1970 ,
, .
1
.
(L/B)
,
.
( , , )
Hull form development of the high speed small fishing boat
Kwi-Joo LEEand Soon-Won JOA*
Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, Chosun University, Gwangju 501-759, Korea
This study is concerned with the development of the basic planing hull form of small fishing boat in 25 knots high speed. A series of model test to determine the optimum performance hull form of actual fishing boat with 10 gross tonnage was carried out for 5 models made available planing hull form in the circulation water channel. Model test was performed with the resistance test to study the hydrodynamic characteristics of model ships and the sinkage and trim measurement to investigate the stability of model ships and also the wave pattern observation to analyze the effectiveness of model ships. As the result, the planing hull form of P-4 with deep V type bow can be derived as the best hull form with good performance especially in ship s resistance efficiency showing less residual resistance and sinkage and trim and the spray effect, etc..
Key words : Planning hull, Deep-V type hull form, Resistance performance, Wave pattern, CWC test
*Corresponding author: joasw@chosun.ac.kr, Tel: 82-62-230-7275, Fax: 82-62-230-7159
. Lee and Lee(1998)
.
, Lee and Lee(1998)
Joa and Lee(2004)
5 ,
(series model test)
. 5 , ,
(WJFEL)
.
( , , )
.
Min et al.(1992) Lee
and Joa(1998) 25
5 .
10 ,
Lee and Joa(1998)
15m, 3.5m, 1.32m .
Fig. 1 Min et
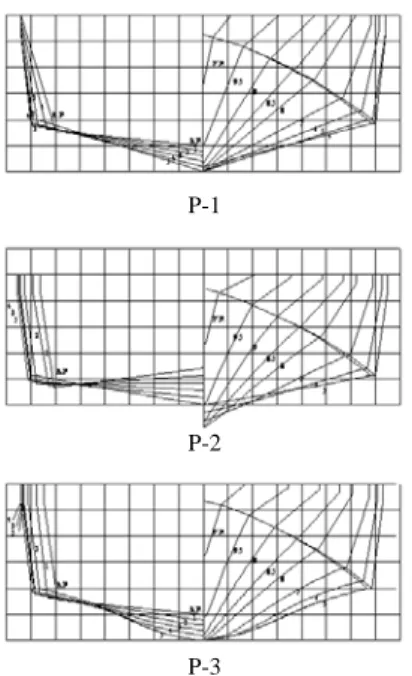
Fig. 1. Comparison of body plans for 5 hull forms.
P-1 P-4
P-5 P-2
P-3
al.(1992) Joa and Lee(2004)
P 3 (centerline)
(chine line)
.
P 1 P 3
, P 2
P 1
(inverted) V , P 4
P 3 Deep V .
P 5 P 4 5
, 6 , 7 3 (step)
.
Table 1 ,
, .
, 5 Fig. 1
.
15m, 25
1/20 5 FRP
. 5
P 4
Table 2 .
.
LCB .
(1) 2
.
CR CTM CFM (1)
5
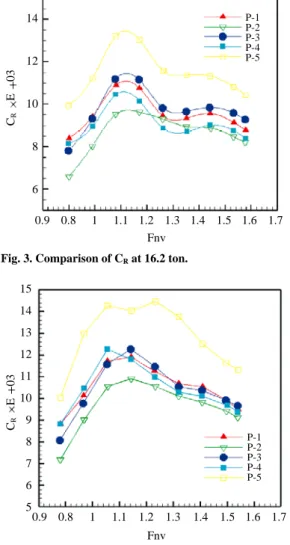
Fig. 2, Fig. 3 Fig. 4 .
Fig. 2, Fig. 3 Fig. 4
. 13.6
P 4
, P 5
, P 2
.
Fig. 2 P 4
13.6 Fig. 3 16.2
Fig. 4 18.2
, P 4
name body body
P 1 S S S & V
P 2 S S S & I/V
P 3 I/B I/B I/B
P 4 C I/B I/B
P 5 C I/B I/B
S: Straight type, C: Concave type,
I/V: Inverted V type, I/B: Inverted Bell type.
Particulars
Ship Model Ship Model
Scale 1 1/20 1 1/20
LPP(m) 15.0 0.750 15.0 0.750
LWL(m) 15.0 20.751 15.03 0.752
B(m) 3.5 0.175 3.5 0.175
T(m) 0.63 0.032 0.73 0.037
LCB(m) 1.17 0.059 1.16 0.058
S( ) 48.8 0.122 52.4 0.131
( ) 13.5 0.0017 17.5 0.0022
CB 0.41 0.41 0.45 0.45
. , P 5 P 4
(step)
, .
P 4 Fig. 2
Fig. 4 Fig. 5 .
F.P.
A.P. (2)
(3) .
dA dF
S (_______2 ) 2g/U2 (2)
t (dA dF) 2g/U2 (3)
, dA : , dF :
g : , U :
16.2
Fig. 6 .
, P 4
Fig. 7 .
Fig. 6 Fig. 7 Fig. 2. Comparison of CRat 13.6 ton.
Fig. 3. Comparison of CRat 16.2 ton.
Fig. 4. Comparison of CRat 18.2 ton.
Fig. 5. Comparison of CRof P 4 as function of displace- ment.
12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5
14
12
10
8
6
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5
0.9 0.8 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7
0.9 0.8 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7
0.9 0.8 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Fnv
Fnv
Fnv
P-1 P-2 P-3 P-4 P-5
P-1 P-2 P-3 P-4 P-5
P-1 P-2 P-3 P-4 P-5 CRE03CRE03CRE03
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6
50.9 0.8 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 CRE03
13.6ton 16.2ton 18.2ton
Fnv
,
,
(spray)
. P 4 P 5
, (step)
.
. 13.6
5 1.75
m/sec(Fnv 1.62)
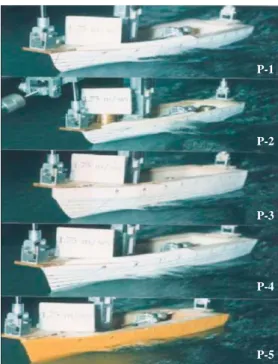
Fig. 8 .
Fig. 8 P 1, P 2
,
.
.
P 4, P 2
P 5 (stepped hull), 3
14~30 ( 1.6~3.5m/s)
.
Table 3 Table 4 ,
P 4
. , (step)
P 2 . Fig. 9 Fig. 10 Fig. 6. Comparison of sinkage and trim at 16.2 ton.
Fig. 7. Comparison of sinkage and trim (P 4).
Fig. 8. Comparison of spray at 13.6 ton (Fnv=1.62).
-0.1 -0.2 -0.3 -0.4
0.1 0 -0.1 -0.2 -0.3 -0.4
0.9 0.8 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2
0.9 0.8 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2 Fnv
Fnv
P-2(Sink) P-3(Sink) P-4(Sink) P-5(Sink) P-1(Trim) P-2(Trim) P-3(Trim) P-4(Trim) P-5(Trim)
13.6ton(Sink) 13.6ton(Trim) 16.2ton(Sink) 16.2ton(Trim) 18.2ton(Sink) 18.2ton(Trim)
Sinkage & trim2guSinkage & trim2gu2
P-1
P-2
P-3
P-4
P-5
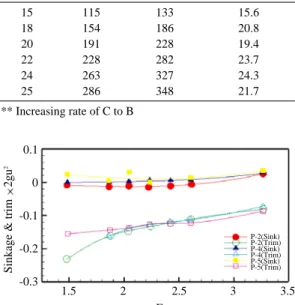
, Fnv=2.0 3
. Fig. 11
(13.5 ) P 2, P 4 P 5
, ,
P 4 P 5 .
Fig. 12 (17.5 ) P 4 P 5
,
.
, P 4
Fig. 13 , P 2
Fig. 14 .
Fig. 13 Fig. 14 Table 3. Comparison of EHP(kW) at ballast condition
Vs(kts) P-2(A) P-4(B) P-5(C) (A-B)/A (C-B)/B 100 (%)* 100 (%)**
15 87 84 86 3.4 2.4
20 167 144 175 13.8 21.5
22 203 170 223 16.3 31.2
25 257 213 282 17.1 32.4
26 271 225 298 17.0 32.4
28 289 245 327 15.2 33.5
30 293 260 353 11.3 35.8
* Decreasing rate of B to A
** Increasing rate of C to B
Table 4. Comparison of EHP(kW) at full load condition
Vs(kts) P 4(B) P 5(C) (C B)/B 100
(%) **
15 115 133 15.6
18 154 186 20.8
20 191 228 19.4
22 228 282 23.7
24 263 327 24.3
25 286 348 21.7
** Increasing rate of C to B
Fig. 10. Comparison of sinkage and trim at 17.5 ton in full load condition.
Fig. 11. CRand trim angle at 13.5 ton in ballast condition.
Fig. 12. CR and trim angle at 17.5 ton in full load condition.
0.1 0 -0.1 -0.2 -0.3
1.4 1.6 1.8 2 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3 Fnv
Sinkage & trim2gu2
P-4(Sink) P-4(Trim) P-5(Sink) P-5(Trim)
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
1.5 2 2.5 3 3.50
Fnv
CRE+03 Trim(deg)
P-2 P-4P-5 P-2(Trim) P-4(Trim) P-5(Trim)
10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2
10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2
1.5 2 2.5
Fnv
CRE+03 Trim(deg)
P-4P-5 P-4(Trim) P-5(Trim)
Fig. 9. Comparison of sinkage and trim at 13.5 ton in ballast condition.
0.1 0 -0.1 -0.2
-0.3 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5
Fnv
Sinkage & trim2gu2
P-2(Sink) P-2(Trim) P-4(Sink) P-4(Trim) P-5(Sink) P-5(Trim)
P 2
. P 4 ,
.
(step)
, .
, Deep
V P 4 5
(step)
. P 4
(concave) (inverted bell)
.
(step) , ( ,
)
.
Joa, S.W. and K.J. Lee, 2004. An experimental study on the improvement of resistance performance at pre planing condition for G/T 100 ton class planing hull form. Journal of the Korean Society of Fisheries Technology, 40(1), 17 22.
Lee, K.J., S.W. Joa and M. Park, 2000. An experimental study for 2500TEU container hull form development.
Autumn symposium of Korea Committee for Ocean Resources and Engineering, 261 264.
Lee, K.J. and K.I. Lee, 1998. A correlation study between section form and L/B ratio for high speed planing hull form. Journal of the Korean Society of Fisheries Technology, 34(3), 221 228.
Lee, K.J. and S.W. Joa, 1998. A study on the hull form development of the medium size high speed fishery patrol ship. Journal of the Society of Naval Architects of Korea, 35(2), 1 7.
Min, K.S, K.J. Lee and M. Park, 1992. An experimental result of planning hull with the variation of L/B and section configuration. Hyundai Maritime Research Institute Report, 15 150.
Min, K.S., K.J. Lee and M. Park, 1992. An experimental result of concave section planning hull with 4 variations of L/B. Hyundai Maritime Research Institute Report, 12 150.
Fig. 13. Wave pattern of P 4 at Fnv=3.24.
Fig. 14. Wave pattern of P 2 at Fnv=3.24.
2008 2 1
2008 2 21