http://dx.doi.org/10.14193/jkfas.2015.19.3.86
가 원위부로 가면서 원통형으로 바뀌는 구조이므로 견고한 고정이 어려워 골절 발생 시 불유합, 지연유합 및 피부괴사 등의 합병증이 흔하게 발생하는 것으로 알려져 있다.3) 이러한 경골 원위부 골절 의 수술적 치료로는 외고정술, 골수강내 금속정고정술, 관혈적 정 복 및 금속판 내고정술 등의 여러 방법들이 이용되어 왔으나 여전 히 치료가 어려운 골절로 알려져 있다.4-7)
이에 저자들은 최소 침습적 금속판 고정술과 골수강내 금속정 고정술을 시행한 후 임상적 결과 및 방사선학적 결과를 비교하고 자 한다.
서 론
경골 원위부는 고에너지에 의한 굴곡력과 회전력에 의해 골절 이 발생하며1) 빈약한 연부조직에 의한 개방성 골절이 많이 동반되 는 것으로 알려져 있다.2,3) 또한 경골 원위부는 전내측부가 피부 직 하에 위치하여 혈액 공급이 풍부하지 않고, 경골의 골간부 삼면체
Original Article
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/CC
by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Copyright 2015 Korean Foot and Ankle Society. All rights reserved.ⓒ
Purpose: We analyzed and compared the clinical and radiologic results between minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis and internal
fixation using intramedullary (IM) nail in the treatment of distal tibia fractures.Materials and Methods: From March 2005 to June 2013, 65 cases of distal tibia fractures treated with either plate fixation or IM nail fix-
ation were analyzed retrospectively by clinical and radiologic evaluations. The clinical results were compared using the American Ortho- paedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) score, Olerud-Molander ankle score (OMAS), and visual analogue scale (VAS) score at the last follow-up. The radiologic results were compared by time to bone union, complications such as nonunion, delayed union, and malunion.Results: The clinical results (according to OMAS, AOFAS score, and VAS score) were 77.47, 84.76, and 1.75, respectively, in the plating
group, and 90.21, 91.00, and 1.25, respectively, in the nailing group, and there was no statistically significant difference. Plating group showed earlier union than the nailing group and the nailing group showed higher frequency of non-union and delayed union than plat- ing group.Conclusion: In treatment of distal tibia fractures, two methods showed appropriate results. Therefore, thorough investigation of the
types of fracture, state of soft tissues, and advantages and disadvantages of the two methods should be conducted in the treatment of dis- tal tibia fractures.Key Words: Distal tibia, Fracture, Plate, Intramedullary nail
원위 경골 골절에서 금속정 및 금속판 고정술의 결과 비교
김정한, 곽희철, 이창락, 정양환
인제대학교 의과대학 부산백병원 정형외과학교실
Comparison of the Results between Intramedullary Nailing and Plate Fixation for Distal Tibia Fractures
Jung-Han Kim, Heui-Chul Gwak, Chang-Rack Lee, Yang-Hwan Jung
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
Received June 8, 2015 Revised July 14, 2015 Accepted July 24, 2015 Corresponding Author: Heui-Chul Gwak
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, 75 Bokji- ro, Busanjin-gu, Busan 47392, Korea
Tel: 82-51-890-6996, Fax: 82-51-892-6619, E-mail: ortho1@hanmail.net Financial support: None.
Conflict of interest: None.
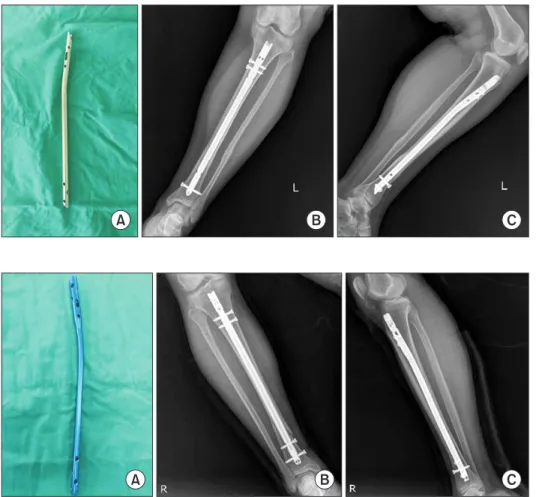
www.jkfas.org 세 이하의 성인 환자를 대상으로 하였으며, 심한 개방성 골절 환 자(Gustilo grade IIIB, IIIC) 및 전위된 관절내 골절 환자 등은 연구 에서 제외하였다. 총 43예 중 18예에서는 골수강내 금속정 고정술 을 시행하였고(금속정 군), 25예에서는 최소 침습적 금속판 고정 술을 시행하였다(금속판 군). 모든 수술은 단일 술자에 의해서 시 행되었으며 사용한 금속정은 cannulated tibia nail (CTN; Synthes, Solothurn, Switzerland) (Fig. 1) 및 2009년 이후로는 원위부에 4개 의 교합나사 고정이 가능한 expert tibial nail (ETN; Synthes) (Fig.
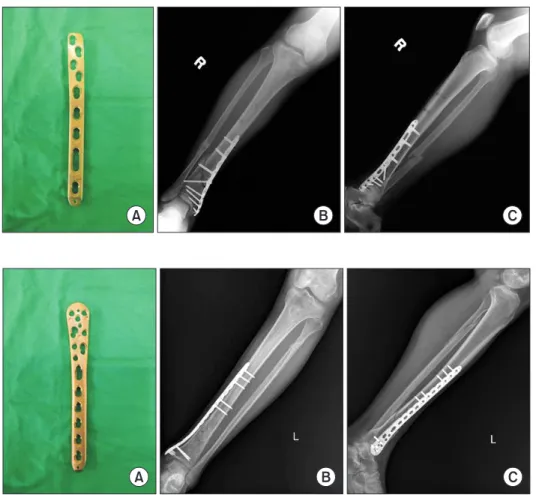
2)을 사용하였다. 금속판 고정술은 방사선 영상 증폭기를 이용하 여 골절을 비관혈적으로 정복 후 족관절 내과 부위에 약 2∼3 cm 의 피부절개를 가한 후 경피적 술식을 이용하여 금속판을 피하조 직과 골막 사이로 삽입하는 내측 술식을 이용하였으며, 금속판은 locking compression plate distal medial tibia (LCP-DMT; Synthes) (Fig. 3) 및 locking compression plate distal medial tibia low bend (LCP-DMT low bend; Synthes) (Fig. 4)를 사용하였다.
환자의 나이, 성별, 손상기전, 수상 후 수술까지 걸린 시간, 합병 증 유무에 따라 분석을 시행하였으며, 술 후 방사선 사진 및 의무 기록으로 골유합 시기, 불유합, 부정유합, 감염의 유무를 조사하였 다. 술 후 3개월까지는 1개월 간격으로, 이후로는 3개월 간격으로 외래 추시를 시행하였다.
임상적 평가는 최종 추시에서의 American Orthopaedic Foot
대상 및 방법
본 연구는 인제대학교 부산백병원 임상연구윤리위원회(Institu- tional Review Board)의 승인하에 후향적으로 시행하였다. 2005년 3월부터 2013년 6월까지 본원에서 원위 경골 골절로 금속판 혹은 골수강내 금속정 고정술을 시행 받은 환자 총 65명 중 1년 이상 추 시관찰이 가능하였던 환자 43명(43예)을 대상으로 의무기록과 방 사선 사진으로 후향적 분석을 시행하였다(Table 1). 원위 경골 골 절 중 발목 관절에서 4∼11 cm 사이의 골절이 있는 20세 이상 60
A B C
Figure 1. (A) This photograph demon- strates cannulated tibia nail (CTN; Syn- thes, Solothurn, Switzerland). (B) Ante- roposterior view of the left tibia show stabilized distal tibial fracture by the CTN. (C) Lateral view of the left tibia show stabi lized distal tibial fracture by the CTN.
Figure 2. (A) This photograph demon- strates expert tibial nail (ETN; Synthes, Solothurn, Switzerland). (B) Anteroposte- rior view of the right tibia show stabilized distal tibial fracture by the ETN. (C) Lateral view of the right tibia show stabilized dis- tal tibial fracture by the ETN.
A B C
Table 1. Demographics Data of Patients Plating group
(n=25)
Nailing group (n=18)
Mean age (yr) 47 (20~59) 52 (24~60)
Gender (male/female) 14/11 10/8
AO/OTA classification
42-A1 2 6
42-A2 2 6
42-A3 6 5
42-C2 8 1
42-C3 7 0
Values are presented as number of patients or mean (range).
AO/OTA: The AO Foundation and Orthopaedic Trauma Association.
결 과
1. 임상적 결과
임상적 지표에 있어서 최소 침습적 금속판 고정술을 시행한 군, 골수강내 금속정 고정술을 이용한 군에서 최종 추시 시의 OMAS 는 금속판 군에서 평균 77.47±16.67, 금속정 군에서 평균 90.21±
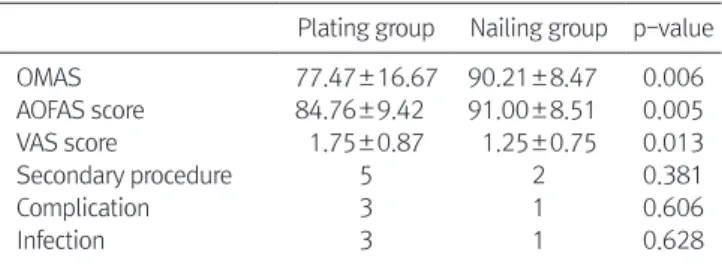
8.47의 값을 나타내었으며, AOFAS score에서는 금속판 군에서 평 균 84.76±9.42, 금속정 군에서 평균 91.00±8.51의 값을 나타내었 다. VAS score에서는 금속판 군에서 평균 1.75±0.87, 금속정 군에 서 평균 1.25±0.75의 값을 나타내었으며 세 개의 임상적 지표에서 두 군 모두 높은 결과가 나타났다(Table 2).
이차적 술기의 시행에 있어서는 금속판 군에서 5예, 금속정 군에 서 2예 관찰되었고, 연부조직 손상에 따른 합병증 역시 금속판 군 에서 3예, 금속정 군에서 1예 관찰되어 금속판 군에서 보다 높은 결과를 나타내었으나 통계적 유의성은 관찰되지 않았다. 감염의 발생은 금속판 군에서는 3예, 금속정 군에서는 1예 관찰되었으나 통계적 유의성은 관찰되지 않았다.
2. 방사선학적 결과
방사선학적 지표에 있어서는 최소 침습적 금속판 고정술을 시 and Ankle Society (AOFAS) score 및 Olerud-Molander ankle score
(OMAS), visual analogue scale (VAS) 점수를 이용하였다.
방사선학적 평가는 매 추시마다 경골의 전후면 및 측면 사진을 촬영하였으며 골유합은 방사선적으로 경골의 전후면 및 측면 사진 에서 가골의 성숙이 골절면의 3/4 이상 폐쇄되고 임상적으로 골절 부위의 압통 및 움직임이 없는 상태로 정의하였다. 불유합은 손상 후 최소 9개월이 경과하였으며 최근 3개월간 가시적인 치유의 과 정을 보이지 않은 경우로 정의하였으며 지연유합은 골유합이 예상 되는 일정 기간이 지난 후에도 유합이 완전히 이루어지지 않은 상 태로 정의하였다.
부정유합은 관상면과 시상면에서 각 형성이 5o 이상이며 회전 변형 10o 이상 및 건측과 비교해서 1 cm 이상의 단축이 발생한 경 우로 정의하였다.
통계 분석은 IBM SPSS Statistics 21.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA) 프로그램을 이용하여 시행하였으며, 분석 방법은 Mann Whitney U-test 및 Pearson’s chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test를 이용하였고 통계적 유의수준은 p<0.05로 하였다.
Figure 3. (A) This photograph demon- strate locking compression plate distal medial tibia (LCP-DMT; Synthes, Solo- thurn, Switzerland). (B) Anteroposterior view of the right tibia show stabilized distal tibial fracture by the LCP-DMT plate using minimal invasive technique. (C) Lat- eral view of the right tibia show stabilized distal tibial fracture by the LCP-DMT plate using minimal invasive technique.
A B C
Figure 4. (A) This photograph demon- strate locking compression plate distal medial tibia low bend (LCP-DMT low bend; Synthes, Solothurn, Switzerland).
(B) Anteroposterior view of the left tibia show stabilized distal tibial fracture by the LCP-DMT low bend plate using mini- mal invasive technique. (C) Lateral view of the left tibia show stabilized distal tibial fracture by the LCP-DMT low bend plate using minimal invasive technique.
A B C
www.jkfas.org 줄이고 높은 골유합률을 얻는 것으로 보고되고 있다. 하지만 완전 한 해부학적 정복을 얻기는 어려우며 관혈적 정복술에 비해 지연 유합, 불유합, 부정유합 등의 발생 가능성이 높은 단점이 있다. 금 속정 고정술은 주위 연부조직 손상을 최소화하여 골유합의 가능성 을 높여 주고 합병증 발생을 줄일 수 있으나, 경골 원위부의 골수 강 면적이 넓어지고 원위부 골절편의 길이가 짧기 때문에 안정적 인 고정이 어렵고, 이로 인하여 금속정이나 교합나사가 파손될 수 있다는 단점이 있다.11-14)
최근까지 여러 저자들은 원위 경골 골절에 있어서 금속판 고정 술과 금속정 고정술을 비교한 연구 결과들을 발표하였다. Im과 Tae15)는 총 64예의 환자군, 금속판 고정술 30예 및 금속정 고정술 34예 사이의 비교를 시행하였으며 수술시간, 방사선학적 유합, 감 염 및 변형 유무 및 관절운동 가능 정도를 기준으로 금속정 고정술 을 시행하였을 때 수술시간의 단축 및 움직임의 회복, 창상 문제의 감소 등 장점이 있었다. 반면 금속판 고정술을 시행하였을 때는 정 렬의 복원에 있어 보다 나은 결과를 나타내었으며, 연부조직 손상 이 심할 때는 금속정 고정술을 시행할 것을 추천하나 나머지 경우 에는 술식 간 큰 차이가 없는 것으로 보고하였다. Vallier 등16)은 총 103예의 환자군 중 금속판 고정술 37예, 금속정 고정술 66예에서 연부조직 손상, 감염, 부정유합, 변형 등 합병증 발생과 이차적인 술기의 필요성 등을 기준으로 연구를 시행하였는데, 지연유합, 부 정유합, 이차적인 술기의 필요성 등은 금속정 고정술을 시행하였 을 때 많이 발생하였으나 두 술식 모두 성공적인 치료를 기대할 수 있다고 보고하였다. 또한 Mauffrey 등17)은 다기관 무작위 연구를 총 24예(금속정 고정술 12예 및 금속판 고정술 12예)에서 시행하였 으나 두 술식 간의 저명한 기능적 결과 차이는 보이지 않는다고 보 고하였다.
본 연구에 따르면 금속판 고정술을 시행한 군에서 연부조직 손 상, 감염 등의 합병증이 상대적으로 많이 발생하였으며, 금속정 고 정술을 시행한 군에서는 지연유합 및 불유합의 빈도가 상대적으로 높았으나 두 술식 간 통계적으로 유의한 차이는 보이지 않았고, 최 종적으로 두 술식 모두 성공적인 결과를 보였다. 결과적으로 명확 한 적응증을 제시하기는 어렵지만 연부조직의 손상 및 자극이 우 려되는 경우에는 금속정 고정술을 고려해 볼 수 있겠고, 분쇄골절 이 동반되거나 보다 정확한 정복이 필요할 경우에는 금속판 고정 술의 이용을 고려해 볼 수 있겠다.
마지막으로, 본 연구는 몇 가지 제한점을 가진다. 후향적 연구로 편향된 결과의 가능성이 있으며 수상 당시 분쇄가 심하거나 골절 선에서 관절면 사이의 거리가 짧을수록 금속정 고정술보다는 최소 침습적 금속판 고정술을 선택하는 선택적 오류가 발생할 가능성이 있을 것으로 생각된다. 그리고 임상적으로 환자의 수가 적은 제한 점이 있으며 또한 동반된 비골 골절에 대해서는 논란의 여지가 있 어 추후 좀 더 많은 사례와 전향적 연구, 동반된 비골 골절에 대한 연구가 진행되어야 할 것으로 생각된다.
기까지의 걸린 시간은 금속판 군에서는 평균 3.5개월, 금속정 군에 서는 평균 3.8개월로 금속판 군에서 다소 빠른 유합을 보였으나 두 군 간의 유의한 차이는 관찰되지 않았다. 지연유합에 대해서는 금 속판 군에서 1예, 금속정 군에서 3예 관찰되었으며 불유합에 대해 서는 금속판 군에서 1예, 금속정 군에서 3예 관찰되었으나 통계적 으로 유의한 차이는 나타내지 않았다. 변형은 금속판 군에서는 관 찰되지 않았으며 금속정 군에서 3o의 외반 변형이 1예 발생하였으 나 동반된 임상적 문제는 관찰되지 않았다(Table 3).
고 찰
원위 경골 골절은 고에너지에 의한 손상으로 발생하는 경우가 많아 분쇄 골절이 흔하게 일어날 수 있으며 연부조직 손상 및 개방 성 창상이 흔히 동반된다. 또한 원위 경골은 연부조직이 얇고 혈액 공급이 다른 부위에 비해 좋지 않은 해부학적 특징이 있다.3) 또한 원위 경골 골절은 원위부로 내려갈수록 골수강이 급격하게 넓어지 기 때문에 정복이 어렵거나 고정력이 부족하여 부정유합이나 고정 의 실패가 발생할 수 있다.8-10) 따라서 원위 경골 골절의 경우 지연 유합, 불유합, 감염, 피부 괴사 등 많은 합병증을 동반할 수 있어 적 절한 치료 방법을 선택하는 것이 중요하다. 최소 침습적 금속판 고 정술의 경우 생물학적 고정 및 간접 정복의 기법을 이용하여 간접 적으로 골정렬을 맞춘 뒤 골막 위로 금속판을 고정하는 방법이다.
따라서 이 방법은 연부조직 손상을 최소화하여 골절 부위 혈류손 상을 줄이면서도 내고정술의 장점인 견고한 고정을 얻을 수 있어 기존 술식으로 인한 감염, 피부괴사, 불유합 등의 합병증을 크게 Table 2. Comparison of Clinical Results between Plating and Nailing Groups
Plating group Nailing group p-value
OMAS 77.47±16.67 90.21±8.47 0.006
AOFAS score 84.76±9.42 91.00±8.51 0.005
VAS score 1.75±0.87 1.25±0.75 0.013
Secondary procedure 5 2 0.381
Complication 3 1 0.606
Infection 3 1 0.628
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number only.
OMAS: Olerud-Molander ankle score, AOFAS: American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society, VAS: visual analogue scale.
Table 3. Comparison of Radiological Results between Plating and Nail- ing Groups
Plating group Nailing group p-value
Time to union (mo) 3.5±1.7 3.8±1.3 0.746
Delayed union 1 3 0.606
Nonunion 1 3 0.505
Deformity 0 1 0.381
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number only.
minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures1 Int Orthop1 2008;32:697-7031
81 Böstman O, Hänninen A. The fibular reciprocal fracture in tibial shaft fractures caused by indirect violence1 Arch Orthop Trauma Surg1 1982;100:115-211
91 Konrath G, Moed BR, Watson JT, Kaneshiro S, Karges DE, Cram- er KE. Intramedullary nailing of unstable diaphyseal fractures of the tibia with distal intraarticular involvement1 J Orthop Trauma1 1997;11:200-51
101 Tyllianakis M, Megas P, Giannikas D, Lambiris E. Interlocking intramedullary nailing in distal tibial fractures1 Orthopedics1 2000;23:805-81
111 Nicoll EA. Closed and open management of tibial fractures1 Clin Orthop Relat Res1 1974;(105):144-531
121 Park IH, Song KW, Shin SI, Lee JY, Lee SY, Kim TH, et al. In- terlocking intramedullary nailing for treating most distal tibial fracture1 J Korean Soc Fract1 2003;16:356-621
131 Robinson CM, McLauchlan GJ, McLean IP, Court-Brown CM.
Distal metaphyseal fractures of the tibia with minimal involve- ment of the ankle1 Classification and treatment by locked intra- medullary nailing1 J Bone Joint Surg Br1 1995;77:781-71
141 Shon OJ, Chung SM. Interlocking intramedullary nail in distal tibia fracture1 J Korean Fract Soc1 2007;20:13-81
151 Im GI, Tae SK. Distal metaphyseal fractures of tibia: a prospec- tive randomized trial of closed reduction and intramedullary nail versus open reduction and plate and screws fixation1 J Trauma1 2005;59:1219-23; discussion 12231
161 Vallier HA, Le TT, Bedi A. Radiographic and clinical comparisons of distal tibia shaft fractures (4 to 11 cm proximal to the pla- fond): plating versus intramedullary nailing1 J Orthop Trauma1 2008;22:307-111
171 Mauffrey C, McGuinness K, Parsons N, Achten J, Costa ML. A randomised pilot trial of "locking plate" fixation versus intra- medullary nailing for extra-articular fractures of the distal tibia1 J Bone Joint Surg Br1 2012;94:704-81
결 론
본 연구에서는 골수강내 금속정 고정술을 시행한 군, 최소 침습 적 금속판 고정술을 시행한 군 모두에서 우수한 결과를 보여 두 가 지 수술 방법이 모두 유용한 치료 방법인 것으로 생각된다. 따라서 원위 경골 골절 시 골절의 양상, 연부조직의 상태 및 각 술식의 장 단점을 파악한 후 적절한 수술을 시행하여야 할 것으로 생각된다.
REFERENCES
11 Kim SK, Lee KB, Lim KY, Moon ES. Minimally invasive osteosyn- thesis with locking compression plate for distal tibia fractures1 J Korean Fract Soc1 2011;24:33-401
21 Lee KB, Song SY, Kwon DJ, Lee YB, Rhee NK, Choi JH. A com- parison between minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis &
interlocking intramedullary nailing in distal tibia fractures1 J Ko- rean Fract Soc1 2008;21:286-911
31 Wyrsch B, McFerran MA, McAndrew M, Limbird TJ, Harper MC, Johnson KD, et al. Operative treatment of fractures of the tibial plafond1 A randomized, prospective study1 J Bone Joint Surg Am1 1996;78:1646-571
41 Chung ST, Kim HS, Cha SD, Yoo JH, Park JH, Kim JH, et al.
Treatment of Distal tibia fracture using mippo technique with locking compression plate: comparative study of the intraarticu- lar fracture and extraarticular fracture1 J Korean Foot Ankle Soc1 2009;13:162-81
51 Edge AJ, Denham RA. External fixation for complicated tibial fractures1 J Bone Joint Surg Br1 1981;63-B:92-71
61 Helfet DL, Shonnard PY, Levine D, Borrelli J Jr. Minimally inva- sive plate osteosynthesis of distal fractures of the tibia1 Injury1 1997;28 Suppl 1:A42-7; discussion A47-81
71 Lau TW, Leung F, Chan CF, Chow SP. Wound complication of