대한소화기학회지 2008;51:259-264
접수: 2007년 10월 8일, 승인: 2008년 3월 5일 연락처: 김형준, 156-755, 서울시 동작구 흑석동 224-1
중앙대학교병원 내과
Tel: (02) 6299-1365, 1399, Fax: (02) 825-7571 E-mail: mdjoon@cau.ac.kr
Correspondence to: Hyung Joon Kim, M.D
Department of Internal Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, 224-1, Heukseok-dong, Dongjak-gu, Seoul 156-755, Korea
Tel: +82-2-6299-1365, 1399, Fax: +82-2-825-7571 E-mail: mdjoon@cau.ac.kr
성인에서 발생한 원발 간 Burkitt 림프종 1예
중앙대학교 의과대학 내과학교실, 병리학교실*
이승현ㆍ김형준ㆍ문장식ㆍ오형철ㆍ이현웅ㆍ최창환ㆍ김정욱ㆍ도재혁ㆍ김재규ㆍ장세경ㆍ김미경*
A Case of Primary Hepatic Burkitt's Lymphoma
Seung Hyun Lee, M.D., Hyung Joon Kim, M.D., Jang Sik Mun, M.D., Hyoung-Chul Oh, M.D., Hyun Woong Lee, M.D., Chang Hwan Choi, M.D.,
Jeong Wook Kim, M.D., Jae Hyuk Do, M.D., Jae Gyu Kim, M.D., Sae Kyung Chang, M.D., and Mi Kyung Kim, M.D.*
Departments of Internal Medicine and Pathology*, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
Burkitt's lymphoma is a rare disease that belongs to the aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Herein, we report a case of primary hepatic Burkitt's lymphoma. A 19-year-old man visited the hospital for right upper quadrant pain. He felt fatigue for two months. Physical examination revealed hepatomegaly and no palpable lymph node.
He had no fever, weight loss, or night sweating. Laboratory finding showed mild anemia (hemoglobin, 12.4 g/dL), mild elevated transaminase (ALT, 52 IU/L), elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH, 437 IU/L), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP, 129 IU/L). The viral marker was positive for HBsAg, HBeAg, anti-HBs, and anti-HBc (IgG), and negative for anti-HBe, anti-HCV, and anti-HIV. CEA, AFP, and CA19-9 levels were within normal ranges.
The HBV DNA quantitation was 1.3×10
9copies/ml. Abdominal-Pelvis CT scan and abdominal MRI finding were compatable with malignant lymphoma. Liver biopsy examination confirmed Burkitt's lymphoma. No metastasis was detected in the thoracic cavity, bone marrow, and spinal fluid. The patient was treated with the combination regimen of cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone and high dose methotrexate. Cytosine arabino- side and methotrexate were added for CNS prophylaxis by intrathecal installation. Chemotherapy was administered every 3 weeks for fifteen cycles. Serial follow-up CT scan showed a marked decrease in the size of hepatic lesions. Follow-up CT scan and PET-CT scan were perfomed 4 weeks after the final cycle disclosed no definite residual or active lesion confirming the state of complete remission. (Korean J Gastroenterol 2008;51:259-264) Key Words: Primary hepatic lymphoma; Burkitt's lymphoma
Introduction
The liver is an uncommon primary site for malignant lymphoma and primary hepatic lymphoma has been found to
make up 0.4% of all extranodal lymphoma.1 Burkitt's lympho- ma is a rare non-Hodgkin's lymphoma which grows rapidly and requiring aggressive therapy and usually occurs in children.
Primary hepatic Burkitt's lymphoma is a very rare disease. Se-
260 대한소화기학회지: 제51권 제4호, 2008
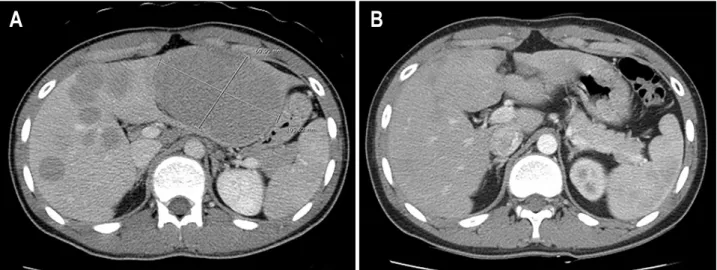
Fig. 1. Abdominal CT. (A) Abdominal CT scan shows multiple variable sized low density nodules on the liver and kidney, and the largest one was 11×7 cm on the lateral segment of left lobe of liver (Lt.). (B) Follow up CT after 6 cycles of chemotherapy shows marked decrease in tumor size (Rt.).
condary periportal Burkitt's lymphoma in a non-AIDS patient was reported in Korea,2 but no primary hepatic Burkitt's lymphoma was reported. We report a case of primary hepatic Burkitt's lymphoma in a 20-year-old patient who is a hepatitis B virus carrier and showed good response to chemotherapy.
Case Report
A 20-year-old man with general fatigue of 2 months' du- ration was admitted to the hospital because of suddenly occurred pain in the right upper quadrant started one day ago. Physical examination revealed three fingerbreadths hepatomegaly and no palpable lymph node and spleen. He had no fever, weight loss, or night sweating. He was a hepatitis B virus healthy carrier and his mother was also a hepatitis B healthy carrier. He denied alcohol or drug history. Laboratoy finding showed WBC 5,800/mm3, Platelet 189,000/mm3, Hemoglobin 12.4 g/dL, alanine aminotransferase 52 IU/L, aspartate aminotransferase 53 IU/L, total bilirubin 0.6 mg/dL, direct bilirubin 0.2 mg/dL, total protein 7.5 g/dL, albumin 4.1 g/dL, gamma-glutamyl transpep- tidase 51 IU/L, lactate dehydrogenase 437 IU/L, and alkaline phosphatase 129 IU/L. The prothrombin time was 1.24 (INR).
Viral marker was positive for HBsAg, HBeAg, anti-HBs, anti-HBc (IgG), and negative for anti-HBe, anti-HCV, anti-HIV.
AFP PIVKA II and CEA, CA19-9 were within a normal range.
The HBV DNA quantitation was 1.3×109 copies/mL.
Abdominal CT scanning revealed multiple variable sized low density nodules in the liver (the largest one was 11×7 cm on
the lateral segment of left lobe of liver) and no spleen involvement (Fig. 1). No cervical, abdominal and chest lympha- denopathy was revealed on the chest, abdominal and pelvis CT.
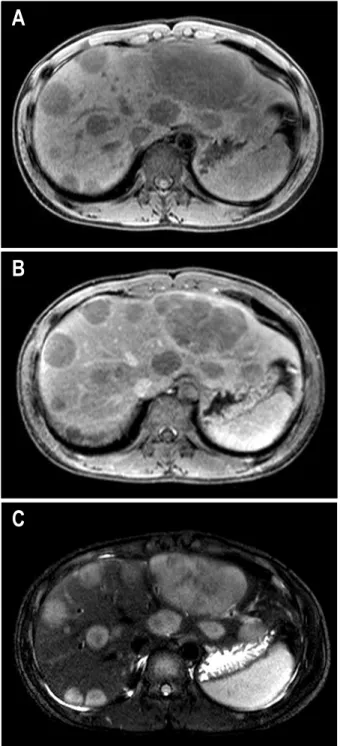
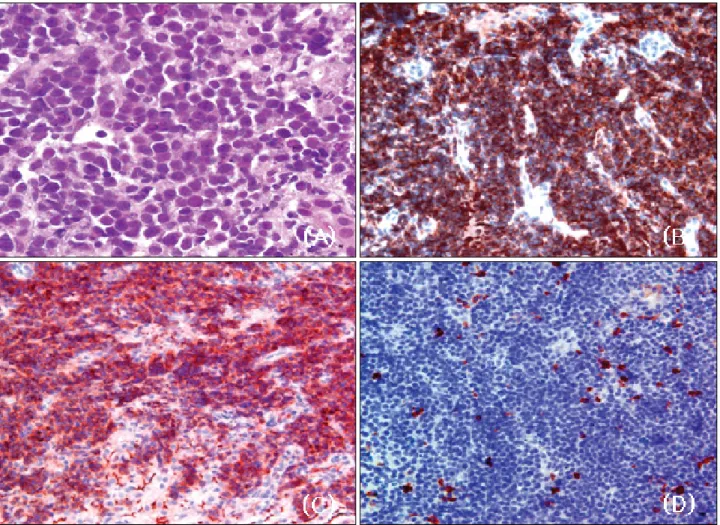
Abdominal MRI scans showed multiple T1 low and T2 hetero- genously high signal intensity lesions in the liver with poor enhancement (Fig. 2). Ultrasonographiy-guided liver biopsy was done and microscopic finding showed diffuse monotonous infiltration of medium-sized cells with basophilic cytoplasm, coarse chromatin, and conspicuous nucleoli. Many mitotic figures were noted. Immunohistochemical stain was positive for CD10 and nagative for CD5. More than 95% of the cells were positive for Ki-67 (Fig. 3). These findings were compatible with pathologic diagnosis of Burkitt's lymphoma. Bone marrow biopsy and spinal fluid exam showed no lymphoma cells. The peripheral blood smear showed no abnormal cells. The patient was treated with the combination regimen of anticancer cytotoxics, cyclophosphamide (1,200 mg/m2 day1), doxorubicin (40 mg/m2 day1), vincristine (1.4 mg/m2 day1), prednisone (40 mg/m2 PO day1-5) and methotrexate (420 mg/m2 day10). CNS prophylaxis was done with intrathecal installations of cytosine arabinoside (30-45 mg/m2 day7) and methotrexate (12.5 mg day10). Chemotherapy was adminstered every 3 weeks for fifteen cycles. The patients was tolerable to the treatment. There has been no serious complication during the chemotherapy.
Four episodes of dose reduction or delay were noted because of chemotherapy-associated neutropenia. Serial follow-up CT scan showed marked decrease of hepatic lesions (Fig. 1). The last evaluation with CT scan and PET-CT scan done 4 weeks after
이승현 외 10인. 성인에서 발생한 원발 간 Burkitt 림프종 1예 261
Fig. 2. Abdominal MRI. (A) (B) T1-weighted image shows low signal intensity in liver with poor enhancement. (C) T2-weighted image shows heterogenously high signal intensity lesions in liver.
the final cycle showed no definite residual or active lesion showing a complete remission.
The patient was comorbid with hepatitis B carrier. So an antiviral drug, lamivudine (100 mg/day) was prescribed from 2 weeks before chemotherapy and continued throughout the che- motherapy schedules.
With lamivudine treatment, HBV viral DNA copy number,
initially 1.3×109 copies/mL was markedly decreased to undetec- table level, and abnormalities of liver function began to nor- malize as well in 1-2 weeks and these laboratory values have been kept within normal range throughout chemotherapy.
Until 4 months after the treatment, he is in remission in both diseases.
Discussion
Burkitt's lymphoma is a undifferentiated malignant lym- phoma originated from B lymphocyte, and it was described first by Denis Burkitt who named the tumor on the African children's jaw sarcoma.3 Burkitt's lymphoma is classified into three types: endemic, sporadic, and immunodeficiency-asso- ciated.4 Endemic type is found in a specific geographic area in Africa, associated with Epstein-Barr viral infection, and mainly involves mandible and maxilla. Non-endemic type usually involves mesenteric lymph nodes or ileocecal area and is usually presented as abdominal mass.5 C-myc rearrangement is important in the pathogenesis of Burkitt's lymphoma and viral infections such as Epstein-Barr virus and HIV affect the genetic instability. In endemic Burkitt's lymphoma the break point in c-myc is more than 100 kb upstream from the first coding exon and the break point in the IgH gene is in the joining segment.
In sporadic and immunodeficiency-associated Burkitt's lympho- ma, the break point in myc is between exons 1 and 2, and the break point in IgH is in the switch lesion.6
The diagnostic criteria for primary hepatic lymphoma has not been established yet. Caccamo suggested strict criteria that primary hepatic lymphoma should have liver involvement only,7 but many cases have regional lymph node, spleen, and bone marrow involvement. So Lei suggested broader criteria that the symptom expression mainly originate from liver infiltration, no distant lymphadenopathy, no leukemoid reaction in peripheral blood smear.8 In our case, we could diagnose primary hepatic lymphoma because it had no evidence of distant lymphadeno- pathy and metastasis.
There are many histologic types of primiary hepatic lympho- ma according to immunohistochemical stain. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma is most common type and lymphoblastic lymphoma, Burkitt's lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, diffuse histiocytic lymphoma, MALT lymphoma, anaplastic large cell lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoam, and T-cell rich B-cell lymphoma are reported.8 Primary hepatic Burkitt's lymphoma make up 3% of primary hepatic lymphoma, and eight cases
262 The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology: Vol. 51, No. 4, 2008
Fig. 3. Microscopic findings of the liver. (A) Diffusely infiltrating medium-sized cells with basophilic cytoplasm, coarse chromatin, and medium-sized nucleoli are seen (H&E stain, ×1000). (B) Immunohistochemical stain is positive for B-cell (×400). (C) Immunohisto- chemical stain is positive for CD10 (×400). (D) Immunohistochemical stain for negative for CD5 (×400).
were reported.9 Burkitt's lymphoma is a rare disease in adult, and no primary hepatic Burkitt's lymphoma was reported in Korea. Our case was a sporadic type Burkitt's lymphoma which primarily developed in the liver.
The pathologic feature of Burkitt's lymphoma is that it typically expresses monotypic surface IgM, pan-B-cell antigens, including CD19, CD20, CD22, and CD79a, and coexpresses CD10, Bcl-6, CD43, and p53, but not CD5, CD23, Bcl-2 CD138 and proliferating fraction is nearly 100%.10 Characte- ristic microscopic finding of Burkitt's lymphoma is that the uniform medium-sized neoplastic cells with round nuclei and several or multiple small basophilic nucleoli are infiltrated and the cytoplasm is moderately abundant. The RNA-rich cytoplasm is deep blue on Giemsa or Wright stain and usually shows multiple vacuoles. The mitotic rate is very high and there are numerous admixed tingible body macrophage, phagocytosing abundant apoptotic debris, creating starry sky pattern.11 However
this characteristic finding is not always seen. We could diagnose our case as Burkitt's lymphoma because CD20 was positive, Ki-67 expression was over 95%, and the infiltrating tumor cells were medium-sized and uniform. A molecular defining feature of Burkitt's lymphoma is the presence of a translocation between the c-myc gene and the IgH gene [t (8;14)], or between c-myc and the gene for either the kappa or lambda light chain [t (2;8) or t (8;22)].12 But we couldn't check the translocation because we didn't have a special equipment.
The clinical features of primary hepatic lymphoma are various from no symptom, mild abnormal liver function to fulminant hepatic failure. Fever, night sweating, weight loss (known as B symptom of malignant lymphoma), right upper quadrant pain, hepatomegaly, jaundice, fatigue, nausea, vomi- tting, and splenomegaly are common symptom, and rarely, hemorrhagic tendency, ascites, pleural effusion, hepatic ence- phalopathy can occur. The biochemical liver function tests are
Lee SH, et al. A Case of Primary Hepatic Burkitt's Lymphoma 263
usually abnormal in more than 85%. Elevated level of LDH and ALP is prominent. CEA and AFP are with in a normal range without exceptions. Most of the lymphomas are solitary or multiple mass, but rarely diffuse hepatosplenomegaly without definite mass. In our case, the patient had right upper quadrant pain with three fingerbreadths hepatomeglaly and no B symp- tome of malignant lymphoma. Laboratory findings revealed mildly elevated level of AST, ALT, LDH and ALP. Dynamic liver CT scan showed multiple nodules in the liver. Because patient was a hepatitis B virus carrier (immune tolerant phase), the differential diagnosis with hepatocelluar carcinoma was needed. The dynamic CT and MRI findings suggesed lym- phoma rather than hepatocelluar carcinoma.
Early adminstration of multiple chemotherapeutic agents increase curative potential of Burkitt's lymphoma. We tried to maintain dose intensity and the patient was tolerable to such kind of dose intensive treatment. Our major concern was comorbid hepatitis B. Several hepatotoxic drugs such as doxorubicin has risk of hepatitis aggravation and corticosteroid such as prednisone could reactivate hepatitis virus. In this patient, although we concerned the notorious rapid tumor cell doubling of Burkitt lymphoma, initiation of hepatitis treatment prior to Burkitt's lymphoma treatment seemed to be safer way than vice versa. This case suggests that it would be the better treatment option for the patient comorbid with hepatitis and lymphoma to clear hepatitis virus before lymphoma chemothe- rapy.
The long term survival rate of Burkitt lymphoma in children is over 80% in some reports,13 but the result in adult was not so good.14 In 1996, Magrath reported the treatment regimen using cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, prednisone, vincristine, and high dose methotrexate by intrathecal installation (CODOX- M) showing remarkable remission rate and survivals. The Magrath regimen we used was effective in this patient.
요 약
Burkitt 림프종은 비호지킨 림프종에 속하는 드문 질환으 로 주로 소아에서 발생한다. 간은 원발 악성 림프종이 잘 발 생하지 않는 장기이며 원발 간 림프종은 림프절 이외 림프 종의 0.4%를 차지한다고 알려져 있다. 저자들은 B형 간염 보균자에서 발생한 항암치료에 완전 관해를 보였던 원발 간 Burkitt 림프종 1예를 경험하였기에 보고하는 바이다. 19세 의 남자가 2개월간의 심한 피곤함과 내원 1일 전부터 시작 된 우상복부 통증을 주소로 내원하였다. 신체검사에서 3횡
지의 간비대가 촉지되었으나 림프절은 만져지지 않았고 야 간발한, 발열, 체중감소는 호소하지 않았다. 혈액 검사에서 혈색소 12.4 g/dL의 경도의 빈혈을 보였으며 생화학 간기능 검사에서 AST 53 IU/L, ALT 52 IU/L였으며 ALP 192 IU/L, LDH는 437 IU/L로 증가되어 있었다. 혈청 바이러스 표지자 검사에서 HBsAg, anti-HBs, anti-HBc (IgG)이 양성이었으며 Anti-HCV, anti-HIV는 음성이었다. 암종배아항원(CEA), 알 파태아단백(AFP), CA19-9은 정상범위였다. HBV DNA 정량 검사는 1.3×109 copies/mL였다. 복부 및 흉부 전산화 단층촬 영에서 다양한 크기의 저밀도 음영을 갖는 결절들이 간에서 관찰되었으며 간에서 가장 큰 것은 11×7 cm였고 복강 및 흉강 내 림프절 비대는 관찰되지 않았다. 자기 공명영상에 서 T1영상에서 저신호강도 T2영상에서 불균일한 고신호강 도를 갖는, 조영증가가 잘되지 않는 결절들이 관찰되었다.
초음파 유도하 세침간생검에서 미만으로 침윤하는 세포들 이 관찰되었고, 침윤된 세포는 중간크기이며 세포질은 호염 기성이었고 거친 염색질의 핵과 호염기성이며 중간크기인 핵소체를 가지고 있었다. 면역조직화학 염색에서 백혈구 공 통항원, B세포에 양성이었고, T세포에는 소수의 세포들만이 양성 반응을 보였으며, Ki-67에 95% 이상의 세포에서 양성 반응을 보여 Burkitt 림프종으로 진단되었다. 흉부 CT 및 골 수, 척수검사에서 전이는 관찰되지 않았다. 환자는 15회의 CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone) 복합항암화학요법과 cytosine arabinoside와 methotrexate를 이 용한 중추신경계 항암화학예방요법치료를 받았으며 완전 관해 후 관찰 중이다.
색인단어: 원발 간 림프종, Burkitt 림프종
References
1. Freeman C, Berg JW, Cutler SJ. Occurrence and prognosis of extranodal lymphomas. Cancer 1972;29:252-260.
2. Park KY, Yu JS, Yoon SW, Park MS, Koo JS, Kim KW.
Burkitt's lymphoma representing periportal infiltrating mass on CT. Yonsei Med J 2004;45:723-726.
3. Burkitt D. A sarcoma involing the jaws in African children.
Br J Surg 1958;46:218-223.
4. Hecht JL, Aster JC. Molecular biology of Burkitt's lympho- ma. J Clin Oncol 2000;18:3707-3721.
5. Magrath IT. African Burkitt's lymphoma. Histology, biology, clinical features, and treatment. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 1991;13:222-246.
6. Shiramizu B, Barriga F, Neequaye J, et al. Patterns of chro- mosomal breakpoint locations in Burkitt's lymphoma: rele- vance to geography and Epstein-Barr virus association. Blood
264 대한소화기학회지: 제51권 제4호, 2008
1991;77:1516-1526.
7. Caccamo D, Pervez NK, Marchevsky A. Primary lymphoma of the liver in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
Arch Pathol Lab Med 1986;110:553-555.
8. Lei KI. Primary non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the liver. Leuk Lymphoma 1998;29:293-299.
9. Kuroda J, Omoto A, Fujiki H, el al. Primary hepatic Burkitt's lymphoma with chronic hepatitis C. Acta Haematol 2001;105:237-240.
10. McClure RF, Remstein ED, Macon WR, et al. Adult B-cell lymphomas with Burkitt-like morphology are phenotypically and genotypically heterogeneous with aggressive clinical behavior. Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1652-1660.
11. Pelicci PG, Knowles DM 2nd, Magrath I, Dalla-Favera R.
Chromosomal Breakpoints and structural alterations of the
c-myc locus differ in endemic and sporadic forms of Burkitt lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1986;83:2984-2988.
12. Burmeister T, Schwartz S, Horst HA, et al. Molecular hetero- geneity of sporadic adult Burkitt-type leukemia/lymphoma as revealed by PCR and cytogenetics: corelation with morphol- ogy, immunology and clinical features. Leukemia 2005;19:
1391-1398.
13. Schwenn MR, Blattner SR, Lynch E, Weinstein HJ. HiC- COM: a 2-month intensive chemotherapy regimen for chil- dren with stage III and IV Burkitt's lymphoma and B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 1991;9:133-138.
14. Morrison VA, Frizzera G, Arthur DC, et al. Prognostic factor for therapeutic outcome of diffuse small non-cleaved cell lymphoma in adults. Am J Hematol 1994;46:295-303.