대한방사선의학회지 1994: 31( 1): 151-156
대퇴골두 무혈성괴사의 자기공명영상:
예후판정 요소의 평가I
진 욱 · 류경남 · 유명철 2 . 윤 엽
목 적 . 대퇴골두 무혈성괴사 환자에서 자기공명영상을 통해 예후 판정에 영할을 미치는 요소를 평 가하고자한다.
대상 및 방법 : 대퇴골두 무혈성괴사 진 단하에 단순 x- 선 촬영과 자기공명영상을 시행하고 6개월 이 상 추적 검사를 시행한 23 명, 30여|를 대상으로 하였다. 환자의 평균연령은 43세 였고, 남여비는 20: 3
이었다. 사용한 기기는 1.5-T MR un it로 T1(450-500/15-20) 및 T2(1800-2000/30/80) 강조 관상영상과
T1 축상 및 시상영상을 얻었다. 단순 X 선 김사를 통한 6개월 추적검사에서 육안적 골변화가 심한 예,
중등도의 예, 그리고 겸한 예로 나누어 자기공염영상에서 대퇴글두의 신호강도 변화와 병변의 크기등 을분석 하였다. 병변의 크기는대퇴글두를 2등분하여 분류하였다.
결 과:겸한 변화를 보인 경우 평균연렁은 37세, 괴샤범위는 17예 중 11 여 [7f 1/2이하였고, 중등도 변화의 경우 평균연렁이 43서[, 괴사범위는 7여| 중 5여|가 1/2초과였으며, 심한 변화를 보인 경우 평균연 령은 60서[, 괴사범위는 6예 모두7f 1/2초과를 보였다. 이들을 신뢰도 95%로 검정하였을 때 심한 변화 대 중등도 변화, 심한번화대 겸한 변화의 연령비교, 그리고 각각의 괴사법위비교에서 통계학적 의의가 있었다 그러나 T1 및 T2 강조영상에서의 신호음영변화는 각기 통계학적 연관성이 없었다.
결 론.대퇴골두 무혈성괴사 환자에서 나이가 젊고, 병변의 크기가 작을수록 굴파괴가 서서히 진행 됨을 알 수 있어 이러한 요소가 예후 판정에 도움이 되고, T1 및 T2 강조영상에서의 신호음영강도의 변 화앙상은 예후판정에 멸 영향이 없는 것으로 사료된다.
서 료응 ‘-
자기공명영상검사(이후 MR) 는 대퇴골두 무혈성괴사의 초기진단에 큰 역할을 하며 가장 민감한 검사방법으로 널 리 이용되고 있다. 대퇴골두 무혈성괴사에 대한 자기공명 영상소견은 많은 보고가 있었으며 최근에는 질환의 진행속 도와 초기 무혈성괴사의 예후판정에 도움을 주는 요소에 대한 평가도 발표되였다. 이에 저자들은 초기 무혈성괴사 만이 아닌 처음 내원시 진단된 여러 단계의 무혈성괴사의 단순 X선 촬영과 MR 소견을 비교하고, 단순 X 선 추적검 사를 통하여 예후판정에 영향을 미치는 소견을 알아보고자 본연구를시행하였다.
대상및방법
1990년 10월부터 1992년 12월까지 대퇴골두무혈성괴사
1경희대학교 의과대학 진 단방사선과학교실 2경희대학교 의과대학 정형외과학교실
이 논문은 1994년 1월 25일 접수하여 1994년 5월 17일에 채택되었음
- 151
진단하에 단순 X선 촬영(고관절 전후면 및 frog leg view) 과 MR을 시행하고 MR 촬영 후 최소 6개월 이상 단순 X
션 촬영으로 추적검사를 시행한 23명, 30예를 대상으로 하 였으며, 이들중 21 예가 추적검사 이후 대퇴골두치환술이 나 대퇴골두 중심생검을 통하여 확진되였고 그 이외의 경 우는 방사선학적 소견으로 진단된 예였다. 환자의 연령분 포는 23세 67세로 평균연령은 43세였고, 남여비는 20: 3 이였다.
사용한 MR 기 기는 1.5-T Unit( Toshiba, MRX-II, Nasu, Japan) 로 pulse sequence는 스펀에코방법으로 하 였으며 T1 (450-500/15-20) 및 T2 (1800 -2000 /30 / 80 ) 강 조 관상영상과 T1 강조 축상 및 시상영상을 얻였다.
단순 X선 촬영은 MR시행 전후 1 주일 사이에 촬영한것 과 MR 촬영후 6개월 이상추적검사한것을비교하였다.
분석 내용은 대퇴골두 침범정도, MR에서 신호강도의 변화 그리고 연령을 비교하였다. 단순 방사선 소견은 크게 3가지 군으로나누어 추적검사동안대퇴골두를감싸는원 의 상부 1/2를 기준으로 초기검사시 높이의 1/2 이하로 줄어든 경우 심한 변화, 거의 변화가 없는 경우 경미한 변 화, 그 사이의 변화를 중등도의 변화라 하였다.MR에서는
대한방사선의학회지 1) ;
괴시의 범위를 대퇴골두 중심을 기준으로 시상영상에서 면적의 1/
2
이하 및 초과로 나누어 분류하였으며, T1 및T2 강조영상에서의 대퇴골두 신호강도의 변회도 관찰하 였다. 그리고 단순 방사선 추적검사에서 보인 3가지 변화 군에서의 평균연령을 분석하였다. 이상의 세가지 결과에 대해 통계학적 의의를검정하였다.
결 과
단순 X션과 MR을 통한 상호 비교에서 단순고관절 X선 사진 추적검사상 경한 변화를 보인 군은 MR 시상영상에 서의 괴사면적이 1/2 이하가 11 예,1/ 2 초과가 6예였고,
중등도의 변화를 보인 군에서는 1/2 이하가 2예,1/ 2 초
과가 5예였으며, 심한 변화를 보인 군에서는 6예가 모두 1/2 초과의 범위를 보였다. 이들을 95% 신뢰도로 통계학 적 검정을 시행한 결과 Chi -square검정에서 8.372, P = 0.015로 서로간에 통계학척 의의가 있었다.
T1 및 T2 강조영상에서의 신호음영의 변화가 저 /저 (섬
유성 조직 혹은 골경화)신호강도 변화인 경우 경한 변화군 8예, 중등도 변화군 2예, 심한 변화군 2 예, 저/고(액체)신 호강도 변화인 경우는 경한 변화군 1예, 심한 변화군 l예,
그리고 고/중간(지방)신호강도 변화의 경우는 경한 변화 군 9예, 중등도 변화군 4예, 심한 변화군 3예로 95% 신뢰 도 Chi -square검정에서 p= 0.528로 각각의 연관성이 없 는것으로판명되었다.
대퇴골두무혈성괴사의 단순 X ←선 추적검사에서 경미한
a b
c
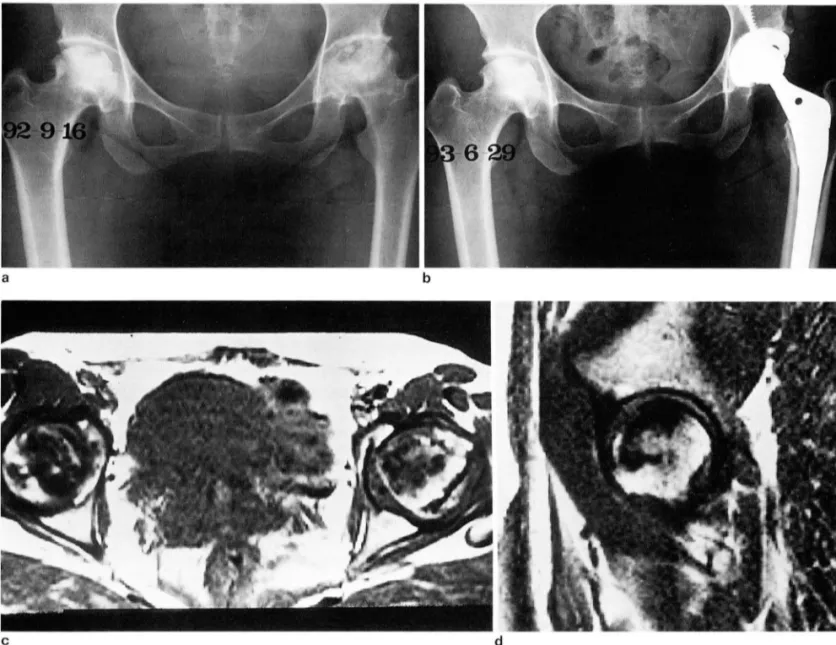
Fig. 1. A 36-year-old lemale with AVN 01 both lemoral heads
a. On plain radiograph, right femoral head shows sclerotic change and irregular border. And left femoral head shows patches of d
increased density with interspersed area of radiolucency and a loss of volume
b. After about 9 months, no change of right femoral head and THR in left hip joint are seen
c. On T1-weighted axial image, extensive low signal intensities in both femoral heads are n 아ed. These signal intensities are not changed on T2-weighted image
d. T1-weighted sagittal image demonstrates irregular shaped right femoral head with low signal intensity and sparing its cortex And necrotic area breaks into about 1/2 of right femoral head
이 ι π
U
변화를 보인 경우 (Fig. 1)는 17예로 평균 연령이 37세였고,
중등도의 변화를 보인 경우 (Fig. 2)는 7예로 평균연령이 43세였으며, 심한 변화를 보인 경우 (Fig. 3) 는 6 예로 평균 연령이 60세였다. 이들 3군의 연령비교에서 신뢰도 95%로 통계학적 검정을 시행하였는데 심한 변화대 중등도 변화 의 경우 t= 6.590 : P= 0.000으로 통계학적 의의가 있었으 며, 심한 변화대 경한 변화의 경우에서도 t=3.624 ; P=
002로 통계학적 의의가 있었으나, 중등도의 변화대 경한 변화의 경우에는 t = 1.220; P = 0.235로 통계학적 의의가
。~O~
,
1Hλ λA'1
고 찰
진 욱 외 : 대퇴골두 무혈성괴사의 자기공명영상
교통사고의 증가 등으로 인한 고관절 골절의 증가로 흔한 임상적 문제점이 되고 있으며(1) 동통과 연골하 허탈 (Sub chondral collapse)을 포함하는 병적인 상태로서 고관절의 이차적인 관절염을 일으킨다 (2). 이 질환에서의 자연치유 나 퇴행은 극히 드문 현상이고 매우 적은 예에서만 보고되 고 있으며(3) 초기에 진단되어야만 중심감압솔 (Core de- compression) 이나 회전골절술 (Rotational osteotomy) 과 같은 방법으로 병의 진행을 막을 수 있다(1).
단순 방사선 소견에서의 변화는 이 질환의 진행후기에 나타나며 일단 이러한 변화가 나타나면 6-24 개월 내에 대부분의 고관절에서 허탈 (C이lapse) 이 진행된다. 이러한 관점에서 대퇴골두괴사는더욱초기진단이 중요하다 (4
).
현재로서 MR이 대퇴골두괴사의 초기진단을 위한 가장 대퇴골두 무혈성괴사는 스테로이드의 상용과 골다공증, 정확하고 예민한 영상진단기기로 알려져있기 때문에 흔히
a b
c d
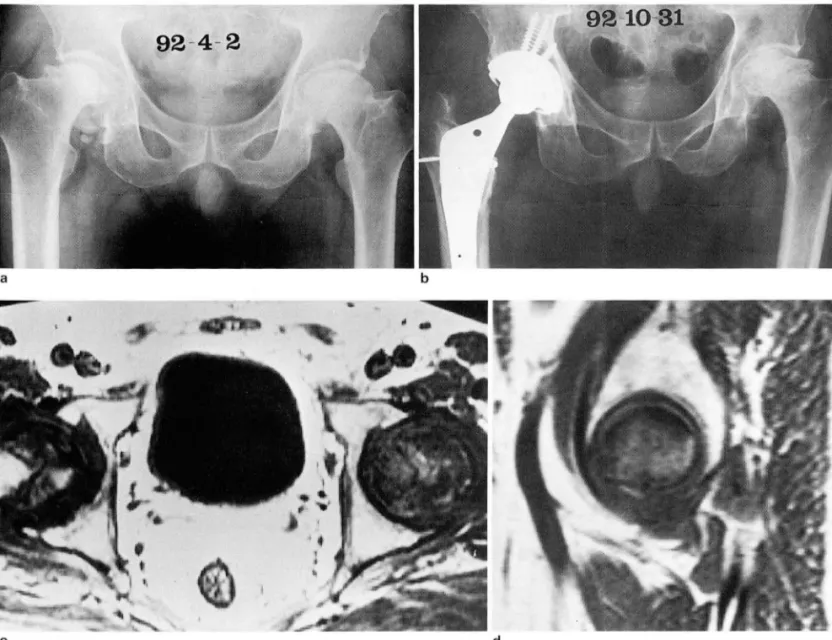
Fig. 2. A 43-year-old man with AVN of left femoral head
a. On plain radiograph, left femoral head reveals cystic and sclerotic changes with some developed collapse
b. After about 6 months, more sclerotic and flattened changes are visible in left femoral head, but flattening of left femoral head is not over 1/2 of primary femoral height
c. On T1-weighted axial image, the extension of about 3/4 area in left femoral head is noted with central low signal intensity which is not changed on T2-wighted image
d. On T1-weighted sagittal image, left femoral head has about 3/4 of necrotic extent
1 J
-‘
J시행되고 있다 (5-8).
대퇴골두 무혈성괴사의 MR 소견은 (a) 저신호강도의 규칙적 흑은 불규칙적 병변 (b)고신호강도의 고리같은 병 변 흑은 감소된 신호강도의 띠 가 둘러 싸며 ( “ Double-line sign") 대퇴골경으로 확장되는 등의 모습이다 (9). 이러한
“Double-line sign"은 대퇴골두괴사 특유의 MR 소견(10) 으로 괴 사골의 저 신호강도를 가지는 둘레의 반응간연 (Re active intersurface) 내의 충혈과 염증에 의한 소견이다 (11).
대퇴골두괴사의 예후를 판정하는 것은 정형외과적 수술 이 필요한지 또 어떠한 수술이 가장 적당한지 결정하는데 중요하다.
대퇴골두괴사의 진행에 영향을 주는 요인들에는 여러가
92 - 4 - 2
a
c
Fig. 3. A 52.year.old man with both AVN 01 lemoral head
b
지가있지만그중에는환자의 나이,골두괴사의 원인흑은 이미 존재하던 골취약성 (Bone fragility) 의 유무 등이 있 다. 그러나 임상적 경험에서는 대퇴골두괴사의 크기나 위 치가 가장 중요하다고 알려져있다 (12) .
대퇴콜두괴사의 범위에 등급을 매기려는 시도는 여러번 있어왔으며. Steinberg 등(13) 은 대퇴골두괴사의 단계를 나눔에 있어 Stage 2 이상에서 득점계 ÁJ- (Point counting), 동심원 (Concentric circles), 구적계 (Planimetry) 를 사용 하여 괴사의 범위를 계산, 방사선학적 Stage의 세분 (Substage)을 병변의 범위에 따라 3개의 군 (Class) 경 도 (Mild) , 중등도 (Moderate) , 중도(Severe) 으로 나누 도록 추천하였다. 더욱 최근에 Ohzono 등(1 4 )이 발표한 바에 따르면 수술받지않은 대퇴골두괴사의 자연경과가 대
d
a. On plain radiograph, right lemoral head shows severe collapse. Left lemoral head shows mild Ilattening and slightly sclerotic changes
b. After about 7 months, right lemoral head is replaced by prosthesis and left lemoral head reveals severe change 01 more col- lapse and sclerosis
c. On T1-weighted axial image, inhomogenous signal intensities in both lemoral heads are noted. These signal intensities are not changed on T2-weighted image‘
d. On T1-weighted sagittal image, left lemoral head shows low signal intensity with nearly 2/2 01 necrotic extent
- 154 -
퇴골두내 괴사의 위치와 깊게 관련 있다고 발표하였고 체 중부하 면적의
1/3
이하의 괴사의 경우와 연골하 경계를 침범하지 않은 경우는 방사선학적 추후관찰에서 더 이상 의 진행이 없음을보였으나이외의 다른예들은흔히 더욱 허탈( Collapse) 됨을 보였다 하였다.또 Pierre Lafforgue 등 (12) 은 환자의 나이, 성별, 초기
“Silent hip"의 수, 초기 방사선학적 등급과 반대편의 진행 된 대퇴골두괴사의 이환은 좋은 예후를 보인 예나 나쁜 예 후를 보인 예에서 큰 차이가 없었다 하였고 결국 예후판정 에 별 역할을 할 수 없다고 보고하였다. 그러나 저자들의 경우에서는 평균연령이 60세인 심한 변화군을 각각 평균 연령이 43세인 중등도 변화군, 37세인 경한 변화군과 비교 하여 보았을때 예후에 있어 통계학적인 차이를보였다.또 이들은 체중부하피질의 45%이상을 침범하는 대퇴골두괴 사는 임상적, 방사선학적 예후가 나쨌으나 45%이하를 침 범하는 경우는 예후가 좋았다고도 보고하였다(1 2). 저자 들의 경우에도 MR 시상영상에서 대퇴골두의 전상방을포 함한 괴사의 면적이 1/ 2이하의 경우는 예후가 비교적 양 호하였으나 1/ 2초과의 경우는 예후가 버교적 불량하였다.
결론적으로 대퇴골두괴사는 MR에서 다양한 양상의 소 견을 보이는데 이러한 괴사 소견중 T1 및 T2 강조영상에 서 신호음영강도의 변화양상은 예후판정에 별 도움을 주 지 못하지만, 환자의 연령과 괴사영역의 범위는 예후판정 에 도움을 준다고 생각한다.
~~ C그 고 헌
진 욱 외 : 대퇴골두 무혈성괴사의 자기공명영상
01 the lemoral head. 11. Experiences and treatment. J 80ne Joint Surg{Am] 1970; 52: 322.329
4. Patterson RJ, Bickel WH, Dahlin DC. Idiopathic avascular necrosis in the head 01 the lemur. J 80ne Joint Surg{Am]
1964; 46 : 267.282
5. Beltran J, Herman LJ, Burk JM, et al. Femoral head avascu- lar necrosis: MR imaging with clinical-pathologic and radio- nuclide correlation. Radiology 1988; 166: 215-220
6. Markisz JA, Knowles RJR, Altchek DW, Schneider R, Whalen JP , Cahill PT. Segmental patterns 01 avascular necrosis 01 the lemoral head: early detection with MR imaging. Radi-
。logy1987;162:717-720
7. Mitchell DG , Rao VM, Danlinka MK, et al. Femoral head avascular necrosis: correlation 01 MR imaging, radiographic staging, radionuclide imaging and clinical lindings. Radiology
1987; 162: 709-715
8. Hauzeur JP , Pasteels JL, Schoutens A, et al. The diagnostic value 01 magnetic resonance imaging in non-traumatic
。steonecrosis 01 the lemoral head. J 80ne Joint Surg{Am]
1989; 71 : 641-649
9. Totty WG , Murphy WA, Ganz WI , et al. Magnetic resonance imaging 01 the normal and ischemic lemoral head. AJR 1984
; 143 : 1273-1280
10. Mitchell DG , Rao VM, Dalinka MK , et al. Femoral head avas- cular necrosis: correlation 01 MR imaging , radiographic staging, radionuclide imaging, and clinical lindings. Radi-
。 logy 1987;162:709-715
11. Mitchell DG, Joseph PM, Fallon M, et al. Chemical Shift MR imaging 01 the lemoral head: an in vitro study 01 normal hips and hips with avascular necrosis. AJR 1987;148:1158-1164 12. Pierre L, Eric D, Christophe C, et al. Early-stage avascular
necrosis 01 the lemoral head: MR imaging lor prognosis in 31 cases with at least 2 years 01 lollow-up. Radiology 1993; 187: 199-204
13. Steinberg ME, Brighton CT, Steinberg DR, et al. Treatment 01 1. Thurman G 111, Harry KG, Clyde AH. Magnetic resonance avascular necrosis 01 the lemoral head by a combination 01 imaging 01 osteonecrosis. RCNA 1986; 24: 193-208 bone grafting, decompression, and electrical stimulation. Clin 2. Glimcher MJ, Kenzora JE. The biology 01 osteonecrosis 01 Orthop 1984;186:137-153
the human lemoral head and its clinical implications. 1. Tis- 14. Ohzono K, Saito M, Takaoka K, et al. Natural history 01 sue biology. Clin Orthop 1979; 138: 284-309 nontraumatic avascular necrosis 01 the lemoral head. J 80ne 3. Boettcher WG, Bonliglio M, Smith K. Nontraumatic necrosis Joint Surg{8r] 1991 ;73: 68-72
야 μ
대 한 밤사 선 의 학회 지 1994:31(1): 151- 156
Journal of the Korean Radiological Society, 1994: 31 (1) : 151- 156
MR Imaging of Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head:
Evaluation of the Prognostic Factors
Uk Jin, M.D., Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D., Myung Chul Yoo, M.D.1, Yup Yoon M.D.
Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Kyung Hee University Hospital
1 Department of Orthopedics, Kyung Hee University Hospital
Purpose: To evaluate the factors influencing the prognosis in avascular necrosis(AVN) of the femoral head by MR
Materials and Methods: Radiographic and MRI findings of twenty-three patients(30 cases, aged 23-67 years) with AVN identified clinically and radiologically were evaluated. The radiography included follow up study for at least 6 months.
The mean age of these patients was 43 years and M : F ratio was 20: 3.
MR imaging was performed at 1. 5T unit using T1- and T2-weighted coronal and T1-weighted sagittal and axial spin echo sequences.
We categorized the changes of the femoral head on radiographic f이 low-ups to three grades of mild, moderate and severe. We also analyzed the changes of the signal intensity and sizes of the lesion at sagittal and coronal MR images
On MR imaging we classified the extent of AVN of the femoral head to 2 grades according to the size of lesion.
Results: In the cases of mild changes in femoral head on radiography, the mean age of the patient was 37 years and the extent of AVN was below 1/2 in eleven out of seventeen cases. In the cases of moderate changes, the mean age was 43 years and the extent was above 1/2 in five out of seven cases. In the cases of severe changes, the mean age was 60 years and the extent was above 1/2 in all 6 cases.
With 95% confidence coefficient, comparisons in the age and necrosis extent revealed statistical significance in severe versus moderate changes and in severe versus mild changes. Comparisons in the change of signal in- tensity on T1 and T2 weighted images showed no statistical relationship between each other.
Conclusion: We conclude that if patient is younger and has smaller extent of the AVN, bone destruction is slower that these factors may be helpf비 in predicting the prognosis of AVN. However, the modes of the chang- es of the signal intensity on T1- and T2- weighted images may not be useful in predicting the prognosis of AVN.
Index Words: Femur, necrosis Femur, MR studies Femur, radiography
Address reprint requests to: Uk Jin, M.D., Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Kyung Hee University Hospital. 1, Hoeki강ong,
Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul, 130-702 Korea. Tel. 82-2-966-5191(2530) Fax.82-2-968 -D787