6 갑상선 외과 분야의 20세기 회고
(Retrospects of Twentieth-Century in Thyroid Surgery)
1) The prelude
갑상선 수술의 시행은 1595년 공식적인 문서상에 처음 으로 기록되어 있으나, 본격적으로는 19세기에 이르러 Billorth (Vienna, 1877), Bruberger등에 의하여 200예 정도 가 시행되었다. 그러나 20세기 갑상선외과의 효시는 스위 스 베른의 Theodor Kocher 교수에서 비롯된다. 그는 1872 년에 처음으로 thyroidectomy를 시행한 후 1901년까지 2,000
예의 수술을 시행하였고 갑상선기능항진증 및 갑상선암 수술을 포함하여 수술 사망률은 4.5%에 불과한 놀라운 성 적을 발표하여 1909년에 노벨 의학상을 수상하였으며(1) 그의 사망때까지 5,000명 이상을 수술하였으나 사망률은 1%(2) 정도 였다. 그러나 20세기 초기에 접어들면서 대부 분의 의학 분야가 그러하였듯이 갑상선 외과와 연구 역시 그 leadership은 미국으로 이동하게 된다. 유럽 연수에서 갑상선 수술의 수기와 합병증 등을 충분히 익힌 Halsted는 Jones Hopkins대학 교수로서 재직하면서 갑상선외과 분야 를 진수시켰으며 1912년 Mayo가 278예의 exophthalmic goi- ter 수술 실적을 발표하였고 Crile, Lahey등도 private clinic 에서 많은 갑상선 수술을 하기 시작하였으며 특히 1923년 Plummer가 hyperthyroidism 수술전에 iodine solution을 투여 하므로(3) 증세를 완화시킨다는 보고에 힘입어 갑상선 수 술은 급격히 증가하기 시작하였다. 1935년 Ward는 folli- cular cancer는 endemic goiter에 빈발하고 papillary cancer는 non-endemic region에 흔히 발생함을 관찰하였다. 1943년 Astwood, MacKenzie는 hyperthyroidism 치료에 propylthiou- racil (PTU)을 사용하여 기능이 억제됨을 확인하였고, 이를 이용하여 Bartels등(4)은 갑상선 기능항진증의 수술 전처치 로 상당기간동안 ATD를 사용하는 “ATD treatment fol- lowed by subtotal thyroidectomy”라는 논문을 발표하였다.
비슷한 시기에 Chapman은 radioiodine을 갑상선기능항진 및 암의 진단과 치료에(5,6) 사용할 수 있음을 시사하였고, McCullagh등을 중심으로 그레브씨병의 새로운 치료방법 으로 혹은 수술의 대치방법으로 많은 병원에서 사용하기 시작하였다. 당시 소아들에서 acne, lymphoid hyperplasia, thymic enlargement의 치료에 radiation을 사용하였는데 1950 년 Duffy & Fitzgerald(7)는 소아기에 경부 방사선 치료를 받은 28예의 갑상선암을 보고하여 방사선이 갑상선암의 개시인자임은 지금까지 정설로 인정되고 있다. 갑상선암 의 특이한 형태인 medullary cancer는 1951년 Horn에 의하 여 보고되었고 1962년 Copp등은 새로운 홀몬인 calcitonin 을 발견하였으며, Melvin, Tashjian등은 parafollicular C-cell carcinoma와 calcitonin의 과다생산 관계를 정립하고 임상 에서 medullary cancer의 tumor marker로 사용할 수 있게 하였다. 이에 관련하여 1968년 Pearse에 의하여 APUD cell 의 개념이 처음으로 발표됨으로서 설사를 일으키는 GI
갑상선 외과 분야의 20세기 회고 및 21세기 전망
인제대학교 의과대학 부산백병원 외과학교실 김 상 효
Retrospects of Twentieth-Century and Pro- spects toward Twenty First-Century in Thyroid Surgery
Sang-Hyo Kim, M.D.
Though the first well-documented thyroidectomy was per- formed in 1595, Kocher at Bern, Switzerland can be called
“Father of thyroid surgery” with his outstanding contributions to the understanding of thyroid disease through both clinical surgery and research. Leadership in the surgery and re- search of thyroid disease shifted largely to the United States in the 20th century beginning with the elegant studies and careful operative techniques of Halsted and his colleagues.
Through this century, there were a lot of progress in surgical treatment of benign and malignant thyroid disease, based on hormonal radioimmunoassay, antithyroid agents, propranolol, FNA, ultrasonography, total thyroidectomy, neck dissection, radioiodine ablation, and molecular thyroidology. Modern te- chnology for genetic analysis has induced detection of gene- tic alterations underlying hereditary forms of MEN and med- ullary carcinoma. Prospects toward 21th century also will be progress in the endoscopic thyroid surgery, molecular thyroi- dology and recontruction or transplantation of larynx, trachea and esophagus. (Korean J Endocrine Surg 2001;1:6-13) ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ Department of Surgery, Pusan Paik Hospital, Inje Medical College, Busan, Korea
peptide 및 MEN에 대한 연구가 활발하게 진행되기 시작하 였다. 1950년경부터는 nodular goiter가 갑상선암의 poten- tial source로 부각됨에 따라 외과적 절제술이 보편화되기 시작하여 많은 갑상선암이 진단되고 부수적으로 radical neck dissection and conservative neck dissection,(8) radio- iodine ablation (Dobyns), suppression with thyroxine(6) 등이 활발히 연구되기 시작하였다. 그러나 갑상선결절의 내과 적 치료로 사용되는 T4 suppression (1956, Glassford)의 효 과는 대부분이 부정적이다.(9) 갑상선기능항진증 병인의 발전은 Adams(10)의 LATS (late acting thyroid stimulator)에 서 시작되며 이는 TSH와는 확연히 다르면서 갑상선을 자 극한다는 사실을 발견하였고 1990년부터 연구되고 있는 molecular thyroidology로서의 TSH-R gene promotor는 21세 기에 들어서 더욱 발전할 것이다. 갑상선기능항진증 수술 의 안전성은 beta-blockers (propranolol, 1968 Hadden, Buck- le)에 의해 더욱 높아지므로 수술적 치료의 적응증이 더욱 광범위해지고 있다.(11)
2) Fine-needle aspiration in the evaluation of thyroid nodules
1930년 Martin and Ellis는 갑상선결절의 수술전 진단에 있어 침생검방법을 발표하였으나 별로 보편화되지 못하 였고 1960년도에 스칸디나비아의 내과의사들이 FNA 경험 을 보고하면서(12) 1970년도부터 미국에서 이의 사용이 증가하고(13) 갑상선결절의 수술전 진단에 변혁이 되는 계기가 되었다. FNA는 암진단에 extremely sensitive and cost-effective하며(1982, Hamburger) 불필요한 갑상선절제 수술을 50%까지 줄인다고 하여(14) 갑상선결절의 진단 (15,16)에 일차적인 방법으로 이용되고 있으나 여기에는 유능한 cytopathologist가 필수적이다.
Indications for thyroid FNA Evaluation of a thyroid nodule
Diagnosis of locally recurrent thyroid cancer
Evaluation of cervical LAP for metastasis Determining the etiology of diffuse goiter Diagnosis and treatment of thyroid cysts
Diagnosis of acute suppurative or subacute thyroiditis
FNA의 전체적인 민감도는 68∼95%, 특이도는 56∼
100%까지 보고되어 있고,(17) 이는 판독상 “suspicious for malignancy”를 cancer or benign 어느 범주에 넣느냐에 따 라서 또한 follicular cancer의 빈도에 따라 통계가 달라진다.
3) Thyroid cancer and neck irradiation
갑상선에 대한 방사선 조사(照射)는 결절이나 암을 유 발할 수 있다. 1930년부터 1960년까지의 기간동안 소아에 서 목의 양성질환 -thymic enlargement, tonsillitis, facial acne, cervical adenitis, hyperthyroidism, pertussis-에 대하여 흔히 방사선 치료를 시행하였고, 1950년 Duffy and Fitz- gerald(7)가 보고한 28예의 갑상선암중 9예에서 흉선비대 로 방사선 치료를 받은 병력이 발견되어 이는 지금까지 정설로 인정되고 있다. 히로시마, 나가사끼에 떨어진 원자 탄으로 순식간에 대량의 감마선에 전신이 노출된 사람들 에서 갑상선암의 빈도가 훨씬 높으며,(18) 특히 30세 이전 의 청년들에게는 빈도가 더 높은 것으로 되어있다. 1986 년 우크라이나(19) 체르노빌의 핵원자로 사고로 I-131에 대량 노출된 소아에서의 갑상선암 발생률은 정상보다 약 6배 가까이 된다. 이는 성인에서도 유사한 빈도를 보이며 두경부암으로 방사선치료를 받은 15∼30년 후에는 27%에 서 갑상선결절이 발생하였고 그중 71%에서 갑상선절제수 술을 시행하였는데 그 1/3이 갑상선암으로 진단되었다.
(20) 경부 방사선 치료후의 갑상선결절 빈도는 1.5∼2.8%
per year(21)이다. 암발생의 위험요인으로서는 방사선 용량 이 많을수록, 여성, 방사선 노출 연령이 낮을수록 증가한 다. 최대 위험시기는 방사선 치료 후 25∼29년째이나 40 년까지 암발생은 계속된다.
Incidence of thyroid cancer in nodules in irradiated patients
ꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚ Frequency of cancer in nodules
Incidence of cancer ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ
irradiated patients Single nodule Multinodular
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ
Refetoff (1975, 100 patients) - - 7%
Favus (1976, 1056 patients) 23% 32% 9%
DeGroot (1983, 416 patients) 37% 18% 9.9%
Schneider (1985, 2958 patients) 26.8% of all nodules 7.0∼12.7%
Dobyns (1992, 245 patients) 29.0% of all nodules 6.28∼6.97%
Nagataki (1994, 2587 patients) - - 0.8%
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ
4) Total thyroidectomy and less than total (partial) thyroidectomy
“Routine total thyroidectomy”는 그 빈도에서 대다수를 차 지하는 유두상암에 대한 논쟁으로 multifocal lesions, 수술 후 radioiodine의 사용, 재발 시 종양 표지자로서의 thyro- globulin, 미분화암발생의 예방 등을 그 이유로 들고 있다.
그러나 술 후 morbidity문제와 특히 low-risk group에서 routine total thyroidectomy에 대한 반론은 만만치않다.
Low-risk younger patient에서 multifocal nature가 흔히 있는 것은 사실이나 대부분이 반대측 혹은 잔여조직의 micro- scopic multifocality이며 macroscopic multifocality는 20% 이 하이다. 이는 수술 시에 촉진으로 쉽게 발견되고 그 경우 에만 total을 시행하면 된다. 설령 microscopic lesion이 남 아 있었다고 하더라도 그 재발률은 대단히 낮고 치명적인 것은 아니다. 즉 잔여 조직의 재발이란 엄밀히 말해서 일 차병소의 extraglandular extension에서의 재발이지 new primary라고는 할 수 없으며(22) 예후에는 일차병소의 완 전절제가 중요하다.
Low-risk patients에서 routine RI ablation은 생존율을 증 가시키지 않는다. 재발률이 10년 후에 3%, 사망률이 20년 에 1%, 폐전이도 0.6%에 지나지 않는다.(23) 그러나 50세 이상의 high-risk group에서는 RI ablation이 필수적이다. 수 술 후 thyroglobulin의 종양 표지자로서의 가치-무증상에서 전이의 확인-도 의문이다. 왜냐하면 전절제가 아니라도 사 망률이 극히 낮기(1∼2%) 때문이다.(24,25) 1930∼1940 기 간에는 폐전이가 5∼6%였으나 최근에는 크게 줄었고 특 히 소아에서 RI 사용 시 radiation pneumonitis로 인한 사망 이 더 많다. 미분화암의 발생은 1930∼1940년도에 흔하였 으나 최근 요드섭취의 보편화로 그 빈도가 대단히 낮으며 (26) 따라서 수술 후 잔여조직 유두상암에서의 발생도 무 시할 수 있다. 문제는 갑상선 전절제수술이 아니라 주위 림프절에 대한 전이를 잘 평가하여야하고 그에 대한 수술 (neck dissection)이 적절히 시행되어야 림프절의 미분화암 을 예방하고 암의 완치율을 높일 수 있다.
5) Neck dissection in thyroid carcinoma
유두상암에서 경부 림프절 전이는 microscopic meta- stasis를 포함하여 약 80%까지 보고되어 있으나 여포성암 에서는 10% 내외로 알려져 있다.
(1) Prophylactic node dissection: 이는 carotid sheath외측 의 non-palpable nodes를 제거하는 술식으로 유두상암에서 microscopic metastasis빈도가 80%까지 된다는 보고도 있으 나 그 재발률이 대단히 낮고(6∼8%) 생존율에 차이가 없 으므로 이는 대부분이 시행않는 술식이다.
(2) Central compartment neck dissection: Carotid sheath 내측의 prelaryngeal, pretracheal, paratracheal, perithyroidal
node (I-IV)를 제거하는 술식으로 갑상선암수술에서는 rou- tine procedure이나 young age, occult cancer에서는 node sampling 혹은 berry picking procedure로 대치하기도한다.
(3) Modified radical neck dissection: Jugular nodes, pos- terior triangular group (spinal accessory chain, transverse cer- vical nodes)를 박리하는 술식으로 clinically positive node 시에 시행하며 별도의 transverse incision이 필요하기도 하 다(I-VII or level II-V).
(4) Classical radical neck dissection: 갑상선암에서는 적 응증이 별로 없으나 matted nodes, massive metastasis, vein or muscle invasion 등에서 시행하며 sternocleido muscle, internal jugular v. NXI 등을 절제한다.
6) Prognostic factors and prognostic scoring system in differentiated thyroid cancer
갑상선암의 재발이나 생존율에 관계되는 예후인자는 대단히 많은 것으로 알려져 있다.
Age, sex, tumor size, histologic grade and type, extrathy- roid invasion, multicentricity, nodal or distant metastasis, tumor persistence after surgical excision 등이 중요 예후인자 로 개발되어 여러 센터에서 prognostic scoring system에 사 용되어 왔고 그 계산방법도 다양하다. 그러나 최근에는 DNA plody,(27) adenylate cyclase activity, extent of resec- tion,(28,29) p53 gene mutation, RI uptake, EGF 등도 예후인 자에 포함되고 있으며 TNM staging system은 현재 무리없 이 국제적으로 통용되고 있으나 이와 관련하여 약간의 수 정이 필요할 것으로 사료된다.
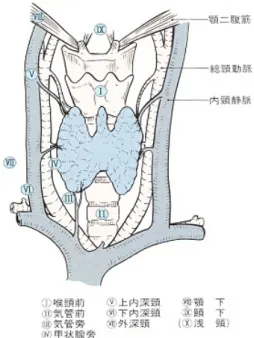
Fig. 1. Regional lymph nodes in thyroid cancer (Japanese So- ciety of Thyroid Surgery).
7) Surgical management of hyperthyroidism
Thyrotoxicosis는 1786년 영국 바스의 의사, Parry에 의하 여 처음으로 기술되었으나 그 보고서의 출판은 그의 사망 후인 1825년에 발표되었다.(34) 1830년에는 아이랜드 더블 린의 Graves(35)에 의하여, 1840년에는 독일 멜세베리의 von Basedow에 의하여 발표되었다.(36) 19세기 중반까지 갑상선기능항진증의 수술은 몇몇 외과의사에 의하여 시 행되었으나 감염과 출혈때문에 사망률이 대단히 높았고 더구나 부갑상선의 기능에 대하여는 전혀 알려지지 않았 다. 그후 스위스 베른의 Kocher(37,38)는 Graves씨 병을 성 공적으로 수술할 수 있는 첫 외과의사가 되었으며 1883년 까지 101명을 수술하여 사망률이 12.8%에 지나지 않았고 이는 그의 철저한 지혈기술과 갑상선에 대한 명확한 해부 학적 지식을 가지고 있었기 때문이라고 하며 더우기 Lister, Pasteur가 연구한 antisepsis의 중요성을 인지하고 있 었기 때문이었다. 1898년에는 600명의 수술에서 단 한 명 의 사망을 보고하였다. 호주 멜버런의 Dunhill (1876∼
1957)은 20세기 초에 thyroidectomized goat의 milk로 치료 를 시도하였으나 실패하였고 total thyroidectomy시에 my- xedema가 발생하고 chloroform 마취는 thyrotoxic heart에서 는 대단히 위험하여 흔히 사망한다는 것 등을 알게되었 다. 그리하여 국소마취로도 수술하였으며 total lobectomy +small remnant of gland on the other side가 가장 좋은 방 법임을 발표하였다. 서론에서 기술한대로 20세기에 들어 오면서 미국의 William Halsted, Mayo brothers, Cleveland
clinic의 George Crile, Boston의 Frank Lahey등에 의하여 갑 상선수술이 급속히 발달되었다. 특히 1차세계대전 당시 Plummer and Boothby에 의하여 preoperative iodine(3,39-41)이 소개되고 2차세계대전 당시 Astwood and Mckenzie에 의하 여 수술 전 thiouracil투여가 안전하다는 것이 알려졌고 Radioactive iodine이 MIT-MGH joint group에 의하여 처음 으로 개발되었으나 1940년경 캘리포니아 대학과 버컬리에 서도 따로 발표되었다.(42) 1941년 양쪽 그룹에서 갑상선 기능항진증 치료에 radioiodine으로 성공적으로 치료한 성 적을 발표하였으나 이차대전 후에는 이 방사성 동위원소 를 널리 사용않고 있다. 대표적인 기능항진증으로서의 Graves' Disease는 다른 자가면역질환들과 마찬가지로 혈 액내 조직특이성 자가항체, 림프구 침윤, MHC class I antigen의 증가, aberrant MHC classII expression 등의 특징 이 있다. 그 병인에 대하여는 1958년 Adams(10) and Pur- ves의 LATS발견으로 밝혀지기 시작하고 1964년에 이는 IgG의 일종임이 알려졌다. 1940년도에는 ATD와 RI 치료 가 보편화되고 외과적수술은 약물치료로 재발한 젊은 층 에 국한되어 시행하였으나 1960년 중반부터는 약물치료의 관해율이 1년간의 치료에도 30∼40% 내외라는 것이 알려 지게 되었다. 이와 동시에 1970년도부터 thyrotoxicosis환자 의 수술 전 처치에 종전의 ATD+iodides외에 propranolol 을 추가하므로 catecholamine대사를 차단하여 자각적 증세 의 호전은 물론 전처치 기간을 2∼3개월 단축시키고 수술 의 안전성을 높이면서 수술적 치료가 보편화되기 시작하였 다. Gough and Neill(1974) 등은 술 후 기능저하에 대하여 Fig. 2. Lymph node compartments in neck and upper mediastinum (Memorial Sloan-Kettering
Cancer Center).
Table 1. Prognostic staging system
ꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚ DeGroot (30)
Class I : Thyroid cancer confined to the thyroid gland Class II : Regional lymph nodes involved
Class III : Thyroid cancer invading adjacent tissues Class IV : Thyroid cancer with distant metastasis
Survival by DeGroot Class (30-year)
I 99%
II 96%
III 86%
IV 30%
EORTC (31) Age (Year)
+12 If male
+10 If medullary or higher grade follicular
+45 If anaplastic
+10 If T3 (invasive, fixed)
+15 If single distant metastasis
+15 If additional distant metastases
Survival by EORTC total score (5-Year)
<50 95%
50∼65 80%
66∼83 51%
84∼108 33%
>108 5%
AGES (32)
Prognostic score = 0.05×age (if age ≥40) +0 (if age <40) +0 (if grade 1) +1 (if grade 2) +3 (if grade 3 or 4) +1 (if extra-thyroid) +3 (distant spread)
+0.2×tumor size (cm max diameter) Survival by AGES score (20-year)
≤3.99 99%
4∼4.99 80%
5∼5.99 67%
≥6 13%
AMES (33)
Low risk Younger patients (male ≤40, female ≤50) with no metastases Older patients: Intrathyroid papillary, minor capsular invasion follicular Primary cancers <5 cm
No distant metastases
High risk All patients with distant Metastases
Extrathyroid papillary, mayor capsular invasion follicular Primary cancers ≥5 cm
Survival by ANES risk-groups
Low risk 98%
High risk 61%
MACIS (23)
score = 3.1 (if age ≤39 years) or 0.08×age (if age ≥40 yrs) +0.3×tumor size (cm max diameter)
+1 (if incompletely resected) +1 (if locally invasive) +3 (distant spread)
Survival by MACIS score (20-year)
<6 99%
6∼6.99 99%
7∼7.99 56%
≥8 24%
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ
chronic thyroiditis의 유무, 술 전 ATD 치료기간, 수술 후 잔여 갑상선조직의 중량, 림프구 침윤 등에 대하여 연구 를 하였으며 일반적으로 수술 후 5년의 추적에서 기능저 하 10%, 기능항진의 재발이 5∼10%로 알려져 있다. ATD 치료에 재발할 가능성이 많은 경우는 약물치료 중 종대의 크기가 감소하지 않을 때, 연령이 어린 환자, suppressed serum TSH, iodine uptake가 높은 경우, persistent TR Ab level, high T3/T4 ratio, 초기 T3, T4가 대단히 높은 경우 등 이므로 애초부터 수술을 고려하여야 한다. 일반적으로 수 술의 적응증은 ATD치료에 재발하거나 약물 부작용이 심 한 청소년 환자, 임산부 혹은 수유중인 부인에서의 중증 항진, 거대한 갑상선종, 갑상선암의 병존이 의심될 때, 환 자가 수술을 선호할 때이다. 수술 시 잔여 갑상선의 중량 과 술 후 갑상선기능의 관계에 대하여는 많은 논문에서 거 론되고 있으나 일률적으로 잔여 중량을 결정하기는 어렵고 endocrine ophthalmopathy 혹은 수술 후 재발한 경우에서는 확실히 그 중량을 작게 하여야 한다. 많은 문헌의 고찰에서 아전절제술은 일반적으로 4∼8그램 정도 남기지만 스웨덴 에서는 2∼4그램이고 최근 일본의 Kurihara등(43)은 young age에서는 super subtotal thyroidectomy을 시행한다고 하나 잔여 조직의 중량은 환자의 체중이나 갑상선의 크기, 기능 검사, 항체의 수치 등을 기준으로 결정하여야 한다. 수술 후 재발을 예측할 수 있는 요소 중에서 TRAb의 상승이 가장 예민한 표지이며, 혈청 TSH의 감소, 잔여 갑상선조직이 클 때, TPO and thyroglobulin Ab의 증가, weak suppression of remnant iodine uptake with T3 administration, unresponsive serum TSH during TRH administration 등이다.
-Total vesus subtotal thyroidectomy-
이 술식의 선택은 외과의사의 경험과 몇가지 요소에 의
하여 결정된다.
Total thyroidectomy는 갑상선암의 공존, 심한 안구돌출 증, 재발 시 재수술을 원치 않거나 RI 치료를 거부할 경우 에 시행하고 그외에는 subtotal을 시행하며 4∼5 gm을 남 기는 수술이다. 수술 후 기능저하의 빈도는 3∼48%이나 관계되는 요소는 1. Remnant size: 잔여조직이 4 gm 이하 이면 기능저하의 가능성은 50% 이상이 된다.(44,45) 2.
Autoimmune activity: thyroid antibody titer와 lymphocyte infilteration의 정도가 심하면 갑상선조직의 파괴로 기능저 하가 된다. 기능저하의 정의에서 subclinical hypothyroidism 이란 TSH의 상승이며 90%는 1년 이내에 정상으로 돌아 오며 약 10%는 2년까지 지속되기도 한다.(46) 잔여조직이 8 gm 이상이면 재발률이 15% 정도이고(47) 특히 소아일 수록 3 gm 이하를 남겨야한다(재발률 5% 내외, 기능저하 40% 내외).(48)
-Bilateral subtotal thyroidectomy versus hartley- dunhill operation-
현재 대부분의 병원에서 시행하고 있는 기능항진의 수 술은 양측아전절제술이나 Dunhill 술식은 편측 total lobec- tomy and isthmusectomy, 반대측 subtotal resection (bigger remnant)이며(49) 이 수술의 장점은 신경 및 부갑상선 문 제가 적고 재발 시 재수술이 보다 쉽다는 것이다.
갑상선 외과 분야의 21세기 전망 (Prospects Toward Twenty First-Century
in Thyroid Surgery) 1) Endoscopic thyroid surgery
1996년 Gagner(50)에 의하여 처음으로 endoscopic para- Table 2. “Favorable” and “Unfavorable” treatment responders in Graves' disease
ꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚꠚ Favorable Low, moderate thyroid hormone excess at diagnosis
Low, moderate TRAb titers responding swiftly to treatment Low, moderate goiter size
Low, moderate eye signs Middle aged and older patients No hereditary trait
No chronic negative stress
Unfavorable High thyroid hormone values at diagnosis High TRAb titers
Unresponsive TRAb titers Severe eye signs Young age Hereditary trait Chronic negative stress Large goiter
ꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏꠏ
thyroidectomy가 발표된 이후 Huscher,(51) Ishii,(52) Shi- mizu(53) 등에 의하여 video-assisted thyroid lobectomy가 시 행되었으며 이 술식은 tissue trauma를 최소화하면서 cos- metic outcome을 좋게하는 특징이 있으므로 향후 많은 발 전이 있을 것으로 예상이 된다. 지금까지 두 가지 기법이 개발되어 있다. Pure endoscopic approach (closed technique) 와 video-assisted technique이며(53,54) 수술공간의 확보 방 법에 따라 CO2 insufflation 혹은 anterior-neck lift 등의 방 법들이 개발되어 있고 투관구의 위치는 유륜부, 액와부, 전경부 등 다양하며 향후 Laser의 사용 등 발전적으로 보 편화 될 수 있을 것이다.
2) Imaging technique in the 21th century
초음파, CT, MRI 등은 그 해상력에서 더욱 발전할 것으 로 보이나 최근에 발전하고 있는 PET (양전자단층촬영술) 은 갑상선암 수술 후 재발진단 및 전이여부를 확인하는데 유용하다. 특히 방사성 옥소전신스캔이 음성인 환자와 미 분화암에서 FDG (포도당 유도체) PET는 재발암을 쉽게 찾을 수 있으므로 향후 갑상선암의 술후 재발의 진단에 많이 사용될 것이다.
3) Total pharyngolarygectomy, reconstruction of eso- phagus and trachea or laryngeal transplantation
4) Molecular thyroidology and genetic testing of medullary thyroid cancer
현재까지 알려진바로는 RET protooncogene이 tyrosine kinase receptor gene family의 일원으로 염색체 10q11.2에 위치하며 cystein-rich ligand-binding extracellular domain을 갖는 transmembrane tyrosine kinase로 갑상선 유두상암, 수 질암에서 표현되는 것으로 알려져 있고(55) MEN-IIa환자 에서 이러한 RET proto-oncogene의 germinal mutation은 90% 이상에서 발견된다고 보고되고 있다.(56) 따라서 수 질암은 DNA analysis를 이용하여 조기진단이 가능하고 예 방적 갑상선절제수술을 시행하는 것이 보편화될 것이다.
갑상선암에서 telomerase activity(57)가 확인됨에 따라 FNA sample에서도 telomerase assay가 가능하게 되고 특히 유두 상암에서 세포의 분화도, 증식 및 주위조직에로 침투 등 과 상호관계가 높으며 routine cytology와 비교할 수 있게 될 것이다.
REFERENCES
1) Sulek K, Prize for T. Kocher in 1909 for his work on the physiology, pathology and surgery of the thyroid gland. Wiad Lek 1967;20:1223.
2) Gemsenjäger E. Goiter surgery from Kocher to today. Schweiz
Med Wochenschr 1993;123:207-13.
3) Keys TE. Historical vignettes: Walter M. Boothby (1880∼
1953). Anesth Analg 1974;53:219-20.
4) Bartels EC. Hyperthyroidism - evaluation of treatment with antithyroid drugs followed by subtotal thyroidectomy. Ann Intern Med 1952;37:1123-34.
5) McCullagh P. Radioactive iodine in the treament of hyper- thyroism. Ann Intern Med 1952;37:739-44.
6) Balme HW. Metastatic cancer of the thyroid successfully treat- ed with thyroxine. Lancet 1954;1:812-13.
7) Duffy BJ, Fitzgerald PJ. Cancer of the thyroid in children: a report of 28 cases. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1950;10:1296.
8) Crile G Jr. Adenoma and carcinoma of the thyroid gland. N Eng J Med 1953;249:585-90.
9) Glassford GH, Fowler EF, Cole WH. Treatment of non- toxic goiter with dessicated thyroid: results and evaluation. Surgery 1965;58:621-5.
10) Adams DD. Presence of abnormal thyroid stimulating hor- mone in serum of some thyrotoxic patients. J Clin Endocrinol 1958;18:699-712.
11) Hadden DR, Montgomery DAD, Shanks RG. Propranolol and iodine-131 in management of thyrotoxicosis. Lancet 1968;2:
852-4.
12) Einhorn J, Franzen S. Thin-needle biopsy in the diagnosis of thyroid disease. Acta Radiol 1962;58:321-36.
13) Gershengorn MC, McClung MR, Chu EW, et al. Fine needle aspiration cytology in the preoperative diagnosis of thyroid nodules. Ann Intern Med 1977;86:265-9.
14) Hamburger B, Gharib H, Melton LF III, Goellner JR, et al.
Fine needle aspiration biopsy of thyroid nodules. Impact on thyroid practice and cost of care. Am J Med 1982;73:381-4.
15) Gharib H. Fine needle aspiration biopsy of thyroid nodules:
Advantages, limitation and effect. Mayo Clin Proc 1994;69:
44-9.
16) Gordon DL, Gattuso P, Castelli M, Bayer W, et al. Effects of fine needle aspiration on the histology of thyroid neoplasm.
Acta Cytol 1993;37:651-4.
17) Keller MP, Crabbe MM, Norwood SH. Accuracy and signi- ficance of fine-needle aspiration and frozen section in deter- mining the extent of thyroid resection. Surgery 1987;101:
632-5.
18) Pretice RL, Kato H, Yoshimoto K, Mason M. Radiation expo- sure and thyroid cancer incidence among Hiroshima and Naga- saki residents. NCI Monogr 1982;62:207-12.
19) Likhtarev IA, Sobolev BG, Kairo IA, et al. Thyroid cancer in the Ukraine. Nature 1995;375:365.
20) Favus MJ, Schneider AB, Stachura ME, et al. Thyroid cancer occurring as a late consequence of head and neck irradiation.
N Eng J Med 1976;294:1019-25.
21) Schneider AB, Beckerman C, Favus M, et al. Continuing occurrence of thyroid nodules after head and neck irradiation.
Ann Intern Med 1981;94:176-80.
22) Grant CS, Hay ID, Gough IR, et al. Local recurrence in pa- pillary thyroid carcinoma: Is extent of surgical resection im- portant? Surgery 1988;104:954-62.
23) Hay ID, Bergstralh EJ, Goellner JR, Ebersold JR, et al. Pre- dicting outcome in papillary thyroid carcinoma: Development of a reliable prognostic scoring system in a cohort of 1779 patients surgically treated at one institution during 1940 through 1989. Surgey 1993;114:1050-8.
24) Cady B, Rossi R. An expanded view of risk-group definition in differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Surgery 1988;104:947-53.
25) Shah JP, Loree TR, Dharker D, et al. Prognostic factors in differentiated carcinoma of the thyroid gland. Am J Surg 1992;164:658-961.
26) Cady B, Sedgwick CE, Meissner WA, et al. Changing clinical, pathological, therapeutic and survival patterns in differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Ann Surg 1976;183:541-53.
27) Cohn KH, Bäckdahl M, Forsslund G, et al. Biologic con- siderations and operative strategy in papillary thyroid carci- noma.: Arguments against the routine performance of total thyroidectomy. Surgery 1984;96:957-70.
28) Clark OH. Total thyroidectomy: The treatment of choice for patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Ann Surg 1982;196:
361-70.
29) Lennquist S. Surgical strategy in thyroid carcinoma.: A clinical review. Acta Chir Scand 1986;152:321-38.
30) DeGroot IJ, Kaplan EL, McCormick M, et al. Natural history, treatment, and course of papillary thyroid cancer. J Clin En- docrinol Metab 1990;71:414-24.
31) Byar DP, Green SB, Dor P, et al. A prognostic index for thyroid carcinoma. A study of the EORTC thyroid cancer cooperative group. Eur J Cancer 1979;15:1033-41.
32) Hay ID, Grant CS, Taylor WF, et al. Ipsilateral lobectomy versus bilateral lobar resection in papillary thyroid car- cinoma.: A retrospective analysis of surgical outcome using a novel prognostic scoring system. Surgery 1987;102:1088-95.
33) Cady B, Rossi R. An expanded view of risk-group definition in differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Surgery 1988;104:947-53.
34) Fye WB. Caleb Hillier Parry. Clin Cardiol 1992;15:619-21.
35) Taylor S. Graves of Graves' disease, 1796∼1853. J R Coll Physicians Lond 1986;20:298-300.
36) Vereckei I. Karl Adolf von Basedow (1799∼1854). Orv Hetil 1980;121:964-6.
37) Giddings AE. The history of thyroidectomy. J R Soc Med 91 (suppl)1998;33:3-6.
38) Modlin IM. Surgical triumvirate of Theodor Kocher, Harvey Cushing and William Halsted. World J Surg 1998;22:103-13.
39) McConahey WM, Pady DS. HenryStanleyPlummer. Endo- crinology 1991;129:2271-3.
40) Nelson CW, Dr. Henry S. Plummer, early Mayo partner. Mayo
Clin Proc 1993;68:730.
41) Vandam LD, Walter M. Boothby, MD-the wellsprings of an- esthesiology. N Eng J Med 1967;276:558-63.
42) Sawin CT, Becker DV. Radioiodine and the treatment of hyperthyroidism. The early history. Thyroid 1997;7:163-76.
43) Kurihara H, Tanimura S, Sasaki J, et al. Surgery for Graves' disease: Supersubtotal thyroidectomy. Thyroidology 1998;10:
181-8.
44) Melliere D, Etienne G, Becquemin JP. Operation for hyper- thyroidism. Methods and rationale. Am J Surg 1988;155:395-9.
45) Miccoli P, Vitti P, Rago T, et al. Surgical treatment of Graves' disease: subtotal or total thyroidectomy? Surgery 1996;120:
1020-4.
46) Torre G, Borgonovo G, Arezzo A, et al. Is euthyroidism the goal of surgical treatment of diffuse toxic goiter? Eur J Surg 1998;164:495-500.
47) Cusick EL, Krukowski ZH, Matheson NA. Outcome of surgery for Graves' disease re-examined. Br J Surg 1987;74:780-3.
48) Söreide JA, van Heerden JA, Lo CY, et al. Surgical treatment of Graves' disease in patients younger than 18 years. World J Surg 1996;20:794-9.
49) Andaker L, Johansson K, Smeds S, et al. Surgery for hyper- thyroidism: Hemithyroidectomy plus contralateral resection or bilateral resection? A prospective randomized study of post- operative complications and log-term results. World J Surg 1992;16:765-9.
50) Gagner M. Endoscopic subtotal parathyroidectomy in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism. Br J Surg 1996;83:875.
51) Hüscher CSG, Chiodini S, Napolitano C, et al. Endoscopic right thyroid lobectomy. Surg Endosc 1997;11:877.
52) Ishii S, Ohgami M, Arisawa Y, et al. Endoscopic thyroidec- tomy with anterior chest wall approach. Surg Endosc 1998;
12:611.
53) Shimizu K, Akira S, Jasmi AY, et al. Video-assisted neck sur- gery-endoscopic resection of thyroid tumors with a very mini- mal neck wound. J Amer Coll Surg 1999;188:697-703.
54) Bellantone R, Lombardi CP, Raffaelli M, et al. Minimally invasive, totally gasless video-assisted thyroid lobectomy:
Amer J Surg 1999;177:342-3.
55) Grieco M, Santoro M, Berlingleri M. PTC is a novel rear- ranged from the RET proto-oncogene and is frequently de- tected in vivo in human thyroid papillary carcinomas. Cell 1990;60:557-63.
56) Mulligan LM, Kwok JBJ, Healey CS. Gem-line mutations of the RET proto-oncogene in multiple endocrine neoplasia type IIa. Nature 1993;363:458-60.
57) Taguchi T, Shiba E, Takai S. Detection of telomerase activity in thyroid nodule using fine-needle aspiration samples. Thyro- idology 1998;10:261-9.