접수일:2011년 11월 4일, 수정일:2011년 12월 3일, 승인일:2011년 12월 3일
경북의 한 2차병원 수혈대상환자에서 검출된 비예기항체의 빈도
안 지 영
순천향대학교 의과대학 구미병원 진단검사의학과
= Abstract =
Frequency of Detection of Unexpected Antibodies in Transfusion Candidates at a Secondary Hospital in Gyeongbuk Province
Jee Young Ahn
Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gumi Hospital, College of Medicine, Soonchunhyang University, Gumi, Korea
Background: Antibody screening and identification tests are indispensable tools for protecting patients from acute hemolytic transfusion reaction. The column agglutination method has been widely used because of its simplicity and superiority to other methods for detecting warm antibodies. The purpose of this study was to analyze the frequency, distribution and clinical characteristics of unexpected antibodies found in transfusion candidates at a secondary hospital in Gyeongbuk Province, Korea.
Methods: The antibody screening tests were carried out with 9,275 sera samples using the column agglutination method from July 2009 to September 2011. The antibodies were screened and identified using the DiaMed-ID system (DiaMed, Murten, Switzerland).
Results: The positive rate for antibody screening tests was 0.5% (50/9,275). Unexpected antibodies were identified in 36 cases (0.4%). The most frequently detected antibody was anti-Lea in 15 cases (30%), followed by anti-Leb in 10 cases (20%) and anti-E in 8 cases (16%). Antibodies that remain unidentified were detected in 11 cases (22%).
Conclusion: Compared with previous reports, this study demonstrated that the frequency and distribution of unexpected antibodies were no different than those found in general hospitals. This study may provide data for the frequency and characteristics of unexpected antibodies in a secondary hospital. (Korean J Blood Transfus 2011;22:231-236)
Key words: Antibody screening test, Column agglutination, DiaMed-ID, Unexpected antibody
서 론
혈액형 비예기항체란 ABO 혈액형의 항-A항체
나 항-B 항체와 같은 예기항체에 상반되는 개념 으로 검사를 하기 전에는 어떤 사람의 혈청 내에 어떤 적혈구항원에 대한 항체가 존재할 것인지
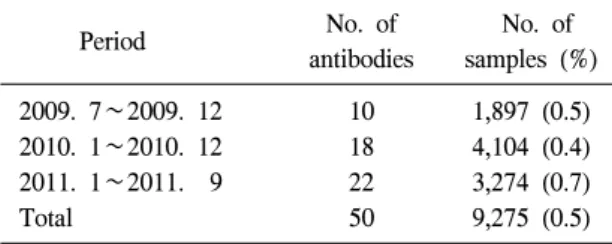
Table 1. The frequency of unexpected antibodies
Period No. of
antibodies
No. of samples (%) 2009. 7∼2009. 12 10 1,897 (0.5) 2010. 1∼2010. 12 18 4,104 (0.4) 2011. 1∼2011. 9 22 3,274 (0.7)
Total 50 9,275 (0.5)
알 수 없는 적혈구 항체로 불규칙항체라고도 한 다. 비예기항체는 자연 발생적으로 생길 수도 있 으나 대부분 임신이나 수혈 등을 통하여 다른 항 원에 노출되어 생기는 면역항체이다.1) 비예기항 체는 수혈 시 지연성 용혈성 수혈부작용을 일으 키는 가장 중요한 원인이 되므로 수혈 전 선별 및 동정 검사가 중요하다.2,3)
비예기항체 선별검사는 임상적으로 중요한 적 혈구 항체를 검출하는 것으로 수혈자의 혈청과 선별 혈구를 여러 가지 조건에서 반응시킴으로 항체의 존재를 알 수 있다. 원주응집법(column agglutination method)은 객관적인 결과판독을 할 수 있을 뿐 아니라 감도와 특이도가 높으며, 시험 관법의 세척과정의 복잡함이 없고, 실제 문제가 되는 온난항체의 검출률이 높다는 장점이 있
다.4-18) 최근에는 원주응집법외에 Erythrocyte
Magnetized Technology를 이용한 전자동 혈액은 행 자동화장비가 개발되고 있다.19) 이와 같이 비 예기항체의 검출기법도 다양해짐에 따라 비예기 항체가 동정되는 경우도 증가하고 있다. 이에 본 연구에서는 한 2차기관에서 비예기항체 검출 빈 도와 분포 및 임상적 특성을 분석하고자 DiaMed- ID system을 이용하여 조사하였다.
대상 및 방법
2009년 7월부터 2011년 9월까지 3년간 수혈이 의뢰된 9,275명을 대상으로 하였다. 이들 중 비예 기항체 선별검사 결과 양성 환자에서 비예기항체 동정검사를 실시한 50명을 대상으로 의무기록을 통해 후향적으로 환자들의 특성을 조사하였다.
비예기항체 선별 및 동정 검사는 DiaMed-ID system (DaiMed, Murten, Switzerland)의 LISS/
Coombs gel card와 ID-DiaCell I, II를 이용하여 검 사하였다. 비예기항체 선별검사는 ID-DiaCell I, II
50 μL에 환자 혈청 25 μL를 넣어 DiaMed incu- bator에서 37oC로 15분간 반응시킨 후 DiaMed Centrifuge에서 10분간 원심분리 하였다. 결과는 원주의 하단에 적혈구가 모두 가라앉으면 음성, 상단에 적혈구가 응집되어 있으면 4+, 그 사이 에는 적혈구가 원주에 분포하는 모습에 따라 1+
에서 3+로 분류하였다. 비예기항체 동정 검사는 LISS/Coombs card와 ID-DiaPanel I, II로 검사하였 다. 자가대조 적혈구를 이용하여 자가항체를 감 별하였으며 검사과정과 결과판독은 항체선별검 사와 동일하였다.
결 과
수혈 전 비예기항체 선별검사의 검출률은 9,275예 중 50예가 DiaMed-ID system 양성을 나타 내어 검사건수에 대한 0.5% 양성률을 나타내었 다(Table 1).
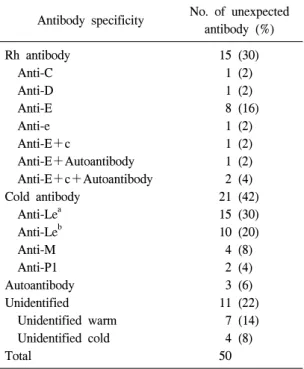
비예기항체의 선별검사 양성 50예 중 36예 (72%)가 항체의 특이성이 동정되었다. 동정된 항 체의 종류는 한랭항체 21예(42%)와 온난항체 15 예(30%)인 것으로 나타났다. 가장 많은 빈도의 계열은 Lewis 계열이었으며 항-Lea가 15예(30%) 로 가장 많았고, 그 다음으로는 항-Leb 항체가 10 예(20%)인 것으로 나타났다. 온난항체로는 Rh 계 열 항체인 항-E 항체가 8예(16%)로 가장 많았다.
Table 2. Distribution of unexpected antibodies
Antibody specificity No. of unexpected antibody (%)
Rh antibody 15 (30)
Anti-C 1 (2)
Anti-D 1 (2)
Anti-E 8 (16)
Anti-e 1 (2)
Anti-E+c 1 (2)
Anti-E+Autoantibody 1 (2) Anti-E+c+Autoantibody 2 (4)
Cold antibody 21 (42)
Anti-Lea 15 (30)
Anti-Leb 10 (20)
Anti-M 4 (8)
Anti-P1 2 (4)
Autoantibody 3 (6)
Unidentified 11 (22)
Unidentified warm 7 (14) Unidentified cold 4 (8)
Total 50
Table 3. Reactivity of unexpected antibodies
Antibody specificity LISS/
Coombs gel test Rh antibody
Anti-C 3+
Anti-D 2+
Anti-E 2+∼4+
Anti-e 3+
Anti-E+c 2+
Anti-E+Autoantibody 2+
Anti-E+c+Autoantibody 2+∼3+
Cold antibody
Anti-Lea 1+∼3+
Anti-Leb 1+∼2+
Anti-M 1+∼2+
Anti-P1 1+∼2+
Autoantibody 1+∼2+
Unidentified
Unidentified warm 1+∼2+
Unidentified cold 2+∼4+
복합항체는 4예(8%)였고, 이중 3예는 자가항체와 동반되었으며 자가항체만 검출된 경우는 3예 (6%)인 것으로 나타났다. 동정되지 않은 경우는 11예(22%)인 것으로 나타났다(Table 2, 3).
비예기항체의 선별검사 양성 환자의 성별은 남자 22명(44%), 여자 28명(56%)이었다. 평균연 령은 47세이었고, 연령 범위로는 60세 이상이 19 명(38%)으로 가장 많았으며 그 다음으로 20세에 서 39세가 15명(30%)인 것으로 나타났다. 환자의 질환 군은 외상 및 골절 12예(24%), 산모 9예 (18%), 암 6예(12%), 소화기계 질환 5예(10%) 순 으로 나타났다(Table 4).
고 찰
한국인에서의 비예기항체 빈도는 0.26%에서
3.4%까지 보고되어 있다. 이는 헌혈자 또는 수혈 대상자 임산부 등 특정 대상 군에서 검출된 결과 이며 대상군, 검사방법, 사용한 판넬 적혈구 종류 에 따라 결과에 큰 차이를 보이고 있다.14-22) DiaMed-ID System을 이용한 원주응집법에서 비 예기항체 양성률은 0.46%에서 1.7%까지 다양하 게 보고되었다.4,6,7,10-14,20,23,24) 본 연구결과 수혈대 상환자에서 비예기항체 양성률은 0.5%로 보고된 범위 내에 분포하였다. Cho 등,23) Park 등12) 및 Jung 등24)의 연구에서는 본 논문과 같이 DiaMed사의 LISS/Coombs card와 ID-diacell I, II 및 ID- DiaPanell I, II를 이용하여 각각 0.54%, 0.58% 및 0.65%의 양성률을 보였다. 추후 정확한 빈도와 분포를 구하기 위하여 더 많은 조사가 필요하리 라 사료되었다.22) 본 연구에서 수혈부작용 예는 발견되지 않았으나 신생아용혈성질환 1예에서
Table 4. Characteristics of patient with unexpected anti- bodies
Characteristics No. of unexpected antibodies (%) Gender
Male 22 (44)
Female 28 (56)
Age
<20 6 (12)
20∼39 15 (30)
40∼59 10 (20)
≥60 19 (38)
Previous transfusion
Yes 7 (14)
No 43 (86)
Diagnosis
Traumatic disease 12 (24) Obstetric patient 9 (18) Malignant disease 6 (12) Gastrointestinal disease 5 (10) Hepatobiliary disease 3 (6) Endocrinologic disease 3 (6) Cerebrovascular disease 3 (6)
Others 10 (20)
항-e 항체가 검출되었다. 비예기항체가 검출된 환 자들의 구성이 여자, 나이가 많은 사람, 그리고 다회 수혈력을 의심할 수 있는 암 환자 군과 산모 등에서 많아 용혈 반응이 수혈이나 임신 등의 기 왕력을 가진 사람, 그리고 수혈량이 많은 경우 더 잘 일어난다고 보고되었다.1,9,12,13,21,25)
본 연구 결 과 비예기항체 양성인 예 중 수혈 기왕력이 있는 경우는 14%로 22%에서 63%로 보고된 바에 비해 낮았고, 7예 중 4예에서 적혈구 농축액 2단위를 수혈 받았다.6,9,12,21) 검출된 환자들의 구성은 남성 환자 22명에 비해 여성 환자는 28명이었으며, 연 령별로는 60세 이상이 19명으로 가장 많았고 그 다음으로 20에서 39세 사이가 15명으로 많았다.
이는 환자의 분포가 교통사고로 인한 외상 및 골 절 환자와 산모가 각각 24%와 18%로 많기 때문 인 것으로 사료되었다. 본 연구에서 가장 높은 빈 도로 동정된 비예기항체는 항-Lea 항체로 30%이 었고 온난항체 중에는 항-E 항체가 16%로 나타 났는데 각각 Ortho BioVue System을 이용한 결과인 Park 등21)의 31.4%, 16.2%와 Lim 등9)의 33.9%, 18.0%와 비슷하였다. 시험관법을 사용한 연구에 서는 한랭항체인 항-Lewis 항체가 26%에서 65%
까지 다양하게 보고되었다.15-17,22) DiaMed-ID System을 이용한 Lee 등13)의 Rh계열의 온난항체 가 68.1%, 한랭항체가 11.9% 검출되어 시험관법 에서 높은 빈도로 검출되던 한랭항체가 검출률이 낮아져 교차 시험시 혈액은행 업무가 지연되던 요소를 줄일 수 있었다고 한 보고와는 달리 본 연 구에서는 한랭항체가 많이 검출되었다. LISS/
Coombs card를 이용했을 때의 양성률이 낮은 것 은 실온에서 반응하는 한랭 비예기항체가 약화되 어 나타나지 않아 Lewis계열이나 P계열 항체의 검출빈도가 감소한 것과 관련이 있다고 하였다.4) 또한 항체선별검사에서 한국인에 많은 Dia 혈구 를 추가하고, NaCl/ Enzyme card를 함께 사용하면 온난항체와 한랭항체의 검출력이 우수하다고 보 고되었다.4,5,12)
본 연구는 DiaMed-ID system을 이용하여 비예 기항체 빈도와 임상적 특성을 조사한 결과 이전 에 보고된 연구 결과와 비교할 때 비예기항체의 빈도와 분포 결과에 차이점이 없었고, 한 2차 기 관에서의 비예기항체 빈도 자료로서 이용될 수 있을 것으로 사료된다.
요 약
배경: 비예기항체의 선별과 동정검사는 용혈 성 수혈부작용을 예방하기 위해 중요한 필수 검
사항목으로 원주응집법(column agglutination me- thod)은 간편하고 온난항체의 검출률이 높아 최 근 널리 사용되고 있다. 비예기항체의 검출기법 도 다양해짐에 따라 비예기항체가 동정되는 경우 도 증가하고 있다. 이에 본 연구에서는 경북지역 의 한 2차병원에서 수혈대상환자의 비예기항체 검출 빈도와 분포 및 임상적 특성을 분석하고자 DiaMed-ID system을 이용하여 조사하였다.
방법: 비예기항체의 선별검사는 2009년 7월부 터 2011년 9월까지 DiaMed-ID system을 이용하여 검사하였고, 선별결과 양성인 검체에서 동정검사 를 시행하였다. 비예기항체의 동정검사는 DiaMed- ID system을 이용하였다.
결과: 9,275예 중 50예가 DiaMed-ID system 양 성을 나타내어 검사건수에 대한 0.5% 양성률을 나타내었다. 비예기항체는 36예에서 동정되었다 (0.4%). 가장 많은 빈도의 계열은 Lewis 계열이었 으며 항-Lea가 15예(30%)로 가장 많았고, 그 다음 으로는 항-Leb 항체가 10예(20%)로 검출되었다.
온난항체로는 Rh 계열 항체인 항-E 항체가 8예 (16%)로 가장 많았다.
결론: 비예기항체 빈도와 임상적 특성을 조사 한 결과 이전에 보고된 연구 결과와 비교할 때 비 예기항체의 빈도와 분포 결과에 차이점이 없었 고, 한 2차 기관에서의 비예기항체 빈도 자료로 서 이용될 수 있을 것으로 사료된다.
참고문헌
1. Han KS, Park MH, Cho HI. Transfusion medicine. 3rd ed. Seoul: Korea Medical Book Publisher, 2006:279-84
2. Kim HH, Park TS, Oh SH, Chang CL, Lee EY, Son HC. Delayed hemolytic transfusion reaction due to anti-Fyb caused by a primary immune response: a case study and a review
of the literature. Immunohematology 2004;20:
184-6
3. Kim KH, Han JY, Kim JM, Park KH, Han KS.
Fatal acute hemolytic transfusion reaction due to Anti-E+Fy(a). Korean J Lab Med 2003;23:
57-9
4. Chae SL, Bang KH, Chang EA, Cha YJ. An evaluation of gel test for irregular antibody screening. Korean J Blood Transfus 1998;9:
31-6
5. Lee SM, Lim YA, Oh JS. An experience of including ID DiaCell Dia cell in unexpected antibody screening test. Korean J Blood Transfus 2005;16:32-7
6. Kim MH, Suh JT, Lee WI. The frequency of unexpected antibodies in transfusion candi- dates in recent 6 years. Korean J Blood Transfus 2004;15:162-7
7. Kim JY, Huh JH, Kim SH, Nam MH, Roh KH, Kim JS, et al. Evaluation of the DG gel system using the microtube column agglutination technique for antibody screening and identi- fication. Korean J Blood Transfus 2007;18:32-8 8. Park JS, Park CM, Chang HE, Kim MJ, Park
KU, Song J, et al. Evaluation of the per- formance of the DG gel test for unexpected antibody screening and identification. Korean J Blood Transfus 2008;19:49-56
9. Lim GY, Park KS, Park TS, Lee HJ, Suh JT, Park SY. The frequency and distribution of unexpected antibodies in transfusion can- didates with the use of the Ortho BioVue system: recent four year experience. Korean J Blood Transfus 2009;20:23-31
10. Yoo BJ, Cho CH, Yun SG, Kim HN, Choi GR, Kim JS, et al. The frequency of unexpected antibodies by using two micro-column agglu- tination systems: DiaMed-ID and Ortho BioVue systems. Korean J Blood Transfus 2010;21:1-8
11. Lee HY, Joo SY, Shin S, Sung SJ, Roh EY, Yoon JH, et al. A comparison of two microcolumn agglutination systems for red cell antibody screening and identification. Korean J Blood Transfus 2008;19:132-8
12. Park JR, Heo WB, Park SH, Park KS, Suh JS.
The frequency unexpected antibodies at Kyungpook national university hospital.
Korean J Blood Transfus 2007;18:97-104 13. Lee WH, Kim SY, Kim HO. The incidence of
unexpected antibodies in transfusion candi- dates. Korean J Blood Transfus 2000;11:99-103 14. Oh DJ, Kim MJ, Seo DH, Song EY, Han KS,
Kim HO. The frequency of unexpected antibodies in blood donors and transfusion candidates in Korea. Korean J Blood Transfus 2003;14:160-72
15. Kim BS, Min HO, Song KS, Lee SY. Frequency of irregular antibodies detected by type and screen procedure. Korean J Blood Transfus 1990;1:47-50
16. Kim CW. A study on identified red cell irregular antibodies in Korean. Korean J Blood Transfus 1994;5:31-7
17. Song DH, Moon IS, Hong SJ, Park JH, Kim JG, Jeon DS. Frequency and distribution of unexpected antibodies of Koreans. Korean J Blood Transfus 1998;9:191-200
18. Oh HB, Cho YJ, Kim SI, Kim DS, Han KS.
Irregular antibody positivity in women blood donors with history of parturition. Korean J
Blood Transfus 1997;8:39-47
19. Choi GR, Min BK, Kim HN, Cho CH, Kim YH, Choi JY, et al. Evaluation of the automated instrument QWALYS-3 for unex- pected antibody screening. Korean J Blood Transfus 2011;22:38-45
20. Chung HR, Park YM. The clinical significance of prenatal antibody screening test. Korean J Blood Transfus 2005;16:14-9
21. Park BM, Song YK, Kim TS, Lee GH, Choi JS, Seong MW, et al. The frequency and distribution of unexpected red cell antibodies at national cancer center. Korean J Blood Transfus 2009;20:120-8
22. Kim HO, Won DI, Kwon OH. The frequencies of unexpected antibodies in transfusion candidates and selection of cross-matching method. Korean J Blood Transfus 1993;4:35-41 23. Cho YK, Kim DS, Lee HS, Choi SI. The frequency and distribution of unexpected anti- bodies in surgical patients at Chonbuk National University Hospital. Korean J Lab Med 2004;24:67-71
24. Jung TK, Lee NY, Bae HG, Kwon EH, Park SH, Suh JS. Unexpected antibody positivity with the use of the. LISS/Coombs gel test.
Korean J Clin Pathol 2001;21:422-5
25. Kim KH, Kim WJ, Han JY, Kim JM. Charac- teristics of RBC alloimmunization detected by unexpected antibody screening tests. Korean J Blood Transfus 2007;18:159-68