320
전립선특이항원 수치 4 ng/ml 미만 환자의 임상 병리학적 특성 분석
Analysis of the Clinicopathologic Characteristics of Men with Prostate Cancer Undergoing Radical
Prostatectomy in the Prostate-Specific Antigen Range of Less than 4 ng/ml
Taekmin Kwon, In Gab Jeong, Jun Hyuk Hong, Hanjong Ahn, Choung-Soo Kim
From the Department of Urology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
Purpose: We analyzed the clinicopathologic characteristics of men under- going radical prostatectomy in the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) range of less than 4 ng/ml and compared this with the results for men who had a PSA range of 4 to 9.9 ng/ml.
Materials and Methods: The study population consisted of 447 men treated for prostate cancer with radical prostatectomy between 1990 and 2006 at our institute who had a prebiopsy PSA of less than 10 ng/ml. The average follow-up period was 37 months. Clinicopathologic characteristics were compared between men with a PSA value of less than 4 ng/ml (low-PSA group) and men with a value in the range of 4 to 9.9 ng/ml (intermediate- PSA group). Survival analysis was performed by the Kaplan-Meier method and Cox proportional hazard regression analysis.
Results: Of these 447 patients, 60 (13.4%) and 387 (86.6%) had a low or an intermediate prebiopsy PSA level, respectively. The pathologic findings of the prostatectomy specimens showed no significant differences between the 2 groups, including Gleason score and pathologic stage. The 5-year biochemical recurrence-free survival in the low- and intermediate-PSA groups was 82.8% and 79.3%, respectively, and there was no significant difference between the 2 groups (p=0.946). Multivariate analysis showed that, in the entire cohort, pathologic Gleason score and lymph node involvement were independent predictors of biochemical recurrence.
Conclusions: No statistically significant differences were found in clinico- pathologic characteristics or clinical outcome between the low- and inter- mediate-PSA groups. These results suggest that a lower PSA cutoff should be considered as an indication for prostate biopsy in the Korean population. (Korean J Urol 2009;50:320-326)
Key Words: Prostate-specific antigen, Prostatic neoplasms, Prostatectomy
Korean Journal of Urology Vol. 50 No. 4: 320-326, April 2009 DOI: 10.4111/kju.2009.50.4.320
울산대학교 의과대학 비뇨기과학교실 권택민ㆍ정인갑ㆍ홍준혁
안한종ㆍ김청수
Received:November 26, 2008 Accepted:March 12, 2009
Correspondence to: Choung-Soo Kim Department of Urology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, 388-1, Pungnap-dong, Songpa-gu, Seoul 138-736, Korea
TEL: 02-3010-3734 FAX: 02-477-8928 E-mail: cskim@amc.seoul.kr
Ⓒ The Korean Urological Association, 2009
서 론
1980년대 후반 전립선특이항원 (prostate-specific antigen;
PSA)을 이용한 전립선암 선별검사가 시작된 이후 PSA 상
승을 동반한 환자에서 전립선 생검을 시행해야 하는 PSA 절단치 (cutoff level)를 결정하기 위한 많은 연구들이 발표 되었으며 현재에는 혈중 PSA 수치 4.0 ng/ml가 전립선 침 생검을 시행하는 절단치로 널리 이용되고 있다.1-3
하지만 PSA 값은 연령에 따라 차이를 보이므로 모든 사
람에게 이를 동일하게 적용하는 데에는 많은 문제점이 내 재해 있다.4 또한 전립선암으로 진단된 환자의 약 20%는 PSA 수치가 2.6-4.0 ng/ml 범위에 있기 때문에 완치가 가능 한 전립선암 환자를 조기에 발견하기 위해서 PSA 절단치를 2.5 ng/ml로 낮추어야 한다는 주장도 제기되고 있다.5 하지 만 전립선암 진단을 위해 시행하는 전립선 침 생검의 PSA 절단치를 낮추면 불필요한 전립선 생검을 받는 사람이 증 가하게 되며 실제 치료 후 질병 진행 가능성이 낮은 임상적 으로 의미 없는 전립선암이 증가한다. 이는 환자에게 불필 요한 전립선암 치료 및 치료로 인한 합병증을 야기 할 수 있다. 더욱이 PSA 절단치를 낮추는 것이 전체 전립선암 사 망률을 감소시키는지에 관한 연구는 아직까지 발표된 바 없다.6-8 한국인의 연령별 PSA 참조 범위는 서양인에 비해 낮아 현재 전립선 생검을 권장하는 서양인의 기준인 PSA 절단치 4.0 ng/ml는 높다고 할 수 있다.9 따라서 일부에서는 PSA 영역에 따른 전립선 침 생검 결과를 바탕으로 한국인 에서 PSA 절단치를 낮춰야 함을 주장하는 의견도 있다.10 하지만 아직까지 한국인에서 PSA 영역에 따른 근치적 전립 선절제술 후 병리 소견 및 임상 경과에 관한 연구는 없는 실정이다. 실제 전립선 침 생검 소견과 전립선절제술 후 병 리 소견 간에는 분화도 분포 등에서 많은 차이를 보이므로 한국인에서 이에 관한 연구는 매우 절실하다고 할 수 있다.
이에 저자들은 전립선암으로 인해 근치적 전립선절제술 을 시행 받은 환자 중 술 전 PSA 수치가 4 ng/ml 미만인 환자들의 술 전 및 술 후 임상 병리학적 특징을 알아보고자 하였다. 또한 이들 환자를 동 기간 내 본원에서 수술 받은 술 전 PSA 수치 4 ng/ml 이상 10 ng/ml 미만 환자와 비교 분석하고자 하였다. 나아가 이를 통해 현재 임상에서 전립 선 침 생검 시 널리 이용되는 PSA 절단치 4.0 ng/ml의 타당 성을 알아보고자 하였다.
대상 및 방법
1990년 1월부터 2006년 12월까지 전립선암으로 본원에서 근치적 전립선절제술을 시행 받은 환자 878명 중 술 전 PSA 수치 10 ng/ml 미만인 환자 447명을 대상으로 후향적 분석을 하였다. 모든 환자에서 근치적 치골 후 전립선절제 술이 시행되었다. 모든 환자에서 골반 내 림프절적출술을 시행하였고 내 골반 근 막을 절개하여 전립선을 골반 벽으 로부터 분리하였다. 전립선의 pedicle이 절단된 후에는 전립 선 측에 있는 Denonvillier 근 막을 중앙에서 절개하여 정관 과 정낭을 노출 시킨 후 정낭의 끝까지 박리하여 각각 절단 하였다. 방광 경부를 절개한 후에 방광 경부를 박리 후 방광 경부를 전단하여 전립선을 제거하였다. 요도 방광 문합은
5-6곳에 봉합을 시행 후 요도 카세터를 방광에 넣고 봉합을 결찰하였고, 방광을 식염수 150-200 cc로 채운 후 유출 여부 를 관찰하였다. 조직학적 등급은 Gleason system과 1997 TNM stage에 따랐다.
대상 환자의 수술 당시 정중 나이는 65세 (42-78)였으며 정중 추적관찰 기간은 37개월 (3-163)이었다. 술 전 PSA 수 치에 따라 4 ng/ml 미만군 (low PSA group: 60명, 13.4%), 4 ng/ml 이상 10 ng/ml 미만군 (intermediate PSA group: 387명, 86.6%) 두 군으로 나누어 두 군 간의 임상 병리학적 특징을 비교하였다. PSA가 4 ng/ml 미만군에서 조직검사를 시행한 경우는 PSA가 지속적으로 3-4 ng/ml 정도로 지속되거나 경 직장수지검사나 검진 경직장 초음파에서 이상소견이 있는 경우 시행하였다. 술 전 PSA에 따른 병리학적 특징을 알아 보기 위해 Student's t-test를 이용하여 나이 차이를 비교하 고, chi square test를 이용하여 술 후 Gleason 점수와 전립선 피막 침범 여부, 정낭 침범 여부, 절개면 양성 여부, 림프선 양성 여부를 비교 분석하였다.
술 후에는 혈중 PSA 수치를 3개월 간격으로 측정하였고 0.2 ng/ml 이상으로 연속해서 2번 측정되는 경우를 생화학 적 재발로 정의하였다. Kaplan-Meier 분석 방법을 이용하여 5년 후 생화학적 무 재발 생존(율)을 비교하였으며 Cox 회 귀 분석 방법을 이용하여 각 인자의 상대적 재발 위험도를 평가하였다. p값이 0.05 미만인 경우 통계적으로 의미 있는 것으로 간주하였고 통계프로그램은 SPSS version 13.0 (Chi- cago, USA)을 사용하였다.
결 과
근치적 전립선절제술 이전 PSA 4 ng/ml 미만군과 PSA 4 ng/ml 이상 10 ng/ml 미만 두 군의 술 전 임상 병리학적 특성 을 비교했을 때 두 군 간 평균 나이는 각각 65.3세와 64.5세 로 유의한 차이가 없었다 (p=0.447). 직장수지검사에서 양 성 소견 및 전립선 침 생검 시 Gleason 점수 또한 두 군 간 유의한 차이가 관찰되지 않았다 (p=0.888, p=0.322). 술 후 병리학적 특성을 비교해 보면 전립선 피막 침범, 정낭 침범, 절제면 양성, 술 후 Gleason 점수, 림프선 양성 모두 유의한 차이를 보이지 않았다 (Table 1).
술 전 PSA 수치 (low versus intermediate PSA group)에 따 른 술 후 생화학적 재발의 차이를 알아보기 위해 Kaplan- Meier 곡선을 작성했을 때 5년 후 생화학적 무 재발 생존은 82.8%와 79.3%로 두 군 간 유의한 차이는 관찰되지 않았다 (p=0.946) (Fig. 1). Cox 회귀 분석을 이용하여 각 예후 인자 들의 생화학적 재발에 대한 상대적 예측 가치를 분석해 보 았을 때, 단변량 분석에서는 조직검사 Gleason 점수, 직장수
Table 1. Characteristics of men undergoing radical prostatectomy by preoperative prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in the entire cohort of patients with a PSA value of less than 10 ng/ml (n=447)
Preoperative serum PSA
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– p-value
<4 ng/ml 4-9.9 ng/ml
No. of patients (%) 60 (13.4) 387 (86.6)
Age (mean±SD) 65.3±6.0 64.5±6.7 0.447a
PSA (ng/ml) <0.001a
Median (range) 2.7 (0.28-3.9) 5.8 (4-9.9)
Mean±SD 2.65±1.07 6.87±1.69
No. biopsy Gleason score (%) 0.322b
Less than 6 26 (43) 203 (52)
7 23 (39) 113 (29)
More than 7 11 (18) 71 (19)
No. abnormal digital rectal exam (%) 25 (42) 156 (40) 0.888b
No. capsular penetration (%) 12 (20) 106 (27) 0.272b
No. seminal vesicle involvement (%) 4 (7) 20 (8) 0.509b
No. surgical margins (%) 11 (18) 87 (22) 0.295b
No. lymph node involvement (%) 4 (7) 11 (3) 0.128b
No. prostatectomy Gleason score (%) 0.296b
Less than 6 22 (36) 105 (27)
7 27 (45) 208 (54)
More than 7 11 (19) 74 (19)
PSA: prostate-specific antigen. a: Student’s t-test, b: chi square test
Fig. 1. Five-year biochemical recurrence-free survival after radical prostatectomy by preoperative prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level in the entire cohort of patients with a PSA value of less than 10 ng/ml (n=447, p=0.946).
지검사 소견, 전립선 피막 침범, 절제면 양성, 림프선 양성, 술 후 Gleason 점수가 유의한 예측 인자였다 (p<0.05). 다변 량 분석에서는 전립선 피막 침범 (hazard ratio; HR=2.20, 95% confidence interval; CI=1.03-4.70, p=0.043), 림프선 양성 (HR=6.13, 95% CI=2.67-14.04, p<0.001) 및 술 후 Gleason 점수 8점 이상 (HR=8.82, 95% CI=2.31-33.70, p=0.001)이 독
립적인 예후 예측 인자였다 (Table 2).
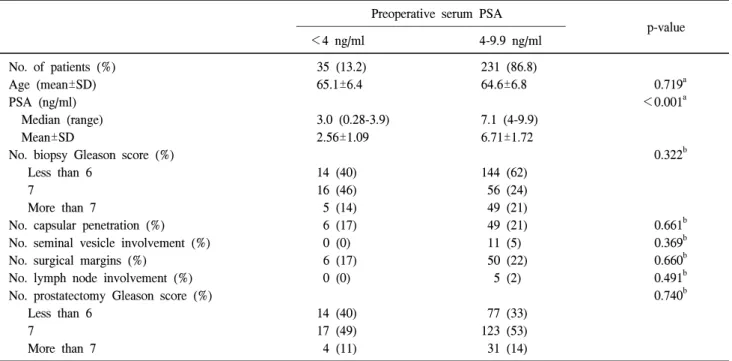
전립선 침 생검 시행 이전 직장수지검사에서 정상 소견 을 보인 환자 266명을 대상으로 분석하였을 때에는 PSA 4 ng/ml 미만군과 PSA 4 ng/ml 이상 10 ng/ml 미만군 두 군 간에 유의한 차이를 보이는 술 전 임상 병리 인자는 관찰되 지 않았다 (Table 3). 이 군에서 술 전 PSA 수치 (low versus intermediate PSA group)에 따른 술 후 생화학적 재발의 차이 를 알아보기 위해 Kaplan-Meier 곡선을 작성했을 때 5년 후 생화학적 무 재발 생존율은 100%와 83.7%로 두 군 간 통계 적으로 유의한 차이는 관찰되지 않았으나 low PSA group의 생존율이 높게 관찰되었다 (p=0.076) (Fig. 2). Cox 회귀 분석 을 이용하여 각 예후 인자들의 생화학적 재발에 대한 상대 적 예측 가치를 분석해 보았을 때 단변량 분석에서는 조직 검사 Gleason 점수, 전립선 피막 침범, 절제면 양성, 림프선 양성, 술 후 Gleason 점수가 유의한 예측 인자였다 (p<
0.05). 다변량 분석에서는 림프선 양성 (HR=29.38, 95%
CI=4.75-181.76, p<0.001)만이 독립적인 예후 예측 인자였 다 (Table 4).
고 찰
전립선암 진단에 PSA 선별 검사가 도입된 1980년대 후반
Table 2. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses for predicting biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy in the entire cohort of patients with a PSA value of less than 10 ng/ml (n=447)
Univariate analysis Multivariate analysis
Variables –––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– ––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
HR 95% CI p-value HR 95% CI p-value
PSA (4-9.9 ng/ml versus <4 ng/ml) 1.03 0.44-2.42 0.946 0.95 0.40-2.28 0.908
Biopsy Gleason score 0.540
Less than 6 Referent Referent
7 1.57 0.75-3.27 0.228 1.14 0.53-2.45 0.304
More than 7 4.01 2.13-7.56 <0.001 1.47 0.73-2.98 0.741
Digital rectal examination 2.07 1.19-3.61 0.010 0.90 0.49-1.67 0.741
Organ confined 6.44 3.65-11.38 <0.001 2.20 1.03-4.70 0.043
Seminal vesicle involvement 8.85 5.06-15.49 <0.001 1.82 0.86-3.85 0.120
Surgical margins 3.05 1.76-5.27 <0.001 1.12 0.59-2.23 0.729
Lymph node involvement 14.62 6.96-30.68 <0.001 6.13 2.67-14.04 <0.001
Prostatectomy Gleason score
Less than 6 Referent Referent
7 3.84 1.13-13.06 0.032 2.70 0.75-9.66 0.127
More than 7 22.28 6.70-74.05 <0.001 8.82 2.31-33.70 0.001
PSA: prostate-specific antigen, HR: hazard ratio, CI: confidence interval
Table 3. Characteristics of men with prostate cancer undergoing radical prostatectomy by preoperative PSA in men without an abnormal digital rectal examination (n=266)
Preoperative serum PSA
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– p-value
<4 ng/ml 4-9.9 ng/ml
No. of patients (%) 35 (13.2) 231 (86.8)
Age (mean±SD) 65.1±6.4 64.6±6.8 0.719a
PSA (ng/ml) <0.001a
Median (range) 3.0 (0.28-3.9) 7.1 (4-9.9)
Mean±SD 2.56±1.09 6.71±1.72
No. biopsy Gleason score (%) 0.322b
Less than 6 14 (40) 144 (62)
7 16 (46) 56 (24)
More than 7 5 (14) 49 (21)
No. capsular penetration (%) 6 (17) 49 (21) 0.661b
No. seminal vesicle involvement (%) 0 (0) 11 (5) 0.369b
No. surgical margins (%) 6 (17) 50 (22) 0.660b
No. lymph node involvement (%) 0 (0) 5 (2) 0.491b
No. prostatectomy Gleason score (%) 0.740b
Less than 6 14 (40) 77 (33)
7 17 (49) 123 (53)
More than 7 4 (11) 31 (14)
PSA: prostate-specific antigen. a: Student’s t-test, b: chi square test
에서 1990년대 초반 이후 진행된 병기에서 발견되는 전립 선암 환자 수는 급격히 감소하였다.11 현재까지는 직장수지 검사에서 전립선에 촉지되는 결절이 만져지는 경우를 제외 하고 전립선암 진단을 위한 전립선 침 생검의 주된 적응은 혈중 PSA 수치 상승이다.12 하지만 전립선 침 생검 여부를 결정해야 하는 중요한 기준인 혈중 PSA 절단치에 관해서는
아직까지 논란이 많은 실정이며 현재까지는 전립선암 존재 유무를 가장 정확히 판단할 수 있는 최적의 PSA 절단치는 없는 실정이다. PSA 절단치를 낮추면 이론상 전립선암을 조기 진단할 수 있지만, 이는 발견하지 않아도 환자의 예후 에 크게 영향을 미치지 않는 저 병기, 저 분화도의 임상적으 로 의미 없는 암의 진단 비율을 높일 수 있다.13-15
Fig. 2. Five-year biochemical recurrence-free survival by pre- operative prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level in men without an abnormal digital rectal examination (n=266, p=0.076).
Table 4. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses for predicting biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy in men without an abnormal digital rectal examination (n=266)
Univariate analysis Multivariate analysis
Variables –––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– ––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
HR 95% CI p-value HR 95% CI p-value
PSA (4-9.9 ng/ml versus <4 ng/ml) 25.08 0.10-6,513.38 0.256 − − −
Biopsy Gleason score 0.599
Less than 6 Referent Referent
7 1.63 0.54-4.96 0.388 1.27 0.34-4.74 0.537
More than 7 3.58 1.33-9.66 0.012 1.81 0.57-5.75 0.270
Organ confined 6.64 2.77-15.91 <0.001 1.48 0.39-5.65 0.565
Seminal vesicle involvement 11.09 4.42-27.83 <0.001 2.67 0.77-9.25 0.122
Surgical margins 3.64 1.54-8.60 0.003 1.64 0.53-5.09 0.392
Lymph node involvement 37.84 10.27-139.49 <0.001 29.38 4.75-181.76 <0.001
Prostatectomy Gleason score
Less than 6 Referent Referent
7 2.79 0.74-10.47 0.130 1.23 0.28-5.42 0.783
More than 7 12.45 3.24-47.78 <0.001 3.68 0.68-19.96 0.131
PSA: prostate-specific antigen, HR: hazard ratio, CI: confidence interval Thompson 등3은 임의로 설정된 PSA 절단치 이상의 상승 된 혈중 PSA만으로는 전립선암 진단을 정확히 할 수 없다 고 주장하였으며 이의 근거로 임상적으로 의미 있는 전립 선암이 정상 PSA수치 (PSA 절단치 이하) 영역에서도 존재 한다고 하였다. 이들의 보고에 의하면 실제 전립선 조직검 사에서 진단되는 전립선암의 15.2%가 직장수지검사에서 정상소견을 보이고 PSA치가 4 ng/ml 미만이었다. 또한 이러 한 전립선암의 14.9%가 Gleason 점수 7점 이상의 분화도가 나쁜 전립선암으로 나타났다.16 본 연구에서는 PSA 4 ng/ml 미만 환자 64명 중 35명 (55%)이 직장수지검사에서 정상소 견을 보였으며, 이 환자 중 64%는 술 후 Gleason score 7점
이상의 고등급 전립선암으로 진단되었다. 따라서 현재의 PSA 절단치 4 ng/ml 미만에서 발견되는 전립선암 환자의 상당수는 임상적으로 유의한 전립선암을 가지고 있음을 알 수 있다. 또한 이는 이전 Park 등10이 한국인에서 전립선암 진단을 위한 침 생검 시 PSA 영역에 따라 발견되는 전립선 암 침 생검 병리 소견을 분석한 결과와 일치한다.
정상 혈중 PSA 범위에서도 고등급의 전립선암이 진단된 다는 여러 보고를 비추어 볼 때 PSA 절단치를 낮춰 암의 완치 가능성이 높을 때 이를 진단하여 조기에 치료하자는 주장이 설득력을 얻고 있다.17-19 하지만 PSA 절단치의 감소 는 전립선암 진단의 개선 효과가 있지만 임상적으로 의미 없는 전립선암의 진단을 높여 불필요한 조직검사에 대한 부담과 비용이 증가하게 된다. 또한 임상적으로 의미 없는 전립선암에 대한 불필요한 치료 비용과 치료에 따른 부작 용을 야기할 수 있다.
PSA 절단치를 낮춤으로써 치료 후 전립선암의 경과가 의 미 있게 좋아진다면 이에 대한 주장은 정당화 될 수 있다.
이전의 여러 연구가 낮은 PSA 수치에서 진단된 전립선암이 더 좋은 경과를 가지는지에 대해 알아보았고 일부는 설정 된 절단치 이상에서 발견된 전립선암 환자의 임상 경과와 비슷하다고 보고하였고 일부는 높은 PSA 수치에서 발견된 전립선암 환자에서 나쁜 경과를 보인다고 보고하였다.20-22 하지만 대부분의 연구는 낮은 PSA 수치에서 발견된 전립선 암 환자의 경우 근치적 전립선절제술 시행 후 좋은 경과를 보인다고 보고하고 있다.13-15,23 하지만 이러한 연구들은 모 든 근치적 전립선절제술을 시행한 환자에 대해서 분석한
것이다. 직장수지검사에서 정상 소견을 보이는 임상적 병 기 T1c 환자에서 근치적 전립선절제술을 시행한 후 분석한 바에 따르면 낮은 PSA 수치에서 발견된 전립선암 환자의 경우 술 후 Gleason 7점 이상의 비율이 낮고, 낮은 생화학적 재발의 비율을 보이는 것으로 보고되었다.24
본 연구에서는 근치적 전립선절제술을 시행 받은 모든 환자를 비교하였을 때는 low PSA group 및 intermediate PSA group 두 군과의 임상병리학적 특성을 비교하였을 때 유의 한 차이가 관찰되지 않았다. 정상 직장수지검사 소견을 가 진 환자만을 비교해 보았을 때도 임상병리학적 차이는 관 찰되지 않았다. 전체 환자를 대상으로 한 생존 분석에서 근 치적 전립선절제술 후 생화학적 재발에 있어서는 두 군 간 의 유의한 차이는 관찰되지 않았지만, 정상 직장수지검사 소견 환자만을 대상으로 한 생존 분석에서는 통계적 유의 성에 도달하지는 못했지만 PSA 4 ng/ml 미만 환자에서는 재발한 환자가 관찰되지 않았다.
일반적으로 PSA 수치에 따른 전립선암 진단율은 2.5-4.0 ng/ml에서 10-20%, 4.1-10.0 ng/ml에서 25%, 10 ng/ml 이상에 서 50-60%이다.25 한국인에서 PSA 수치에 따른 전립선암 진 단율은 각각 PSA 4.0-10 ng/ml에서 15.9%, 10.0-20.0 ng/ml에 서 34.1%로 보고되고 있다.26 한국인의 전립선암 진단율이 낮은 것은 전립선암 유병률이 낮은 것이 한 이유가 될 수 있지만 이러한 사실은 서양인의 PSA 절단치인 4.0 ng/ml가 한국인에게 높기 때문이어서 한국인에서 PSA 절단치를 낮 추자는 주장 또한 제기되고 있다. 전립선암 선별검사가 전 립선암 사망률을 낮출 수 있는지에 대해서는 논란이 있으 나 PSA 절단치를 낮추면 치료 가능한 전립선암을 진단할 확률은 높아진다고 할 수 있다.27
Cho 등28에 따르면 한국인에서 PSA 절단치를 낮추어야 하는 타당한 근거에도 불구하고 PSA 절단치를 4.0 ng/ml에 서 3.0 ng/ml와 2.5ng/ml로 낮추었을 때 전립선 생검을 시행 할 환자 수는 PSA 절단치가 4.0 ng/ml일 때 204,000명에 비 해 각각 1.75배와 2.49배 증가하는 것으로 보고되고 있다.
전립선 생검 비용을 최소로 추정하기 위해 전립선 생검 대 상 환자 전부를 외래에서 전립선 생검을 시행한다고 가정 할 경우 전립선 생검 비용은 PSA 절단치가 3.0 ng/ml일 때 514억 원, 2.5 ng/ml일 때 1,025억 원의 추가 비용이 들 것이 라고 추정된다. 따라서 PSA 절단치를 낮췄을 경우 추가적 인 경제적 비용이 크게 증가하므로 PSA 절단치를 낮추는데 신중을 기해야 한다는 의견도 있다.
본 연구에서 PSA 4 ng/ml 미만인 환자의 경우 직장수지 검사 소견에 관계없이 병리학적 소견에서 Gleason 점수 7 이상의 고등급 전립선암이 높은 PSA 영역의 환자와 비슷한 비율로 발견되었으며, 근치적 전립선절제술 후 생화학적
재발률의 차이가 관찰되지 않았다. 따라서 본 연구 결과는 현재의 PSA 수치 4 ng/ml로 설정되어 있는 전립선 생검의 절단치를 낮출 필요가 있음을 제시하며 이에 관한 향후 전 향적인 추가 연구가 필요성을 제기한다고 할 수 있다.
결 론
전립선암으로 근치적 전립선절제술을 시행 받은 환자 중 술 전 PSA 4 ng/ml 미만의 환자에서도 PSA 4 ng/ml 이상 10 ng/ml 미만의 환자와 비슷한 술 후 병리 소견을 보이며 추적 관찰 시에도 두 군 간 생화학적 재발의 차이는 관찰되 지 않았다. 따라서 술 전 PSA 4 ng/ml 미만의 환자에서도 임상적으로 의미 있는 전립선암이 있을 수 있다. 하지만 PSA 절단치의 타당성을 알아보기 민감도와 특이도에 대한 더 많은 연구가 있어야 할 것으로 생각한다.
REFERENCES
1. Catalona WJ, Smith DS, Ratliff TL, Dodds KM, Coplen DE, Yuan JJ, et al. Measurement of prostate-specific antigen in serum as a screening test for prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 1991;324:1156-61
2. Cooner WH, Mosley BR, Rutherford CL Jr, Beard JH, Pond HS, Bass RB Jr, et al. Clinical application of transrectal ultrasonography and prostate specific antigen in the search for prostate cancer. J Urol 1988;139:758-61
3. Thompson IM, Ankerst DP, Chi C, Lucia MS, Goodman PJ, Crowley JJ, et al. Operating characteristics of prostate-specific antigen in men with an initial PSA level of 3.0 ng/ml or lower.
JAMA 2005;294:66-70
4. Oesterling JE, Jacobsen SJ, Chute CG, Guess HA, Girman CJ, Panser LA, et al. Serum prostate-specific antigen in a community-based population of healthy men. Establishment of age-specific reference ranges. JAMA 1993;270:860-4 5. Catalona WJ, Ramos CG, Carvalhal GF, Yan Y. Lowering
PSA cutoffs to enhance detection of curable prostate cancer.
Urology 2000;55:791-5
6. de Koning HJ, Auvinen A, Berenguer Sanchez A, Calais da Silva F, Ciatto S, Denis L, et al. Large-scale randomized prostate cancer screening trials: program performances in the European Randomized Screening for Prostate Cancer trial and the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovary cancer trial. Int J Cancer 2002;97:237-44
7. Postma R, Schroder FH. Screening for prostate cancer. Eur J Cancer 2005;41:825-33
8. Vis AN, Kranse R, Roobol M, van der Kwast TH, Schroder FH. Serendipity in detecting disease in low prostate-specific antigen ranges. BJU Int 2002;89:384-9
9. Ku JH. Race-specific reference ranges of serum prostate-
specific antigen levels in countries with a low incidence of prostate cancer. BJU Int 2006;97:69-72
10. Park HK, Hong SK, Byun SS, Lee SE. T1c prostate cancer detection rate and pathologic characteristics: comparison between patients with serum prostate-specific antigen range of 3.0 to 4.0 ng/mL and 4.1 to 10.0 ng/mL in Korean population.
Urology 2006;68:85-8
11. Hankey BF, Feuer EJ, Clegg LX, Hayes RB, Legler JM, Prorok PC, et al. Cancer surveillance series: interpreting trends in prostate cancer--part I: Evidence of the effects of screening in recent prostate cancer incidence, mortality, and survival rates. J Natl Cancer Inst 1999;91:1017-24
12. Aus G, Abbou CC, Bolla M, Heidenreich A, Schmid HP, van Poppel H, et al. EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Eur Urol 2005;48:546-51
13. Shekarriz B, Upadhyay J, Bianco FJ Jr, Tefilli MV, Tiguert R, Gheiler EL, et al. Impact of preoperative serum PSA level from 0 to 10 ng/ml on pathological findings and disease-free survival after radical prostatectomy. Prostate 2001;48:136-43 14. Aleman M, Karakiewicz PI, Kupelian P, Kattan MW, Graefen
M, Cagiannos I, et al. Age and PSA predict likelihood of organ-confined disease in men presenting with PSA less than 10 ng/ml: implications for screening. Urology 2003;62:70-4 15. Berger AP, Volgger H, Rogatsch H, Strohmeyer D, Steiner H,
Klocker H, et al. Screening with low PSA cutoff values results in low rates of positive surgical margins in radical prostatec- tomy specimens. Prostate 2002;53:241-5
16. Thompson IM, Pauler DK, Goodman PJ, Tangen CM, Lucia MS, Parnes HL, et al. Prevalence of prostate cancer among men with a prostate-specific antigen level < or =4.0 ng per milliliter. N Engl J Med 2004;350:2239-46
17. Catalona WJ, Smith DS, Ornstein DK. Prostate cancer detection in men with serum PSA concentrations of 2.6 to 4.0 ng/ml and benign prostate examination. Enhancement of specificity with free PSA measurements. JAMA 1997;277:
1452-5
18. Gann PH, Hennekens CH, Stampfer MJ. A prospective evaluation of plasma prostate-specific antigen for detection of
prostatic cancer. JAMA 1995;273:289-94
19. Lee HW, Kwak WK, Choi YH, Choi HY, Lee HM. New thresholds for prostate-specific antigen velocity for prostate cancer screening in Korean patients younger than 60 years old.
Korean J Urol 2008;49:113-7
20. Chung JS, Han BK, Jeong SJ, Hong SK, Byun SS, Choe G, et al. Prognostic significance of the tumor volume and tumor percentage for localized prostate cancer. Korean J Urol 2008;
49:1074-80
21. Stamey TA, Johnstone IM, McNeal JE, Lu AY, Yemoto CM.
Preoperative serum prostate specific antigen levels between 2 and 22 ng./ml. correlate poorly with post-radical prostatectomy cancer morphology: prostate specific antigen cure rates appear constant between 2 and 9 ng./ml. J Urol 2002;167:103-11 22. Welch HG, Schwartz LM, Woloshin S. Prostate-specific
antigen levels in the United States: implications of various definitions for abnormal. J Natl Cancer Inst 2005;97:1132-7 23. Freedland SJ, Aronson WJ, Kane CJ, Terris MK, Presti JC Jr,
Trock B, et al. Biochemical outcome after radical prostatec- tomy among men with normal preoperative serum prostate- specific antigen levels. Cancer 2004;101:748-53
24. Antenor JA, Roehl KA, Eggener SE, Kundu SD, Han M, Catalona WJ. Preoperative PSA and progression-free survival after radical prostatectomy for Stage T1c disease. Urology 2005;66:156-60
25. Schmid HP, Riesen W, Prikler L. Update on screening for prostate cancer with prostate-specific antigen. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2004;50:71-8
26. Yang WJ, Lee DH, Chung BH, Cho JS, Choi YD, Kim SJ, et al. Detection rate of prostate cancer on biopsy according to serum prostate-specific antigen in Korean men: a multicenter study. Urology 2006;67:333-6
27. Crawford ED, Thompson IM. Controversies regarding screen- ing for prostate cancer. BJU Int 2007;100(Suppl 2):5-7 28. Cho JS, Kim SI, Kim SJ, Kim YS, Kim CI, Kim HS, et al.
Lowering prostate-specific antigen threshold for prostate biopsy in Korean men: impact on the number needing biopsy.
Korean J Urol 2008;49:118-21