LPS로 유도된 RAW 264.7 cell로부터 NF-κB 조절 억제와 마우스 모델을 통한 큰잎모자반 에탄올 추출물의 항염증 효과
강보경1, 김꽃봉우리2, 김민지2, 박시우1, 박원민1, 안나경1, 최연욱1, 배난영1, 박지혜1, 안동현1*
1부경대학교식품공학과
/
식품연구소2부경대학교수산과학연구소
Received: April 29, 2015 / Revised: June 4, 2015 / Accepted: June 6, 2015
서 론
체내의염증반응은상처나세균감염등의물리적
,
화학 적자극이일어날때손상부위를복구시키는신체방어기 전중하나이며,
자극이가해지면국소적으로혈관활성물 질들이유리되어혈관투과성이증대되면서염증을유발한다
[10].
하지만지속적인염증반응은오히려점막손상을촉진시켜결과적으로통증
,
부종,
발적,
발열등기능장애를 유발하며,
관절염및암등의발병과깊은연관을갖고있다[11].
대식세포(machrophage)
는염증반응에관여하는주요 세포로알려져있으며,
자극에노출되거나면역세포들이분비하는사이토카인등에의해활성화되며
,
감염초기에nitric oxide (NO)
와cytokine
을생산하여생체방어에중요한역할을한다
[7].
그람음성균의세포외막에존재하는내독소로잘알려진
lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
는대식세포또는단핵구를 자극하여tumor necrosis factor-
α(TNF-
α), interleukin-1
β(IL-1
β)
및IL-6
와같은염증매개성cytokine
들의분비를촉 진한다.
이러한염증매개물질들의형성은arachidonic acid
가cyclooxygenase (COX)
의 작용을 거쳐leukotriene, thromboxane, prostaglandin
등으로바뀌는과정및nitric oxide (NO)
의대량생성에관여하게되며,
숙주에치명적결 과를초래한다고알려져있다[8, 16].
이중NO
는반응성이 높은물질로NO synthase (NOS)
에의해L-arginine
으로부 터생성되며, NOS
는constitutive NOS
와inducible NOS
로 나누어진다.
특히iNOS
는외부자극이나pro-inflammatory cytokine
등에의해자극을받게되면다량의NO
를생산하Anti-inflammatory Effect of Sargassum coreanum Ethanolic Extract through Suppression of NF-κB Pathway in LPS Induced RAW264.7 Cells in Mice
Bo-Kyeong Kang
1, Koth-Bong-Woo-Ri Kim
2, Min-Ji Kim
2, Si-Woo Bark
1, Won-Min Pak
1, Na-Kyung Ahn
1, Yeon-Uk Choi
1, Nan-Young Bae
1, Ji-Hye Park
1, and Dong-Hyun Ahn
1*
1
Department of Food Science & Technology/Institute of Food Science, Pukyong National University, Busan 608-737, Republic of Korea
2
Institute of Fisheries Sciences, Pukyong National University, Busan 619-911, Republic of Korea
The anti-inflammatory effect of Sargassum coreanum ethanolic extract (SCEE) was investigated using lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory responses in this study. It was shown that there was no cytotoxicity in the viability of macrophages treated with SCEE when compared to the control. The production of NO was considerably suppressed by SCEE, approxi- mately up to 50% at 100 µg/ml. This significantly decreased levels of IL-6, TNF- α, and IL-1β. In addition, the expression of iNOS, COX-2, NF- κB was suppressed by SCEE treatment. In in vivo testing, the croton oil-induced mouse ear edema was attenuated by SCEE and there were no mortalities in mice administered with 5000 mg/kg body weight of SCEE over a 2 week observation period. From these results, SCEE inhibits the release of LPS-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines and mediators, suggesting that SCEE could be a potential agent for anti-inflammatory therapies.
Keywords: Sargassum coreanum, anti-inflammation, nuclear factor kappa B, ear edema
*Corresponding author
Tel: +82-51-629-5831, Fax: +82-51-629-5824 E-mail: dhahn@pknu.ac.kr
© 2015, The Korean Society for Microbiology and Biotechnology
며과잉생산된
NO
는혈관투과성및부종등의염증반응 을촉진한다고보고되고있다[12].
또다른주요염증매개 인자인COX
는세포막의인지질로부터arachidonic acid
가유리된후
prostaglandin
으로의변화를촉진시키는효소이며
, COX-2
는growth factors, cytokine
및lipopolysaccharide
등다양한자극에의해서macrophage
나monocyte
등의세 포에서다량발현되고이로인해발생된prostaglandin
은종양 의세포사멸을억제하고혈관생성을유도하여종양생성에관 여한다[1].
또한,
염증반응에서중요한역할을하는nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-
κB)
는다양한cytokine, chemokine, growth factor
의합성을조절하는transcription factor
이다[4]. NF-
κB
는p50
과p65
로구성되어핵안으로들어가전사인자로 서작용하여iNOS, COX-2
및염증관련cytokine
을합성하 며,
일반적으로세포질에서inhibitor NF-
κB
α(I
κB
α)
와결 합함으로NF-
κB
의작용이억제된다[17].
이들의활성조절 은염증반응을조절하기위한핵심요소로서NF-
κB
의활성 을조절하여염증반응을완화시키는천연소재를찾기위한 연구가활발히진행되고있다.
최근각광받고있는천연물의하나로해조류를들수있 다
.
해조류는종류와시기에따라다양한성분의차이를보 이며육상식물과는다른구조로항균[18],
고지혈증개선[21],
콜레스테롤침착방지[9]
등의생리활성이보고되고있으며,
그 중에서도갈조류는fucoidan, phycocolloids, phlorotannins
등과같은생리활성물질로부터항산화,
항응고,
항암등의다 양한생리활성을보인다고알려져있다[5].
따라서본연구 에서는갈조류에속하는대표적인해조류로서큰잎모자반(Sargassum coreanum)
을이용하여항염증효과를알아보 고자한다.
재료 및 방법
실험 재료
본실험에사용한큰잎모자반
(Sargassum coreanum)
은부 산연화리에서채취하였으며이를담수로깨끗이수세하고 동결건조한후분말화하고진공포장하여-20
oC
에서저장 하며사용하였다.
에탄올 추출방법
큰잎모자반건조분말에
10
배의95%
에탄올을가하고,
교 반기(H-0820, Dongwon Science Co., Busan, Korea)
를 이 용하여24
시간동안상온에서교반하여추출하였다.
원심분 리기(UNION 32R, Hanil Co., Incheon, Korea)
를이용하여1,977
×g
에서10
분간원심분리한후상층액을취하였고,
이 후남은잔사를이와동일한방법으로2
회반복추출하였다.
추 출한상층액은37
oC
에서 감압농축기(RE200, Yamoto Co.,
Tokyo, Japan)
로농축하였으며,
농축하여건조된 시료는-20
oC
에서보관하며실험에이용하였다.
실험 동물
ICR
마우스(
생후8
주령,
수컷)
을오리엔트바이오(Orient Co., Seongnam, Korea)
로부터구입하여귀부종및귀조직 실험에사용하였으며,
단기독성평가실험을위해Balb/c
마 우스(
생후10
주령의 암컷)
를 사용하였다.
마우스는 온도20
±2
oC,
습도50
±10%, 12
시간명암주기가유지되는동물 실에서1
주일간예비사육한후실험에사용하였다.
세포배양대식세포인
RAW 264.7
세포는 한국세포주은행(KCLB 40071)
에서 분양받아사용하였으며, DMEM
에100 mg/ml inactivated fetal bovine serum
과10 mg/ml penicillin- streptomycin
을첨가한배지를배양액으로37
oC, 5% CO
2조 건에서배양하였다.
실험과정의모든세포는80
−90%
정도 의밀도로자랐을때계대배양하였고, 20 passages
를넘기 지않은세포만사용하였다.
세포 독성 측정
시료의 세포독성을 평가하기 위해
tetrazolium-based colorimetric assay (MTT assay)
를실시하였다. RAW 264.7 cell 1
×10
6cells/ml
를well plate
에분주하고20
시간전배 양 후, 1
μg/ml
의LPS
와 추출물을 농도별(0.1, 1, 10, 50, 100
μg/ml)
로 첨가하여37
oC, 5% CO
2incubator(MCO- 15AC, Sanyo, Osaka, Japan)
에서24
시간배양하였다.
배양 후, 5 mg/ml
농도의3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide(MTT)
시약을첨가하여2
시간재배양 하고이를4
oC, 1,318
×g
에서10
분간원심분리(UNION 32R, Hanil Co., Incheon, Korea)
하여상층액을제거하였다.
그후,
각well
에DMSO
를첨가하고이를microplate reader (Model 550, Bio-rad, Richmond, USA)
를이용하여540 nm
에서흡 광도(absorbance at 540 nm (Abs540))
를측정하였다.
세포 증식능은다음식에의해계산하였다.
Proliferation Index(%) =
(sample Abs540 / control Abs540) × 100
Nitric Oxide 생성량 측정
NO
의농도는배양액내의nitrite
농도를griess
반응을이 용하여측정하였다[10]. Raw 264.7 cell
은DMEM
배지를이 용하여2.5
×10
5cells/ml
로조절한후24 well plate
에접종하 고5% CO
2incubator (MCO-15AC, Sanyo, Osaka, Japan)
에 서20
시간전배양하였다.
세포에1
μg/ml
의LPS
와0.1, 1, 10,
50, 100
μg/ml
의추출물을처리하여24
시간재배양하였다.
배 양액의 상층액을 얻은 후,
동량의griess
시약(10 mg/ml sulfanilamide + 1 mg/ml naphthylendiamine dihydrochloride, 1:1)
을첨가하여실온에서10
분간 반응시키고, microplate reader (Model 550, Bio-rad, Richmond, USA)
를이용하여540 nm
에서흡광도를측정하였다.
세포배양액내NO
의농 도는sodium nitrite (NaNO
2)
의농도별표준곡선과비교하 여산출하였다.
염증 관련 cytokines 분비량 측정
세포배양액내의
TNF-
α, IL-6
및IL-1
βcytokine
의분비 량을ELISA kit (Mouse ELISA set, BD Bioscience, San Diego, USA)
를 이용하여 측정하였다.
이를 위해ELISA microplate
에capture antibody
로anti-mouse TNF-
α, IL-6
및IL-1
β를분주하여4
oC
에서하룻밤동안coating
시켰다.
이 를0.5 mg/ml Tween 20
이 포함된PBST
로 세척하고100 mg/ml FBS
용액으로blocking
하였다. PBST
로세척한 뒤,
각microplate
에NO
를측정하였던것과동일한배양상 층액을분주하고실온에서2
시간반응시켰다.
다시PBST
로 세척한 뒤 희석한biotinylated anti-mouse TNF-
α, IL-6 detection antibody
와streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase conjugate
를첨가하여실온에서1
시간반응시켰다. IL-1
β의 경우, biotinylated anti-mouse IL-1
βdetection antibody
를 첨가하고1
시간반응후, streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase conjugate
를첨가하여30
분반응시켰다.
그후,
이를다시PBST
로세척한다음, o-phenylenediamine-dihydrochloride (OPD)
용액을첨가하여실온에서30
분동안암반응시켰다. 2 M H
2SO
4로 반응을 종료시킨 후, microplate reader (Model 550, Bio-rad, Richmond, USA)
를이용하여490 nm
에서흡 광도를측정하였다.
iNOS, COX-2 및 NF-κB 발현량 측정
배양이끝난세포를수집하여
3
회PBS (phosphate buffered saline)
로세척한 후, lysis buffer (50 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, 10 mg/ml deoxycholate, 5 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF), 1
μg/ml aprotinin, 10 mg/ml Triton X-100, and 1 mg/ml NP-40)
를첨가하여30
분간4
oC
에서lysis
시킨후, 7,908
×g
에서20
분간원심분 리하여세포막성분등을제거하였다.
단백질농도는BCA protein assay kit (Pierce, IL, USA)
를사용하여정량하였으 며, 30
μl
의lysate
를10% SDS-PAGE
로분리하였다.
분리된 단백질은polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane (Bio- rad, CA, USA)
에70 mA
에서1
시간30
분동안전사시킨후, 50 mg/ml skim milk
가포함된TBST (tris buffered saline;
pH7.5)
용액으로 상온에서2
시간 동안blocking
하였다.
iNOS, COX-2
및NF-
κB
의발현양을검토하기위한항체로 는anti-mouse iNOS, COX-2
및NF-
κB
를사용하여1:500
으로희석하고상온에서2
시간반응시킨후TBST
로3
회세 정하였다. 2
차항체로HRP (horse radish peroxidase)
가결 합된anti-mouse IgG
및anti-rabbit IgG
를1:2000
으로 희 석하여상온에서1
시간반응시킨후, TBST
로3
회세정하여enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL)
기질과1-3
분간반응 한후각각의단백질밴드는Gene tool (Syngene software)
를이용하여가시화하였다.
귀 부종 측정 및 조직 관찰
ICR
마우스에추출물을10, 50
및250 mg/kg·body weight
농도로200
μl
씩경구투여하였다.
한시간후,
오른쪽귀에25 mg/ml croton oil
을20
μl/ear
농도로도포하였다.
귀두 께는croton oil
을처리하고5
시간후에측정하였으며croton oil
처리한후두께의증가를부종의형성으로간주하였다.
조직관찰은
ICR
마우스의오른쪽귀에추출물을100 mg/
ml
농도로20
μl
씩도포하고15
분뒤, 50 mg/ml croton oil
을20
μl
씩도포하였다. 6
시간뒤, diethylether
로마취시키 고,
귀조직을절제하여100 mg/ml formaldehyde
에72
시간 고정하였다.
고정후파라핀블록을만들어박편을제조하고hematoxylin-eosin
및toluidine-blue
염색을하여조직을관 찰하였다.
단기 독성 평가
Balb/c
마우스를실험시작전에4
−6
시간정도절식시킨 후에추출물을300, 2000
및5000 mg/kg·body weight
농도 로경구투여하였다. 6
시간동안비정상적인행동등의경과 를관찰하였고2
주까지지속적으로관찰하였다.
통계처리
모든실험결과에대한유의차검정은
SAS software (SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA)
에서평균값을분산분석한 후, Duncan's multiple range test
법에 따라p < 0.05
수준 에서검정하였다.
결과 및 고찰
세포 독성 측정
대식세포로부터염증매개물질의억제효과는세포독성으
로인해
RAW264.7
세포가사멸되는것에의해서도나타날수있으므로이러한가능성을배제하고자
RAW 264.7 cell
에 미치는 추출물의 세포 독성을 알아보기 위하여MTT
assay
를수행하였다.
추출물을0.1, 1, 10, 50
및100
μg/ml
의농도로첨가하여배양한결과,
세포의생존율은모든처리농도에서유의적인차이를보이지않음을관찰하였다
(Fig. 1).
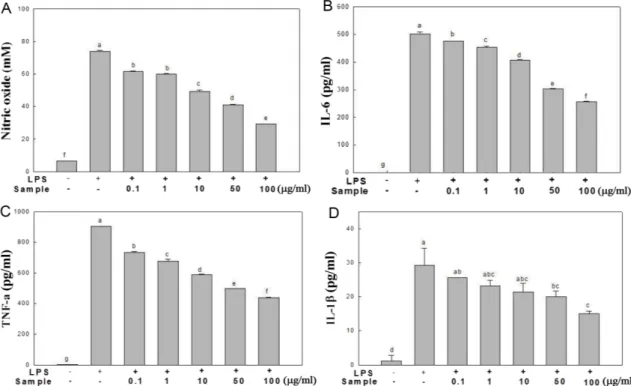
Nitric oxide 생성 억제 효과
병리적인조건하에서
NO
발현량의과도한증가는염증 을유발하게되고조직의손상을가져오는것으로알려져있 다[19].
따라서추출물처리에의한NO
생성정도를측정하 기위하여RAW 264.7
세포를LPS
로활성시킨후,
추출물을각농도별로
(0.1, 1, 10, 50
및100
μg/ml)
첨가하고생성 된NO
를griess
시약을이용하여측정하였다.
그결과(Fig.
2A),
추출물을처리하였을경우, NO
생성량이LPS
처리구 보다농도의존적인감소를보임을확인하였다.
특히10
μg/
ml
이상의농도로추출물을처리하였을때그분비량이약25%
이상감소한것을확인하였다.
염증 관련 cytokines 생성 억제 효과
인체에서염증반응이진행되기위해서는
NO
와PGE
2와 같은염증매개물이외에면역반응에서필연적으로염증성cytokine
이 동반되는데,
대표적인cytokine
으로는IL-6, TNF-
α및IL-1
β이다[20]. IL-6
는단핵구를포함한여러종류의세포에서분비되며다양한기능을가지는대표적인
pro-
inflammatory cytokine
중의하나로초기면역반응에서중요한역할을한다
.
종양괴사인자인TNF-
α는체내에서대식세포나림프구등백혈구에의해생성되는
cytokine
으로정상상태에서는만들어지지않으며
LPS
등에의한대식세 포의자극으로합성되어분비된다[14]. IL-1
β는IL-6, TNF-
α와함께대표적인염증성cytokine
으로NO
를생성하게하 는매개물질이며,
국소염증을발생시키고T
세포의활성화, B
세포의성숙및NK cell
을활성화시키는cytokine
이다[15].
따라서추출물이염증성
cytokine
의생성에미치는영향을Fig. 1. Effect of SCEE on the proliferation of RAW 264.7 cells.
Proliferation index = (sample Abs540/control Abs540) × 100. ND means no significant difference.
Fig. 2. Inhibitory effect of SCEE on the production of nitric oxide (A), IL-6 (B), TNF- α (C), and IL-1β (D) in RAW 264.7 cells. RAW
264.7 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of SCEE (0.1, 1, 10, 50, and 100 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of LPS
(1 μg/ml) for 24 h. Culture supernatants were then isolated and analyzed using the Griess reagent for nitric oxide and ELISA kit for cyto-
kines. a-g indicates significant differences (p < 0.05).
알아보기위하여
RAW 264.7
세포에LPS
처리후,
추출물을농도별로처리하여
ELISA
방법으로측정하였다.
그결과(Fig. 2B,C,D),
세가지cytokine (IL-6, TNF-
α및IL-1
β)
모 두농도의존적으로유의적감소를보였다.
특히,
추출물을50
μg/ml
농도로처리하였을때,
그분비량이각각약39, 45
및31%
감소함을보였으며, 100
μg/ml
로처리하였을경우LPS
단독처리비교해볼때,
각각약49, 51
및48%
의높은 분비량감소효과를보였다.
이러한결과를통해큰잎모자반 에탄올추출물이RAW 264.7
세포에서염증매개성cytokine
을효과적으로억제하여항염증기능에관여하는것을확인 하였다.
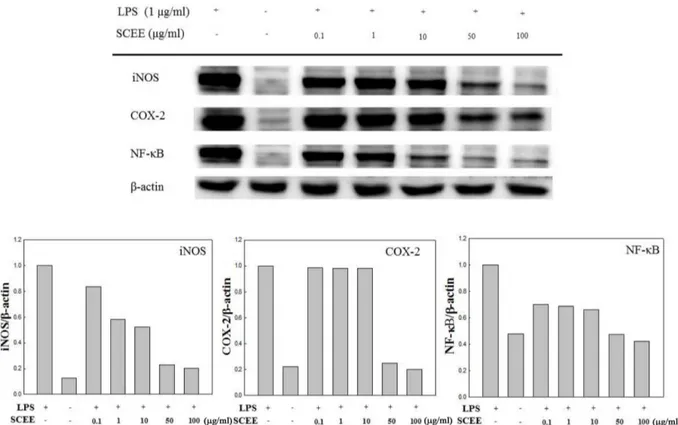
iNOS, COX-2 및 NF-κB 발현 억제 효과
NO
를형성하는NOS
들은 L-arginine
을L-citrullin
으로전 환시키면서NO
를생성하며,
이들NOS
는iNOS
에의한발 현성이절대적으로많으며,
이는염증유발등병리적으로 중요한작용을한다고알려져있다[13].
따라서염증반응이일어나면관련세포에서
iNOS
의발현이증가하여많은양의
NO
가생성되고,
과도하게생성된NO
는조직의손상,
유 전자변이,
신경손상등을유발하고,
혈관투과성을증가시켜부종등의염증반응을촉진시킨다
[23].
또한, COX-2
는 염증매개물질인PGE
2의형성에관여하며[3], NF-
κB
는염 증반응과관련된유전자의promoter
에결합하며cytokine
및lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
등에대한노출에의해활성화되 어COX-2
및iNOS
발현에관여하는것으로알려져있다[2].
따라서염증반응에서
iNOS, COX-2
및NF-
κB
의생성억제 를확인하여항염증효과를확인하였다. RAW 264.7
세포에 추출물을0.1
−100
μg/ml
농도로처리하고iNOS
발현량을측 정한결과(Fig. 3), LPS
단독처리구에의해각단백질의발 현량이현저히증가하였으나,
추출물을처리하였을때그발 현량이농도의존적으로감소하는것을확인할수가있었다.
특히50
및100
μg/ml
농도에서PBS
처리구와유사한발현 량을보여우수한항염증효과를가짐을확인하였다.
이러한 결과를종합해볼때,
큰잎모자반에탄올추출물의NF-
κB
의활성억제를통해COX-2
및iNOS
발현을억제함으로써PGE
2와NO
의생성을억제함에따라항염증효과를나타낸다고사료된다
.
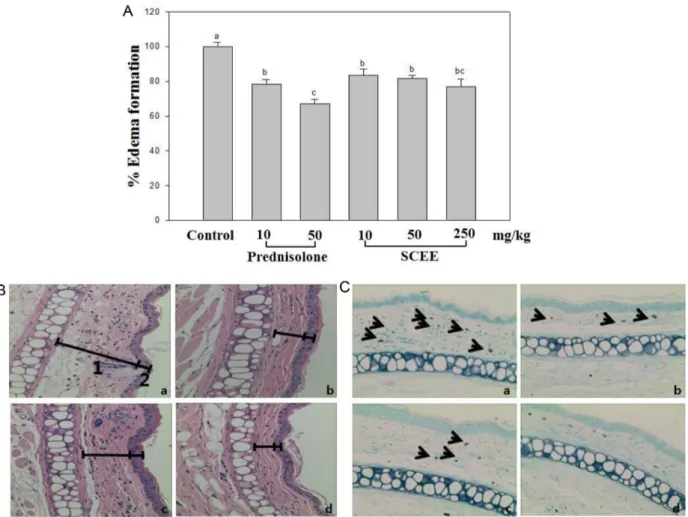
귀 부종 억제 효과 및 조직 관찰
피부는외부환경에의해손상된부위를복구시키려는
Fig. 3. Effect of SCEE on LPS-induced iNOS, COX-2, and NF- κB p65 expression in RAW 246.7 cells. The levels of iNOS, COX-2
in the cytosolic protein and the p65 subunit of NF- κB in nuclear protein were determined by a western blot analysis. RAW 264.7 cells
were treated with the indicated concentrations of SCEE (0.1, 1, 10, 50, and 100 μg/ml) and LPS (1 μg/ml) for 18 h or 30 min and the
proteins were detected using specific antibodies. One of the similar results from three separate experiments is represented.
일련의생체과정으로서혈관확장
,
부종등의생리현상을 나타나며이는피부염증에서일어나는대표적인반응이다[6].
현재사용되고있는합성스테로이드제인prednisolone 10
및50 mg/kg
과 추출물10, 50
및250 mg/kg
농도를200
μl
씩경구투여한후, croton oil
로염증유발하고귀두 께를측정하였다.
그결과(Fig. 4), control
과비교하여모든농 도에서유의적으로귀두께가감소한것을확인하였다.
특히,
추출물250 mg/kg
농도에서positive control
인prednisolone
처리구와비교하였을때, prednisolone 10 mg/kg
처리와유 사하게감소함을보였다.
추출물의귀부종억제효과는조 직관찰결과에서도나타났는데, croton oil
로부종을유발한마우스귀조직에서
croton oil
만을처리한경우에비해추출물을
100 mg/ml
농도로처리한경우prednisolone
처리구 와유사한정도로경피및진피두께가얇아진것을확인하였다
(Fig. 4B).
또한, toluidine-blue
염색을 통해 조직 내mast cell
침윤정도를확인한결과(Fig. 4C),
추출물의처리 가조직내mast cell
침윤을현저히억제함을보였다.
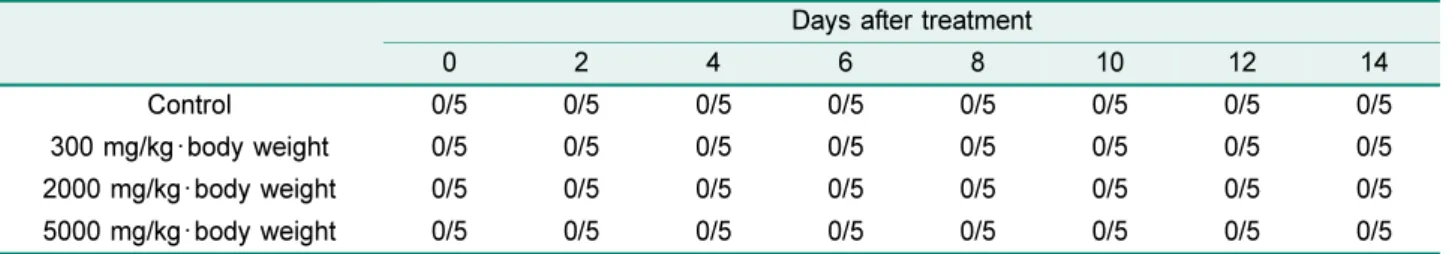
단기 독성 평가기능성식품소재로써이용가능성을알아보기위해
World
Health Organization (WHO) [22]
에 따라 추출물을300, 2000
및5000 mg/kg
농도로200
μl
씩경구투여하고2
주간 행동변화및치사율을 관찰하였다(Table 1).
경구투여 후4
시간까지행동변화를관찰하였을때, 30
분정도약간흥 분상태를보였으나1
시간이후진정하였으며, 2
주간치사 율은0%
로나타났다.
따라서동물실험을통해추출물이인 체에도무해할것으로사료되며새로운기능성식품소재 로이용이가능할것으로사료된다.
Fig. 4. SCEE-mediated inhibition of croton oil-induced mouse ear edema (A). Photomicrographs of transverse sections of mice ears
sensitized with topical application of 50 mg/ml croton oil in acetone (a-c) or acetone alone (d, non-inflamed), stained with hematoxylin-
eosin (B) or toluidine-blue (C). Photomicrographs recorded under light microscopy (magnification: 200 ×). Treatments: vehicle 20 mg/ml
Tween 80 (a), prednisolone 0.08 mg/ear (b), SCEE 20 μl/ear (c), and acetone (d). The numbers 1 and 2 indicate dermis and epidermis,
respectively. a-c indicates significantly different results (p < 0.05).
요 약
본연구에서는큰잎모자반의항염증효과를알아보기위 해
LPS
에의해염증반응이유도된RAW 264.7
세포에대한 큰잎모자반에탄올추출물의항염증효과를살펴보았다.
세 포내염증매개성cytokine (IL-6, TNF-
α및IL-1
β)
분비량의 측정결과,
농도의존적으로유의적감소를보였으며,
특히, 100
μg/ml
로처리하였을경우LPS
단독처리와비교시약48%
이상의높은분비량감소효과를보였다.
추출물이iNOS, COX-2
및NF-kB
발현억제에미치는효과를알아본결과, LPS
단독처리구에의해각단백질의발현량이현저히증가 하였으나,
추출물을처리하였을때그발현량이농도의존적 으로감소하는것을확인할수가있었다.
특히50
및100
μg/
ml
농도에서PBS
처리구와유사한발현량을보여우수한항염증효과를가짐을확인하였다
.
귀부종억제효과및조직 관찰을수행한결과,
추출물250 mg/kg
농도에서prednisolone 10 mg/kg
처리와유사하게감소함을보였다.
또한, croton oil
로부종을유발한마우스귀조직에서
croton oil
만을처리한경우에비해 추출물을
100 mg/ml
농도로 처리한경우prednisolone
처리구와유사한정도로경피및진피두께가얇아진것을확인하였으며
,
조직내mast cell
침윤을현저 히억제함을보였다.
이결과를종합해볼때,
큰잎모자반에 탄올추출물이염증치료제로써의소재로이용될가치가충 분할것으로사료된다.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Pro- gram through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2012R1A6A1028677).
References