간경병증의 원인과 병리
소화기내과학 교실 신 현필
Histopathological diagnosis
Pathology 특징
· Irreversible loss of functioning hepatocyte
· Extensive fibrosis
· Formation of regenerative nodule
Irreversible reversal of fibrosis 일부 가능 .
Fibrosis 발달되어 architectural distortion + regenerative nodules 형성할 정도 .
hepatocellular mass 와 function 저하 , blood flow 변화 유도 .
Fiborsis
Hepatic stellate cells activation : fibrosis induction collagen 과 다른 extracellular matrix 양 증가 .
임상적 특성 : pathologic changes 의 결과로 간질환 정도 반영
Pathologic grading and staging (Advanced fibrosis)
Bridging fibrosis with nodularity : stage 3 Cirrhosis : stage 4.
Hepatocellular function 상실의 결과 :
jaundice, coagulation disorders, hypoalbuminemia, portosystemic encephalopathy.
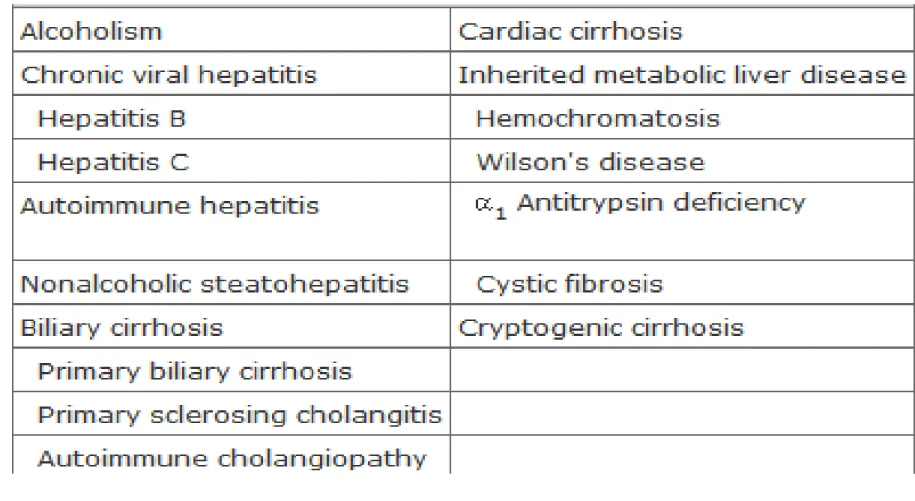
Table 302-1 Causes of Cirrhosis
Alcoholic cirrhosis
Excessive chronic alcohol use
Alcoholic fatty liver, hepatitis, cirrhosis.
동반시 liver damage 증가 : hepatitis C,
hemochromatosis, fatty liver disease (obesity)
Chronic alcohol use can produce fibrosis ( 동반된 inflammation 이나 necrosis 없이 ).
Fibrosis : centrilobular, pericellular, periportal
Fibrosis 일정수준 : normal liver architecture 파괴 + liver cells 의 regenerative nodules 로
Micronodular. :cessation mixed micronodular and macronodular
cirrhosis
Pathogenesis
Ethanol absorption : small intestine>>
stomach
Gastric alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) : alcohol metabolism initiation .
Three enzyme system: liver 내 alcohol metabolism
- cytosolic ADH
- microsomal-oxidizing system (MEOS), - peroxisomal catalase.
Highly reactive molecule
Effect of ethanol
Ethanol 섭취 : 세포 내 triglycerides 증가시킴 (fatty acid uptake 증가 ,
fatty acid oxidation 과 lipoprotein secretion 감소 )
Oxidative damage to hepatocyte membranes by
formation of reactive oxygen species;
- Acetaldehyde : highly reactive molecule
protein-acetaldehyde adducts 형 성 .
특정 enzyme activities 방해
Pathogenesis
Acetaldehyde-mediated hepatocyte damage + certain reactive oxygen species
Kupffer cell activation (profibrogenic
cytokine 생산 ) stellate cell activation
Production of excess collagen and ECM
Liver size shrinkage
1. Hepatocyte loss
2. Increased collagen production and deposition
3. Continuing hepatocyte destruction
Regenerative nudule
Connective tissue 가 periportal and pericentral zones 모두에서 portal triads 를 central veins 연결
Clinical Features and physical examination
Accurate history :amount and duration
Nonspecific symptoms
More specific complications :ascites, edema, upper gastrointestinal (GI) hemorrhage.
Liver and spleen enlarement, liver edge firm and nodular.
Laboratory
Normal : early compensated alcoholic cirrhosis.
Anemia : chronic GI blood loss, nutritional deficiencies, hypersplenism related to portal hypertension, BM
supression
Hemolytic anemia (with spur cells and acanthocytes)
Zieve's syndrome : severe alcoholic hepatitis.
Thrombocytopenia
Serum bilirubin 초기 정상
Prothrombin times,
parenteral vitamin K response ?
Hyponatremia: ascites 동반시
Serum aminotransferases (ALT, AST) : > 2:1 ratio.
Diagnosis
과거력 :
alcohol. + other forms of chronic liver disease (e.g., chronic viral hepatitis, metabolic or
autoimmune liver diseases).
Liver biopsy 6 개월 정도 금주 잔존 기능 , 가역성 판단가능
LC with complication + alcohol 지속 <50% 5-year survival.
Treatment
Abstinence
good nutrition
Glucocorticoids : severe alcoholic hepatitis in the absence of infection
Discriminant function (DF) value of >32.
improved survival at 28 days
Pentoxifylline: TNF alpha and other proinflammatory cytokines 감소 .
Glucocorticoid 보다 투여 쉽고 적은 side effects.
nutritional therapies 효과 ?
infliximab or etanercept 로 TNF –Alpha 감소
Treatment
금주 - 가장 중요
Portal HTN 의한 정맥류 출혈 줄이고 생존률 증가
good nutrition( 고영양식 - 단백제한 ?)
Glucocorticoids : severe alcoholic hepatitis in the absence of infection
Discriminant function (DF) value of >32.
improved survival at 28 days
Pentoxifylline: TNF alpha and other proinflammatory cytokines 감소 .
Glucocorticoid 보다 투여 쉽고 적은 side effects.
nutritional therapies 효과 ?
infliximab or etanercept 로 TNF –alpha 감소
Cirrhosis Due to Chronic Viral Hepatitis B or C
만성화율 , LC
Chronic hepatitis C 간질환 악화의 특징 :
Portal-based fibrosis with bridging fibrosis and nodularity cirrhosis.
Mixed micro- and macronodular cirrhosis :
Bx HCV genotype 3: steatosis 자주 관찰
바이러스성 간염의 만성화와 진행
급성 간
급성 간
염
염만성간염 , 보유자
간경변증 간암
C 형 간염 바이러스
한국 0.8-1.7%
B 형 간염 바이러스
한국 5.5%
90%
영유아 수직감염
5 % 성인
80%
20-30%.
/20-30 년 20%
1.5-6.6%/
년 2-4%/ 년
Alcohol
Clinical Features, Diagnosis, Treatment
Symptoms and signs of chronic liver disease.
Diagnosis
- Quantitative HCV RNA testing, HCV genotype,
- Hepatitis B serologies : HBsAg, anti-HBs, HBeAg, anti-HBe, and quantitative HBV DNA levels.
- Treatment : underlying, complication B 형 간염 경구 약제 - 간섬유화 조직학적 호전 C 형 인터페론 - SVR 지속시 좋은 반응
Cirrhosis from Autoimmune
Hepatitis and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) present with cirrhosis - No benefit from immunosuppressive therapy
(glucocorticoids or azathioprine)
- Liver biopsy : no significant inflammatory infiltration
Diagnosis :
(+) autoimmune markers : ANA or ASMA
Active inflammation + elevated liver enzymes considerable benefit from the use of
immunosuppressive therapy.
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis 에서 cirrhosis 증가 . - obesity
- cryptogenic cirrhosis
Biliary Cirrhosis
- Different from either alcoholic or posthepatitic cirrhosis
- Manifestations of end-stage liver disease : same
-
Cholestatic liver disease :
- necroinflammatory lesions,
- congenital or metabolic processes
- external bile duct compression
Anatomic sites of abnormal bile retention
- Extrahepatic obstruction :surgical or endoscopic biliary tract decompression
- Intrahepatic cholestatic processes : interventions ?
Chronic cholestatic syndromes
The major causes
- primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC)
- autoimmune cholangitis
- primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)
- idiopathic adulthood ductopenia.
DDx by antibody testing, cholangiographic findings, clinical presentation
- 비슷한 histopathologic features : cholate stasis, copper deposition,
xanthomatous transformation of hepatocytes, irregular so-called biliary fibrosis.
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
- 여성에서 호발 9:1, 진단 시 평균 50 세 .
- 원인 미상
병리 특징
- Portal inflammation, necrosis of cholangiocytes in small and medium-sized bile ducts.
Cholestatic features and biliary cirrhosis :
elevated bilirubin level and progressive liver failure.
Antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA) : 약 90%.
intermitochondrial membrane proteins 을 인식
AMA : not pathogenic useful markers for diagnosis
Pathology
가장 초기소견 :
chronic nonsuppurative destructive cholangitis :necrotizing inflammatory process of the portal tract - Medium and small bile ducts: lymphocyte infiltration - 경도의 fibrosis 와 간혹 bile stasis 관찰
진행 :
inflammatory infiltration 은 감소하면서 bile duct 수 감소
더 작은 bile ductules proliferation
Increased fibrosis 최종적으로 cirrhosis (micronodular or macronodular)
Liver biopsy: stage 확인 - 강의록 참조
Clinical Features
- 대부분 end-stage manifestations 전에 진단
- 무증상 많다
- Pruritus : 진단 시 약 50%, 간헐적이고 저녁
- Jaundice 발생 전 pruritus :
severe disease and poor prognosis
- Physical examination : jaundice and other complications of chronic liver disease
- Unique to PBC : hyperpigmentation, xanthelasma, and xanthomata (altered cholesterol metabolism)
- Hyperpigmentation : 몸통이나 각질부 .
- Bone pain :osteopenia or osteoporosis
Laboratory Findings
- cholestatic liver enzyme 상승 :
gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase, ALP
- IgM 상승 전형 .
- Hyperbilirubinemia : cirrhosis 진행 후 .
- Liver biopsy
-
- PBC 환자 10% 에서 AIH 특성 : "overlap"
syndrome.
PBC 환자 처럼 치료 받고 cirrhosis 진행 가능함
Diagnosis
10% : AMA-negative.
Liver biopsy is most important
AMA-negative with
cholestatic liver enzymes
PSC 를
cholangiography 로 감별
PBC PSC
F:M 9:1 1:2
Enz 상승 ALP, rGT ALP, rGT AutoAb AMA, AMA-
M2 pANCA
Serum Ig
elevatio n
IgM IgM, IgG
Histolo
gy Florid bile
duct lesion Fibrosing bild duct lesion
Diganos
is AMA-M2 Bile duct stenosis/
Dilatation IBD
pANCA
Treatment
UDCA : only approved treatment
- 생화학 검사 ( 빌리루빈 저하 ) -90% 이상에서 1 년이내
- 조직학적 ( 섬유화 진행 방지 ) 모두를 개선
- 초기 치료시 예후 좋아
- 13–15 mg/kg per day
- 일부서 부작용 - diarrhea or headache
- progression 을 느리게 , 치유나 회복불가
LT : decompensated cirrhosis
Treatment
Fatigue, pruritis 증상에 대한 치료 (UDCA 효과 없 어 )
- 피로에 낮잠 ?
- antihistamines, naltrexone, rifampin.
- Cholestyramine
(UDCA 와 병용시 투여시간 4 시간 이상 차이 두어야 )
Osteopenia and osteoporosis : bisphosphonate
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
- 원인 미상의 chronic cholestatic syndrome
- 특징 : diffuse inflammation fibrosis ( 전체 biliary tree) chronic cholestasis 유발
intra- and extrahepatic biliary tree obliteration biliary cirrhosis, portal HTN, and liver failure.
원인 ?
- bacterial and viral infections, toxins, genetic predisposition, immunologic mechanisms
Pathologic changes :
- bile duct proliferation, ductopenia and fibrous cholangitis (pericholangitis).
Liver biopsy 서 periductal fibrosis 가 진단에 부분적 도움 biliary tree imaging 중요 .
Clinical Features
- 일반적인 cholestatic liver disease 특징들 : fatigue, pruritus, steatorrhea, fat-soluble
vitamins 부족 등
- Pruritus 가 cholestasis 관련되어 나타나지만 질병 중등도와 비례 안 해
- Metabolic bone disease 가 PBC 처럼 가능
Laboratory Findings
- ALP 두 배 이상 상승 , aminotransferases 가능
- Albumin levels 저하 , prothrombin times 증가
- Aminotransferase elevations 5 배 이상 증가시 조직검사서 AIH 소견 보이기도 .
overlap syndrome between PSC and AIH.
- Overlap syndrome -autoantibodies (+) 많다
- PSC 단독시는 p-ANCA 외 음성
- P-ANCA(+): 약 65%
- Ulcerative colitis (UC) 동반 : 약 50%
colonoscopy
Diagnosis
Definitive diagnosis of PSC : cholangiographic imaging
MRI, MRCP screen 뒤 ERCP 시행되어야 .
Imaging : intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary tree
침범하는 multifocal stricturing and beading classic beaded appearance.
The gallbladder and cystic duct : 약 15% 에서 침 범 .
High-grade, diffuse stricturing of the intrahepatic bile ducts : poor prognosis.
결국 biliary cirrhosis
Treatment
No specific proven treatment
UDCA?
Endoscopic dilatation :dominant strictures 에나
결국 liver transplantation 가 치료
Cholangiocarcinoma serious Cx : relative contraindication to liver
transplantation.
Pruritus : PBC 에서와 같은 치료
Cardiac Cirrhosis
지속적인 right-sided congestive heart failure chronic liver injury 유발 .
매우 드물다
Etiology and Pathology
장기간 right-sided heart failure 로 증가된 venous pressure 가 inferior vena cava 와 hepatic veins 을 통해 liver sinusoids 로 전달됨
Long-term passive congestion and relative
ischemia, centrilobular hepatocytes 가 necrotic
pericentral fibrosis periphery 로 진행 cirrhosis
Clinical Features
Signs of congestive heart failure
Enlarged firm liver on physical examination.
ALP levels 특징적으로 증가
aminotransferases 정상이거나 다소 증가 AST > ALT 많아 .
Variceal hemorrhage or encephalopathy.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Clear-cut cardiac disease + elevated ALP + enlarged liver.
Liver biopsy : pattern of fibrosis 가 중요
감별진단
1. Budd-Chiari syndrome (BCS) : hepatic vein occlusion 으로 extravasation of RBC.
2. Venoocclusive disease : hepatic outflow 영향 - liver 내 small vein occlusion
- BMT with radiation and chemotherapy
Treatment : underlying cardiac disease.