 수술 뒤 얻은 대장 검체의 내부는 오랫동안 염증에 노출되어 점막이 위 축되어 있었으며, 횡결장에는 가성용종들이 관찰되었다 (Fig. 1). 조직학적 소견은 점막층에 궤양이 있었으며 점막 하층에 급, 만성 염증세포의 심한 침윤이 있었고 배낭세포 의 소실 및 장샘염이 관찰되어 궤양성 대장염에 합당하였 다(Fig. 2). 회장루재건술 3개월 뒤 하루에 20회 이상의 혈 변과 복통을 주소로 내원하였다. 가족력 및 과거력에서 특 이 사항은 없었다. 내원 당시 혈압은 100/60 mmHg였으며 체온은 36.2oC, 맥박 분당 72회, 호흡 분당 20회였다. 결막 은 창백하였고 흉부 진찰에서 특이 소견 없었다. 복부는 부 드럽고 편평하였으며 압통이 있거나 종괴가 만져지지는 않 았다. 말초혈액검사에서 혈색소 7.5 g/dL, 헤마토크리트 24.6%, MCV 71.7 fL, MCH 23.5 pg, MCHC 32.4 g/dL로 빈혈 소견을 보였고, 백혈구 및 혈소판은 각각 7,200/mm3, 400,000/mm3으로 정상이었다. 생화학검사상 혈중 철 46 µg/dL, TIBC 250 µg/dL이었고 전해질검사 소견은 정상이 었다. 대변배양검사에서 균은 검출되지 않았으며 항 amoeba항체, Clostridium difficile toxin 결과는 음성이었다.
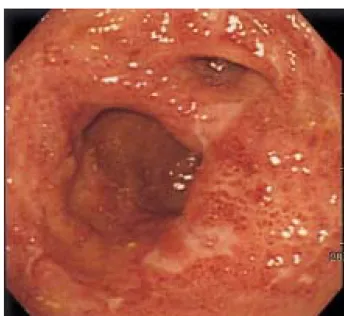
CRP < 0.5 mg/dL, ESR > 50 mm, pANCA (perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody) 양성이었다. 종양표지 자검사에서 CEA 4.5 ng/mL, CA 19-9 0.1 U/mL로 정상범 위였다. 복부 초음파검사에서 특이 소견은 보이지 않았으 며 회장낭 내시경에서 회장낭 내에 작은 미란과 궤양이 산 재하고, 점막에 심한 염증 소견을 보였다(Fig. 3). 세균 감염 에 의한 설사를 배제하였고, 회장낭염으로 진단하고 metronidazole 1.0 g/일 1주 투여하였으나 배변 횟수의 감소 가 없고 증세 호전이 없어 ciprofloxacin 1.0 g/일 2주간 투 여하였다. 이후 배변 횟수가 7-8회/일로 감소하였고 복통과 혈변이 사라졌다. Ciprofloxacin 1.0 g/일 8주간 유지치료에 도 하루에 배변 횟수가 10회/일 이상 증가하고 복통이 심 하여 mesalazine 100 mg/일 관장, metronidazole 1.0 g/일 경 구 투여하여 이후 증세는 호전되었으나 1999년 7월 다시 배변 횟수 증가와 복통, 야간에 3회 이상의 설사 증세로 내원하였다. 회장낭 내시경과 조직검사를 시행하였다. 내 시경상 회장낭내 전체적으로 부종과 염증이 심하였고, 궤
양이 여러 군데 발견되었다. 회장낭 내 조직 소견은 배낭 세포가 보이고 소낭 변형, 급만성 염증세포의 점막내 침윤 이 심했다(Fig. 4). 회장의 결장상피세포화 소견이 있고 심 한 회장낭염 소견을 보였다. mesalazine 100 mg/일 관장, ciprofloxacin 1.0 g/일, 유산균 정장제를 투여하였고 처음 1주일간은 치료에 반응을 보였으나 다시 복통, 혈변 증세 를 호소하여 budesonide 관장과 methotrexate 50 mg 피하 주사를 투여하였다. 환자는 methotrexate 투여 후 기운이 없고 전신상태가 저하되어 4주 치료 후 methotrexate 투여 를 중단하였다(Fig. 5). 2000년 3월 여러 가지 치료에도 배 변 횟수가 20회/일로 증가하고, 혈변, 복통 호소 등 증세의 호전이 없어 회장낭 기능 실패(pouch failure)로 간주하고 수술 을 권유하였으나 환자는 거부하고 약물치료를 원해
Fig. 1. Gross finding of total colon. It shows shallow, longitudinal ulcerations and polyps in the transverse and sigmoid colon and rectum. It shows a mucosal atrophy due to long standing inflammations.
Fig. 2. Microscopic findings of the resected colon. It shows ulceration with pseudopolyp formation, and distortion of cryptal glands with mucin depletion and crypt abscess, chronic inflammatory cell infiltration consisted predominantly of plasma cells with lymphoid aggregates (H&E stain, ×40).
73
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology: Vol. 42, No. 1, 2003
Fig. 3. Poucheoscopy. It shows marked erythema and multiple ulcer- ations.
Fig. 4. Microscopic finding of poucheal biopsy. It shows distorted cryptal glands and diffuse chronic inflammatory cell infiltration in the lamina propria with lymphoid follicles (H&E stain, ×100).
① metronidazole 1.0. g/day ② ciprofloxacin 1.0 g/day
③ mesalazine enema 100 mg/day ④ budesonide enema 2.3 mg/day
⑤ methotrexate 50 mg s.c. ⑥ prednisolone 50 mg/day PADI, pouchitis disease activity index.
Fig. 5. Clinical course of the patient.
budesonide 관장, prednisolone 50 mg 투여 후 점차 감량 중 이나 증세의 호전이 없고 외래 추적관찰 중이다.
고 찰
궤양성 대장염의 치료는 대개 내과적 치료가 우선이나, 내과적 치료에 반응이 없거나, 천공, 중독성 거대결장, 출 혈, 장폐쇄, 암 등이 발생하면 수술을 받는다.8 1960년대 이 전에 전대장절제술 및 회장루조성술이 시행된 이후로 최근 궤양성 대장염과 가족성 선종성 용종증의 수술로 전대장절 제술과 회장낭-항문문합술이 시행되고 있다.1 IPAA의 장점 은 거의 모든 장점막의 제거가 가능하고, 배설 통로인 항문 의 기능과 항문괄약근이 유지되고 성기능의 유지가 가능하 다는 점이다.9 그러나 IPAA 시행받은 후 10년 내 환자의 반수에서 회장낭염이 발생한다.10 회장낭염은 회장낭내에 발생하는 비특이적 급성 염증으로 IPAA 후 발생하는 가장 흔한 만성 합병증 중의 하나이다. 발병률은 보고자마다 다 르지만 20-50%로 보고하는데,1 이는 회장낭염의 진단기준 이 전세계적으로 확립되어 있지 않고 보고자마다 추적관찰 기간이 다르기 때문이다.11,12 회장낭염의 원인은 아직 밝혀 지지 않았지만 궤양성 대장염의 재발2과 회장낭내 기생하 는 세균의 과증식 등이 주 요소로 추측된다.4 이러한 근거 로 회장낭염은 가족성 선종성 용종증 환자에서 시행한 IPAA 후에는 거의 발생하지 않지만 궤양성 대장염 환자에 게서는 대부분 발생하는 점에서 유추할 수 있고12대부분의 환자에서 항생제를 사용할 경우 효과가 좋다는 점을 들 수 있으며, 그 외에 점막의 허혈 상태, 크론병 등도 관련이 있 을 것으로 생각되고 있다.6
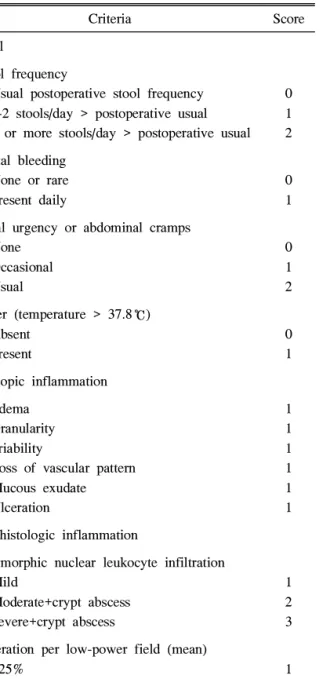
회장낭염 발생의 예측인자로 pANCA 양성 반응이 중요 한 혈청 지표라는 보고가 있고,13 원발성 경화성 담관염과 같은 장외 증세가 있을 때 회장낭염이 더 잘 발생한다.14회 장낭염의 흔한 임상 증상으로 배변 횟수의 증가, 복통, 배 변 긴급감, 혈변을 보이며, 때때로 열, 회복부 불편감, 장외 소견을 보인다. IPAA 후 이러한 임상 증상은 회장낭염을 의심하게 하지만 회장낭 내시경과 조직검사를 통해 진단해 야 한다.15 회장낭염 진단시 전세계적으로 확립된 진단기준 이 없어 1994년 Mayo clinic에서 The Pouchitis Disease Activity Index (PDAI) 개념이 도입되었다.16 PDAI 점수는 임상 증세, 내시경 소견, 조직 소견 등 크게 3부분으로 나누 어 각각 점수를 매겨 총 18점 중 7점 이상일 경우 회장낭염 으로 진단한다(Table 1). 임상 증세는 배변 횟수, 혈변 유무, 복통, 열 등이 있고 내시경 소견에 의한 지표로는 부종, 과 립성, 점막 삼출, 궤양 등이 있고, 조직검사에 의한 지표로 는 다형백혈구세포의 침윤과 장샘염의 유무, 저배율상 궤 양 발견 빈도 등에 따라 점수를 매긴다. 본 환자에서는 74
PADI
Chang JY, et al. A Case of Chronic Pouchitis Resistant to Medical Treatment
1998년 12월, 수술 후 회장낭염 진단시 임상적 증세 3점, 내시경 소견 5점, 조직학적 소견 3점, 총 11점으로 회장낭 염에 합당하였다. 1999년 12월, 2000년 6월, 약물치료에도 불구하고 PDAI 점수는 각각 13점, 15점으로 회장낭염이 지 속되었다.
만성 회장낭염 중 임상 증상을 조절하기 위한 항생제 치 료에도 불구하고 1년에 2회 이상 재발한 경우를 만성 재발 성 회장낭염이라고 하며, 치료에 저항군은 항생제 (metroni- dazole, ciprofloxacin, amoxicillin/clavulanic acid)를 적어도 4주 이상 투여해도 효과가 없을 때로 정의한다.17항생제 치 료는 대부분의 회장낭염에 있어 효과적이지만 5-15%에서
는 재발을 잘하고 치료에 반응하지 않는다.5 재발을 잘하고 치료에 반응하지 않는 회장낭염은 대개 항문외 질환으로 치루, 치열, 회장과 항문 문합 부위의 협착, 항문괄약근 손 상과 관련이 많고 원발성으로 오는 경우는 1-2% 정도이 다.7 이러한 치료에 반응하지 않는 군의 치료로 4종류의 유 산균이 포함된 정장제,18 ciprofloxacin과 rifaximin 병합요 법,19 스테로이드, 5-aminosalicylic acid 관장, short chain fatty acid 관장 등이 시도되었지만 그 효과가 만족스럽지는 못하다. 이러한 만성 회장낭염은 회장낭 기능 실패를 초래 한다. 회장낭 기능 실패로 인해 회장낭을 제거해야 했던 원 인으로 크론병을 궤양성 대장염으로 오진하고 수술한 경우, 회장낭이 제대로 기능을 못했던 경우, 골반내 패혈증 등이 있다.20 이 중 회장낭 기능 실패의 원인으로 수술 후 문합 부위의 누출이 가장 중요하다고 하였다. IPAA로 수술한 470명 중 1.4%에서 회장낭의 제거가 필요하며 이 중 50%
는 조직학적으로 크론병으로 확진되었고 이것이 치료에 반 응하지 않는 회장낭염의 주된 원인이다.8 본 환자의 경우는 수술전 궤양성 대장염으로 진단되었고 약물에 반응이 없어 수술을 시행하였다. 수술 3개월 후 회장낭염이 발생하여 시 행한 조직검사에서 회장점막의 융모 길이가 짧아지고 음와 의 길이가 길어지는 등 결장상피세포로 변형된 것을 관찰 할 수 있었고 다시 궤양성 대장염이 재발한 것으로 추정하 였다. 항생제 치료를 하였으나 투여 초기만 증세가 호전되 는 양상을 보였고 다시 증세가 악화되는 것이 반복되어 정 장제, mesalazine 관장, budesonide 관장, 전신적 스테로이드 치료를 시행하였지만 반응을 보이지 않았다. 원발성 만성 회장낭염에 의한 회장낭 기능 실패로 간주하고 수술을 권 유하였으나 환자는 거부하였다. 저자들은 궤양성 대장염 환자에서 IPAA 수술 후 3년여 추적 관찰기간 동안 치료에 반응하지 않는 만성 회장낭염 1예를 문헌 고찰과 함께 보 고한다.
REFERENCES
1. Setti-Carraro P, Ritchie JK, Wilkinson KH, Nicholls RJ, Hawley PR. The first 10 years’ experience of restorative proctocolectomy for ulcerative colitis. Gut 1994;35: 1070-1075.
2. Yu CS, Kim HC, Yang SK, Min YI, Kin JC. Restorative proctocolectomy in 50 patients with ulcerative colitis. Korean J Gastroenterol 2002;40:379-385.
3. Luukkonen P, Jarvinen H, Tanskanen M, Kahri A. Pouchitis- recurrence of the inflammatory bowel disease? Gut 1994;
35:243-246.
4. Ruseler-Van Embden JG, Schouten WR, van Lieshout LM.
Pouchitis: result of microbial imbalance? Gut 1994;35:658-664.
Table 1. The Pouchitis Disease Activity Index
Criteria Score Clinical
Stool frequency
Usual postoperative stool frequency 1-2 stools/day > postoperative usual 3 or more stools/day > postoperative usual
0 1 2 Rectal bleeding
None or rare Present daily
0 1 Fecal urgency or abdominal cramps
None Occasional Usual
0 1 2 Fever (temperature > 37.8℃)
Absent Present
0 1 Endoscopic inflammation
Edema Granularity Friability
Loss of vascular pattern Mucous exudate Ulceration
1 1 1 1 1 1 Acute histologic inflammation
Polymorphic nuclear leukocyte infiltration Mild
Moderate+crypt abscess Severe+crypt abscess
1 2 3 Ulceration per low-power field (mean)
<25%
25% - 50%
>50%
1 2 3
75
대한소화기학회지: 제42권 제1호, 2003
5. Keranen U, Luukkonen P, Jarvinen H. Functional results after restorative procto-colectomy complicated by pouchitis. Dis Colon Rectum 1997;40:764-769.
6. Foley EF, Schoetz DJ Jr, Roberts PL, et al. Rediversion after ileal pouch-anal anastomosis. Causes of failures and predictors of subsequent pouch salvage. Dis Colon Rectum 1995;38:793-798.
7. Becker JM, Stucchi AF, Bryant DE. How do you treat refractory pouchitis and when do you decide to remove the pouch? Inflamm Bowel Dis. 1998;4:167-169.
8. Podolsky DK. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (1). N Engl J Med 1991;325:928-937.
9. Pemberton JH, Phillips SF. Ileostomy and its alternatives. In:
Sleisenger MH, ed. Gastro intestinal Disease. Volume 2. 7th ed. Philadelphia: W.B.Saunders Company, 2002;2068-2079.
10. Meagher AP, Farouk R, Dozois RR, Kelly KA, Pemberton JH. J ileal pouch-anal anastomosis for chronic ulcerative colitis: complications and long-term outcome in 1310 patients.
Br J Surg 1998;85:800-803.
11. Zuccaro G Jr, Fazio VW, Church JM, Lavery IC, Ruderman WB, Farmer RG. Pouch ileitis. Dig Dis Sci 1989;34:1505- 1510.
12. Salemans JM, Nagengast FM, Lubbers EJC, Kuijpers JH.
Postoperative and long-term results of ileal pouch-anal anastomosis for ulcerative colitis and familial polyposis coli.
Dig Dis Sci 1992;37:1882-1889.
13. Sandborn WJ, Launders CJ, Tremaine WJ, Targan SR.
Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody correlates with chronic
pouchitis after ileal pouch-anal anastomosis. Am J Gastro- enterol 1995;90:740-747.
14. Penna C, Dozois R, Tremaine W, et al. Pouchitis after ileal pouch-anal anastomosis for ulcerative colitis occurs with increased frequency in patients with associated primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gut 1996;38:234-239.
15. Sandborn WJ. Pouchitis following ileal pouch-anal anasto- mosis: definition, pathogenesis, and treatment. Gastroenterology 1994;107:1856-1860.
16. Sandborn WJ, Tremaine WJ, Batts KP, Pemberton JH, Phillips SF. Pouchitis after ileal pouch-anal anastomosis: a pouchitis disease activity index. Mayo Clin Proc 1994;69:
409-415.
17. Mimura T, Rizzello F, Helwig U, et all. Four-week open- label trial of metronidazole and diprofloxacin for the treatment of recurrent or refractory pouchitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002;16:909-917.
18. Gionchetti P, Rizzello F, Venturi A, et al. Oral bacterio- therapy as maintenance treatment in patients with chronic pouchitis: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2000;119:305-309.
19. Gionchetti P, Rizzello F, Venturi A, et al. Antibiotic combination therapy in patients with chronic, treatment- resistant pouchitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1999;13:713-718.
20. MacRae HM, McLeod RS, Cohen Z, O'Connor BI, Ton EN.
Risk factors for pelvic pouch failure. Dis Colon Rectum 1997;40:257-262.
76