위전절제술 후 Early Enteral Nutrition과 Total Parenteral Nutriton의 전향적 비교 연구
권희, 손은선, 고종희, 안지현, 송승은*, 이은주*, 이호선*, 조미화**, 강정애**,신혜선**, 윤석준
#, 윤호영
#, 김충배
#연세대학교 세브란스병원 약무국, 영양팀*, 간호국**, 외과학교실
#A Comparison of Early Enteral Nutrition and Total Parenteral Nutrition after Total Gastrectomy
Hee Kwon, Eun Sun Son, Jong Hee Ko, Ji Hyune Ahn, Sung Eun Song*, Eun Joo Lee*, Ho Sun Lee*, Mi Hwa Cho**, Jeong Ae Kang**, Hye Sun Shin**, Seok Jun Yoon
#, Ho Young Yoon
#, Choong-Bai Kim
#Division of Pharmacy, Department of Dietitian*, Division of Nursing**, Department of Surgery
#, Yonsei University Health System, Seoul, Korea
회원학술보고
Abstract : This study was aim to compare nutritional parameter, immune competency, and types of complication between early enteral nutrition (EN) and total parenteral nutrition (TPN) after total gastrectomy.
Patients were prospectively randomized to receive early EN by nasoenteral tube (n=17) or TPN via central venous catheter (n=16) after total gastrectomy in Yonsei University Health System from March 2006 to July 2007. The nutritional goals were 25kcal/kg/day for total daily calories and 1.5g/kg/day for total daily protein. No significant differences were found between the two groups regarding nutritional parameters and length of stay. However, AST/ALT level on post operating day (POD) 7 was slightly higher in the TPN group compared to the early EN group.
There were no infectious complications in either group. Complications encountered in the early
EN group were GI complications such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal distension and increased
AST/ALT levels whereas in the TPN group, total bilirubin and ASL/ALT elevations. Considering
the fact that both groups showed small decrease in weight, active nutritional support is essential
in patients with total gastrectomy. There were no statistically significant differences between
early EN and TPN group following total gastrectomy in terms of nutritional parameters and
immune competency. Based on this result, both early EN and TPN seem to be appropriate in sup-
plying nutrition after total gastrectomy.
연구배경
위장관 수술 후에는 여러가지 원인에 의하여 영양 불량이 나타나게 되는데, 경구섭취량 부족에 의한 체 중감소가 가장 큰 영양불량의 원인으로 보고되고 있 으며, 수술 후 일주일 이내 체중감소, 수술 후 입원기 간 내 영양불량에 대한 관리의 필요성이 언급되고 있 다. 이러한 영양불량의 지속은 수술 후 유병율, 사망 률과도 관련이 있으며 사회로의 복귀, 활동에 영향을 줄 수 있다. 따라서, 위장관 수술에 의해 경구 섭취가 불가능한 환자에서 수술 후 적극적인 영양 공급은 환 자 회복에 긍정적 영향을 미친다. 특히 위전절제술을 시행한 환자는 수술 전부터 영양상태가 좋지 못하며 위장관 운동이 원활하지 못한 경우가 많으므로 수술 후 영양공급은 더욱 중요하다고 할 수 있다. 수술 후 초기 경장 영양(Early enteral nutrition) 공급은 장관 기능 유지 및 감염의 문제, hepatic steatosis, 비용 등에 있어서 total parenteral nutrition (TPN)에 비해 장점이 있으나, 설사, 장마비 등의 단 점이 있다. TPN은 소화관으로 영양 흡수가 불가능 한 환자나 경구섭취가 불충분한 환자에게 영양 공급 을 충분히 해줄 수 있으나, 카테터 관련 합병증, 고혈 당, 간기능 이상 등의 문제가 발생할 수 있다.
이에, 본 병원 영양지원팀은 위전절제술 후 early EN과 TPN을 투여 받은 환자의 영양상태 회복, 면 역기능 유지, 합병증 발생의 전향적 비교 연구를 통 하여 위전절제술 후의 영양학적 critical pathway 의 초석을 마련하고자 한다.
연구대상 및 방법
2006월 3월부터 2007년 7월까지 세브란스병원에 서 위전절제술을 시행 받은 환자 중 56명을 대상으 로 하였다. 56명의 환자를 early EN군과 TPN군으 로 무작위 배정하여 전향적 연구를 시행하였다.
Inclusion criteria 와 exclusion criteria는 다음
과 같다.
Inclusion criteria - 18세 이상
- Total gastrectomy 시행한 환자
Exclusion criteria - 18세 미만
- Hepatic dysfunction
- End stage renal disease (ESRD) - Cardiac dysfunction
- 임신
- 감염상태의 환자
환자군 목표 영양공급 kcal는 25 kcal/kg/day, protein은 1.5 g/kg/day로 하였다.
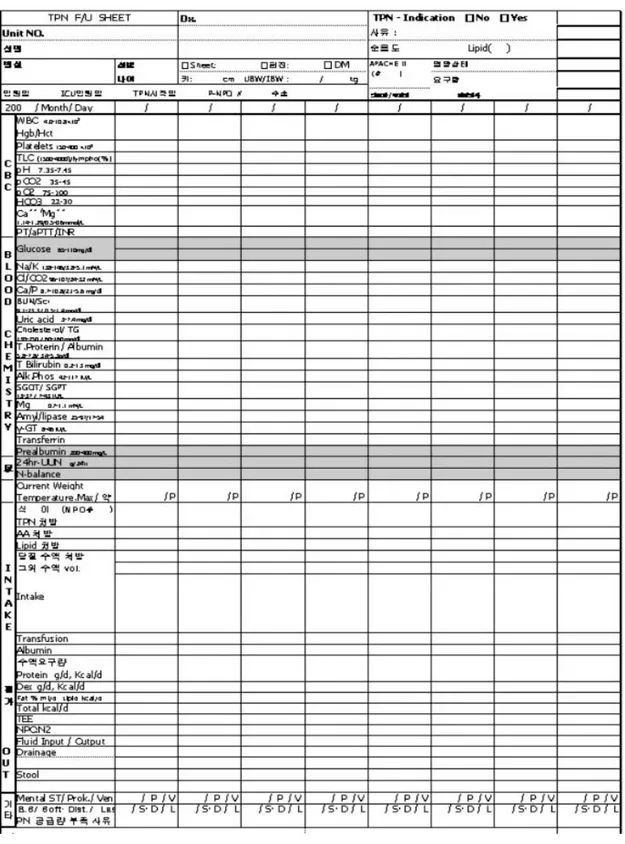
early EN군은 수술 중 nasoenteral tube를 소장 에 삽입하고(Figure 1.), pump를 사용하여 Post operating day(POD) 1일에 EN 400~500ml (400~500kcal)로 시작, 매일 투여량을 증가하였으 며 , 부 족 한 칼 로 리 와 단 백 질 은 Peripheral Parenteral Nutriton(PPN)으로 보충하였다. POD 4~5일에는 EN으로 필요량 모두를 투여하였다. 이 후 POD 6일, POD 7일에는 경구로 Postgastrec- tomy Liquid diet(위절제 후 유동식), Postgastr- ectomy soft diet (위 절제 후 연식)을 섭취하였 다.(Figure 2.)
TPN군은 central venous catheter를 유지하며 POD 1~5일까지 TPN으로 영양공급을 하였고, POD 6일, POD 7일에는 경구로 위절제 후 유동식, 위절제 후 연식을 섭취하였다. laboratory data를 포함한 환자 영양상태와 면역기능의 지표가 되는 항 목들(weight change, 면역력을 나타내는 TLC, acute inflammation을 나타내는 CRP, visceral protein(prealbummin, transferrin), total pro- tein, albumin, Hgb, Hct, BUN, AST/ALT,
손은선:위전절제술 후 Early Enteral Nutrition 과 Total Parenteral Nutriton의 전향적 비교 연구
[Key words] Total gastrectomy, Early enteral nutrition (EN), Total parenteral nutrition (TPN)
Figure 1. early EN군의 nasoenteral tube 삽입한 모습
Figure 2. early EN군과 TPN군의 영양공급
손은선:위전절제술 후 Early Enteral Nutrition 과 Total Parenteral Nutriton의 전향적 비교 연구
Table 1. 경과기록지
Triglyceride, glucose 등)은 수술 전과 POD 7일에 측정, 비교하였다. 관찰을 위해 사용한 경과기록지는
<Table 1>과 같다.
분석은 SPSS program을 이용하여 Student t- test, Mann-Whitney test(=Wilcoxon rank sum test)를 사용하였다.
결과
위전 절제술을 시행한 환자 중 56명이 early EN군 과 TPN군으로 무작위 배정되었다. 이 중 23명은 Enteral tube와 관련된 문제(12명), 복부팽만 및 통증 (6명), 칼로리 및 단백질 투여 오류(4명), hiccup 지속 (1명)으로 인해 분석대상에서 제외되었다.<Table 2>
무작위 배정된 56명 중 early EN군 17명과 TPN
군 16명이 최종 분석 대상이 되었으며, 수술 전 각 군의 age, weight, height, 영양상태인 TLC, Hgb, Hct, BUN, AST, TG, glucose, total protein albumin, transferrin, prealbumin 에 유의한 차 이가 없었다.<Table 3>, <Table 4>
Early EN군과 TPN군으로 영양공급을 하였을 때
영양학적 지표인 weight change, total protein, albumin, prealbumin, transferrin의 차이를 POD 7일 값에서 수술 전 값을 뺀 수치에 있어서 두 군에서 수술 전후 유의한 차이를 보이지 않았으며 면 역학적 지표인 Total Lymphocyte Count(TLC) 와 수술 후 재원일수에도 <Table 5>에서 보듯이 유의한 차이를 보이지 않았다. 이를 그래프로 나타내면
<Figure 3>와 같다.
Early EN군과 TPN군의 영양학적 지표와 면역학 적 지표에서 수술 전 후 차이는 없는 것으로 나왔으 며, 특히 몸무게 있어 두 군 모두 수술 전 후 큰 차이 를 나타내지 않았다.<Figure 4>
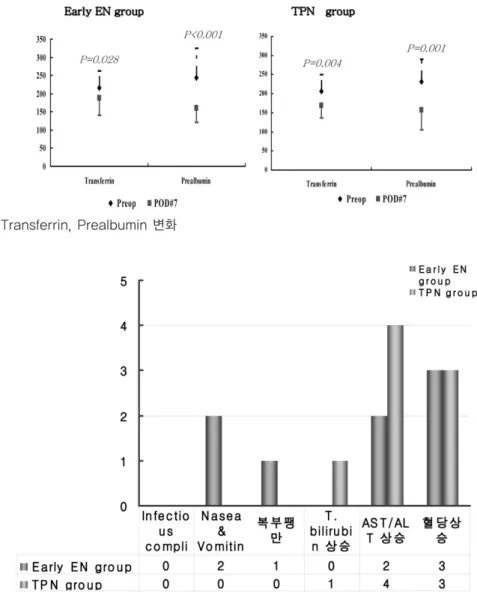
아울러 early EN군과 TPN군에서 수술 전후 각 군 의 대응표본 검정을 실시했다. 대응표본 검정 결과 early EN군에서는 AST/ALT의 유의한 상승을 볼 수 없었으나 TPN군에서 수술 후 AST/ALT가 유의 하게 상승하였음을 확인하였다.(p=0.023, 0.032) 그리고 두 군 모두 TG는 수술 전후 유의한 상승을 볼 수 없었다. <Figure 5> 또한 두 군 모두에서 영양 학적 지표인 trasferrin과 prealbumin 모두 수술 후 유의적으로 감소함을 볼 수 있었다.(early EN군 : p=0.028, <0.001, TPN군 : p=0.004, 0.001)<Figure 6>
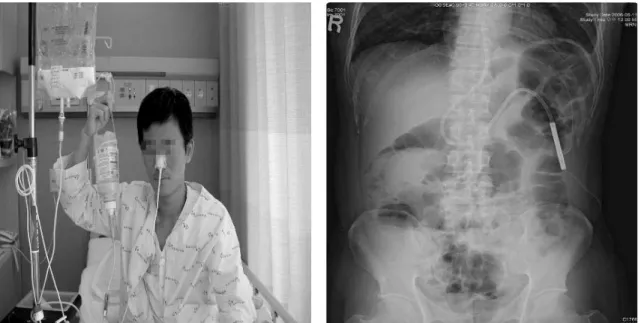
수술 후 합병증에서 두 군 모두 Infectious com- plications는 없었으며, early EN군에서 nausea, vomiting, 혈당상승이 있었고, TPN군에서는 total bilirubin, ASL/ALT 상승, 혈당상승이 있었 다.<Figure 7>
손은선:위전절제술 후 Early Enteral Nutrition 과 Total Parenteral Nutriton의 전향적 비교 연구
Characteristics Early EN group(n=17) TPN group(n=16)
Male/Female 12 / 5 13 / 3
Age(years)* 50 (27-74) 64.5 (28-82)
Height(cm)* 162 (154-174) 166.5 (143-178)
Weight(kg)* 62.3 (47.6-75.9) 58 (52-82)
BMI* 23.46 (18.91-26.94) 22.38 (17.99-27.88)
* median (range), BMI : Body Mass Index
원인 Early EN group TPN group
Tube 막힘 9 0
Tube 빠짐 3 0
복부팽만 및 통증 6 0
hiccup 지속 1 0
Over nutrition 0 4
Table 2. 분석 대상 제외 원인
Table 3. 수술 전 Early EN군과 TPN의 비교
결론
결과에서 보는바와 같이 early EN과 TPN군 모두 에서 체중 감소가 적은 연구 결과를 보았을 때 위전 절제술 후 적극적인 영양지원은 반드시 필요하다. 또 한 early EN과 TPN군에서 수술 후 환자의 total protein, albumin, prealbumin, transferrin, 면
역학적 지표인 Total Lymphocyte Count(TLC)와 수술 후 재원일수에 두 군간의 통계적으로 유의한 차 이를 보이지 않았으므로 위전절제술 후 early EN이 나 TPN을 통한 영양공급은 환자의 영양상태, 면역 기능 유지에 있어서 모두 적절한 방법이라 판단된다.
향후 환자의 순응도, 경제적 효과 및 지속적 관찰 등 을 고려한 좀더 세부적인 연구도 진행하고자 한다.
Early EN group (n=17)
TPN group
(n=16) p-value
TLC 1908.71 ±347.94 2107.9 ± 608.62 0.264
Hgb 16.2 ± 41.32 18.76 ± 1.61 0.534
Hct 39.41 ± 4.52 38.45 ± 5.35 0.583
BUN 14.29 ± 4.25 14.94 ± 3.25 0.627
AST 22.41 ± 8.77 19.06 ± 3.53 0.16
TG 124.12 ± 92.12 97.56 ± 47.38 0.304
Glucose 110.82 ± 30.85 106.19 ± 29.29 0.661
Total protein 6.76 ± 0.50 6.98 ± 0.51 0.231
Albumin 4.12 ± 0.49 4.2 ± 0.43 0.611
Transferrin 216.23 ± 47.32 206.56 ± 43.59 0.546
Prealbumin 243.41 ± 82.57 232.00 ± 58.77 0.649
Mean Mean SD SD
Early EN group (n=17)
TPN group (n=16)
Early EN group (n=17)
TPN group (n=16)
Wt change -1.01 -0.35 4.57 3.62
BUN 3.74 4.9 5.88 4.6
AST 4.06 17.31 71.78 31.94
ALT 19.24 23.56 65.27 39.99
TG -20.82 -8.44 59.44 32.24
Glucose 2.76 4.5 20.61 30.08
Protein -0.81 -0.74 0.7 0.78
Albumin -0.85 -0.73 0.49 0.65
Transferrin -28.41 -37.56 48.42 43.76
Prealbumin -83.75 -74.48 69.54 69.81
LOS 11.8 13 2.6 3.29
TLC -837.32 -837.39 353.01 594.85
Table 4. 수술 전 Early EN군과 TPN의 비교
Table 5. 수술 전후 두 군의 각 parameter의 차이; [POD 7 value] - [Preoperative day value]
손은선:위전절제술 후 Early Enteral Nutrition 과 Total Parenteral Nutriton의 전향적 비교 연구
Figure 3. 수술 전후 두 군의 각 검사치 차이; [POD 7일] - [수술전]
Figure 5. AST/ALT, TG 변화
Figure 4. 수술 전 후 early EN군과 TPN군의 몸무게비교
참고문헌
1) Mackay S, Hayes T, Yeo A : Management of gastric cancer. Aust Fam Physician.
Apr;35(4):208-11. Review.(2006)
2) Nomura S, Kaminishi M : Surgical treat- ment of early gastric cancer. Dig Surg.
24(2):96-100. Epub Apr 25. Review.(2007)
3) Zaloga GP : Crit Care Med 27:259(1999) 4) Dervenis C, Avgerinos C, Lytras D, Delis S
: Benefits and limitations of enteral nutrition in the early postoperative peri- od. Langenbecks Arch Surg. Feb;387(11- 12):441-9. Epub Feb 7.(2003)
5) Moore F, et al : Ann Surg 216:172-183 (1992)
Figure 6. Transferrin, Prealbumin 변화
Figure 7. 수술 후 합병증
6) Sand J, Luostarinen M, Matikainen M : Enteral or parenteral feeding after total gastrectomy: a prospective randomized pilot study. Eur J Surg 163:761(1997) 7) Mullen JL, Gertner MH, Buzby GP,
Goodhart MH, Rosato EF Implications of malnutrition in the surgical patient.
Arch Surg 114:121(1979)
8) Beattie AH, Prach AT, Baxter JP : Pennington CR A randomized controlled trial evaluating the use of enteral nutri- tional supplements postoperatively in malnourished surgical patients. Gut 46:813(2000)
9) ga M, Gianotti L, Nespoli L, Radaelli G, Di Carlo V : Nutritional approach in malnourished patients. Arch Surg 137:174(2002)
10) Baigrie RJ, Devitt PG, Watkin DS : Enteral versus parenteral nutrition after oesophagogastric surgery: a prospective randomized comparison. Aust NZ J Surg 66:668(1996)
11) Bisgaard T, Kehlet H : Early oral feeding after elective abdominal surgery. What are the issues? Nutrition 18:944(2002) 12) Koretz RL, Avenell A, Lipman TO,
Braunschweig CL, Milne AC : Does enteral nutrition affect clinical outcome?
A systematic review of the randomized trials. Am J Gastroenterol. Feb;102(2):
412-29; quiz 468.(2007)
13) Uchida K, Takahashi T, Inoue M, Morotomi M, Otake K, Nakazawa M, Tsukamoto Y, Miki C, Kusunoki M : Immunonutritional effects during synbi- otics therapy in pediatric patients with short bowel syndrome Pediatr Surg Int.
Mar;23(3):243-8. Epub Jan 5.(2007 ) 14) Hosseini S, Amirkalali B, Nayebi N,
Heshmat R, Larijani B : Nutrition status of patients during hospitalization, Tehran, Iran. Nutr Clin Pract. Oct;21(5):
518-21.(2006)
15) Yunsheng Ma, Jennifer A Griffith, Lisa Chasan-Taber, Barbara C Olendzki, Elizabeth Jackson, Edward J Stanek, III, Wenjun Li, Sherry L Pagoto, Andrea R Hafner and Ira S Ockene : Association between dietary fiber and serum C- reactive protein, American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, April (2006)
16) Seres DS. Surrogate nutrition markers, malnutrition, and adequacy of nutrition support. Nutr Clin Pract. Jun;20(3):
308-13.(2005)
17) Vel´ asquez Rodr´iguez CM, Parra Sosa B, Morales Mira G, Agudelo Ochoa G, Cardona Henao O, Bernal Parra C, Burgos Herrera L, Betancur Acosta M :
“Free”iron, transferrin and ferritin lev- els in serum and their relation with severe malnutrition. An Pediatr (Barc).
Jan;66(1):17-23(2007)
18) Frank N, Urinary Urea Nitrogen : Too Insensitive for Calculating Nigrogen Balance Studies in Surgical Clinical Nurition, JPEN vol.15,No2, 15:189-193, (1991)
손은선:위전절제술 후 Early Enteral Nutrition 과 Total Parenteral Nutriton의 전향적 비교 연구

![Table 5. 수술 전후 두 군의 각 parameter의 차이; [POD 7 value] - [Preoperative day value]](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dokinfo/4721056.263655/7.798.85.719.485.801/table-수술-전후-군의-parameter의-차이-value-preoperative.webp)
![Figure 3. 수술 전후 두 군의 각 검사치 차이; [POD 7일] - [수술전]](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dokinfo/4721056.263655/8.798.163.639.145.465/figure-수술-전후-군의-검사치-차이-pod-수술전.webp)