60
Received:October 12, 2016, Revised:December 28, 2016, Accepted:December 28, 2016
Corresponding to:Jinseok Kim, Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Jeju National University School of Medicine, 102 Jejudaehak-ro, Jeju 63243, Korea. E-mail:slera@yahoo.com
pISSN: 2093-940X, eISSN: 2233-4718
Copyright ⓒ 2017 by The Korean College of Rheumatology. All rights reserved.
This is a Open Access article, which permits unrestricted non-commerical use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Clinical Image
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 24, No. 1, February, 2017 https://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2017.24.1.60
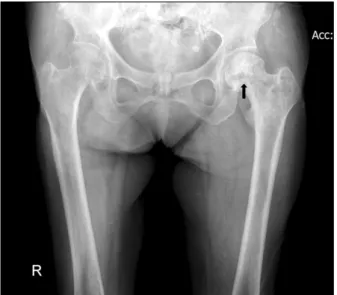
Figure 2. Sunburst lesion of left proximal femur on plain ra- diography of hips (arrow).
Figure 1. (A) Multiple distal interphalangeal joints destruction with tophi on plain radiography of hands, (B) active arthritis and osteomyelitis bilateral hands on delayed phase of 3-phase bone scan and (C) active bone lesion on pelvic bone, left femo- ral head and proximal femur on bone scan.
A Case of Paget’s Disease Involving Pelvic Bone in a Patient with Tophaceous Gouty Arthritis
Eun-Jung Park1, Sun Hyung Kim2, Jinseok Kim1
Departments of 1Medicine and 2Laboratory Medicine, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea
Paget’s disease is a localized disorder of bone remodel- ing that typically begins with excessive bone resorption followed by an increase in bone formation [1,2]. This os- teoclastic overactivity followed by compensatory osteo-
blastic activity leads to a structurally disorganized mosaic of bone (woven bone), which is mechanically weaker, larger, less compact, more vascular, and more susceptible to fracture than normal adult lamellar bone.
Several studies reported association between Paget’s disease of bone and gout, which have speculated that high turn-over of bone in Paget’s disease produces an in- creased nucleic acid turnover with resultant hyper- uricemia [3,4]. However, the incidence of Paget’s disease is in Asia is rare.
A 84-year-old woman presented with erythematous swelling of right third fingertip and tophi discharge last- ing over several weeks, and was admitted to hospital for
Paget’s Disease in Patients with Gout
www.jrd.or.kr 61
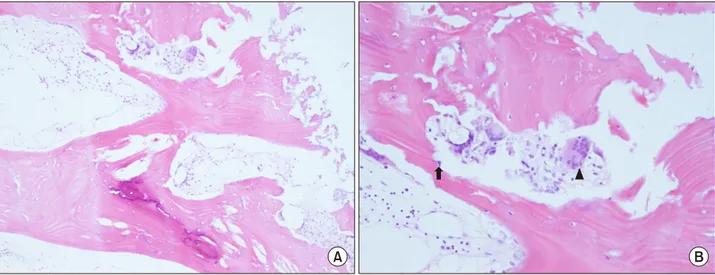
Figure 3. Bone marrow biopsy. (A) Irregularly thickened bony trabeculae with distinct cement lines (H&E stain, ×100), and (B) in- creased activity of multinucleated osteoclast (arrowhead) and osteoblast (arrow) (H&E stain, ×200).
evaluation. The patient was diagnosed with gout about 15 years ago. She denied trauma and injection of affected joint. She had chronic kidney disease stage 4 and hypertension. The patient had fever 38.2oC and blood pressure was 145/92 mmHg. Erythematous swelling with tenderness of right third fingertip and whitish tophi discharge was detected. Laboratory examination revealed hemoglobin 10.6 g/dL, hematocrit 30.7%, platelets 204,000/mm3, and white blood cell count 7,200/mm3. Blood urea nitrogen was 57.8 mg/dL, creatinine 2.43 mg/dL, albumin 3.6 g/dL, and total calcium 8.7 mg/dL.
Liver function test was unremarkable, whereas alkaline phosphatase was elevated to 802 IU/L (reference, 104∼
338 IU/L). Pain radiography of bilateral hands showed destruction of multiple distal interphalangeal joints with tophi (Figure 1A). Three phase bone scan revealed possi- ble soft tissue infection with reactive bone change of the fingertip (Figure 1B). Furthermore active bone lesions in right pelvic bone, sacrum, left femoral head and left prox- imal femur were detected incidentally (Figure 1C). Plain radiography showed sunburst lesion in left proximal fe- mur (Figure 2). Biopsy of bone marrow and pelvic bone demonstrated variable cellularity from nearly acellular to normocellular marrow with thickened bony trabeculae, distinct cement line, and mosaic pattern bone (Figure 3A). Numerous, large multineucleated osteoclast and os- teoblast along the bone line was noticed, which are specif- ic finding of Paget’s disease (Figure 3B). This gout patient
was diagnosed with secondary infection and osteomyeli- tis of right third fingertip. Paget’s disease detected and confirmed incidentally in the process of evaluation.
Paget’s disease is rare in Asia and should be considered in cases of high turn-over disease of bone. Bone biopsy is helpful when Paget’s disease could not be confirmed with image findings.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by the 2016 scientific pro- motion program funded by Jeju National University.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
REFERENCES
1. Bolland MJ, Cundy T. Paget's disease of bone: clinical review and update. J Clin Pathol 2013;66:924-7.
2. Ralston SH, Langston AL, Reid IR. Pathogenesis and man- agement of Paget's disease of bone. Lancet 2008;372:155-63.
3. Lluberas-Acosta G, Hansell JR, Schumacher HR Jr. Paget's disease of bone in patients with gout. Arch Intern Med 1986;146:2389-92.
4. Altman RD. Musculoskeletal manifestations of Paget's dis- ease of bone. Arthritis Rheum 1980;23:1121-7.