Printed in the Republic of Korea
36
Micro-PCR 과 Real-Time PCR 을 이용한 B 형 간염 바이러스 검출
강 원·박상범·남윤형·안영창·이상현·장원철*·박수민†·김종완‡·정성춘#
단국대학교첨단과학부화학과, 기초과학연구소
†제넷바이오
‡단국대학교의과대학임상병리과
#삼성테크윈
(2006. 5. 22 접수)
Detection of Hepatitis B Virus Using Micro-PCR and Real-Time PCR Methods
Won Kang, Sang-Bum Park, Youn-Hyoung Nam, Young-Chang An, Sang-Hyun Lee, Won-Cheoul Jang*, Su-Min Park
†, Jong-Wan Kim
‡, and Song-Chun Chong
#Dept. of Chemistry, School of Advanced Science and Basic Science Research Institute Dankook University, Cheonan 330-714, Korea
†Chungnam Animal Science Center GenetBio, Konyang Univ, Nonsan 320-711, Korea
‡Dept. of Clinical Pathology, Dankook University Medical College, Cheonan 330-714, Korea
#Samsung Techwin, Sungnam 462-121, Korea (Received May 22, 2006)
요 약. B형간염바이러스(Hepatitis B Virus, HBV)는만성감염, 간암의원인이되는등가장큰공중보건문 제중의하나이다. 그리하여감염초기에바이러스의 DNA 농도를측정하여관찰하는것이중요하다. 본연 구에서는기존의 Real Time-PCR과새로운방법인 Micro-PCR를이용하여 HBV를검출하였다. 단국대학교병원
에서 HBV 감염환자의혈청샘플 120개를얻은후분석하였고각각장비에서의검출한계와재현성, 민감성, 특
이성, 분석시간을비교해보았다. 그결과 Micro-PCR과 Real-Time PCR은높은검출한계와재현성, 민감성, 특이 성을가지고있었다. 그러나 Micro-PCR은 Real-Time PCR보다빠른시간안에증폭이가능하며조작하는데있 어간편하였고적은양의시약이소모됨을알수있었다. 그러므로 Micro-PCR은신뢰성있고빠른임상적진단 이나각종검사가요구되는곳에서이용가치가높은장비라할수있겠다.
주제어: B형간염바이러스, Real-Time PCR, Micro-PCR
ABSTRACT. Hepatitis B is a serious public health problem leading to chronic infection and liver cancer. Quantitation of circulating hepatitis B virus (HBV) is important for monitoring disease progression and for assessing the response to antiviral therapy. In this study, by using Real-Time PCR and novel Micro-PCR assay method, we measured HBV con- centration in the clinical sample. A total of 120 serum samples from patients with HBV infection collected was in Dank- ook university hospital to compare the detection limit, sensitivity, specificity and reproducibility of the two assay methods. These findings of this study suggest that Micro-PCR and Real-Time PCR assay methods are comparable to each other in there detection limit, sensitivity, and reproducibility for HBV DNA quantitation. However, Micro-PCR assay is more efficient than Real-Time PCR method, because Real-Time PCR is not so time - consuming, technically easy and need to reagent of a small quantity. It will be useful for rapid and reliable clinical diagnosis of HBVin many countries.
Keywords: Hepatitis B Virus, Real Time-PCR, Micro-PCR
서 론
세계전체인구의약 20억에해당되는사람들이 HBV
에감염된적이있고 3억 5천만명정도가만성 HBV
감염자이다. 매해마다약 1백만명이 HBV로인한간 암혹은간기능마비로사망한다.
HBV는내부에 genome을함유하는 core와외부에
B형간염표면항원(HBsAg)이있는 lipoprotein envelope
으로구성되어있다. 혈청에서전자현미경으로관찰 하면 3가지 particle(Dane particle, spherical particle, filamentous particle)이관찰된다. Genome은 3200개의
nucleotide로구성되어있으며긴 minus-strand DNA와 짧은 plus-strand DNA로구성되어 있고 4개의 ORF (open reading frame) 또는 gene을포함하고있다. Core (pre-c/c) gene은 nucleocapsid를, pol(p) gene은 DNA polymerase를, surface(S) gene은 envelop protein의생 산에관여한다. S gene에는 pre-S1, pre-S2 있고그외 에 X gene이있다. X gene의기능은정확히규명되어 있지않으나 HBx는바이러스증식을증가시키고세포 유전자와바이러스유전자의 transcription을 transactivation
시켜서간세포암의발생에관여한다.1-10
최근 HBV를검출하기위해기존 PCR법보다빠르 고농도측정을정확하게할수있는 Real-Time PCR
법이도입되었다. Real-Time PCR법은반응용액속에
형광물질을첨가하여 이형광물질이 DNA 이중나선
사이에결합되면서실시간으로정량측정할수있는
장비이다. Real-Time PCR법에첨가하는 형광물질로
는 SYBRGreen, TaqMan probe, Molecular beacon, Scorpion probe, FRET probe 등이있으며이중 SYBR
Green이저렴하면서비교적정확한값을나타내어가
장많이사용되고있다.
SYBRGreen은반응중에나타나는 threshold cycle(Ct) value와반응이끝난후 melting temperature(Tm) value
를이용하는방법으로 Ct value는 baseline 형광값표
준편차의 10배의수치에도달하는 PCR cycle 수로
정의한다. template의농도가높을수록빠른시간안
에나타나는점을이용하여시간대별로정량곡선을 그려측정할수있다. Tm value는증폭된 PCR산물에 SYBR Green이 intrecalating 된후온도가 높아짐에
따라이중나선이떨어지면서같이 SYBR Green도 PCR
산물에서분리된다. 분리되기시작한온도부터모두
분리된온도의값의평균을구한값이 Tm이된다.
따라서이를이용하여증폭여부및종을판단할수 있다.11-18
Micro-PCR법은 Real-Time PCR법과 검출방법은 같지만마이크로칩의개념을 도입하여소량의 시료 를이용하고온도조절을 보다빠르고정확하게할 수있는새로운 Real-Time PCR법이다.19
본연구에서는 HBV의검출을위해 Real-Time PCR
과 Micro-PCR법을사용하였고두장비의검출한계와
재현성, 민감성, 특이성, 분석시간에대한 반복테스 트를시행하여비교, 평가하였다.
실험 및 방법
환자 및 Control 샘플
본연구에서는단국대학교 병원에서 HBV에감염 된환자의혈청샘플 120개를대상으로하였다.
Positive Control(HBV plasmid DNA, ATCC 45020D)
은제넷바이오(GeNet Bio, Korea)에서구입하여사용 하였다.
시약 및 기기 시약
혈청에서 HBV-DNA 추출에는PrimePrepTM Genomic DNA Isolation Kit(GeNet Bio, Korea)를 사용하였고
Real-Time PCR과 Micro-PCR에사용된반응시약은
Master mixTM(GeNet Bio, Korea)을사용하였다. 전기
영동의 agarose는 QA-AgaroseTM(Q-bio gene, USA)을
이용하였다.
기기
DNA의증폭은 GeneAmp PCR System 2700(Applied Biosystems, USA), GENSPECTORTMC-1000 SYSTEM (Samsung, Korea), Rotor-GeneTM 3000(Corbett research, USA)을 사용하였고, PCR 증폭물 확인은 Mupid-a (Advance, Japan) 전기영동장치를이용하였다.
실험 방법
혈청에서 HBV-DNA를추출하여 PCR법을통하여
타겟(target) 부위를증폭을시킨후증폭된 DNA를전
기영동법에의해확인하였고이를정제하였다. 정제
된증폭산물이 HBV-DNA가맞는지최종적으로확인
하기위해서 DNA 염기서열분석법을시행하였다. 그
후동일한 Master mix를가지고 HBV plasmid DNA
와임상샘플을 Micro-PCR과 Real-Time PCR법에적 용시켰다.
혈청에서 HBV-DNA의 추출
혈청 600 µL를 1.5 mL 원심 분리관에 proteinase K(20 mg/mL) 20 µL와결합완충용액(binding buffer) 200 µL 넣고 vortex 시킨후 56oC에서 10 분간반응 시켰다.
2 mL 시험관에수집컬럼(collection column)을넣 고컬럼에반응용액을조심스럽게옮긴후 8000 rpm
에서 1 분간원심분리하여여과되어서모아진용액 은버리고 500 µL 세척완충용액 1(washing buffer 1)
로세척하고이것을 12,000 rpm에서 1 분간원심분 리후여과되어서모아진용액을버리고 500 µL 세 척완충용액 2 (washing buffer 2)로반복하였다. 마지 막으로 12,000 rpm에서 2 분간원심분리하였다. 그
리고수집컬럼을깨끗한시험관에옮긴후 50 µL 용
리완충용액(elution buffer)을넣고실온에서 2 분간반
응하고 13,000 rpm에서 1 분간원심분리하여모아진 용액을 1.5 mL 마이크로시험관에옮긴후 4oC에보 관하거나, 장기간보관하기위해서는 -20oC에저장하
였다.
프라이머 제작(Primer design)
HBV-DNA core region에서 증폭하기위한 프라이
머세트(Table 1)를제작하였다.
중합효소연쇄반응(PCR)
우선 94oC에서 5 분간주형 DNA를완전히변성시
킨후(hot start) 다시 94oC에서 30 초간변성(denaturation), 60oC에서 30 초간결합(annealing), 72oC에서 40 초
간신장(extension) 단계를 40 회반복하고마지막으
로 72oC에서 7 분간마지막신장(last extension)을실 시하였다. PCR 반응용액은총볼륨 20 µL이며 10X reaction buffer(100 mM tris-HCl; pH 9.0(NH4)2SO4, 20 mM MgCl2, PCR enhancers) 2 µL, 10 mM dNTP mix (2.5 mM each.) 2 µL, forward and reverse primer(10 pmole/µL each.) 1 µL, Taq. polymerase(5 U/µL) 0.1 µL, template DNA(1 ng/µL) 10 µL, deionized water 3.9 µL
로구성되어있다. DNA 증폭은 GeneAmp® PCR System 2700(Applied Biosystems, USA)를이용해서 DNA를 증폭시켰다.
Agrose gel 전기영동에 의한 증폭산물의 확인
2%(w/v) agarose gel을이용하여 Mupid-a(Advance, Japan) 전기영동장치로 PCR 산물을분석하였다.
Agarose 2 g과 0.5X TBE(tris boric acid EDTA) 완 충용액 100 mL 섞어 2% gel을만든후 PCR 산물 4 µL
와 6X bromophenol blue(BPB) dye 0.8 µL를섞어서
gel에 loading하고 100 V에서 25 분동안전기영동시켰 다. 그후에 gel을 ethidium bromide(EtBr)로 10 분간 염색하고다시 10 분간증류수로 DNA와결합하지못 한 EtBr을씻어냈다.
마지막으로 UV transilluminator 위에 agarose gel을
올려놓고 PCR 여부를확인했다.
실시간 중합효소연쇄반응(RT-PCR)
Master mix와 DNA를 1:1로섞어 20 µL의 PCR 반 응용액을 0.2 mL PCR 반응시험관에넣은후, Real- Time PCR(Corbett, Rotor-Gene, USA)을이용해서우 선 50oC에서 2 분간 Uracil-N-Glycosylase를활성화 시키고 95oC에서 1 분간주형 DNA를완전히변성시
킨후다시 94oC에서 20 초간변성, 60oC에서 20 초
간결합, 72oC에서 30 초간신장단계를 40회반복하 여 DNA를증폭시켰고 마지막으로 60~90oC 까지 melting curve를그려분석하였다.
PCR 반응을위한 Master mix는한번에 100 µL를
제조하여 사용하였으며 조성은 아래와 같다. 10X reaction buffer(100 mM tris-HCl; pH 9.0, (NH4)2SO4, PCR enhancers, BSA, Stabilizer) 20 µL, 10 mM dNTP mix (2.5 mM each.) 20 µL, MgCl2(100 mM) 10 µL, SYBR® Green (20X) 10 µL, Primer mix(10 pmole/µL each.) 10 µL, Taq. Polymerase(5 U/µL) 4 µL, Deionized water 26 µL.
Table 1. Primer sequence sets used to amplify HBV-core region for PCR
Sequence of primers Sence (5' →3') Antisence (5' → 3')
Size of fragment Sence ATT TGG TGT CTT TCG GAG TGT G 113(bp) Antisence GGA CCT GCC TCG TCG TCT AA
마이크로칩 중합효소연쇄반응(Micro-PCR) Master mix와 DNA를 1:1로섞어 3 µL의 PCR 반 응용액을준비한후마이크로칩표면에붙어있는보
호 tape을뾰족한핀셋을이용하여조심스럽게떼어
낸다. 준비된반응용액에서 1 µL을취하여마이크로
칩안에분사하고 optical tape을붙인 후모듈안에 넣는다. Micro-PCR(Samsung, TMC-1000, Korea)을이 용해서우선 50oC에서 2 분간 Uracil-N-Glycosylase를 활성화시키고 91oC에서 1 분간주형 DNA를완전히 변성시킨후다시 92oC에서 1 초간변성, 62oC에서
15 초간결합및신장, 단계를 40 회반복하여 DNA
를증폭시켰고마지막으로 60~90oC 까지 melting curve
를그려분석하였다.
Master mix는 Real-Time PCR과동일한것으로사 용하였다.
결과 및 고찰
HBV plasmid DNA를 통한 재현성 테스트 동일한샘플을 Micro-PCR과 Real-Time PCR법을이 용하여한번에 6 개의동일샘플을 30 번반복시행
하여각실험간재현성을 테스트하였다. 실시간모
니터링 시스템은 Master mix속에 들어있는 SYBR
Green이 DNA 이중나선사이로결합되어나타나는형
광을측정함으로써 Ct와 Tm을알수있고이를통해
샘플의농도, 증폭유무및종을확인할수있다. Ct value는증폭이초기에나타나는 copy의형광값으로
Template의농도가많을수록 빠른시간내에나타난
다. Tm value는반응이끝난후 65~90oC까지온도를
올려주게되면 DNA의이중나선이단일가닥으로떨
어지면서 SYBR Green이방출되게 되는데염기서열
에따라방출되는온도가다르다. 이특정온도를이
용하여원하는 DNA가맞는지확인할수있다. 재현
성테스트결과 Real-Time PCR법의 Ct value와Tm value
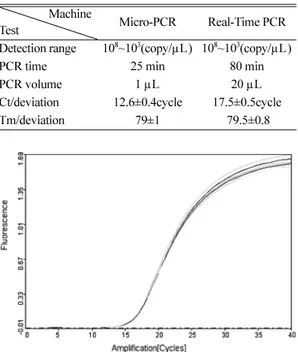
는 17.5±0.5 cycle과 79.5±0.8를 Micro-PCR법의경우는 12.6±0.4 cycle과 79±1를나타냈다(Table 2, Fig. 1-4).
HBV plasmid DNA를 통한 민감성 테스트
HBV-DNA 원액(1.3×108copy/µL)을 serial dilution 하
여 1.3×108~1.3×103copy/µL의농도에서검출테스트를
한결과각각의장비에서농도별 Ct간격이 3~4 cycle
을유지하며나타나는것을확인하였다(Table 3, Fig. 5-7).
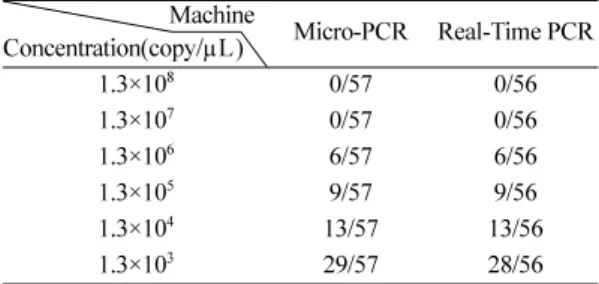
임상 샘플을 통한 특이성 테스트
HBV 감염환자로판정된혈청샘플 120 개이용하
여두장비에대한특이성테스트하였다(Table 4). 그 결과 Micro-PCR법은 57 개의샘플에서 Real-Time PCR
법은 56 개의샘플에서검출이되었다.
결 론
HBV-DNA를실시간으로모니터링하기위하여기
Table 2. Comparison of the PCR results conducted on Micro- PCR with Real-Time PCR
Machine
Test Micro-PCR Real-Time PCR
Detection range 108~103(copy/µL) 108~103(copy/µL)
PCR time 25 min 80 min
PCR volume 1 µL 20 µL
Ct/deviation 12.6±0.4cycle 17.5±0.5cycle
Tm/deviation 79±1 79.5±0.8
Fig.1. Micro-PCR amplification of HBV plasmid DNA (108copies/µL).
Fig.2. Real-Time PCR amplification of HBV plasmid DNA (108copies/µL).
존에알려져있고현재많이사용하고있는 Real-Time PCR법과마이크로칩의개념을도입하여새롭게개발 된 Micro-PCR법을가지고비교실험을하였다.
첫번째로재현성테스트결과 Real-Time PCR법의
Ct와Tm value는 17.5±0.5 cycle과 79.5±0.8, Micro-PCR
법의경우는 12.6±0.4 cycle과 79±1가나타남으로써 편차범위가비슷함을알수있었다. 두번째로검출 가능한농도범위테스트결과는 1.3×108~1.3×103copy/
µL의범위로동일한결과를나타냈다. 세번째로임
상샘플에대한특이성테스트결과에서는전체 120
개의혈청샘플중에서 Real-Time PCR법은 56 개의 샘플에서 Micro-PCR법은 57 개샘플에서검출이됨 Table 3. Comparison of the sensitivity conducted on Micro-
PCR with Real-Time PCR Machine
Concentration(copy/µL) Micro-PCR Real-Time PCR 1.3×108 10.3 cycle 14.4 cycle 1.3×107 13.4 cycle 17.9 cycle 1.3×106 17.4 cycle 21.4 cycle 1.3×105 21.6 cycle 25.0 cycle 1.3×104 26.1 cycle 28.6 cycle 1.3×103 31.2 cycle 30.9 cycle
Fig. 3. Melting curve analysis of Micro-PCR.
Fig.4. Melting curve analysis of Real-Time PCR.
Fig.5. In situ monitoring of Real-Time PCR with a broad range of concentration from 1.3×103 to 1.3×108copies/µL of HBV plasmid DNA, from left to right (108, 107, 106, 105, 104, 103, N).
Fig.6. In situ monitoring of Micro-PCR with a broad range of concentration from 1.3×103 to 1.3×108copies/µL of HBV plasmid DNA, from left to right (108, 107, 106, 105, 104, 103, N).
Fig.7. Serially diluted HBVplasmid DNA was amplified and analysed in real time. The Ct values were plotted against virus concentration.
으로써두장비가가지고있는특이성또한매우유 사하다는것을보여줬다. 검출된수가 낮은이유는
B형간염바이러스 DNA의소멸과낮은검출한계의
영향이라볼수있다. 그외에 PCR에소요되는시간 은 Micro-PCR법이 25 분, Real-Time PCR법은 80 분
이소요됐고소모되는시약의 양도 Micro-PCR법이
1/10~1/50 적게 소모됨을확인함으로서각종 진단이
나검사법에 매우유용하다는사실을알수있었다.
더욱이 Micro-PCR법은 6 개의모듈로이루어져있어 여러가지의조건으로실험할수있고서로다른유 전자를 동시에 검출해 낼 수 있고 컴퓨터와 PCR
machine이하나로이루어져 있어이동이 용이하여
다방면에응용할수있는강점을가지고있다. 그러 나 Micro-PCR법은많은수의샘플을동시에할수없
고 PCR 볼륨이적기때문에연구목적으로사용하기
에는다소어려운점이있다.
본저자는앞으로 Micro-PCR과 Real-Time PCR법 을응용하여 B형간염바이러스이외에도결핵, 탄저 균, 살모넬라, 브루셀라등다양한균및바이러스에 적용할계획이다. 그리고마지막으로인간유전자의
돌연변이검출까지확대, 응용하여 기존의방법으로
5시간이상걸리는돌연변이검출시간을 1 시간이내 로단축시킴으로써돌연변이검출의새로운 방법을 제시하고자한다.
인 용 문 헌
1. Ruben Bonilla Guerrero, Lewis R. Roberts. The role of hepatitis B virus integrations in the pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of Hepatol- ogy 2005, 42,760.
2. Ponsiano Ocama, MD, Christopher K. Opio, MD, Wil- liam M. Lee, MD. Hepatitis B virus infection: Current
status. The American Journal of Medicine 2005, 118, 1413.e15.
3. Chemin, I.; Tre´po. C. Clinical impact of occult HBV infections. Journal of Clinical Virology 2005, 34,S15.
4. Barros, M. F.; Rodrigues, P. A.; Matias, S. R.; Carreira, L. M.; Machado-Caetano. J. A. Detection of hepatitis B virus core mutants by PCR-RFLPin chronically infected patients. Journal of Virological Methods 2004, 120, 5. Guy Vernet, Nathalie Tran.125. The DNA-Chip technology as a new molecular tool for the detection of HBV mutants.
Journal of Clinical Virolog. 2005,34, S49.
6. Stephen Locarnini, William S. Mason. Cellular and virological mechanisms of HBV drug resistance. Jour- nal of Hepatology 2006, 44, 422.
7. Rodolfo H. Campos, Viviana A. Mbayed, Flavia G.
Pineiro y Leone. Molecular epidemiology of hepatitis B virus in Latin America. Journal of Clinical Virology 2005,34, S8.
8. Xiaodong Zhang, Hang Zhang and Lihong Ye. Effects of hepatitis B virus X protein on the development of liver cancer. Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Med- icine 2006, 147, 58.
9. Alba Maria Ropero, M. Carolina Danovaro-Holliday,;
Jon K. Andrus. Progress in vaccination against hepa- titis B in the Americas. Journal of Clinical Virology 2005, 34,S14.
10. Faure, E. Alternative peptide-fusion proteins generated by out-of-framemutations, just upstream ORFs or elon- gations in mutants of Human HepatitisB Viruses Virus Research. 2006, 117,185.
11. Sunchai Payungporn, Pisit Tangkijvanich, Pojchanad Jantaradsamee, Apiradee Theamboonlers, Yong Poo- vorawan. Simultaneous quantitation and genotyping of hepatitis B virus by real-time PCR and melting curve analysis.Journal of Virological Methods 2004, 120, 131.
12. Shiou-Hwei Yeh, Ching-Yi Tsai, Jia-Horng Kao; Chun- Jen Liu, Ti-Jung Kuo, Ming-Wei Lin, Wen-Ling, Huang, Shu-Fen Lu, Jane Jih, Ding-Shinn Chen, Pei-Jer Chen.
Quantification and genotyping of hepatitis B virus in a single reaction by real-time PCR and melting curve analysis. Journal of Hepatology 2004, 41, 659.
13. Watzinger, F.; Ebner, K.; Lion,T. Detection and mon- itoring of virus infections by real-time PCR. Molecular Aspects of Medicine. 2006, 27,254.
14. Garson, J. A.; Grant, P. R.; Ayliffe, U.; Ferns, R. B.;
Tedder, R. S. Real-time PCR quantitation of hepatitis B virus DNA using automated sample preparation and murine cytomegalovirus internal control. Journal of Virological Methods. 2005, 126, 207.
15. Jim O’Mahony, Colin Hill. A real time PCR assay for
Table 4. Comparison of the clinical sensitivity and specificity conducted on Micro-PCR with Real-Time PCR.
Machine
Concentration(copy/µL) Micro-PCR Real-Time PCR
1.3×108 0/57 0/56
1.3×107 0/57 0/56
1.3×106 6/57 6/56
1.3×105 9/57 9/56
1.3×104 13/57 13/56
1.3×103 29/57 28/56
the detection and quantitation of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis using SYBR Green and the Light Cycler. Journal of Microbiological Methods 2002, 51, 283.
16. Dixon, T. J.; Taggart, J. B.; George, S. G. Application of real time PCR determination to assess interanimal vari- abilities in CYP1A induction in the European flounder (Platichthys flesus). Marine Environmental Research 2002, 54, 267.
17. Martin E. Adelson, Melanie Feola, Jason Trama, Rich- ard C. Tilton, Eli Mordechai. Simultaneous detection of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 by real-time PCR and Pyrosequencing. Journal of Clinical Virology2005, 33, 25.
18.김재현, 최국선. Clinical evaluation of micro-scale chip-based PCR system for rapid detection of hepatitis B virus. 생물학전문연구정보센터(BRIC) BioWave 2003, 5, 2.
19. Yoon-Kyoung Choa, Jintae Kima, Youngsun Lee, Young-A. Kim, Kak Namkoong, Heekyun Lim, Kwang W. Oha, Suhyeon Kim, Jungim Han, Chinsung Park, Y. Eugene, Pak, Chang-Seok Ki, Jong Rak Choi, Hyeon-Koon Myeong, Christopher Ko. Clinical eval- uation of micro-scale chip-based PCR system for rapid detection of hepatitis B virus. Biosensors and Bioelec- tronics 2006, 21, 2161.